Deck 4: Nuclear Chemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/92
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Nuclear Chemistry
1
The process in which a nucleus spontaneously breaks down by emitting radiation is known as
A) transmutation.
B) transformation.
C) fusion.
D) a chain reaction.
E) radioactive decay.
A) transmutation.
B) transformation.
C) fusion.
D) a chain reaction.
E) radioactive decay.
radioactive decay.
2
When a positron is emitted from the nucleus of an atom, the nuclear mass
A) increases by two units.
B) decreases by one unit.
C) increases by one unit.
D) decreases by two units.
E) remains the same.
A) increases by two units.
B) decreases by one unit.
C) increases by one unit.
D) decreases by two units.
E) remains the same.
remains the same.
3
Which is NOT a way to minimize your exposure to radiation?
A) wearing a lead apron
B) keeping a good distance
C) standing behind a thick concrete wall
D) wearing lead-lined gloves
E) staying a longer time
A) wearing a lead apron
B) keeping a good distance
C) standing behind a thick concrete wall
D) wearing lead-lined gloves
E) staying a longer time
staying a longer time
4
For 85
38 Sr, there are
A) 85 protons and 38 neutrons.
B) 47 protons and 38 neutrons.
C) 38 protons and 47 neutrons.
D) 38 protons and 85 neutrons.
E) 85 protons and 47 neutrons.
38 Sr, there are
A) 85 protons and 38 neutrons.
B) 47 protons and 38 neutrons.
C) 38 protons and 47 neutrons.
D) 38 protons and 85 neutrons.
E) 85 protons and 47 neutrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The nuclear reaction shown below is an example of what type of process?
224
90 Th ? 220
88 Rn + 4
2 He
A) fusion
B) fission
C) translation
D) alpha emission
E) beta emission
224
90 Th ? 220
88 Rn + 4
2 He
A) fusion
B) fission
C) translation
D) alpha emission
E) beta emission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When a gamma ray is emitted from the nucleus of an atom, the nuclear mass
A) increases by two units.
B) decreases by one unit.
C) increases by one unit.
D) decreases by two units.
E) remains the same.
A) increases by two units.
B) decreases by one unit.
C) increases by one unit.
D) decreases by two units.
E) remains the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The damaging effects of radiation on the body are a result of
A) the formation of unstable ions or radicals.
B) the formation of radioactive atoms in the body.
C) transmutation reactions in the body.
D) extensive damage to nerve cells.
E) the production of radioactive sodium ions in the body.
A) the formation of unstable ions or radicals.
B) the formation of radioactive atoms in the body.
C) transmutation reactions in the body.
D) extensive damage to nerve cells.
E) the production of radioactive sodium ions in the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is suitable as a minimum shielding for beta particles?
A) air
B) 1 m of water
C) gloves
D) 1 m of concrete
E) 1 cm of lead
A) air
B) 1 m of water
C) gloves
D) 1 m of concrete
E) 1 cm of lead

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A positron is a particle emitted from the nucleus that has the same mass as a(n)
A) electron but has a positive charge.
B) neutron but has a positive charge.
C) alpha particle.
D) beta particle.
E) proton emitted from the nucleus.
A) electron but has a positive charge.
B) neutron but has a positive charge.
C) alpha particle.
D) beta particle.
E) proton emitted from the nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Gamma rays require the heaviest shielding of all the common types of nuclear radiation because gamma rays have the
A) highest energy.
B) most intense color.
C) lowest energy.
D) largest particles.
E) heaviest particles.
A) highest energy.
B) most intense color.
C) lowest energy.
D) largest particles.
E) heaviest particles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following types of radiation has the highest energy?
A) α-particles
B) β-particles
C) γ-rays
D) visible light
E) All of these have the same energy.
A) α-particles
B) β-particles
C) γ-rays
D) visible light
E) All of these have the same energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In the nuclear equation of a beta emitter,
A) the new nucleus contains 2 fewer protons.
B) the new nucleus contains 2 more protons.
C) the mass number of the new nucleus is 4 less than that of the original nucleus.
D) the new nucleus contains 1 more proton.
E) the new nucleus contains 1 less proton.
A) the new nucleus contains 2 fewer protons.
B) the new nucleus contains 2 more protons.
C) the mass number of the new nucleus is 4 less than that of the original nucleus.
D) the new nucleus contains 1 more proton.
E) the new nucleus contains 1 less proton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
When an alpha particle is emitted from the nucleus of an atom, the nuclear mass
A) increases by two units.
