Deck 8: Import Tariffs and Quotas Under Perfect Competition
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/183
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Import Tariffs and Quotas Under Perfect Competition
1
One feature of the GATT and now the WTO is that all member nations get the same treatment from their trading partners in terms of trade rules and restrictions. This provision is:
A) beggar thy neighbor.
B) the good neighbor policy.
C) rotating obligations.
D) most favored nation status.
A) beggar thy neighbor.
B) the good neighbor policy.
C) rotating obligations.
D) most favored nation status.
D
2
In 1995, the United States considered levying a tariff on luxury cars imported from Japan. How did Japan react to this possibility?
A) It reduced its purchases of U.S. Treasury bills, causing U.S. interest rates to increase.
B) It considered levying a tariff on beef imported from the United States.
C) It submitted an unfair trade practice complaint to the World Trade Organization.
D) It moved production of its luxury automobiles to the United States.
A) It reduced its purchases of U.S. Treasury bills, causing U.S. interest rates to increase.
B) It considered levying a tariff on beef imported from the United States.
C) It submitted an unfair trade practice complaint to the World Trade Organization.
D) It moved production of its luxury automobiles to the United States.
A
3
Import tariffs are ___________ on imports, and import quotas are ____________ on imports.
A) subsidies; taxes
B) quantity limits; subsidies
C) taxes; quantity limits
D) quantity limits; taxes
A) subsidies; taxes
B) quantity limits; subsidies
C) taxes; quantity limits
D) quantity limits; taxes
C
4
Most favored nation status requires that a WTO member:
A) reduces a tariff on imports from one WTO trading partner and applies the lower tariff to imports from all other WTO members.
B) reduces a tariff on imports from one WTO trading partner and applies the lower tariff to imports from all other countries.
C) increases a tariff on imports from one WTO trading partner and raises the tariff on imports from all other WTO members.
D) increases a tariff on imports from one WTO trading partner and raises the tariff on imports from all other countries.
A) reduces a tariff on imports from one WTO trading partner and applies the lower tariff to imports from all other WTO members.
B) reduces a tariff on imports from one WTO trading partner and applies the lower tariff to imports from all other countries.
C) increases a tariff on imports from one WTO trading partner and raises the tariff on imports from all other WTO members.
D) increases a tariff on imports from one WTO trading partner and raises the tariff on imports from all other countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is the name of the MOST recent round of WTO negotiations?
A) the Doha round
B) the Kyoto round
C) the Geneva accord
D) the Paris round
A) the Doha round
B) the Kyoto round
C) the Geneva accord
D) the Paris round

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An international conference in Geneva, Switzerland, in 1947 resulted in the formation of:
A) the European Union.
B) the International Monetary Fund.
C) the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT).
D) the International Red Cross.
A) the European Union.
B) the International Monetary Fund.
C) the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT).
D) the International Red Cross.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Under the WTO provision of Article XIX, countries can:
A) never charge a tariff on an import.
B) always charge a tariff on imports.
C) temporarily charge a higher tariff on certain imports.
D) provide subsidies to all domestic producers of import competing products.
A) never charge a tariff on an import.
B) always charge a tariff on imports.
C) temporarily charge a higher tariff on certain imports.
D) provide subsidies to all domestic producers of import competing products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Under the GATT framework, nations met periodically to negotiate lower trade restrictions. These negotiations are known as:
A) conferee sessions.
B) plenary meetings.
C) sesqui-sessions.
D) rounds.
A) conferee sessions.
B) plenary meetings.
C) sesqui-sessions.
D) rounds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is an exception to the most favored nation principle?
A) trade in petroleum
B) trade with Japan
C) tariff concessions negotiated within a free-trade area or a customs union
D) trade in services
A) trade in petroleum
B) trade with Japan
C) tariff concessions negotiated within a free-trade area or a customs union
D) trade in services

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
According to the GATT, a tariff applied under the safeguard provision must:
A) be temporary.
B) be permanent.
C) apply to all imports.
D) be no higher than 10%.
A) be temporary.
B) be permanent.
C) apply to all imports.
D) be no higher than 10%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
GATT is the acronym (or abbreviation) for:
A) the General Agreement on Taxes and Tariffs.
B) the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade.
C) the General Agreement on Trade and Taxes.
D) the General Agreement on Trade.
A) the General Agreement on Taxes and Tariffs.
B) the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade.
C) the General Agreement on Trade and Taxes.
D) the General Agreement on Trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What GATT provision did the United States use to justify levying tariffs on tire imports in fall 2009?
A) antidumping duties
B) export subsidization
C) safeguard clause
D) national security
A) antidumping duties
B) export subsidization
C) safeguard clause
D) national security

