Deck 5: The Government Budget, Foreign Borrowing, and the Twin Deficits
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/79
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: The Government Budget, Foreign Borrowing, and the Twin Deficits
1
Figure 5-1 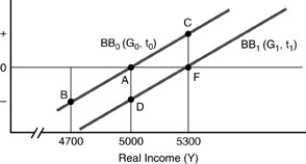
In the figure above, if the budget line is BB0 and the natural real GDP is $5300, the structural surplus or deficit is
A) FC.
B) AD.
C) FA.
D) none of the above.

In the figure above, if the budget line is BB0 and the natural real GDP is $5300, the structural surplus or deficit is
A) FC.
B) AD.
C) FA.
D) none of the above.
FC.
2
A deliberate change in the government's deficit
A) constitutes discretionary fiscal policy.
B) leads to automatic stabilization.
C) acts as a drag on the economy.
D) is implemented by the Fed.
A) constitutes discretionary fiscal policy.
B) leads to automatic stabilization.
C) acts as a drag on the economy.
D) is implemented by the Fed.
constitutes discretionary fiscal policy.
3
Figure 5-1 
In the figure above, the impact of automatic stabilization is depicted by the movement from
A) A to F.
B) A to B.
C) A to C.
D) D to A.

In the figure above, the impact of automatic stabilization is depicted by the movement from
A) A to F.
B) A to B.
C) A to C.
D) D to A.
A to B.
4
Figure 5-1 
Employing the government budget diagram shown in the figure above, assume that the economy is initially in equilibrium at point A. The movement A to D represents
A) an increase in government spending and/or a decrease in taxes.
B) a decrease in government spending and/or an increase in taxes.
C) a decrease in government spending and a decrease in taxes.
D) an increase in government spending and an increase in taxes.

Employing the government budget diagram shown in the figure above, assume that the economy is initially in equilibrium at point A. The movement A to D represents
A) an increase in government spending and/or a decrease in taxes.
B) a decrease in government spending and/or an increase in taxes.
C) a decrease in government spending and a decrease in taxes.
D) an increase in government spending and an increase in taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The natural employment deficit ________ be used to determine the effectiveness of discretionary fiscal policy actions because ________.
A) cannot; it excludes non-discretionary spending changes
B) can; it includes non-discretionary spending changes
C) cannot; it includes non-discretionary spending changes
D) can; it excludes automatic stabilization expenditures
A) cannot; it excludes non-discretionary spending changes
B) can; it includes non-discretionary spending changes
C) cannot; it includes non-discretionary spending changes
D) can; it excludes automatic stabilization expenditures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The three ways of reducing a government budget deficit are to
A) decrease government spending, reduce consumption, increase the tax rate.
B) increase government spending, decrease real income, reduce the tax rate.
C) decrease government spending, increase real income, reduce the tax rate.
D) decrease government spending, increase real income, increase the tax rate.
A) decrease government spending, reduce consumption, increase the tax rate.
B) increase government spending, decrease real income, reduce the tax rate.
C) decrease government spending, increase real income, reduce the tax rate.
D) decrease government spending, increase real income, increase the tax rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The natural employment surplus ________ be used to determine the effectiveness of discretionary fiscal policy actions because ________.
A) cannot; it excludes non-discretionary spending changes
B) can; it includes non-discretionary spending changes
C) cannot; it includes non-discretionary spending changes
D) can; it excludes automatic stabilization expenditures
A) cannot; it excludes non-discretionary spending changes
B) can; it includes non-discretionary spending changes
C) cannot; it includes non-discretionary spending changes
D) can; it excludes automatic stabilization expenditures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
During the fiscal expansion associated with the Vietnam war, what type of expenditures was initially "crowded out?"
A) autonomous consumption
B) nonresidential fixed investment
C) residential construction
D) nonresidential construction
A) autonomous consumption
B) nonresidential fixed investment
C) residential construction
D) nonresidential construction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following effects takes place as a result of automatic stabilization?
A) extra tax revenues are generated in a boom
B) tax revenues remain constant during a recession
C) leakages increase during a recession, helping to stimulate the economy
D) Both A and C are correct.
A) extra tax revenues are generated in a boom
B) tax revenues remain constant during a recession
C) leakages increase during a recession, helping to stimulate the economy
D) Both A and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Persistent government budget deficit result in ________ taxes and a ________ stock of capital in the future.
A) higher, larger
B) lower, larger
C) higher, smaller
D) lower, smaller
A) higher, larger
B) lower, larger
C) higher, smaller
D) lower, smaller