B) decreases by four units.
C) increases by one unit.
D) decreases by two units.
E) remains the same.
A) increases by two units.
B) decreases by four units.
C) increases by one unit.
D) decreases by two units.
E) remains the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The nuclear symbol of helium, 4
2 He, is also the symbol for designating a(n)
A) proton.
B) neutron.
C) gamma ray.
D) beta particle.
E) alpha particle.
2 He, is also the symbol for designating a(n)
A) proton.
B) neutron.
C) gamma ray.
D) beta particle.
E) alpha particle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The symbol 0
+1 e is a symbol used for a(n)
A) proton.
B) positron.
C) gamma ray.
D) beta particle.
E) alpha particle.
+1 e is a symbol used for a(n)
A) proton.
B) positron.
C) gamma ray.
D) beta particle.
E) alpha particle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is the nuclear symbol for a radioactive isotope of copper with a mass number of 60?
A) 60
29 Cu
B) 29
60 Cu
C) 29Cu
D) 60
31 Cu
E) 31
29 Cu
A) 60
29 Cu
B) 29
60 Cu
C) 29Cu
D) 60
31 Cu
E) 31
29 Cu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The symbol 0
-1 e is a symbol used for a(n)
A) proton.
B) neutron.
C) gamma ray.
D) beta particle.
E) alpha particle.
-1 e is a symbol used for a(n)
A) proton.
B) neutron.
C) gamma ray.
D) beta particle.
E) alpha particle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If absorbed internally, alpha particle emitters are the most damaging because alpha particles
A) have the largest charge.
B) have the greatest energy.
C) have the greatest mass.
D) consist of high energy electrons.
E) consist of pure energy.
A) have the largest charge.
B) have the greatest energy.
C) have the greatest mass.
D) consist of high energy electrons.
E) consist of pure energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A nuclear equation is balanced when
A) the same elements are found on both sides of the equation.
B) the sum of the mass numbers and the sum of the atomic numbers of the particles and atoms are the same on both sides of the equation.
C) the same particles and atoms are on both sides of the equation.
D) different particles and atoms are on both sides of the equation.
E) the charges of the particles and atoms are the same on both sides of the equation.
A) the same elements are found on both sides of the equation.
B) the sum of the mass numbers and the sum of the atomic numbers of the particles and atoms are the same on both sides of the equation.
C) the same particles and atoms are on both sides of the equation.
D) different particles and atoms are on both sides of the equation.
E) the charges of the particles and atoms are the same on both sides of the equation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The product from the alpha decay of
235
92
U is
A)
235
93
Np.
B) 239
94 Pu.
C) 231
90 Th.
D) 233
80 Ra.
E)
236
92
U.
235
92
U is
A)
235
93
Np.
B) 239
94 Pu.
C) 231
90 Th.
D) 233
80 Ra.
E)
236
92
U.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A patient receives 10 mrads of gamma radiation. If the factor that adjusts for biological damage for for gamma radiation is 1, how many mrems did the patient receive?
A) 2 mrem
B) 5 mrem
C) 10 mrem
D) 20 mrem
E) 200 mrem
A) 2 mrem
B) 5 mrem
C) 10 mrem
D) 20 mrem
E) 200 mrem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The recommended dosage of I-131 for a test is 4.2 microcuries per kg of body weight. How many millicuries should be given to a 55 kg patient? (1 mCi = 1000 μCi)
A) 230 millicuries
B) 0.23 millicuries
C) 0.076 millicuries
D) 760 millicuries
E) 13.8 millicuries
A) 230 millicuries
B) 0.23 millicuries
C) 0.076 millicuries
D) 760 millicuries
E) 13.8 millicuries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the radioactive particle released in the following nuclear equation?
90
38 Sr ? 90
39 Y + ?
A) alpha particle
B) beta particle
C) gamma ray
D) proton
E) neutron
90
38 Sr ? 90
39 Y + ?
A) alpha particle
B) beta particle
C) gamma ray
D) proton
E) neutron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the radioactive particle released in the following nuclear equation? 159
74 W ? 155
72 Hf + ?
A) alpha particle
B) beta particle
C) gamma ray
D) proton
E) neutron
74 W ? 155
72 Hf + ?
A) alpha particle
B) beta particle
C) gamma ray
D) proton
E) neutron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A patient receives 4.2 × 103 mrads of iodine-131, which emits β-particles. If the factor that adjusts for biological damage is 1 for β-particles, how many rems did the patient receive?