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade focused on:
A) raising tariffs on agricultural products.
B) lowering trade restrictions between countries.
C) promoting full employment worldwide.
D) increasing trade restrictions between countries.
A) raising tariffs on agricultural products.
B) lowering trade restrictions between countries.
C) promoting full employment worldwide.
D) increasing trade restrictions between countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
How large a tariff did Donald Trump, the Republican candidate in the 2016 presidential campaign, indicate that he would levy on Chinese exports to the United States?
A) 10%
B) 25%
C) 45%
D) 75%
A) 10%
B) 25%
C) 45%
D) 75%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What organization emerged from the GATT, starting January 1, 1995, with expanded responsibilities and global interaction?
A) the Doha round
B) the World Trade Organization
C) the United Nations
D) the Institute for International Economics
A) the Doha round
B) the World Trade Organization
C) the United Nations
D) the Institute for International Economics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is an "export subsidy"?
A) a payment by one government to another for exports
B) a payment (or other benefit) to domestic firms by their government to help them sell exports more cheaply
C) the rule that says all exports must be taxed before they leave the port
D) a provision that exporters must get their payments indirectly through a third party
A) a payment by one government to another for exports
B) a payment (or other benefit) to domestic firms by their government to help them sell exports more cheaply
C) the rule that says all exports must be taxed before they leave the port
D) a provision that exporters must get their payments indirectly through a third party

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which organization acts as a forum for countries to come to agreement on trade policies and to resolve trade policy disputes?
A) the International Trade Organization
B) the United Nations
C) the World Trade Organization
D) the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development
A) the International Trade Organization
B) the United Nations
C) the World Trade Organization
D) the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
WTO is the acronym for:
A) the World Traffic Organization.
B) the World Trade Organization.
C) the World Tariff Organization.
D) the World Tax Organization.
A) the World Traffic Organization.
B) the World Trade Organization.
C) the World Tariff Organization.
D) the World Tax Organization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The escape clause in U.S. trade law:
A) enables the United States to withdraw from NAFTA.
B) permits the U.S. government to impose trade barriers if fairly traded imports are the cause of significant injury to a U.S. industry and its workers.
C) permits the government to impose trade remedies against nations that unfairly subsidize their exports to the United States.
D) enables immigrants to return to their home countries.
A) enables the United States to withdraw from NAFTA.
B) permits the U.S. government to impose trade barriers if fairly traded imports are the cause of significant injury to a U.S. industry and its workers.
C) permits the government to impose trade remedies against nations that unfairly subsidize their exports to the United States.
D) enables immigrants to return to their home countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
An international conference in Bretton Woods, New Hampshire, in 1944 resulted in the formation of:
A) the European Union.
B) the International Monetary Fund.
C) the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT).
D) the International Red Cross.
A) the European Union.
B) the International Monetary Fund.
C) the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT).
D) the International Red Cross.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Consumer surplus is:
A) the difference between the price of a product and consumers' valuation of the last unit of the product purchased.
B) the difference between the price of a product and what consumers were willing to pay for the product.
C) the difference between the discounted price of a product and its retail price.
D) the difference between the price paid by consumers and the price required of producers.
A) the difference between the price of a product and consumers' valuation of the last unit of the product purchased.
B) the difference between the price of a product and what consumers were willing to pay for the product.
C) the difference between the discounted price of a product and its retail price.
D) the difference between the price paid by consumers and the price required of producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
China is now a member of the World Trade Organization. For China, one of the benefits of WTO membership is:
A) the right to impose antidumping duties on its exports.
B) the right to increase tariffs on all its imports.
C) the right to subsidize all its exports.
D) the right to impose antidumping duties on its imports.
A) the right to impose antidumping duties on its exports.
B) the right to increase tariffs on all its imports.
C) the right to subsidize all its exports.
D) the right to impose antidumping duties on its imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The difference between the price consumers are willing to pay and the price that they actually pay is known as:
A) price discrimination.
B) government surplus.
C) consumer surplus.
D) producer surplus.
A) price discrimination.
B) government surplus.
C) consumer surplus.
D) producer surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
One interpretation of producer surplus is that it equals:
A) the profits of a firm.
B) the return to the fixed factors of production in an industry.
C) consumer surplus.
D) the difference between the price of a product and its average cost of production.
A) the profits of a firm.
B) the return to the fixed factors of production in an industry.
C) consumer surplus.
D) the difference between the price of a product and its average cost of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
(Figure: Consumer Surplus) When the price of the product is $15, the consumer surplus is: 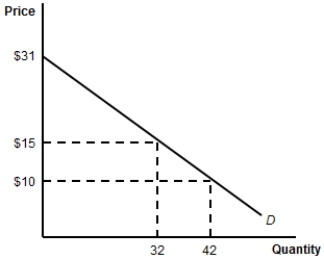
A) $441.
B) $256.
C) $13.
D) $15.

