Deck 25: DNA Metabolism
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/101
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: DNA Metabolism
1
In a mammalian cell, DNA repair systems:
A) are extraordinarily efficient energetically.
B) are generally absent, except in egg and sperm cells.
C) can repair deletions, but not mismatches.
D) can repair most types of lesions except those caused by UV light.
E) normally repair more than 99% of the DNA lesions that occur.
A) are extraordinarily efficient energetically.
B) are generally absent, except in egg and sperm cells.
C) can repair deletions, but not mismatches.
D) can repair most types of lesions except those caused by UV light.
E) normally repair more than 99% of the DNA lesions that occur.
E
2
The Meselson-Stahl experiment established that:
A) DNA polymerase has a crucial role in DNA synthesis.
B) DNA synthesis in E. coli proceeds by a conservative mechanism.
C) DNA synthesis in E. coli proceeds by a semiconservative mechanism.
D) DNA synthesis requires dATP, dCTP, dGTP, and dTTP.
E) newly synthesized DNA in E. coli has a different base composition than the preexisting DNA.
A) DNA polymerase has a crucial role in DNA synthesis.
B) DNA synthesis in E. coli proceeds by a conservative mechanism.
C) DNA synthesis in E. coli proceeds by a semiconservative mechanism.
D) DNA synthesis requires dATP, dCTP, dGTP, and dTTP.
E) newly synthesized DNA in E. coli has a different base composition than the preexisting DNA.
C
3
At replication forks in E. coli:
A) DNA helicases make endonucleolytic cuts in DNA.
B) DNA primers are degraded by exonucleases.
C) DNA topoisomerases make endonucleolytic cuts in DNA.
D) RNA primers are removed by primase.
E) RNA primers are synthesized by primase.
A) DNA helicases make endonucleolytic cuts in DNA.
B) DNA primers are degraded by exonucleases.
C) DNA topoisomerases make endonucleolytic cuts in DNA.
D) RNA primers are removed by primase.
E) RNA primers are synthesized by primase.
E
4
E. coli DNA polymerase III:
A) can initiate replication without a primer.
B) is efficient at nick translation.
C) is the principal DNA polymerase in chromosomal DNA replication.
D) represents over 90% of the DNA polymerase activity in E. coli cells.
E) requires a free 5'-hydroxyl group as a primer.
A) can initiate replication without a primer.
B) is efficient at nick translation.
C) is the principal DNA polymerase in chromosomal DNA replication.
D) represents over 90% of the DNA polymerase activity in E. coli cells.
E) requires a free 5'-hydroxyl group as a primer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
An Okazaki fragment is a:
A) fragment of DNA resulting from endonuclease action.
B) fragment of RNA that is a subunit of the 30S ribosome.
C) piece of DNA that is synthesized in the 3' 5' direction.
D) segment of DNA that is an intermediate in the synthesis of the lagging strand.
E) segment of mRNA synthesized by RNA polymerase.
A) fragment of DNA resulting from endonuclease action.
B) fragment of RNA that is a subunit of the 30S ribosome.
C) piece of DNA that is synthesized in the 3' 5' direction.
D) segment of DNA that is an intermediate in the synthesis of the lagging strand.
E) segment of mRNA synthesized by RNA polymerase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which statement about enzymes that interact with DNA is TRUE?
A) E. coli DNA polymerase I is unusual in that it possesses only a 5' 3' exonucleolytic activity.
B) Endonucleases degrade circular but not linear DNA molecules.
C) Exonucleases degrade DNA at a free end.
D) Many DNA polymerases have a proofreading 5' 3' exonuclease.
E) Primases synthesize a short stretch of DNA to prime further synthesis.
A) E. coli DNA polymerase I is unusual in that it possesses only a 5' 3' exonucleolytic activity.
B) Endonucleases degrade circular but not linear DNA molecules.
C) Exonucleases degrade DNA at a free end.
D) Many DNA polymerases have a proofreading 5' 3' exonuclease.
E) Primases synthesize a short stretch of DNA to prime further synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The function of the eukaryotic DNA replication factor PCNA (proliferating cell nuclear antigen) is similar to that of the subunit of bacterial DNA polymerase III in that it:
A) facilitates replication of telomeres.
B) forms a circular sliding clamp to increase the processivity of replication.
C) has a 3ʹ 5ʹ proofreading activity.
D) increases the speed but not the processivity of the replication complex.
E) participates in DNA repair.
A) facilitates replication of telomeres.
B) forms a circular sliding clamp to increase the processivity of replication.