A) 4
B) 0.4
C) 0.3
D) 2
E) 40
A) 4
B) 0.4
C) 0.3
D) 2
E) 40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A person begins to suffer radiation sickness at an exposure level of
A) 25 rem.
B) 5 rem.
C) 500 rem.
D) 100 rem.
E) 600 rem.
A) 25 rem.
B) 5 rem.
C) 500 rem.
D) 100 rem.
E) 600 rem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A sample of cerium-141 for a diagnostic test was dissolved in saline solution to an activity of 4.5 millicuries/mL. If the patient undergoing the test needs a dose of 10. millicuries, how much of the solution should be injected into the patient?
A) 45 mL
B) 45 mL.
C) 2.2 mL
D) 22 mL
E) 4.5 mL
A) 45 mL
B) 45 mL.
C) 2.2 mL
D) 22 mL
E) 4.5 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Nitrogen-17 is a beta emitter. What is the isotope produced in the radioactive decay?
A) 18
6 C
B) 13
5 B
C) 18
7 N
D) 13
9 F
E) 17
8 O
A) 18
6 C
B) 13
5 B
C) 18
7 N
D) 13
9 F
E) 17
8 O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When aluminum-27 is bombarded with a neutron, a gamma ray is emitted. What radioactive isotope is produced?
A) silicon-27
B) silicon-28
C) aluminum-28
D) magnesium-27
E) magnesium-28
A) silicon-27
B) silicon-28
C) aluminum-28
D) magnesium-27
E) magnesium-28

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Gamma rays may be detected using
A) a Geiger counter.
B) a film badge.
C) X-ray film.
D) all of the above devices.
E) none of the above devices.
A) a Geiger counter.
B) a film badge.
C) X-ray film.
D) all of the above devices.
E) none of the above devices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is missing in the nuclear reaction shown below?
10
5
B + 4
2 He ? _____ + 1
0 n
A) a neutron
B) 13
7 B
C) 14
7 N
D) 13
7 N
E) 13
5 N
10
5
B + 4
2 He ? _____ + 1
0 n
A) a neutron
B) 13
7 B
C) 14
7 N
D) 13
7 N
E) 13
5 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The unit used to measure the amount of radiation absorbed by a gram of material is called then
A) rad.
B) RBE.
C) curie.
D) rem.
E) MPD.
A) rad.
B) RBE.
C) curie.
D) rem.
E) MPD.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The nuclear reaction
126
50
Sn ?
126
51
Sb + ? is an example of
A) fusion.
B) fission.
C) translation.
D) alpha emission.
E) beta emission.
126
50
Sn ?
126
51
Sb + ? is an example of
A) fusion.
B) fission.
C) translation.
D) alpha emission.
E) beta emission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is missing in the nuclear reaction shown below?
10
5
B + 4
2 He ? 13
7 N + _____
A) gamma radiation
B) a positron
C) a neutron
D) an alpha particle
E) a beta particle
10
5
B + 4
2 He ? 13
7 N + _____
A) gamma radiation
B) a positron
C) a neutron
D) an alpha particle
E) a beta particle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A sample of technetium-99m has an activity of 1.5 Ci. How many disintegrations occur in the technetium-99m sample in 5.0 sec?
A) 5.6 × 1011
B) 2.8 × 1011
C) 1.1 × 1010
D) 7.5
E) 2.0 × 10-10
A) 5.6 × 1011
B) 2.8 × 1011
C) 1.1 × 1010
D) 7.5
E) 2.0 × 10-10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Why is it important that radioisotopes used in diagnostic tests have short half-lives?
A) These radioisotopes have a greater activity so they are easier to monitor.
B) This minimizes the harmful side effects of the radiation.
C) This is necessary so the radioisotopes will have high energy.
D) These radioisotopes are less expensive.
E) These radioisotopes are more abundant in nature.
A) These radioisotopes have a greater activity so they are easier to monitor.
B) This minimizes the harmful side effects of the radiation.
C) This is necessary so the radioisotopes will have high energy.
D) These radioisotopes are less expensive.
E) These radioisotopes are more abundant in nature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the radiation particle used in the bombardment of nitrogen-14?
14
7 N + ? ? 14
6 C +
1
1
H
A) alpha particle
B) beta particle
C) gamma ray
D) proton
E) neutron
14
7 N + ? ? 14
6 C +
1
1
H
A) alpha particle
B) beta particle
C) gamma ray
D) proton
E) neutron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is missing in the nuclear reaction shown below?
