Deck 6: Formation of Metamorphic Rocks
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/84
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Formation of Metamorphic Rocks
1
A weakly foliated metamorphic rock composed of calcite is classified as a
A) hornfels.
B) marble.
C) migmatite.
D) quartzite.
A) hornfels.
B) marble.
C) migmatite.
D) quartzite.
B
2
A coarse-grained, shiny, foliated metamorphic rock that exhibits well developed mineral cleavage is classified as a
A) hornfels.
B) slate.
C) schist.
D) phyllite.
A) hornfels.
B) slate.
C) schist.
D) phyllite.
C
3
What aluminosilicate polymorph is stable at a pressure of 3.5 kilobars and a temperature of 550 degrees C?
A) andalusite
B) sillimanite
C) kyanite
D) andalusite, sillimanite and kyanite
A) andalusite
B) sillimanite
C) kyanite
D) andalusite, sillimanite and kyanite
B
4
What grade of metamorphism occurs at a depth of 6 km and a temperature of 100 degrees C?
A) lithification of sedimentary rocks
B) medium-grade metamorphism
C) not found on Earth
D) low-grade metamorphism
A) lithification of sedimentary rocks
B) medium-grade metamorphism
C) not found on Earth
D) low-grade metamorphism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Temperature decreases with depth below Earth's surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What aluminosilicate polymorph is stable at a pressure of 1 kilobar and a temperature of 700 degrees C?
A) andalusite and kyanite
B) sillimanite and kyanite
C) andalusite and sillimanite
D) andalusite, sillimanite and kyanite
A) andalusite and kyanite
B) sillimanite and kyanite
C) andalusite and sillimanite
D) andalusite, sillimanite and kyanite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A fine-grained, foliated metamorphic rock that exhibits a silky sheen is classified as a
A) slate.
B) schist.
C) hornfels.
D) phyllite.
A) slate.
B) schist.
C) hornfels.
D) phyllite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What aluminosilicate polymorph is stable at a pressure of 4 kilobars and a temperature of 400 degrees C?
A) kyanite
B) andalusite
C) sillimanite
D) kyanite and andalusite stable
A) kyanite
B) andalusite
C) sillimanite
D) kyanite and andalusite stable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which mineral is not a polymorph of Al2SiO5?
A) andalusite
B) garnet
C) kyanite
D) sillimanite
A) andalusite
B) garnet
C) kyanite
D) sillimanite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What grade of metamorphism occurs at a depth of 5 km and a temperature of 1100 degrees C?
A) magma
B) medium-grade metamorphism
C) high-grade metamorphism
D) low-grade metamorphism
A) magma
B) medium-grade metamorphism
C) high-grade metamorphism
D) low-grade metamorphism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The starting composition of a metamorphic rock, with slight modification, is identical to the ending composition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What aluminosilicate polymorph is stable at a pressure of 8 kilobars and a temperature of 800 degrees C?
A) sillimanite
B) andalusite
C) kyanite
D) kyanite and sillimanite
A) sillimanite
B) andalusite
C) kyanite
D) kyanite and sillimanite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What aluminosilicate polymorph is stable at a pressure of 8 kilobars and a temperature of 600 degrees C?
A) kyanite
B) andalusite
C) sillimanite
D) andalusite and sillimanite
A) kyanite
B) andalusite
C) sillimanite
D) andalusite and sillimanite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What grade of metamorphism occurs at a depth of 19 km and a temperature of 700 degrees C?
A) high-grade metamorphism
B) medium-grade metamorphism
C) low-grade metamorphism
D) magma
A) high-grade metamorphism
B) medium-grade metamorphism
C) low-grade metamorphism
D) magma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following parameters does not determine the mineral composition and texture of a metamorphic rock?
A) environment of deposition
B) original rock composition
C) temperature and pressure
D) abundance and composition of fluid
A) environment of deposition
B) original rock composition
C) temperature and pressure
D) abundance and composition of fluid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What aluminosilicate polymorph is stable at a pressure of 1.5 kilobars and a temperature of 600 degrees C?
A) sillimanite
B) kyanite
C) sillimanite and kyanite
D) andalusite
A) sillimanite
B) kyanite
C) sillimanite and kyanite
D) andalusite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What grade of metamorphism occurs at a depth of 5 km and a temperature of 300 degrees C?
A) high-grade metamorphism
B) not found on Earth
C) medium-grade metamorphism
D) low-grade metamorphism
A) high-grade metamorphism
B) not found on Earth
C) medium-grade metamorphism
D) low-grade metamorphism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Metamorphic rocks can form from the metamorphism of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Metamorphic processes can be seen because metamorphic rocks form on Earth's surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What grade of metamorphism occurs at a depth of 1 km and a temperature of 75 degrees C?
A) low-grade metamorphism
B) lithification of sedimentary rocks
C) medium-grade metamorphism
D) not found on Earth
A) low-grade metamorphism
B) lithification of sedimentary rocks
C) medium-grade metamorphism
D) not found on Earth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A shale metamorphosed to medium metamorphic grade would become a(n)
A) slate.
B) gneiss.
C) amphibolite.
D) schist.
A) slate.
B) gneiss.
C) amphibolite.
D) schist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What type of reaction is this? KAl3Si3O10(OH)2 + SiO2 --> Al2SiO5 + KAlSi3O8 + H2O
A) degassing
B) dehydration
C) decomposition
D) decay
A) degassing
B) dehydration
C) decomposition
D) decay