C) has a 3ʹ 5ʹ proofreading activity.
D) increases the speed but not the processivity of the replication complex.
E) participates in DNA repair.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which compound is NOT required for initiation of DNA replication in E. coli?
A) DnaB (helicase)
B) DnaG (primase)
C) Dam methylase
D) DNA ligase
E) DnaA (a AAA+ ATPase)
A) DnaB (helicase)
B) DnaG (primase)
C) Dam methylase
D) DNA ligase
E) DnaA (a AAA+ ATPase)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The role of the Dam methylase is to:
A) add a methyl group to uracil, converting it to thymine.
B) modify the template strand for recognition by repair systems.
C) remove a methyl group from thymine.
D) remove a mismatched nucleotide from the template strand.
E) replace a mismatched nucleotide with the correct one.
A) add a methyl group to uracil, converting it to thymine.
B) modify the template strand for recognition by repair systems.
C) remove a methyl group from thymine.
D) remove a mismatched nucleotide from the template strand.
E) replace a mismatched nucleotide with the correct one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which factor is NOT required for elongation during DNA replication in E. coli?
A) DnaB (helicase)
B) DnaG (primase)
C) DnaC
D) a -sliding clamp
E) a clamp loader
A) DnaB (helicase)
B) DnaG (primase)
C) DnaC
D) a -sliding clamp
E) a clamp loader

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The ABC excinuclease is essential in:
A) base-excision repair.
B) methyl-directed repair.
C) mismatch repair.
D) nucleotide-excision repair.
E) SOS repair.
A) base-excision repair.
B) methyl-directed repair.
C) mismatch repair.
D) nucleotide-excision repair.
E) SOS repair.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In base-excision repair, the first enzyme to act is:
A) AP endonuclease.
B) Dam methylase.
C) DNA glycosylase.
D) DNA ligase.
E) DNA polymerase.
A) AP endonuclease.
B) Dam methylase.
C) DNA glycosylase.
D) DNA ligase.
E) DNA polymerase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which enzyme is NOT directly involved in methyl-directed mismatch repair in E. coli?
A) DNA glycosylase
B) DNA helicase II
C) DNA ligase
D) DNA polymerase III
E) exonuclease I
A) DNA glycosylase
B) DNA helicase II
C) DNA ligase
D) DNA polymerase III
E) exonuclease I

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The proofreading function of DNA polymerase does NOT involve:
A) a 3' 5' exonuclease.
B) base pairing.
C) detection of mismatched base pairs.
D) phosphodiester bond hydrolysis.
E) reversal of the polymerization reaction.
A) a 3' 5' exonuclease.
B) base pairing.
C) detection of mismatched base pairs.
D) phosphodiester bond hydrolysis.
E) reversal of the polymerization reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When a DNA molecule is described as replicating bidirectionally, that means that it has two:
A) chains.
B) independently replicating segment.
C) origins.
D) replication forks.
E) termination points.
A) chains.
B) independently replicating segment.
C) origins.
D) replication forks.
E) termination points.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When bacterial DNA replication introduces a mismatch in a double-stranded DNA, the methyl-directed repair system:
A) cannot distinguish the template strand from the newly replicated strand.
B) changes both the template strand and the newly replicated strand.
C) corrects the DNA strand that is methylated.
D) corrects the mismatch by changing the newly replicated strand.
E) corrects the mismatch by changing the template strand.
A) cannot distinguish the template strand from the newly replicated strand.
B) changes both the template strand and the newly replicated strand.
C) corrects the DNA strand that is methylated.
D) corrects the mismatch by changing the newly replicated strand.
E) corrects the mismatch by changing the template strand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The 5' 3' exonuclease activity of E. coli DNA polymerase I is involved in:
A) formation of a nick at the DNA replication origin.
B) formation of Okazaki fragments.
C) proofreading of the replication process.
D) removal of RNA primers by nick translation.
E) sealing of nicks by ligase action.
A) formation of a nick at the DNA replication origin.
B) formation of Okazaki fragments.
C) proofreading of the replication process.
D) removal of RNA primers by nick translation.
E) sealing of nicks by ligase action.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Prokaryotic DNA polymerase III:
A) contains a 5' 3' proofreading activity to improve the fidelity of replication.
B) does not require a primer molecule to initiate replication.
C) has a subunit that acts as a circular clamp to improve the processivity of DNA synthesis.
D) synthesizes DNA in the 3' 5' direction.
E) synthesizes only the leading strand; DNA polymerase I synthesizes the lagging strand.
A) contains a 5' 3' proofreading activity to improve the fidelity of replication.