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An increase in the tax rate (t)
A) will rotate the budget line upward.
B) will increase the slope of the budget line.
C) will shift the budget line downward.
D) A and B.
A) will rotate the budget line upward.
B) will increase the slope of the budget line.
C) will shift the budget line downward.
D) A and B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The actual government budget surplus ________ be used to determine the effectiveness of discretionary fiscal policy actions because ________.
A) cannot; it excludes non-discretionary spending changes
B) can; it includes non-discretionary spending changes
C) cannot; it includes non-discretionary spending changes
D) can; it excludes automatic stabilization expenditures
A) cannot; it excludes non-discretionary spending changes
B) can; it includes non-discretionary spending changes
C) cannot; it includes non-discretionary spending changes
D) can; it excludes automatic stabilization expenditures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The progressive income tax is an automatic stabilizer with respect to the Federal government's budget surplus or deficit because
A) individuals must "automatically" pay taxes even when they have a deficit.
B) during periods of output growth, a greater percentage of real income "leaks" from the expenditure stream.
C) during periods of output growth, the marginal leakage rate increases as taxes decrease.
D) None of the above.
A) individuals must "automatically" pay taxes even when they have a deficit.
B) during periods of output growth, a greater percentage of real income "leaks" from the expenditure stream.
C) during periods of output growth, the marginal leakage rate increases as taxes decrease.
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In the 1980s, expansionary fiscal policy is believed to have crowded out
A) domestic investment as interest rates rose.
B) exports and imports as interest rates rose.
C) exports but not domestic investment as interest rates rose.
D) domestic investment as interest rates fell.
A) domestic investment as interest rates rose.
B) exports and imports as interest rates rose.
C) exports but not domestic investment as interest rates rose.
D) domestic investment as interest rates fell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The structural surplus is
A) the difference between the actual surplus and the natural employment surplus and it increases whenever income rises.
B) identical to the natural employment surplus and it increases whenever tax rates are cut.
C) identical to the natural employment surplus and it decreases whenever the natural level of output increases.
D) identical to the natural employment surplus and it increases whenever the natural level of output increases.
A) the difference between the actual surplus and the natural employment surplus and it increases whenever income rises.
B) identical to the natural employment surplus and it increases whenever tax rates are cut.
C) identical to the natural employment surplus and it decreases whenever the natural level of output increases.
D) identical to the natural employment surplus and it increases whenever the natural level of output increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In the 1980s national savings declined as a percentage of GDP. Assuming that domestic private investment's percentage share has not declined, this situation requires, ceteris paribus,
A) net foreign investment (NX) to decrease.
B) net foreign investment (NX) to increase.
C) U.S. exports to decrease.
D) A and C are both necessary outcomes.
A) net foreign investment (NX) to decrease.
B) net foreign investment (NX) to increase.
C) U.S. exports to decrease.
D) A and C are both necessary outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The structural deficit is
A) the difference between the actual deficit and the natural employment deficit and it increases whenever income rises.
B) identical to the natural employment deficit and it decreases whenever tax rates are cut.
C) identical to the natural employment deficit and it increases whenever the natural level of output increases.
D) identical to the natural employment deficit and it decreases whenever the natural level of output increases.
A) the difference between the actual deficit and the natural employment deficit and it increases whenever income rises.
B) identical to the natural employment deficit and it decreases whenever tax rates are cut.
C) identical to the natural employment deficit and it increases whenever the natural level of output increases.
D) identical to the natural employment deficit and it decreases whenever the natural level of output increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The actual government budget deficit ________ be used to determine the effectiveness of discretionary fiscal policy actions because ________.
A) cannot; it excludes non-discretionary spending changes
B) can; it includes non-discretionary spending changes
C) cannot; it includes non-discretionary spending changes
D) can; it excludes automatic stabilization expenditures
A) cannot; it excludes non-discretionary spending changes
B) can; it includes non-discretionary spending changes
C) cannot; it includes non-discretionary spending changes
D) can; it excludes automatic stabilization expenditures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The natural employment surplus is
A) G + T.
B) Y - tYN.
C) tYN - G.
D) YN + G + tYN.
A) G + T.
B) Y - tYN.
C) tYN - G.
D) YN + G + tYN.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Figure 5-1 
In the figure above, if the budget line BB0, the natural real GDP is $5300, and actual real GDP is $5000, then the cyclical budget surplus or deficit is the
A) horizontal distance between A and F.
B) vertical distance between F and D.
C) vertical distance A and F.
D) horizontal distance between B and D.