A) $441.
B) $256.
C) $13.
D) $15.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is NOT an important provision of GATT?
A) the most favored nation clause
B) the safeguard provision or escape clause
C) antidumping tariffs
D) approval of export subsidies
A) the most favored nation clause
B) the safeguard provision or escape clause
C) antidumping tariffs
D) approval of export subsidies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A free-trade area is defined as:
A) a trading agreement that allows for free flow of resources.
B) a trading agreement that binds member countries to have a uniform tariff on other countries.
C) a trading agreement that lets countries rely on subsidies on domestic production.
D) a trading agreement in which a group of countries voluntarily agree to remove trade barriers between themselves.
A) a trading agreement that allows for free flow of resources.
B) a trading agreement that binds member countries to have a uniform tariff on other countries.
C) a trading agreement that lets countries rely on subsidies on domestic production.
D) a trading agreement in which a group of countries voluntarily agree to remove trade barriers between themselves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When consumers are able to buy a product at a price lower than its marginal value to them, it is called:
A) consumer surplus.
B) consumer sovereignty.
C) producer surplus.
D) marginal utility.
A) consumer surplus.
B) consumer sovereignty.
C) producer surplus.
D) marginal utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
GATT maintained a provision that nations could enact temporary emergency tariffs or quotas if imports threatened the existence of domestic producers. The WTO has maintained that provision. Economists call this:
A) the tariff bill.
B) the escape clause.
C) justifiable means.
D) domestic job security provision.
A) the tariff bill.
B) the escape clause.
C) justifiable means.
D) domestic job security provision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A customs union is different from a free-trade area, in that:
A) a free-trade area allows for free movement of factors, whereas a customs union does not.
B) a free-trade area allows for uniform tariffs, whereas a customs union does not.
C) a free-trade area removes trade barriers between member countries, whereas a customs union adopts identical tariffs with the rest of the world.
D) a customs union removes trade barriers between member countries, whereas a free-trade area adopts identical tariffs with the rest of the world.
A) a free-trade area allows for free movement of factors, whereas a customs union does not.
B) a free-trade area allows for uniform tariffs, whereas a customs union does not.
C) a free-trade area removes trade barriers between member countries, whereas a customs union adopts identical tariffs with the rest of the world.
D) a customs union removes trade barriers between member countries, whereas a free-trade area adopts identical tariffs with the rest of the world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Producer surplus is:
A) the difference between the price of a product and marginal cost of producing the product.
B) the difference between the price of a product and what consumers were willing to pay for the product.
C) the difference between the discounted price of a product and its retail price.
D) the difference between the price of a product and its average cost of production.
A) the difference between the price of a product and marginal cost of producing the product.
B) the difference between the price of a product and what consumers were willing to pay for the product.
C) the difference between the discounted price of a product and its retail price.
D) the difference between the price of a product and its average cost of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Normally the WTO does not allow discriminatory treatment in trade of member nations, but it makes an exception for nations:
A) that have a large trade surplus.
B) using environmentally harmful production techniques.
C) that cannot control drugs and other illegal activities.
D) engaging in regional free-trade agreements.
A) that have a large trade surplus.
B) using environmentally harmful production techniques.
C) that cannot control drugs and other illegal activities.
D) engaging in regional free-trade agreements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The safeguard provision or escape clause allows a country to:
A) import products below cost from foreign countries.
B) export products by selling below cost to foreign countries.
C) avoid tariffs in foreign countries temporarily.
D) temporarily increase tariffs on certain imported goods.
A) import products below cost from foreign countries.
B) export products by selling below cost to foreign countries.
C) avoid tariffs in foreign countries temporarily.
D) temporarily increase tariffs on certain imported goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
(Figure: Consumer Surplus) By how much will consumer surplus increase if the price of the product decreases to $10? 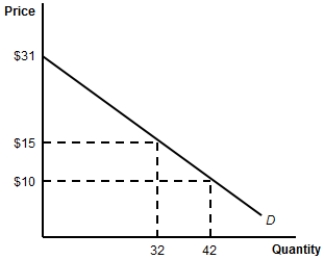
A) $441.
B) $256.
C) $185.
D) $160.