B) does not require a primer molecule to initiate replication.
C) has a subunit that acts as a circular clamp to improve the processivity of DNA synthesis.
D) synthesizes DNA in the 3' 5' direction.
E) synthesizes only the leading strand; DNA polymerase I synthesizes the lagging strand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In contrast to bacteria, eukaryotic chromosomes need multiple DNA replication origins because:
A) eukaryotic chromosomes cannot usually replicate bidirectionally.
B) eukaryotic genomes are not usually circular, like the bacterial chromosome is.
C) the processivity of the eukaryotic DNA polymerase is much less than the bacterial enzyme.
D) their replication rate is much slower, and it would take too long with only a single origin per chromosome.
E) they have a variety of DNA polymerases for different purposes, and need a corresponding variety of replication origins.
A) eukaryotic chromosomes cannot usually replicate bidirectionally.
B) eukaryotic genomes are not usually circular, like the bacterial chromosome is.
C) the processivity of the eukaryotic DNA polymerase is much less than the bacterial enzyme.
D) their replication rate is much slower, and it would take too long with only a single origin per chromosome.
E) they have a variety of DNA polymerases for different purposes, and need a corresponding variety of replication origins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The Ames test is used to:
A) detect bacterial viruses.
B) determine the rate of DNA replication.
C) examine the potency of antibiotics.
D) measure the mutagenic effects of various chemical compounds.
E) quantify the damaging effects of UV light on DNA molecules.
A) detect bacterial viruses.
B) determine the rate of DNA replication.
C) examine the potency of antibiotics.
D) measure the mutagenic effects of various chemical compounds.
E) quantify the damaging effects of UV light on DNA molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which mechanism is used to repair a thymidine dimer in DNA?
A) mismatch repair
B) base-excision repair
C) nucleotide-excision repair
D) direct repair
E) More than one mechanism is used for this type of lesion.
A) mismatch repair
B) base-excision repair
C) nucleotide-excision repair
D) direct repair
E) More than one mechanism is used for this type of lesion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
DnaA binds to what sites in the E. coli origin?
A) R sites only
B) I sites only
C) DUE sites only
D) both R and I sites
E) both R and DUE sites
A) R sites only
B) I sites only
C) DUE sites only
D) both R and I sites
E) both R and DUE sites

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The repair of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers by bacterial DNA photolyase involves the cofactor:
A) coenzyme A.
B) coenzyme Q.
C) FADH-.
D) pyridoxal phosphate (PLP).
E) thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP).
A) coenzyme A.
B) coenzyme Q.
C) FADH-.
D) pyridoxal phosphate (PLP).
E) thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In homologous recombination in E. coli, the protein that moves along a double-stranded DNA, unwinding the strands ahead of it and degrading them, is:
A) chi.
B) DNA ligase.
C) RecA protein.
D) RecBCD enzyme.
E) RuvC protein (resolvase).
A) chi.
B) DNA ligase.
C) RecA protein.
D) RecBCD enzyme.
E) RuvC protein (resolvase).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In homologous genetic recombination, RecA protein is involved in:
A) formation of Holliday intermediates and branch migration.
B) introduction of negative supercoils into the recombination products.
C) nicking the two duplex DNA molecules to initiate the reaction.
D) pairing a DNA strand from one duplex DNA molecule with sequences in another duplex, regardless of complementarity.
E) resolution of the Holliday intermediate.
A) formation of Holliday intermediates and branch migration.
B) introduction of negative supercoils into the recombination products.
C) nicking the two duplex DNA molecules to initiate the reaction.
D) pairing a DNA strand from one duplex DNA molecule with sequences in another duplex, regardless of complementarity.
E) resolution of the Holliday intermediate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
How many rounds of replication would result in a 1:1 distribution of hybrid to new DNA helices in the Meselson and Stahl experiment?
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) four
E) five
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) four
E) five

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If DNA replication was conservative, what would be observed after two rounds of the Meselson and Stahl experiment?
A) 1:1 high-density to low-density bands.
B) 1:1 high-density to hybrid-density bands.
C) 1:2 high-density to low-density bands.
D) 1:2 high-density to hybrid-density bands.
E) 1:4 high-density to low-density bands.
A) 1:1 high-density to low-density bands.
B) 1:1 high-density to hybrid-density bands.
C) 1:2 high-density to low-density bands.
D) 1:2 high-density to hybrid-density bands.
E) 1:4 high-density to low-density bands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In homologous recombination in E. coli, the protein that assembles into long, helical filaments that coat a region of DNA is:
A) DNA methylase.