In the figure above, if the budget line BB0, the natural real GDP is $5300, and actual real GDP is $5000, then the cyclical budget surplus or deficit is the
A) horizontal distance between A and F.
B) vertical distance between F and D.
C) vertical distance A and F.
D) horizontal distance between B and D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A structural budget deficit
A) appeared during the Vietnam War era from 1966-68.
B) appeared after 1982 due to tax cuts and spending increases.
C) peaked at 5 percent of GDP in mid-1986 and had become a structural surplus by 1997.
D) all of the above.
A) appeared during the Vietnam War era from 1966-68.
B) appeared after 1982 due to tax cuts and spending increases.
C) peaked at 5 percent of GDP in mid-1986 and had become a structural surplus by 1997.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The cyclical deficit is
A) the amount by which the actual government budget deficit exceeds the structural deficit.
B) the amount by which structural deficit exceeds the actual budget deficit.
C) the same as the structural deficit.
D) what the budget deficit would be if the economy were operating at the natural real GDP level.
A) the amount by which the actual government budget deficit exceeds the structural deficit.
B) the amount by which structural deficit exceeds the actual budget deficit.
C) the same as the structural deficit.
D) what the budget deficit would be if the economy were operating at the natural real GDP level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A crucial national income accounting identity sets the government budget deficit equal to
A) S - I - NX.
B) S + I - NX.
C) S - I + NX.
D) S + I + NX.
A) S - I - NX.
B) S + I - NX.
C) S - I + NX.
D) S + I + NX.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the late 1980s the U.S. government ran a succession of large budget ________ which resulted mainly in ________ crowding-out.
A) deficits, domestic
B) deficits, international
C) surpluses, domestic
D) surpluses, international
A) deficits, domestic
B) deficits, international
C) surpluses, domestic
D) surpluses, international