66
30 Zn +
1
1
p ? _____
A) a proton
B) 67
31 Ga
C) 66
31 Ga
D) 67
31 Zn
E) 65
29 Cu
66
30 Zn +
1
1
p ? _____
A) a proton
B) 67
31 Ga
C) 66
31 Ga
D) 67
31 Zn
E) 65
29 Cu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Iodine-131 decays by beta emission to
A) iodine-132.
B) tellurium-131.
C) iodine-130
D) bromine-131
E) xenon-131.
A) iodine-132.
B) tellurium-131.
C) iodine-130
D) bromine-131
E) xenon-131.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Radium-226 decays by alpha emission to
A) barium-131.
B) cobalt-60.
C) carbon-14.
D) polonium-218.
E) radon-222.
A) barium-131.
B) cobalt-60.
C) carbon-14.
D) polonium-218.
E) radon-222.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The half-life of bromine-74 is 25 min. How much of a 4.0 mg sample is still active after 75 min?
A) 0.50 mg
B) 1.0 mg
C) 2.0 mg
D) 0.25 mg
E) 4.0 mg
A) 0.50 mg
B) 1.0 mg
C) 2.0 mg
D) 0.25 mg
E) 4.0 mg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The radiation dose required to produce death in one-half of the exposed subject animals is termed the __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When an atom of uranium-235 is bombarded with neutrons, it splits into smaller nuclei and produces a great amount of energy. This nuclear process is called
A) fission.
B) fusion.
C) decomposition.
D) chain reaction.
E) ionization.
A) fission.
B) fusion.
C) decomposition.
D) chain reaction.
E) ionization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
 Sr → __________ +
Sr → __________ + 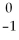 e + energy
e + energy
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Krypton-79 has a half-life of 35 hours. How many half-lives have passed after 105 hours?
A) 1 half-life
B) 2 half-lives
C) 3 half-lives
D) 4 half-lives
E) 5 half-lives
A) 1 half-life
B) 2 half-lives
C) 3 half-lives
D) 4 half-lives
E) 5 half-lives

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
 Tc →
Tc → 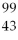 Tc + __________
Tc + __________
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the Sun, nuclei of hydrogen combine to form a larger nucleus and release a great amount of energy. The process is known as
A) fission.
B) fusion.
C) metathesis.
D) chain reaction.
E) ionization.
A) fission.
B) fusion.
C) metathesis.
D) chain reaction.
E) ionization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The half-life of a radioisotope is
A) one-half of the time it takes for the radioisotope to completely decay to a nonradioactive isotope.
B) the time it takes for the radioisotope to become an isotope with one-half of the atomic weight of the original radioisotope.
C) the time it takes for the radioisotope to become an isotope with one-half the atomic number of the original radioisotope.
D) the time it takes for the radioisotope to lose one-half of its neutrons.
E) the time it takes for one-half of the sample to decay.
A) one-half of the time it takes for the radioisotope to completely decay to a nonradioactive isotope.
B) the time it takes for the radioisotope to become an isotope with one-half of the atomic weight of the original radioisotope.
C) the time it takes for the radioisotope to become an isotope with one-half the atomic number of the original radioisotope.
D) the time it takes for the radioisotope to lose one-half of its neutrons.
E) the time it takes for one-half of the sample to decay.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A patient receives 3.0 mL of a solution containing technetium-99m for a breast image. If the activity of the technetium-99m is 9.5 mCi/mL, what is the dose received by the patient?
A) 3.2 mCi
B) 29 mCi
C) 320 μCi
D) 9.5 mCi
E) 28.5 mCi
A) 3.2 mCi
B) 29 mCi
C) 320 μCi
D) 9.5 mCi
E) 28.5 mCi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The most widely used medical isotope in nuclear medicine is
A) Tc-99m.
B) I-131.
C) P-32.
D) I-125.
E) Co-60.
A) Tc-99m.
B) I-131.
C) P-32.
D) I-125.
E) Co-60.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
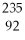 U +
U +  n → __________ +
n → __________ + 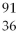 Kr + 3
Kr + 3 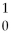 n + energy
n + energy
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A wooden object from a prehistoric site has a carbon-14 activity of 10 counts per minute (cpm) compared to 40 cpm for new wood. If carbon-14 has a half-life of 5730 years, what is the age of the wood?
A) 1430 yr
B) 5730 yr
C) 11,500 yr
D) 17,200 yr
E) 22,900 yr
A) 1430 yr
B) 5730 yr
C) 11,500 yr
D) 17,200 yr
E) 22,900 yr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
One symbol for the β particle is 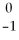 β. Another symbol for the same particle is __________.