B) DNA polymerase.
C) histone.
D) RecA protein.
E) RecBCD enzyme.
A) DNA methylase.
B) DNA polymerase.
C) histone.
D) RecA protein.
E) RecBCD enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which feature is NOT applicable to homologous recombination during meiosis?
A) a double strand break
B) cleavage of two crossover events
C) alignment of homologous chromosomes
D) formation of a single Holliday intermediate
E) exposed 3ʹ ends invade the intact duplex DNA of the homolog
A) a double strand break
B) cleavage of two crossover events
C) alignment of homologous chromosomes
D) formation of a single Holliday intermediate
E) exposed 3ʹ ends invade the intact duplex DNA of the homolog

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which compound is NOT a protein that binds to the origin of replication of E. coli (oriC)?
A) DnaA
B) DnaB
C) integration host factor (IHF)
D) histone-like protein (HU)
E) Tus
A) DnaA
B) DnaB
C) integration host factor (IHF)
D) histone-like protein (HU)
E) Tus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which statement does NOT accurately describe a difference between E. coli DNA polymerases Pol I and Pol III?
A) Pol I has a 3' to 5'exonuclease, and DNA Pol III does not.
B) Pol I has a slower polymerization rate than Pol III.
C) Pol I is less processive than Pol III.
D) Pol I is a single subunit, while Pol III is a multisubunit protein.
E) All of these statements accurately describe differences between Pol I and Pol III.
A) Pol I has a 3' to 5'exonuclease, and DNA Pol III does not.
B) Pol I has a slower polymerization rate than Pol III.
C) Pol I is less processive than Pol III.
D) Pol I is a single subunit, while Pol III is a multisubunit protein.
E) All of these statements accurately describe differences between Pol I and Pol III.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
An alternative repair system by error-prone translesion DNA synthesis can result in a high mutation rate because:
A) alternative modified nucleotides can be incorporated more readily.
B) interference from the RecA and SSB proteins hinders the normal replication accuracy.
C) replication proceeds much faster than normal, resulting in many more mistakes.
D) the DNA polymerases involved cannot facilitate base-pairing as well as DNA polymerase III.
E) the DNA polymerases involved lack exonuclease proofreading activities.
A) alternative modified nucleotides can be incorporated more readily.
B) interference from the RecA and SSB proteins hinders the normal replication accuracy.
C) replication proceeds much faster than normal, resulting in many more mistakes.
D) the DNA polymerases involved cannot facilitate base-pairing as well as DNA polymerase III.
E) the DNA polymerases involved lack exonuclease proofreading activities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which statement is FALSE?
A) In vitro, the strand-exchange reaction can include formation of a Holliday intermediate.
B) In vitro, the strand-exchange reaction is accompanied by ATP hydrolysis.
C) In vitro, the strand-exchange reaction may involve transient formation of a three- or four-stranded DNA complex.
D) In vitro, the strand-exchange reaction needs RecA protein.
E) In vitro, the strand-exchange reaction requires DNA polymerase.
A) In vitro, the strand-exchange reaction can include formation of a Holliday intermediate.
B) In vitro, the strand-exchange reaction is accompanied by ATP hydrolysis.
C) In vitro, the strand-exchange reaction may involve transient formation of a three- or four-stranded DNA complex.
D) In vitro, the strand-exchange reaction needs RecA protein.
E) In vitro, the strand-exchange reaction requires DNA polymerase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which mechanism is used to repair a chemically modified base in DNA?
A) mismatch repair
B) base-excision repair
C) nucleotide-excision repair
D) direct repair
E) More than one mechanism is used for this type of lesion.
A) mismatch repair
B) base-excision repair
C) nucleotide-excision repair
D) direct repair
E) More than one mechanism is used for this type of lesion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which phrase describes a role for E. coli DNA Pol III?
A) lagging strand synthesis only
B) base excision repair only
C) mismatch repair only
D) both lagging strand synthesis and mismatch repair
E) All of these are roles for DNA Pol III.
A) lagging strand synthesis only
B) base excision repair only
C) mismatch repair only
D) both lagging strand synthesis and mismatch repair
E) All of these are roles for DNA Pol III.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which statement is FALSE regarding the E. coli DNA unwinding element (DUE)?
A) This sequence appears in tandem.
B) The sequence is part of the origin of replication.
C) This sequence binds to DnaA.
D) This sequence is where the helicase binds during initiation of replication.
E) This sequence will be hemi-methylated after replication begins.
A) This sequence appears in tandem.
B) The sequence is part of the origin of replication.