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
An example of "automatic stabilizers" is a rise in ________ causing the budget deficit to ________.
A) real GDP, fall
B) real GDP, rise
C) government expenditures, fall
D) government expenditures, rise
E) the average tax rate, fall
A) real GDP, fall
B) real GDP, rise
C) government expenditures, fall
D) government expenditures, rise
E) the average tax rate, fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
An increase in government expenditures that ________ the budget deficit in an example of ________.
A) raises, automatic stabilization
B) raises, discretionary fiscal policy
C) lowers, automatic stabilization
D) lowers, discretionary fiscal policy
A) raises, automatic stabilization
B) raises, discretionary fiscal policy
C) lowers, automatic stabilization
D) lowers, discretionary fiscal policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Suppose we are modeling a "closed" economy. The only way its government can obtain more goods and services than it can claim with net tax revenues is for
A) exports to exceed imports.
B) imports to exceed exports.
C) investment to exceed saving.
D) saving to exceed investment.
A) exports to exceed imports.
B) imports to exceed exports.
C) investment to exceed saving.
D) saving to exceed investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The 2001 recession was caused principally by
A) a slowing in the growth of the money supply.
B) a drop in autonomous consumption spending.
C) a decrease in government spending
D) a drop in real business investment.
A) a slowing in the growth of the money supply.
B) a drop in autonomous consumption spending.
C) a decrease in government spending
D) a drop in real business investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Suppose we have an economy for which G = 1100, T = 800, S = 230, and I = 230. If I falls to 150, the economy's trade deficit
A) increases from 0 to 80.
B) decreases from 300 to 220.
C) decreases from 0 to -80.
D) decreases from 70 to -10.
E) increases from 0 to 70.
A) increases from 0 to 80.
B) decreases from 300 to 220.
C) decreases from 0 to -80.
D) decreases from 70 to -10.
E) increases from 0 to 70.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
By far the largest real government budget deficits measured as a percentage of natural real GDP occurred during
A) World War I.
B) the Great Depression.
C) World War II.
D) the late 1960s.
E) the late 1980s and early 1990s.
A) World War I.
B) the Great Depression.
C) World War II.
D) the late 1960s.
E) the late 1980s and early 1990s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A recession normally causes ________ in government net tax revenues, ________ the budget deficit is an example of ________ automatic stabilization.
A) an increase, increasing, the working of
B) an increase, decreasing, a failure of
C) a decrease, decreasing, the working of
D) a decrease, increasing, a failure of
E) a decrease, increasing, the working of
A) an increase, increasing, the working of
B) an increase, decreasing, a failure of
C) a decrease, decreasing, the working of
D) a decrease, increasing, a failure of
E) a decrease, increasing, the working of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Historical data suggests that a trend toward ________ natural employment ________.
A) larger, deficits from the early 1960s to the mid-1980s.
B) larger, surpluses form the early 1960s to the mid-1980s.
C) smaller, surpluses form the mid-1980s to 1995.
D) larger, surpluses from the mid-1980s to 1995.
A) larger, deficits from the early 1960s to the mid-1980s.
B) larger, surpluses form the early 1960s to the mid-1980s.
C) smaller, surpluses form the mid-1980s to 1995.
D) larger, surpluses from the mid-1980s to 1995.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A prominent postwar pattern of U.S. government budget deficits was broken in 1983-1990 as
A) recession was accompanied by a shrinking deficit.
B) recession was accompanied by a growing deficit.
C) recovery from recession was accompanied by a shrinking deficit.
D) recovery from recession was accompanied by a growing deficit.
A) recession was accompanied by a shrinking deficit.
B) recession was accompanied by a growing deficit.
C) recovery from recession was accompanied by a shrinking deficit.
D) recovery from recession was accompanied by a growing deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Suppose we have an economy for which G = 300, T = 240, S = 80, I = 45, and imports = 40. Exports must be
A) 25.
B) 40.
C) 15.
D) 65.
E) -25.
A) 25.
B) 40.
C) 15.
D) 65.
E) -25.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A government budget deficit is financed by a combination of
A) saving rising relative to domestic investment and imports rising relative to exports.
B) saving rising relative to domestic investments and exports rising relative to imports.
C) domestic investment rising relative to saving and imports rising relative to exports.
D) domestic investment rising relative to saving and exports rising relative to imports.
A) saving rising relative to domestic investment and imports rising relative to exports.
B) saving rising relative to domestic investments and exports rising relative to imports.
C) domestic investment rising relative to saving and imports rising relative to exports.
D) domestic investment rising relative to saving and exports rising relative to imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In the period 1980-92, United States net national saving fell due to
A) large budget deficits and an increase in private saving.
B) small budget deficits and a decrease in private saving.
C) small budget deficits and an increase in private saving.
D) large budget deficits and a decrease in private saving.
A) large budget deficits and an increase in private saving.
B) small budget deficits and a decrease in private saving.
C) small budget deficits and an increase in private saving.
D) large budget deficits and a decrease in private saving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Given the average tax rate t, a general expression for the budget deficit is
A) tG - Y.
B) Y - tG.
C) G - tY.
D) Y - (G/t).
A) tG - Y.
B) Y - tG.
C) G - tY.
D) Y - (G/t).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In 1990-1991, the government budget deficit ________ mainly due to the ________.
A) rose, recession's effect on tax collection
B) rose, expenditures of the Persian Gulf War
C) fell, recession's effect on government expenditures
D) fell, economic stimulus provided by the Persian Gulf War
A) rose, recession's effect on tax collection
B) rose, expenditures of the Persian Gulf War
C) fell, recession's effect on government expenditures
D) fell, economic stimulus provided by the Persian Gulf War