A) $441.
B) $256.
C) $185.
D) $160.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A country that becomes a member of the World Trade Organization agrees to bind its tariffs. "Binding" means that the country agrees not to increase existing tariffs and that it will not introduce new tariffs. However, GATT allows three exceptions to binding. Which of the following is NOT an exception to binding?
A) antidumping duties against dumped imports
B) countervailing duties against subsidized imports
C) safeguard or escape clause tariffs
D) tariff reductions negotiated in free-trade areas
A) antidumping duties against dumped imports
B) countervailing duties against subsidized imports
C) safeguard or escape clause tariffs
D) tariff reductions negotiated in free-trade areas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
To help its domestic producers, the United States unilaterally raised tariffs on _____ in early 2002, but after a ruling against the United States by the WTO, it was forced to rescind the tariff.
A) autos
B) steel
C) oil
D) dairy products
A) autos
B) steel
C) oil
D) dairy products

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Suppose that the supply curve for widgets is described by this equation: P = 1/2Q. What is the value of producer surplus when P = 5?
A) $5
B) $12.50
C) $25
D) $50
A) $5
B) $12.50
C) $25
D) $50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Suppose that consumer demand is given by this equation: P = 10 - Q. What is the value of consumer surplus when P = 5?
A) $5
B) $12.50
C) $25
D) $50
A) $5
B) $12.50
C) $25
D) $50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When firms are able to sell units of a good at a price higher than the marginal cost of production, they are getting:
A) consumer surplus.
B) higher efficiency.
C) producer surplus.
D) marginal utility.
A) consumer surplus.
B) higher efficiency.
C) producer surplus.
D) marginal utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
GATT/WTO allows nations to impose tariffs in response to unfair trade practices such as:
A) dumping.
B) transportation costs.
C) environmental degradation.
D) import subsidies.
A) dumping.
B) transportation costs.
C) environmental degradation.
D) import subsidies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Suppose that Norway is a small country and currently produces 100,000 board feet of lumber at $600 per 1,000 board feet. Then it begins to trade at the world price of $500 per 1,000 board feet. As a result of trade, Norway's production falls to 50,000 board feet and its consumption increases to 200,000 board feet. What is Norway's total gain in consumer surplus once it begins to trade?
A) $10,000
B) $15,000
C) $100,000
D) $150,000
A) $10,000
B) $15,000
C) $100,000
D) $150,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
(Figure: Home's Import-Competing Industry) What is the consumer surplus after trade? 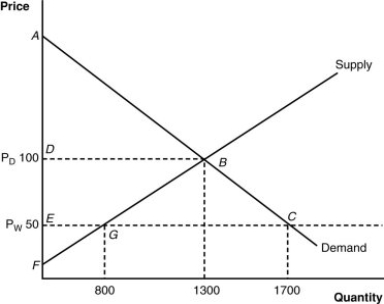
A) triangle ADB
B) triangle AEC
C) quadrangle DEBC
D) triangle EFG

A) triangle ADB
B) triangle AEC
C) quadrangle DEBC
D) triangle EFG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
(Figure: The Import-Competing Industry) In the figure, what is the value of producer surplus in the absence of trade? 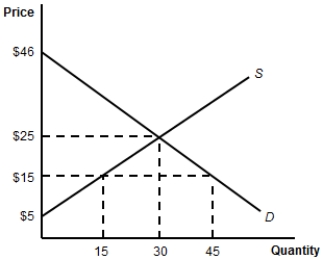
A) $510.
B) $150.
C) $25.
D) $15.