C) This sequence binds to DnaA.
D) This sequence is where the helicase binds during initiation of replication.
E) This sequence will be hemi-methylated after replication begins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which statement does NOT describe a feature of site-specific recombination?
A) A specific recombinase enzyme is required.
B) The energy of the phosphodiester bond is preserved in covalent enzyme-DNA linkage.
C) Recombination sites have non-palindromic sequences.
D) Formation of Holliday intermediates is required.
E) Insertions or deletions can result from site-specific recombination.
A) A specific recombinase enzyme is required.
B) The energy of the phosphodiester bond is preserved in covalent enzyme-DNA linkage.
C) Recombination sites have non-palindromic sequences.
D) Formation of Holliday intermediates is required.
E) Insertions or deletions can result from site-specific recombination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
DNA replication in E. coli:
A) of the leading strand requires multiple primers.
B) is mostly 3'to 5'.
C) always finishes at a conserved terminator sequence.
D) requires DNA-dependent RNA synthesis.
E) does not require the action of topoisomerases.
A) of the leading strand requires multiple primers.
B) is mostly 3'to 5'.
C) always finishes at a conserved terminator sequence.
D) requires DNA-dependent RNA synthesis.
E) does not require the action of topoisomerases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which statement is FALSE about transposition of DNA?
A) The diversity of immunoglobins is in part due to DNA recombination by transposition.
B) Transposition occurs in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
C) Enzymes are not required for transposition.
D) The first step of transposition can be single- or double-stranded DNA cleavage.
E) Transposition can lead to simple movement of a DNA region or duplication of that region in a new location.
A) The diversity of immunoglobins is in part due to DNA recombination by transposition.
B) Transposition occurs in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
C) Enzymes are not required for transposition.
D) The first step of transposition can be single- or double-stranded DNA cleavage.
E) Transposition can lead to simple movement of a DNA region or duplication of that region in a new location.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which statement is FALSE regarding DnaA?
A) DnaA is a sequence that is part of oriC in E. coli.
B) DnaA is an important component in DNA replication initiation.
C) DnaA affects the writhe in oriC in E. coli.
D) All of the statements are false.
E) None of the statements is false.
A) DnaA is a sequence that is part of oriC in E. coli.
B) DnaA is an important component in DNA replication initiation.
C) DnaA affects the writhe in oriC in E. coli.
D) All of the statements are false.
E) None of the statements is false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In humans, what repair mechanism is used to correct thymine dimers?
A) base-excision repair
B) nucleotide-excision repair
C) mismatch repair
D) photolyase
E) both nucleotide-excision repair and photolyase
A) base-excision repair
B) nucleotide-excision repair
C) mismatch repair
D) photolyase
E) both nucleotide-excision repair and photolyase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which statement is FALSE regarding the repair of 1-methyladenine in DNA to adenine?
A) This is an example of direct repair.
B) This repair process requires iron atoms as cofactors.
C) -Ketoglutarate and oxygen are also substrates in this reaction.
D) The protein responsible for carrying out this reaction can also repair 3-methylcytosine.
E) The process involves carboxylation followed by hydrolysis.
A) This is an example of direct repair.
B) This repair process requires iron atoms as cofactors.
C) -Ketoglutarate and oxygen are also substrates in this reaction.
D) The protein responsible for carrying out this reaction can also repair 3-methylcytosine.
E) The process involves carboxylation followed by hydrolysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In the Ames test, the clear region of no growth near the center of the plate (where the compound of interest is placed) typically indicates that the compound is:
A) not mutagenic.
B) an antibiotic.
C) an amino acid.
D) lethal at high enough concentrations.
E) not taken up by bacteria.
A) not mutagenic.
B) an antibiotic.
C) an amino acid.
D) lethal at high enough concentrations.
E) not taken up by bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which protein does NOT contribute in some fashion to the low rate of errors in DNA replication in E. coli?
A) MutS
B) DNA Pol III
C) Dam methylase
D) DnaG
E) UvrD
A) MutS
B) DNA Pol III
C) Dam methylase
D) DnaG
E) UvrD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is/are NOT made out of DNA?
A) Ter
B) telomeres
C) DNA unwinding elements
D) TUS
E) All of these are made out of DNA.
A) Ter
B) telomeres
C) DNA unwinding elements
D) TUS
E) All of these are made out of DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which statement is FALSE regarding the DNA ligase mechanism?
A) The mechanism is an example of covalent catalysis.
B) Either ATP or NAD+ may contribute an adenyl group to the reaction.