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A government budget surplus
A) decreases a country's ability to finance domestic and foreign investment.
B) increases a country's ability to finance domestic and foreign investment.
C) increases a country's ability to finance domestic investment and decreases its ability to finance foreign investment.
D) decreases a country's ability to finance domestic investment and increases its ability to finance foreign investment.
A) decreases a country's ability to finance domestic and foreign investment.
B) increases a country's ability to finance domestic and foreign investment.
C) increases a country's ability to finance domestic investment and decreases its ability to finance foreign investment.
D) decreases a country's ability to finance domestic investment and increases its ability to finance foreign investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The economic policy response to the 2001 recession consisted of
A) a rapid change in fiscal policy and monetary policy.
B) a sluggish change in fiscal policy and monetary policy.
C) a rapid change in fiscal policy and a sluggish change in monetary policy.
D) a sluggish change in fiscal policy and a rapid change in monetary policy.
A) a rapid change in fiscal policy and monetary policy.
B) a sluggish change in fiscal policy and monetary policy.
C) a rapid change in fiscal policy and a sluggish change in monetary policy.
D) a sluggish change in fiscal policy and a rapid change in monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Suppose we have an economy in which G = 100, t = 0.26, Y = 3800, and YN = 4000. Then t rises to 0.28 as the same time as G rises to 1150. The overall impact of this resettling of the fiscal variables is ________ because ________.
A) expansionary, the actual deficit rises
B) expansionary, the natural employment deficit falls
C) contractionary, the natural employment deficit falls
D) contractionary, the natural employment deficit rises
E) contractionary, the actual deficit rises
A) expansionary, the actual deficit rises
B) expansionary, the natural employment deficit falls
C) contractionary, the natural employment deficit falls
D) contractionary, the natural employment deficit rises
E) contractionary, the actual deficit rises

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Suppose we have an economy in which G = 1100, t = 0.26, Y = 3800, and YN = 4000. At Y, the actual deficit is
A) 60.
B) 200.
C) 112.
D) 286.
E) -60.
A) 60.
B) 200.
C) 112.
D) 286.
E) -60.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
With a vertical LM curve, an increase in the money supply can be matched by an equal increase in money demand only through ________, which causes monetary policy to be particularly ________.
A) a rise in income, strong
B) a rise in income, weak
C) a fall in the interest rate, strong
D) a fall in the interest rate, weak
A) a rise in income, strong
B) a rise in income, weak
C) a fall in the interest rate, strong
D) a fall in the interest rate, weak