A) $510.
B) $150.
C) $25.
D) $15.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If there is free trade in a small economy, the nation will be able to import unlimited quantities of the product at:
A) the domestic price.
B) the world price.
C) the price measured in euros.
D) the price determined after all tariffs are assessed.
A) the domestic price.
B) the world price.
C) the price measured in euros.
D) the price determined after all tariffs are assessed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
(Figure: The Import-Competing Industry) Suppose that, with free trade, the world price of the product is $15. What is the value of consumer surplus? 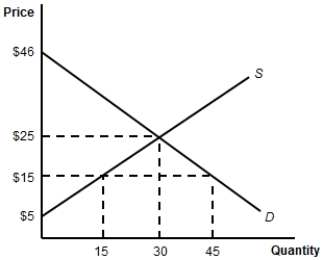
A) $1,395.
B) $697.50.
C) $22.50.
D) $2,250.

A) $1,395.
B) $697.50.
C) $22.50.
D) $2,250.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
(Figure: The Import-Competing Industry) What is the increase in producer surplus if the demand for the product increases and the new equilibrium price is 30 and quantity is 50? 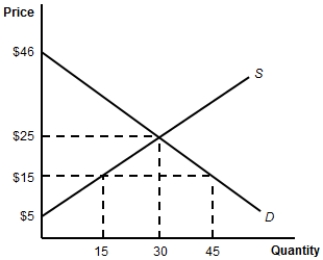
A) $525
B) $475
C) $255
D) $325

A) $525
B) $475
C) $255
D) $325

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
(Figure: Home's Import-Competing Industry) What is this nation's "welfare" after trade? 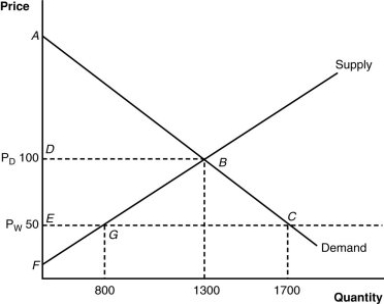
A) triangle AFB
B) triangle AEC + triangle EFG
C) quadrangle DEB
D) triangle EFG

A) triangle AFB
B) triangle AEC + triangle EFG
C) quadrangle DEB
D) triangle EFG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
We can measure producer and consumer surplus by looking at a graph of supply and demand. Producer surplus is:
A) the area above the supply curve but below the equilibrium price.
B) the area below the demand curve but greater than the equilibrium price.
C) the area below the demand curve all the way down to the quantity axis.
D) the combined triangular area below the demand curve and above the supply curve.
A) the area above the supply curve but below the equilibrium price.
B) the area below the demand curve but greater than the equilibrium price.
C) the area below the demand curve all the way down to the quantity axis.
D) the combined triangular area below the demand curve and above the supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
(Figure: The Import-Competing Industry) Suppose that, with free trade, the world price of the product is $15. In comparison to a no-trade situation, with free trade, producer surplus: 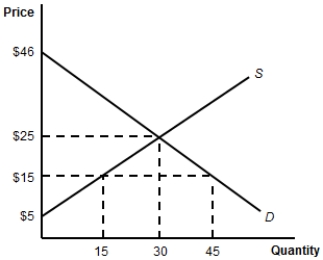
A) increases to $75.
B) decreases to $75.
C) increases to $150.
D) decreases to $150.

A) increases to $75.
B) decreases to $75.
C) increases to $150.
D) decreases to $150.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A small country in international trade faces:
A) a perfectly elastic world supply curve.
B) a perfectly inelastic world supply curve.
C) a perfectly elastic world demand curve.
D) a perfectly inelastic world demand curve.
A) a perfectly elastic world supply curve.
B) a perfectly inelastic world supply curve.
C) a perfectly elastic world demand curve.
D) a perfectly inelastic world demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
We can measure producer and consumer gains by looking at a graph of supply and demand. Total welfare in the economy would be:
A) the area above the supply curve but below the equilibrium price.
B) the area below the demand curve but greater than the equilibrium price.
C) the area below the demand curve all the way down to the quantity axis.
D) the combined triangular area below the demand curve and above the supply curve.
A) the area above the supply curve but below the equilibrium price.
B) the area below the demand curve but greater than the equilibrium price.
C) the area below the demand curve all the way down to the quantity axis.
D) the combined triangular area below the demand curve and above the supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
(Figure: Home's Import-Competing Industry) What is the domestic price before trade? 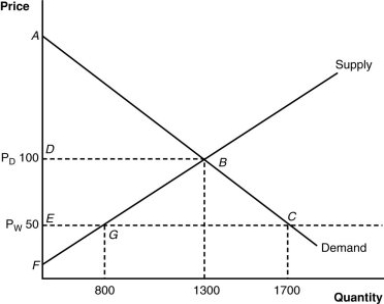
A) $100
B) $800
C) $50
D) $1,300