C) Energy from a phosphoanhydride bond is used to make a phosphodiester bond.
D) One of the products of the reaction is ADP.
E) A lysine is found in the active site of the enzyme.
A) The mechanism is an example of covalent catalysis.
B) Either ATP or NAD+ may contribute an adenyl group to the reaction.
C) Energy from a phosphoanhydride bond is used to make a phosphodiester bond.
D) One of the products of the reaction is ADP.
E) A lysine is found in the active site of the enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
It is possible to mutate E. coli DNA Pol I so that it no longer has any exonuclease activity. What would be a potential result of this change?
A) The enzyme would become more processive.
B) The enzyme would be more error prone.
C) The enzyme would become more efficient in base excision repair.
D) The enzyme would become more processive and more error-prone.
E) None of these is a potential outcome.
A) The enzyme would become more processive.
B) The enzyme would be more error prone.
C) The enzyme would become more efficient in base excision repair.
D) The enzyme would become more processive and more error-prone.
E) None of these is a potential outcome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which repair mechanism does NOT require an endonuclease?
A) base-excision repair
B) nucleotide-excision repair
C) mismatch repair
D) photolyase
E) All of these require an endonuclease.
A) base-excision repair
B) nucleotide-excision repair
C) mismatch repair
D) photolyase
E) All of these require an endonuclease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which process or aspect is NOT associated with RecBCD?
A) helicase activity
B) ATP hydrolysis
C) nuclease activity
D) sequence-specific binding interactions
E) generation of 5' overhangs
A) helicase activity
B) ATP hydrolysis
C) nuclease activity
D) sequence-specific binding interactions
E) generation of 5' overhangs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which process does NOT require the 5' to 3' exonuclease activity of Pol I in E. coli?
A) joining of Okazaki fragments
B) nucleotide-excision repair
C) base-excision repair
D) nick translation
E) All of these require the 5' to 3' exonuclease activity of Pol I.
A) joining of Okazaki fragments
B) nucleotide-excision repair
C) base-excision repair
D) nick translation
E) All of these require the 5' to 3' exonuclease activity of Pol I.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which eukaryotic DNA polymerase carries out replication in a manner analogous to E. coli DNA polymerase III?
A) DNA polymerase (alpha)
B) DNA polymerase (beta)
C) DNA polymerase (gamma)
D) DNA polymerase (delta)
E) DNA polymerase (epsilon)
A) DNA polymerase (alpha)
B) DNA polymerase (beta)
C) DNA polymerase (gamma)
D) DNA polymerase (delta)
E) DNA polymerase (epsilon)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which statement regarding the regulation of initiation in E. coli is CORRECT?
A) DnaA binds its consensus sequence at oriC only when the sequence is fully acetylated.
B) After replication, the DNA at oriC is hemi-acetylated and in this state it cannot bind DnaA.
C) After replication the DNA at oriC is hemi-methylated, and in this state it binds DnaA with high affinity.
D) The binding affinity of DnaA for its binding sites in oriC is dependent only on methylation of DNA.
E) DnaA binds its consensus sequence at oriC only when the sequence is fully methylated.
A) DnaA binds its consensus sequence at oriC only when the sequence is fully acetylated.
B) After replication, the DNA at oriC is hemi-acetylated and in this state it cannot bind DnaA.
C) After replication the DNA at oriC is hemi-methylated, and in this state it binds DnaA with high affinity.
D) The binding affinity of DnaA for its binding sites in oriC is dependent only on methylation of DNA.
E) DnaA binds its consensus sequence at oriC only when the sequence is fully methylated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What is the role of the chi sequence in recombination DNA repair?
A) It directs RecBCD binding to DNA.
B) It acts as a target for an endonuclease activity.
C) It acts as a binding site for protein/DNA interactions.
D) It triggers the activity of a DNA helicase.
E) It acts as a signal for branch migration of double-stranded intermediates.
A) It directs RecBCD binding to DNA.
B) It acts as a target for an endonuclease activity.
C) It acts as a binding site for protein/DNA interactions.
D) It triggers the activity of a DNA helicase.
E) It acts as a signal for branch migration of double-stranded intermediates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What role does AP endonuclease have in the base-excision repair system?
A) It removes the damaged base from the nucleic acid.
B) It cleaves the phosphodiester backbone after base removal.
C) It removes nucleotides from the broken strand of the nucleic acid.
D) It adds new nucleotides to replace the excised ones.
E) It creates a new phosphodiester bond to repair the backbone.
A) It removes the damaged base from the nucleic acid.
B) It cleaves the phosphodiester backbone after base removal.