β. Another symbol for the same particle is __________.
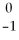 β. Another symbol for the same particle is __________.
β. Another symbol for the same particle is __________.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
An imaging technique in which a computer monitors the degree of absorption of X-ray beams is known as
A) positron emission tomography (PET).
B) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
C) computerized tomography (CT).
D) radioactive iodine uptake (RAIU).
E) a scan.
A) positron emission tomography (PET).
B) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
C) computerized tomography (CT).
D) radioactive iodine uptake (RAIU).
E) a scan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Sodium-24 has a half-life of 15 hours. How many hours is three half-lives?
A) 60 hours
B) 45 hours
C) 30 hours
D) 15 hours
E) 7.5 hours
A) 60 hours
B) 45 hours
C) 30 hours
D) 15 hours
E) 7.5 hours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Iodine-123, which is used for diagnostic imaging in the thyroid, has a half-life of 13 hours. If 50.0 mg of I-123 were prepared at 8:00 a.m. on Monday, how many mg remain at 10:00 a.m. on the following day?
A) 50.0 mg
B) 25.0 mg
C) 12.5 mg
D) 6.25 mg
E) 3.13 mg
A) 50.0 mg
B) 25.0 mg
C) 12.5 mg
D) 6.25 mg
E) 3.13 mg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
An imaging technique that detects the energy emitted by hydrogen atoms in a magnetic field is known as
A) positron emission tomography (PET).
B) computerized tomography (CT).
C) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
D) radioactive tracer study.
E) supermagnetic tomography (SMT).
A) positron emission tomography (PET).
B) computerized tomography (CT).
C) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
D) radioactive tracer study.
E) supermagnetic tomography (SMT).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The dosage of technetium-99m for myocardial imaging is 280 μCi/kg of body weight. How many mCi should be given to a patient weighing 65 kg? (1 mCi = 1000 μCi)
A) 0.0043 mCi
B) 4.3 mCi
C) 18 mCi
D) 230 mCi
E) 1.8 × 104 mCi
A) 0.0043 mCi
B) 4.3 mCi
C) 18 mCi
D) 230 mCi
E) 1.8 × 104 mCi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
One symptom of mild radiation sickness is
A) a lowered white cell count.
B) a raised white cell count.
C) a lowered red blood cell count.
D) a raised red blood cell count.
E) a white cell count of zero.
A) a lowered white cell count.
B) a raised white cell count.
C) a lowered red blood cell count.
D) a raised red blood cell count.
E) a white cell count of zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A sample of phosphorus-32 with an activity of 2.0 mCi produces __________ disintegrations per second. (1 Ci = 3.7 × 1010 disintegration/sec).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
One mCi of a radioactive substance emits more radiation than one μCi of the same substance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The radioisotope used as a diagnostic tool to measure thyroid function is __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Irradiated food contains small amounts of added radioactive isotopes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Nuclear fission as used in nuclear power plants produces radioactive waste with long half-lives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The process by which a large nucleus breaks into smaller pieces, releasing large amounts of energy is called nuclear __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If the half-life of hydrogen-3 is 11.8 years, after two half-lives the radioactivity of a sample will be reduced to one-half of the original amount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A beta particle is emmited when Co-60 decays to Fe-60.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Medical radioisotopes used for diagnostic purposes typically have short half-lives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The common unit of radioactivity which is used to measure the biological damage is the __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Nuclear fusion does not occur naturally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Exposure to radiation is unavoidable because some radioactive elements occur naturally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The correct symbol for hydrogen-3 is 3
2 He.
2 He.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
One type of radiation that is not usually used for medical procedures is the cosmic ray.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
One symptom of radiation sickness is an increased production of red blood cells. (4,3)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The production of nitrogen-13 and a neutron from boron-10 by bombardment with a helium-4 nucleus is an example of radioactive decay.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Irradiation of food for sterilization is usually carried out using gamma irradiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The diagnostic imaging technique that depends on magnetic fields and radio waves, not radioactivity, is called __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The time needed for a radioactive sample to decay to one-half of its original activity is called the __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
An alpha particle is emitted when Am-241 decays to Np-237.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Indicate whether each of the following is characteristic of the fission or fusion process.
A large nucleus is split into smaller nuclei.
A)both fission and fusion
B)fusion
C)fission
A large nucleus is split into smaller nuclei.
A)both fission and fusion
B)fusion
C)fission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