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A foliated, greasy metamorphic rock composed of graphite is classified as a(n)
A) lignite.
B) anthracite.
C) subbituminous coal.
D) bituminous coal.
A) lignite.
B) anthracite.
C) subbituminous coal.
D) bituminous coal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A shale metamorphosed to low metamorphic grade would become a(n)
A) amphibolite.
B) gneiss.
C) slate.
D) schist.
A) amphibolite.
B) gneiss.
C) slate.
D) schist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A shale metamorphosed to high metamorphic grade would become a(n)
A) slate.
B) amphibolite.
C) schist.
D) gneiss.
A) slate.
B) amphibolite.
C) schist.
D) gneiss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A felsic igneous rock metamorphosed to low metamorphic grade would become a(n)
A) schist.
B) amphibolite.
C) gneiss.
D) slate.
A) schist.
B) amphibolite.
C) gneiss.
D) slate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Figure 6.2 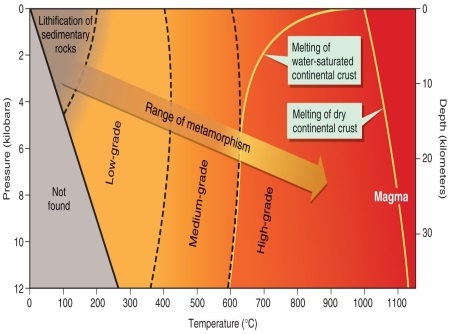
Using Figure 6.2 in your textbook, what grade of metamorphism is found at 400C and 4 kilobars of pressure?
A) low-grade
B) medium-grade
C) high-grade
D) melting

Using Figure 6.2 in your textbook, what grade of metamorphism is found at 400C and 4 kilobars of pressure?
A) low-grade
B) medium-grade
C) high-grade
D) melting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What causes the breakdown of dolomite?
A) volcanic eruptions
B) plate tectonics
C) earthquakes
D) baked near a hot magma intrusion
A) volcanic eruptions
B) plate tectonics
C) earthquakes
D) baked near a hot magma intrusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Figure 6.2 
According to Figure 6.2 in your textbook, when metamorphism occurs, the range of temperatures and pressures encompasses all of the following except
A) the boiling temperature of water.
B) conditions for lithification of sedimentary rocks.
C) conditions for melting water-rich rocks.
D) conditions for melting dry rocks.