C) It removes nucleotides from the broken strand of the nucleic acid.
D) It adds new nucleotides to replace the excised ones.
E) It creates a new phosphodiester bond to repair the backbone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which phrase does NOT describe an aspect of the nucleotide addition reaction catalyzed by E. coli DNA Pol III?
A) activation of the 3' OH of the newly synthesized strand by a metal ion
B) a properly positioned phosphate
C) specific protein/base-pair interactions in the major groove
D) charge stabilization of all three phosphates on the substrate
E) All of these are important aspects of the addition reaction.
A) activation of the 3' OH of the newly synthesized strand by a metal ion
B) a properly positioned phosphate
C) specific protein/base-pair interactions in the major groove
D) charge stabilization of all three phosphates on the substrate
E) All of these are important aspects of the addition reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which factor does NOT consume energy by breaking phosphoanhydride bonds?
A) the action of DnaB
B) the action of DnaG
C) DNA gyrase
D) TUS/Ter binding
E) DNA ligase
A) the action of DnaB
B) the action of DnaG
C) DNA gyrase
D) TUS/Ter binding
E) DNA ligase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which protein is NOT required for E. coli Pol III elongation?
A) SSBP
B) DnaB
C) DnaG
D) DNA gyrase
E) All of these are required for elongation.
A) SSBP
B) DnaB
C) DnaG
D) DNA gyrase
E) All of these are required for elongation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which process or proteins is/are NOT generally required in homologous recombination to occur?
A) helicase activity
B) DNA-dependent DNA polymerases
C) primases
D) ligases
E) nucleases
A) helicase activity
B) DNA-dependent DNA polymerases
C) primases
D) ligases
E) nucleases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which sequences are palindromic?
A) DNA unwinding elements (DUE)
B) terminator sequences (Ter)
C) EcoRI restriction sites
D) both DUE and Ter
E) None of these sequences is palindromic.
A) DNA unwinding elements (DUE)
B) terminator sequences (Ter)
C) EcoRI restriction sites
D) both DUE and Ter
E) None of these sequences is palindromic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is NOT a process or characteristic associated with recA?
A) It binds to ssDNA.
B) It forms part of DNA polymerase V.
C) It is involved in the homologous genetic recombination.
D) It facilitates strand invasion in repair pathways.
E) It forms a dimer with single-stranded DNA binding protein (SSB) and single-stranded DNA.
A) It binds to ssDNA.
B) It forms part of DNA polymerase V.
C) It is involved in the homologous genetic recombination.
D) It facilitates strand invasion in repair pathways.
E) It forms a dimer with single-stranded DNA binding protein (SSB) and single-stranded DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Briefly describe the biochemical role of the following enzymes in DNA replication in E. coli:
(a) DNA helicase; (b) primase; (c) the 3' 5' exonuclease activity of DNA polymerase; (d) DNA 1igase; (e) topoisomerases; (f) the 5' 3' exonuclease activity of DNA polymerase I.
(a) DNA helicase; (b) primase; (c) the 3' 5' exonuclease activity of DNA polymerase; (d) DNA 1igase; (e) topoisomerases; (f) the 5' 3' exonuclease activity of DNA polymerase I.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The DNA below is replicated from left to right. Label the templates for leading strand and lagging strand synthesis.
(5')ACTTCGGATCGTTAAGGCCGCTTTCTGT(3')
(3')TGAAGCCTAGCAATTCCGGCGAAAGACA(5')
(5')ACTTCGGATCGTTAAGGCCGCTTTCTGT(3')
(3')TGAAGCCTAGCAATTCCGGCGAAAGACA(5')

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
All known DNA polymerases catalyze synthesis only in the 5' 3' direction. Nevertheless, during semiconservative DNA replication in the cell, they are able to catalyze the synthesis of both daughter chains, which would appear to require synthesis in the 3' 5' direction. Explain the process that occurs in the cell that allows for synthesis of both daughter chains by DNA polymerase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Nucleotide polymerization appears to be a thermodynamically balanced reaction (because one phosphodiester bond is broken and one is formed). Nevertheless, the reaction proceeds efficiently both in a test tube and in the cell. Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
DNA replication in E. coli begins at a site in the DNA called the (a) _____. At the replication fork the (b) _____ strand is synthesized continuously while the (c) _____ strand is synthesized discontinuously. On the strand synthesized discontinuously, the short pieces are called (d) _____ fragments. An RNA primer for each of the fragments is synthesized by an enzyme called (e) _____, and this RNA primer is removed after the fragment is synthesized by the enzyme (f) _____, using its (g) _____ activity. The nicks left behind in this process are sealed by the enzyme (h) _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What is an Okazaki fragment? What enzyme(s) is (are) required for its formation in E. coli?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which statement is TRUE regarding the process catalyzed by the bacteriophage integrase?