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In the diagram of the budget line BB, a rise in government expenditure shifts BB ________, so that an unchanged GDP the budget deficit ________.
A) downward, rises
B) downward, falls
C) downward, remains unchanged
D) upward, rises
E) upward, falls
A) downward, rises
B) downward, falls
C) downward, remains unchanged
D) upward, rises
E) upward, falls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An increase in the average tax rate that ________ the budget deficit in an example of ________.
A) raises, automatic stabilization
B) raises, discretionary fiscal policy
C) lowers, automatic stabilization
D) lowers, discretionary fiscal policy
A) raises, automatic stabilization
B) raises, discretionary fiscal policy
C) lowers, automatic stabilization
D) lowers, discretionary fiscal policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In a closed economy, a decrease in government spending while taxes remain the same will be accompanied by:
A) a decrease in private investment and an increase in privates saving
B) an increase in private investment and a decrease in private savings
C) a decrease in private investment only
D) an increase in private savings only
A) a decrease in private investment and an increase in privates saving
B) an increase in private investment and a decrease in private savings
C) a decrease in private investment only
D) an increase in private savings only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In a small open economy, an increase in government spending, while taxes remain the same, will be accompanied by:
A) a decrease in private investment and an increase in privates saving
B) an increase in private investment and a decrease in private savings
C) a decrease in national savings and an increase in foreign borrowing
D) an increase in national savings and a decrease in foreign borrowing
A) a decrease in private investment and an increase in privates saving
B) an increase in private investment and a decrease in private savings
C) a decrease in national savings and an increase in foreign borrowing
D) an increase in national savings and a decrease in foreign borrowing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If an economy uses monetary policy as its stabilization tool, the real interest rate and thus ________-run economic welfare depend on that economy's ________ policy.
A) short, monetary
B) short, fiscal
C) long, monetary
D) long, fiscal
A) short, monetary
B) short, fiscal
C) long, monetary
D) long, fiscal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If monetary policy is used to control GDP, there is greater sacrifice of long-run economic growth in pursuing short-run stabilization the ________ is fiscal policy and thus the ________ is the real interest rate.
A) tighter, higher
B) tighter, lower
C) easier, higher
D) easier, lower
A) tighter, higher
B) tighter, lower
C) easier, higher
D) easier, lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Actual output exceeds the natural output when
A) the actual budget surplus is above the structural surplus.
B) the actual budget surplus is below the structural surplus.
C) the structural surplus is positive.
D) the structural surplus is negative.
A) the actual budget surplus is above the structural surplus.
B) the actual budget surplus is below the structural surplus.
C) the structural surplus is positive.
D) the structural surplus is negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The clearest indicator of a switch to a less expansionary fiscal policy is a
A) rise in the actual surplus.
B) fall in the actual surplus.
C) rise in the natural employment surplus.
D) fall in the natural employment surplus.
A) rise in the actual surplus.
B) fall in the actual surplus.
C) rise in the natural employment surplus.
D) fall in the natural employment surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Actual output exceeds the natural output when
A) the actual budget deficit is above the structural deficit.
B) the actual budget deficit is below the structural deficit.
C) the structural deficit is positive.
D) the structural deficit is negative.
A) the actual budget deficit is above the structural deficit.
B) the actual budget deficit is below the structural deficit.
C) the structural deficit is positive.
D) the structural deficit is negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
An increase in tax revenues ________ government saving and ________ national saving.
A) raises, raises
B) raises, lowers
C) lowers, raises
D) lowers, lowers
A) raises, raises
B) raises, lowers
C) lowers, raises
D) lowers, lowers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The clearest indicator of a switch to a less expansionary fiscal policy is a
A) rise in the actual deficit.
B) fall in the actual deficit.
C) rise in the natural employment deficit.
D) fall in the natural employment deficit.
A) rise in the actual deficit.
B) fall in the actual deficit.
C) rise in the natural employment deficit.
D) fall in the natural employment deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A large government budget deficit ________ government saving and ________ national saving.
A) raises, raises
B) raises, lowers
C) lowers, raises
D) lowers, lowers
A) raises, raises
B) raises, lowers
C) lowers, raises
D) lowers, lowers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Suppose we have an economy in which G = 1100, t = 0.26, Y = 3800, and YN = 4000. The natural employment deficit is
A) 60.
B) 200.
C) 840.
D) 286.
E) -112.
A) 60.
B) 200.
C) 840.
D) 286.
E) -112.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In a closed economy, an increase in government spending, while taxes remain the same, will be accompanied by:
A) a decrease in private investment and an increase in privates saving
B) an increase in private investment and a decrease in private savings
C) a decrease in private investment only
D) an increase in private savings only
A) a decrease in private investment and an increase in privates saving
B) an increase in private investment and a decrease in private savings
C) a decrease in private investment only
D) an increase in private savings only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In a small open economy, when exports exceed imports, all of the following are true except:
A) net capital outflows are positive
B) net exports are positive
C) domestic investment exceeds domestic saving
D) domestic output exceeds spending
A) net capital outflows are positive
B) net exports are positive
C) domestic investment exceeds domestic saving
D) domestic output exceeds spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In a small open economy, the real interest rate will always be:
A) above the world real interest rate
B) below the world real interest rate
C) equal to the world real interest rate
D) independent of the world real interest rate
A) above the world real interest rate
B) below the world real interest rate
C) equal to the world real interest rate
D) independent of the world real interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Suppose we have an economy in which G = 1100, t = 0.26, Y = 3800, and YN = 4000. At Y the cyclical deficit is
A) 60.
B) 112.
C) -172.
D) -52.
E) 52.
A) 60.
B) 112.
C) -172.
D) -52.
E) 52.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If S = 200, T = 700, G = 950, and NX = -200, this makes net domestic investment
A) 150.
B) -150.
C) 50.
D) -50.
E) 650.
A) 150.
B) -150.
C) 50.
D) -50.
E) 650.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In the late 1980s, ________ domestic private investment led to ________ in net foreign borrowing.
A) higher, an increase
B) higher, a decrease
C) lower, an increase
D) lower, a decrease
A) higher, an increase
B) higher, a decrease
C) lower, an increase
D) lower, a decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If S = 250, T = 170, NX = -20, this makes government saving
A) -50.
B) -70.
C) 70.
D) 50.
E) -100.
A) -50.
B) -70.
C) 70.
D) 50.
E) -100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In the 1980s, the United States on net ________ foreign nations so that its private firms could absorb through domestic investment ________ goods than what was being left for them by national saving.
A) borrowed from, more
B) borrowed from, fewer
C) lent to, more
D) lent to, fewer
A) borrowed from, more
B) borrowed from, fewer
C) lent to, more
D) lent to, fewer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
When a nation's national saving falls short of its domestic investment, it must be
A) experiencing a government budget surplus.
B) experiencing a government deficit.
C) a net lender to foreign nations.
D) a net borrower from foreign nations.
A) experiencing a government budget surplus.
B) experiencing a government deficit.
C) a net lender to foreign nations.
D) a net borrower from foreign nations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If a nation's budget deficit rises, domestic private investment can remain unchanged through some combination of ________ private saving and ________ importing relative to exporting.
A) increased, less
B) increased, more
C) decreased, less
D) decreased, more
A) increased, less
B) increased, more
C) decreased, less
D) decreased, more