According to Figure 6.2 in your textbook, when metamorphism occurs, the range of temperatures and pressures encompasses all of the following except
A) the boiling temperature of water.
B) conditions for lithification of sedimentary rocks.
C) conditions for melting water-rich rocks.
D) conditions for melting dry rocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Coal metamorphosed to medium metamorphic grade would become a(n)
A) lignite.
B) anthracite.
C) subbituminous coal.
D) bituminous coal.
A) lignite.
B) anthracite.
C) subbituminous coal.
D) bituminous coal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
An anhydrous, very-high grade metamorphic rock composed of garnet and pyroxene is classified as a(n)
A) anthracite.
B) eclogite.
C) amphibolite.
D) quartzite.
A) anthracite.
B) eclogite.
C) amphibolite.
D) quartzite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In what type of metamorphism does this reaction occur? KAl3Si3O10(OH)2 + SiO2 --> Al2SiO5 + KAlSi3O8 + H2O
A) high temperature
B) high pressure
C) high grade
D) hydrothermal
A) high temperature
B) high pressure
C) high grade
D) hydrothermal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Geologists use the following methods to study metamorphic processes except
A) inference and theory.
B) direct observation and conclusion.
C) experiment and conclusion.
D) indirect observation and inference.
A) inference and theory.
B) direct observation and conclusion.
C) experiment and conclusion.
D) indirect observation and inference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A weakly foliated metamorphic rock composed of green minerals such as chlorite is classified as a(n)
A) amphibolite.
B) greenslate.
C) greenstone.
D) green hornfels.
A) amphibolite.
B) greenslate.
C) greenstone.
D) green hornfels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A fine-grained, greasy metamorphic rock composed of serpentine is classified as a(n)
A) greenstone.
B) amphibolite.
C) marble.
D) serpentinite.
A) greenstone.
B) amphibolite.
C) marble.
D) serpentinite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
When geologists study metamorphism in the laboratory, which factor would they probably not vary?
A) rock composition
B) temperature
C) volume available for reaction to occur
D) abundance and composition of fluid
A) rock composition
B) temperature
C) volume available for reaction to occur
D) abundance and composition of fluid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A very hard, non-foliated metamorphic rock composed microscopically small crystals is classified as a(n)
A) amphibolite.
B) greenstone.
C) slate.
D) hornfels.
A) amphibolite.
B) greenstone.
C) slate.
D) hornfels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which does not occur as a result of metamorphic change?
A) New minerals form and old ones disappear.
B) Fluid intrusions wash away minerals.
C) Rocks break apart and crumble.
D) Rock texture is altered by changes in orientation of minerals.
A) New minerals form and old ones disappear.
B) Fluid intrusions wash away minerals.
C) Rocks break apart and crumble.
D) Rock texture is altered by changes in orientation of minerals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A coarse-grained weakly foliated metamorphic rock composed of plagioclase feldspar and hornblende (an amphibole) is classified as a(n)
A) marble.
B) greenstone.
C) amphibolite.
D) hornfels.
A) marble.
B) greenstone.
C) amphibolite.
D) hornfels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A weakly foliated metamorphic rock composed of quartz is classified as a
A) quartzite.
B) marble.
C) hornfels.
D) gneiss.
A) quartzite.
B) marble.
C) hornfels.
D) gneiss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which is not a clue indicating that hornfels forms under conditions of high temperature but not high pressure?
A) chemical composition
B) lack of foliation
C) cleavage planes
D) grain size
A) chemical composition
B) lack of foliation
C) cleavage planes
D) grain size

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is the difference between limestone and marble?
A) chemical composition
B) crystal size and shape
C) color
D) source rock
A) chemical composition
B) crystal size and shape
C) color
D) source rock

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Andalusite, kyanite, and sillimanite are described as polymorphs. What does this mean?
A) They have the same atomic structure but different chemical compositions.
B) They have the same chemical composition but different atomic structures.
C) They all morphed at the same time.
D) They are exact opposites of one another.
A) They have the same atomic structure but different chemical compositions.
B) They have the same chemical composition but different atomic structures.
C) They all morphed at the same time.
D) They are exact opposites of one another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When trying to recognize if a rock is metamorphic, why would a geologist not consider bedding?
A) Bedding in metamorphic rock is too complicated to study
B) There is so much bedding in metamorphic rock to identify a rock by it.
C) There are no obvious signs of bedding in metamorphic rock.
D) Bedding indicates the presence of metamorphic minerals.
A) Bedding in metamorphic rock is too complicated to study
B) There is so much bedding in metamorphic rock to identify a rock by it.
C) There are no obvious signs of bedding in metamorphic rock.
D) Bedding indicates the presence of metamorphic minerals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Choose the option that puts the minerals in order of formation from low-grade metamorphism to high-grade metamorphism.
A) garnet, feldspar, muscovite
B) chlorite, garnet, biotite
C) biotite, muscovite, staurolite
D) chlorite, feldspar, staurolite
A) garnet, feldspar, muscovite
B) chlorite, garnet, biotite
C) biotite, muscovite, staurolite
D) chlorite, feldspar, staurolite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What information can be concluded by the rock name, staurolite-garnet-muscovite schist?
A) The rock is nonfoliated and contains more staurolite than garnet or muscovite.
B) The rock is foliated and contains staurolite, garnet, and muscovite in approximately equal quantities.
C) The rock is nonfoliated, has undergone low-grade metamorphism, and contains the three minerals listed in dominant quantities.
D) The rock is foliated, has large mica grains, and contains more muscovite than staurolite or garnet.
A) The rock is nonfoliated and contains more staurolite than garnet or muscovite.
B) The rock is foliated and contains staurolite, garnet, and muscovite in approximately equal quantities.
C) The rock is nonfoliated, has undergone low-grade metamorphism, and contains the three minerals listed in dominant quantities.
D) The rock is foliated, has large mica grains, and contains more muscovite than staurolite or garnet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What does the prefix meta, such as in metaconglomerate, mean?
A) formed near to
B) changed
C) formed by process of
D) made of
A) formed near to
B) changed
C) formed by process of
D) made of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which is not an effect of metamorphic dehydration?
A) The melting temperature of silicate minerals decreases.
B) Magma formation is enhanced.
C) Crystallization occurs more quickly.
D) Water vapor fills spaces between mineral grains.
A) The melting temperature of silicate minerals decreases.
B) Magma formation is enhanced.
C) Crystallization occurs more quickly.
D) Water vapor fills spaces between mineral grains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What apparent difference is there between a gneiss that is formed from igneous rock and one formed from sedimentary rock?
A) crystal size
B) mineral content
C) age
D) color
A) crystal size
B) mineral content
C) age
D) color