A) Serines in the protein active site become covalently attached to the nucleic acids during the mechanism.
B) The reaction is an ATP-dependent process.
C) The reaction steps are successive tranesterifications.
D) The integrase can be classified as a hydrolase.
E) The target DNA sequence for this protein is nonspecific.
A) Serines in the protein active site become covalently attached to the nucleic acids during the mechanism.
B) The reaction is an ATP-dependent process.
C) The reaction steps are successive tranesterifications.
D) The integrase can be classified as a hydrolase.
E) The target DNA sequence for this protein is nonspecific.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In the bacterial cell, what are catenated chromosomes, when do they arise, and how does the cell resolve the problem posed by their structure?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
DNA synthesis on the lagging strand in E. coli is a complex process known to involve several proteins. Initiation of a new chain is catalyzed by the enzyme (a) _____, and elongation is catalyzed by the enzyme (b) _____. Synthesis is discontinuous, yielding short segments called (c) _____, which are eventually joined by the enzyme (d) _____, which requires the cofactor (e) _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
All known DNA polymerases can only elongate a preexisting DNA chain (i.e., require a primer) but cannot initiate a new DNA chain. Nevertheless, during semiconservative DNA replication in the cell, entirely new daughter DNA chains are synthesized. Explain the process that occurs in the cell that allows for the synthesis of daughter chains by DNA polymerase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Diagram the reaction catalyzed by DNA polymerase that occurs between deoxyribose at the end of a DNA chain and the 5' phosphates of a deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate. Include the chemical structure of the phosphate group, indicate the locations of the sugar and base, and show the rearrangements of electrons that occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which factor is NOT responsible for the variations in IgG light-chain variations?
A) variations in the V segment sequence
B) variations in the J segment sequence
C) variations in the C-segment sequence
D) variations in the V-J junction
E) All of these contribute to the variation in light-chain variations.
A) variations in the V segment sequence
B) variations in the J segment sequence
C) variations in the C-segment sequence
D) variations in the V-J junction
E) All of these contribute to the variation in light-chain variations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which recombination or repair mechanism does NOT generally conserve the original DNA sequence?
A) recombinational DNA repair
B) site-specific recombination
C) nonhomologous end joining
D) photolyase repair
E) nucleotide-excision repair
A) recombinational DNA repair
B) site-specific recombination
C) nonhomologous end joining
D) photolyase repair
E) nucleotide-excision repair

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Describe briefly how equilibrium density gradient centrifugation was used to demonstrate that DNA replication in E. coli is semiconservative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The high fidelity of DNA replication is due primarily to immediate error correction by the 3' 5' exonuclease (proofreading) activity of the DNA polymerase. Some incorrectly paired bases escape this proofreading, and further errors can arise from challenges to the chemical integrity of the DNA. List the four classes of repair mechanisms that the cell can use to help correct such errors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
What concept does NOT generally apply to bacterial transposons?
A) Transposons are sometimes referred to as "jumping genes."
B) Transposons contain segments of repeating DNA at either end.
C) Insertion of a transposon followed by excision results in damage to the sequence at the insertion site.
D) "Transposases" are the enzymes involved in transposition.
E) Transposition is a homologous-recombination process.
A) Transposons are sometimes referred to as "jumping genes."
B) Transposons contain segments of repeating DNA at either end.
C) Insertion of a transposon followed by excision results in damage to the sequence at the insertion site.
D) "Transposases" are the enzymes involved in transposition.
E) Transposition is a homologous-recombination process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
List two proteins or enzymes, other than DNA polymerase III, that are found at the replication fork in E. coli. Describe each of their functions with no more than one sentence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
List three types of DNA damage that require repair.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A suitable substrate for DNA polymerase is shown below. Label the primer and template, and indicate which end of each strand must be 3' or 5'. 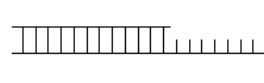 To observe DNA synthesis on this substrate in vitro, what additional reaction components must be added?
To observe DNA synthesis on this substrate in vitro, what additional reaction components must be added?
 To observe DNA synthesis on this substrate in vitro, what additional reaction components must be added?
To observe DNA synthesis on this substrate in vitro, what additional reaction components must be added?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Why is the drug acyclovir effective against the herpes simplex virus?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