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Current account includes all of the following except:
A) net exports
B) net income from abroad
C) net unilateral transfers
D) net regulations
A) net exports
B) net income from abroad
C) net unilateral transfers
D) net regulations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Compared to 1960-79, U.S. net national saving form 1980-92 as a proportion of national income
A) rose tremendously.
B) rose slightly.
C) fell slightly.
D) fell precipitously.
A) rose tremendously.
B) rose slightly.
C) fell slightly.
D) fell precipitously.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If a country's private saving is 100 and government saving is -100, domestic private investment
A) must be 200.
B) must be zero.
C) is equal to the net amount the economy borrows from other countries.
D) is equal to the net amount the economy lends to other countries.
A) must be 200.
B) must be zero.
C) is equal to the net amount the economy borrows from other countries.
D) is equal to the net amount the economy lends to other countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If S = 300, T = 800, G = 1100, and I = 150, this makes net foreign investment
A) 150.
B) -150.
C) 450.
D) 750.
E) -450.
A) 150.
B) -150.
C) 450.
D) 750.
E) -450.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
From 2004 to 2006, the European Union budget was ________, private saving was ________ domestic investment, and foreign lending ________.
A) balanced, roughly equal to, negligible
B) balanced, less than, substantial.
C) surplus, greater than, negligible
D) in deficit, greater than, negligible
A) balanced, roughly equal to, negligible
B) balanced, less than, substantial.
C) surplus, greater than, negligible
D) in deficit, greater than, negligible