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
How does foliation occur?
A) physical rotation of preexisting minerals
B) recrystallization
C) dissolution and new mineral growth along a preferred orientation
D) all of the above
A) physical rotation of preexisting minerals
B) recrystallization
C) dissolution and new mineral growth along a preferred orientation
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which rock is described below? "This rock is shiny and contains scattered, well-formed crystals of garnet, staurolite, and kyanite."
A) slate
B) phyllite
C) schist
D) gneiss
A) slate
B) phyllite
C) schist
D) gneiss

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What is one way that polymorph minerals, such as aluminum-silicates, change from one form to another?
A) Temperature and pressure conditions change with depth, causing metamorphosis.
B) They break up and change form during resedimentation.
C) Other minerals join the polymorphs during contact with igneous intrusions.
D) Fluid metamorphosis allows other elements to fit between the main mineral bonds.
A) Temperature and pressure conditions change with depth, causing metamorphosis.
B) They break up and change form during resedimentation.
C) Other minerals join the polymorphs during contact with igneous intrusions.
D) Fluid metamorphosis allows other elements to fit between the main mineral bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Why is pressure so important in metamorphism?
A) Increasing pressure causes many minerals to metamorphose into denser minerals that are more stable at high pressure.
B) It isn't important.
C) Decreasing pressure causes many minerals to metamorphose into denser minerals that are more stable at high pressure.
D) Increased pressure means low temperature which is a key factor of metamorphism
A) Increasing pressure causes many minerals to metamorphose into denser minerals that are more stable at high pressure.
B) It isn't important.
C) Decreasing pressure causes many minerals to metamorphose into denser minerals that are more stable at high pressure.
D) Increased pressure means low temperature which is a key factor of metamorphism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Why don't diamonds turn back to graphite once they reach Earth's surface?
A) Diamonds are too hard to undergo reactions.
B) Temperatures need to be lower than those found on Earth.
C) There is not enough heat on the surface of the earth to drive the reverse reactions.
D) Humans harvest diamonds before they can turn back to graphite.
A) Diamonds are too hard to undergo reactions.
B) Temperatures need to be lower than those found on Earth.
C) There is not enough heat on the surface of the earth to drive the reverse reactions.
D) Humans harvest diamonds before they can turn back to graphite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Figure 6.23 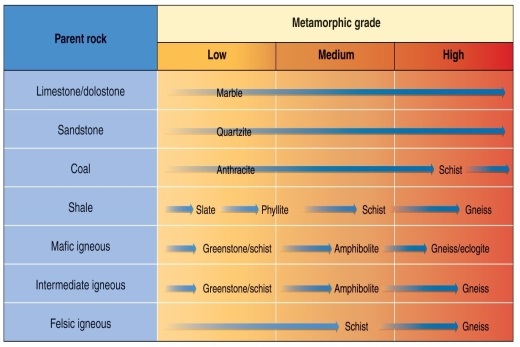
Using Figure 6.23 from your textbook, choose the option that correctly matches parent rocks with possible metamorphic products.
A) shale: gneiss; marble: schist; mafic igneous: amphibolite
B) sandstone: quartzite; coal: phyllite; intermediate igneous: greenstone
C) shale: slate; limestone: marble; sandstone: quartzite
D) felsic igneous: greenstone; limestone: schist; dolostone: marble