A) $100
B) $800
C) $50
D) $1,300

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
How many units will a country import if S = 1P represents its home supply curve, D = 100 - 1P represents its home demand curve, and the world price is $25?
A) 25
B) 50
C) 75
D) 100
A) 25
B) 50
C) 75
D) 100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Suppose that Norway is a small country and currently produces 100,000 board feet of lumber at $600 per 1,000 board feet. Then it begins to trade at the world price of $500 per 1,000 board feet. As a result of trade, Norway's production falls to 50,000 board feet and its consumption increases to 200,000 board feet. What is Norway's total welfare gain once it begins to trade?
A) $5,000
B) $7,500
C) $15,000
D) $17,500
A) $5,000
B) $7,500
C) $15,000
D) $17,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
(Figure: Home's Import-Competing Industry) What is the domestic price after trade? 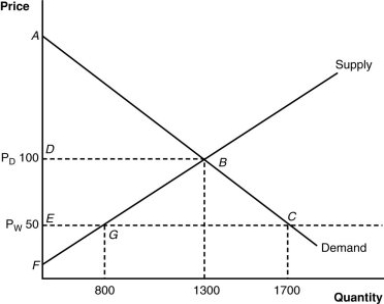
A) $100
B) $800
C) $50
D) $1,300

A) $100
B) $800
C) $50
D) $1,300

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
(Figure: Home's Import-Competing Industry) What is this nation's "welfare" before trade? 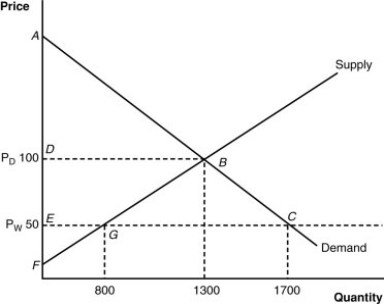
A) triangle AFB
B) triangle AEC
C) quadrangle DEBC
D) triangle EFC

A) triangle AFB
B) triangle AEC
C) quadrangle DEBC
D) triangle EFC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
We can measure producer and consumer surplus by looking at a graph of supply and demand. Consumer surplus is:
A) the area above the supply curve but below the equilibrium price.
B) the area below the demand curve but greater than the equilibrium price.
C) the area below the demand curve all the way down to the quantity axis.
D) the combined triangular area below the demand curve and above the supply curve.
A) the area above the supply curve but below the equilibrium price.
B) the area below the demand curve but greater than the equilibrium price.
C) the area below the demand curve all the way down to the quantity axis.
D) the combined triangular area below the demand curve and above the supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Suppose that Norway is a small country and currently produces 100,000 board feet of lumber at $600 per 1,000 board feet. Then it begins to trade at the world price of $500 per 1,000 board feet. As a result of trade, Norway's production falls to 50,000 board feet and its consumption increases to 200,000 board feet. How many board feet of lumber does Norway now import?
A) 250,000 board feet
B) 200,000 board feet
C) 150,000 board feet
D) 100,000 board feet
A) 250,000 board feet
B) 200,000 board feet
C) 150,000 board feet
D) 100,000 board feet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
(Figure: Home's Import-Competing Industry) What is the consumer surplus before trade? 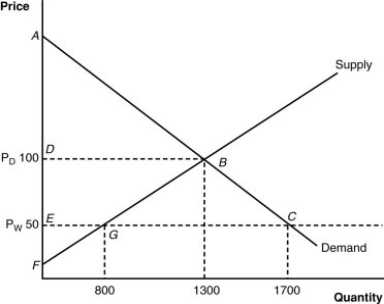
A) triangle ADB
B) triangle AEC
C) quadrangle DEBC
D) triangle EFG