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In the current debate over fiscal policy, advocates of returning to significant budget surpluses
A) contended that the economic miracle of the late 1990s caused the budget surpluses
B) think that tax cuts will benefit the wealthy
C) believe that tax cuts will continue the dependence of the United States on borrowing from foreigners.
D) All of the above.
A) contended that the economic miracle of the late 1990s caused the budget surpluses
B) think that tax cuts will benefit the wealthy
C) believe that tax cuts will continue the dependence of the United States on borrowing from foreigners.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
From 1980 to 1992 net national saving in the United States averaged approximately ________ percent of national income.
A) 32
B) 18
C) 12
D) 4.7
E) 2.2
A) 32
B) 18
C) 12
D) 4.7
E) 2.2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
From 2004 to 2006, the U.S. budget was ________, private saving was ________ domestic investment, and foreign borrowing was ________.
A) in deficit, less than, needed to finance deficit
B) balanced, roughly equal to, not needed to finance deficit
C) balanced, less than, substantial.
D) surplus, greater than, negligible
A) in deficit, less than, needed to finance deficit
B) balanced, roughly equal to, not needed to finance deficit
C) balanced, less than, substantial.
D) surplus, greater than, negligible

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Switching to a faster economic growth path comes at the cost of lower
A) present investment.
B) present consumption.
C) future investment.
D) present saving.
E) future saving.
A) present investment.
B) present consumption.
C) future investment.
D) present saving.
E) future saving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
From 2004 to 2006, the Japanese budget was ________, private saving was ________ domestic investment, and foreign lending ________.
A) in deficit, greater than, moderate
B) balanced, roughly equal to, negligible
C) balanced, less than, moderate.
D) surplus, greater than, negligible
A) in deficit, greater than, moderate
B) balanced, roughly equal to, negligible
C) balanced, less than, moderate.
D) surplus, greater than, negligible

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In 1980, the U.S. budget was ________, private saving was ________ domestic investment, and foreign borrowing was ________.
A) in deficit, higher than, not needed to finance deficit
B) balanced, roughly equal to, not needed to finance deficit
C) balanced, less than, substantial.
D) surplus, greater, negligible
A) in deficit, higher than, not needed to finance deficit
B) balanced, roughly equal to, not needed to finance deficit
C) balanced, less than, substantial.
D) surplus, greater, negligible

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
From 1988 to 1990, the U.S. budget was ________, private saving was ________ domestic investment, and foreign borrowing was ________.
A) in deficit, higher than, still needed to finance deficit
B) balanced, roughly equal to, not needed to finance deficit
C) balanced, less than, substantial.
D) surplus, less than, negligible
A) in deficit, higher than, still needed to finance deficit
B) balanced, roughly equal to, not needed to finance deficit
C) balanced, less than, substantial.
D) surplus, less than, negligible

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The "twin deficits" refer to government expenditures being ________ than net tax revenues at the same time as exports ________ imports.
A) less, are below
B) less, exceed
C) greater, are below
D) greater, exceed
A) less, are below
B) less, exceed
C) greater, are below
D) greater, exceed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