Using Figure 6.23 from your textbook, choose the option that correctly matches parent rocks with possible metamorphic products.
A) shale: gneiss; marble: schist; mafic igneous: amphibolite
B) sandstone: quartzite; coal: phyllite; intermediate igneous: greenstone
C) shale: slate; limestone: marble; sandstone: quartzite
D) felsic igneous: greenstone; limestone: schist; dolostone: marble

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which type of stress always causes change in shape but not in volume?
A) normal stress
B) shear stress
C) strain
D) pressure
A) normal stress
B) shear stress
C) strain
D) pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What is the definition of strain?
A) a type of normal stress where the forces are equal in all three dimensions
B) a force applied perpendicular to a surface
C) deformation of rock as a result of an applied stress
D) force applied parallel to a surface
A) a type of normal stress where the forces are equal in all three dimensions
B) a force applied perpendicular to a surface
C) deformation of rock as a result of an applied stress
D) force applied parallel to a surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Evaluate the following statement. "Tectonic processes help metamorphism by burying rocks."
A) This statement is false. Tectonic processes lift rocks up to the surface, where they are worn away by weathering.
B) This statement is true. Tectonic processes cause lava flows to bury large slabs of rock.
C) This statement is false. Metamorphism only occurs under very thick layers of deposited sediment.
D) This statement is true. Tectonic processes can push rocks deeper into Earth.
A) This statement is false. Tectonic processes lift rocks up to the surface, where they are worn away by weathering.
B) This statement is true. Tectonic processes cause lava flows to bury large slabs of rock.
C) This statement is false. Metamorphism only occurs under very thick layers of deposited sediment.
D) This statement is true. Tectonic processes can push rocks deeper into Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which rock is described below? "This first-formed metamorphic rock preferentially splits along planes of parallel microscopic micas."
A) slate
B) phyllite
C) schist
D) gneiss
A) slate
B) phyllite
C) schist
D) gneiss

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is different between quartz and quartzite's formation processes?
A) Quartz is metamorphosed into quartzite.
B) Quartzite is formed in volcanoes.
C) Quartzite is heavily foliated, a result of forming deep within the earth.
D) Chemicals change quartzite's makeup extensively.
A) Quartz is metamorphosed into quartzite.
B) Quartzite is formed in volcanoes.
C) Quartzite is heavily foliated, a result of forming deep within the earth.
D) Chemicals change quartzite's makeup extensively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
How might hydrothermal ore genesis occur?
A) Hot seawater rushes through porous rocks and crystallizes on contact with the rocks.
B) Cold seawater meets hot circulating hydrothermal fluids and precipitation occurs.
C) Two rock masses meet at a hydrothermal vent and the heat of the water dissolves ions from both masses. They recrystallize when they are carried to cooler water.
D) Hot water from a hydrothermal vent dissolves ions from one rock mass and reprecipitates them as ore in cooler water.
A) Hot seawater rushes through porous rocks and crystallizes on contact with the rocks.
B) Cold seawater meets hot circulating hydrothermal fluids and precipitation occurs.
C) Two rock masses meet at a hydrothermal vent and the heat of the water dissolves ions from both masses. They recrystallize when they are carried to cooler water.
D) Hot water from a hydrothermal vent dissolves ions from one rock mass and reprecipitates them as ore in cooler water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Why do metamorphic rocks exist at the surface?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If a rock containing kyanite and andalusite were to undergo a decrease in pressure, what must happen to temperature in order for that rock to continue to have stable kyanite and andalusite?
A) temperature must increase
B) temperature must decrease
C) temperature must stay the same
D) It is impossible for it to continue to have stable kyanite and andalusite.
A) temperature must increase
B) temperature must decrease
C) temperature must stay the same
D) It is impossible for it to continue to have stable kyanite and andalusite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
How do geologists know how to determine the stability of minerals?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What is metamorphism?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A well know example of a paired metamorphic belt occurs in
A) Japan.
B) England.
C) Mexico.
D) Australia.
A) Japan.
B) England.
C) Mexico.
D) Australia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following pairs of index minerals do not overlap in metamorphic grade?
A) chlorite and pyroxene
B) biotite and garnet
C) staurolite and kyanite
D) amphibole and sillimanite
A) chlorite and pyroxene
B) biotite and garnet
C) staurolite and kyanite
D) amphibole and sillimanite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What is the role of pressure in metamorphism?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If a rock containing kyanite, sillimanite, and andalusite were to undergo an increase in pressure, what must happen to temperature in order for that rock to continue to have stable kyanite, sillimanite, and andalusite?
A) temperature must increase
B) temperature must decrease
C) temperature must stay the same
D) It is impossible for it to continue to have stable kyanite, sillimanite, and andalusite.
A) temperature must increase
B) temperature must decrease
C) temperature must stay the same
D) It is impossible for it to continue to have stable kyanite, sillimanite, and andalusite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which type of metamorphism occurs exclusively at lower pressures?
A) Regional metamorphism occurs exclusively at lower pressures.
B) Contact metamorphism occurs exclusively at lower pressures.
C) Hydrothermal metamorphism occurs exclusively at lower pressures.
D) All three types of metamorphism occur exclusively at lower pressures.
A) Regional metamorphism occurs exclusively at lower pressures.
B) Contact metamorphism occurs exclusively at lower pressures.
C) Hydrothermal metamorphism occurs exclusively at lower pressures.
D) All three types of metamorphism occur exclusively at lower pressures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If a rock containing kyanite and sillimanite were to undergo an increase in pressure, what must happen to temperature in order for that rock to continue to have stable kyanite and sillimanite?
A) temperature must increase
B) temperature must decrease
C) temperature must stay the same
D) It is impossible for it to continue to have stable kyanite and sillimanite.
A) temperature must increase
B) temperature must decrease
C) temperature must stay the same
D) It is impossible for it to continue to have stable kyanite and sillimanite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What role does temperature play in metamorphism?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Although muscovite, feldspar and quartz are not considered useful as index minerals, which of the following situations could be useful in determining the grade of metamorphism in a region?
A) the coexistence of muscovite, feldspar and quartz
B) the disappearance of rocks containing muscovite and quartz
C) the coexistence of feldspar and quartz
D) the disappearance of rocks containing quartz
A) the coexistence of muscovite, feldspar and quartz
B) the disappearance of rocks containing muscovite and quartz
C) the coexistence of feldspar and quartz
D) the disappearance of rocks containing quartz

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
When do black smokers occur?
A) during plate tectonics movement
B) during underwater volcanic reactions
C) components dissolve below the seafloor, but then precipitate when they contact cold water
D) components squeezed from beneath the sea floor dissolve upon contact of cold water
A) during plate tectonics movement
B) during underwater volcanic reactions
C) components dissolve below the seafloor, but then precipitate when they contact cold water
D) components squeezed from beneath the sea floor dissolve upon contact of cold water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What role does fluid play in metamorphism?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following pairs of index minerals do not overlap in metamorphic grade?
A) chlorite and biotite
B) amphibole and garnet
C) staurolite and sillimanite
D) kyanite and pyroxene
A) chlorite and biotite
B) amphibole and garnet
C) staurolite and sillimanite
D) kyanite and pyroxene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which process makes it the most difficult to trace metamorphic rocks to their parent rocks?
A) fluid metamorphism
B) regional metamorphism
C) contact metamorphism
D) melting
A) fluid metamorphism
B) regional metamorphism
C) contact metamorphism
D) melting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
If a rock containing andalusite and sillimanite were to undergo an increase in pressure, what must happen to temperature in order for that rock to continue to have stable andalusite and sillimanite?
A) temperature must increase
B) temperature must decrease
C) temperature must stay the same
D) It is impossible for it to continue to have stable andalusite and sillimanite.
A) temperature must increase
B) temperature must decrease
C) temperature must stay the same
D) It is impossible for it to continue to have stable andalusite and sillimanite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
When a shale metamorphoses into a slate why do some slates contain muscovite and some slates contain chlorite?
A) The chlorite slates form at different pressures than the muscovite slates.
B) The chlorite slates have a different composition than the muscovite slates.
C) The chlorite slates form at different temperatures than the muscovite slates.
D) The chlorite slates form at different temperatures and pressures than the muscovite slates.
A) The chlorite slates form at different pressures than the muscovite slates.
B) The chlorite slates have a different composition than the muscovite slates.
C) The chlorite slates form at different temperatures than the muscovite slates.
D) The chlorite slates form at different temperatures and pressures than the muscovite slates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A gneiss containing kyanite and sillimanite most likely formed from a metamorphosed
A) limestone.
B) mafic igneous rock.
C) coal.
D) shale.
A) limestone.
B) mafic igneous rock.
C) coal.
D) shale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