A) triangle ADB
B) triangle AEC
C) quadrangle DEBC
D) triangle EFG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If we assume perfect competition in the product markets, producer surplus is:
A) maximized.
B) minimized.
C) equal to the firm's monopoly profits.
D) equal to the return to the fixed factors of production.
A) maximized.
B) minimized.
C) equal to the firm's monopoly profits.
D) equal to the return to the fixed factors of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If S = 1P represents a country's home supply curve and D = 100 - 1P represents its home demand curve, then the equilibrium price and quantity in autarky are:
A) $100 and 0 units.
B) $50 and 50 units.
C) $0 and 100 units.
D) $75 and 25 units.
A) $100 and 0 units.
B) $50 and 50 units.
C) $0 and 100 units.
D) $75 and 25 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Suppose that the free-trade price of a ton of steel is €500. (Note: € is the symbol for the euro, a common currency used in 19 European countries, including Finland.) Finland, a small country, imposes a €60 per-ton specific tariff on imported steel. With the tariff, Finland produces 300,000 tons of steel and consumes 600,000 tons of steel. Suppose that the €60-per-ton tariff caused Finnish production of steel to increase by 100,000 tons and Finnish consumption of steel to fall by 100,000 tons. What is the value of Finland's welfare loss due to the tariff?
A) 200,000 tons
B) €6 million
C) €12 million
D) €15 million
A) 200,000 tons
B) €6 million
C) €12 million
D) €15 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Suppose that the free-trade price of a ton of steel is €500. (Note: € is the symbol for the euro, a common currency used in 19 European countries, including Finland.) Finland, a small country, imposes a €60 per-ton specific tariff on imported steel. With the tariff, Finland produces 300,000 tons of steel and consumes 600,000 tons of steel. What will happen to the Finnish price of steel if Finnish demand increases and the tariff remains at €60-per-ton?
A) It will not change.
B) It will increase.
C) It will decrease.
D) It will first increase, then decrease.
A) It will not change.
B) It will increase.
C) It will decrease.
D) It will first increase, then decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Suppose that the free-trade price of a ton of steel is €500. (Note: € is the symbol for the euro, a common currency used in 19 European countries, including Finland.) Finland, a small country, imposes a €60 per-ton specific tariff on imported steel. With the tariff, Finland produces 300,000 tons of steel and consumes 600,000 tons of steel. What is likely to happen to Finnish production of steel and the price of steel sold in Finland after the €60-per-ton tariff is imposed?
A) Finnish steel production will fall, and the Finnish price of steel will fall.
B) Finnish steel production will rise, and the Finnish price of steel will fall.
C) Finnish steel production will fall, and the Finnish price of steel will rise.
D) Finnish steel production will rise, and the Finnish price of steel will rise.
A) Finnish steel production will fall, and the Finnish price of steel will fall.
B) Finnish steel production will rise, and the Finnish price of steel will fall.
C) Finnish steel production will fall, and the Finnish price of steel will rise.
D) Finnish steel production will rise, and the Finnish price of steel will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Suppose that the free-trade price of a ton of steel is €500. (Note: € is the symbol for the euro, a common currency used in 19 European countries, including Finland.) Finland, a small country, imposes a €60 per-ton specific tariff on imported steel. With the tariff, Finland produces 300,000 tons of steel and consumes 600,000 tons of steel. What is the purpose of this €60-per-ton tariff?
A) Its purpose is to protect Finnish steel consumers from foreign competition.
B) Its purpose is to protect Finnish steel producers and consumers from the World Trade Organization.
C) Its purpose is to protect Finnish steel producers from foreign competition.
D) Its purpose is to cause Finland to comply with provisions of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade.
A) Its purpose is to protect Finnish steel consumers from foreign competition.
B) Its purpose is to protect Finnish steel producers and consumers from the World Trade Organization.
C) Its purpose is to protect Finnish steel producers from foreign competition.
D) Its purpose is to cause Finland to comply with provisions of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Suppose that the free-trade price of a ton of steel is €500. (Note: € is the symbol for the euro, a common currency used in 19 European countries, including Finland.) Finland, a small country, imposes a €60 per-ton specific tariff on imported steel. With the tariff, Finland produces 300,000 tons of steel and consumes 600,000 tons of steel. Who will gain and who will lose as a result Finland's €60-per-ton tariff on imported steel?
A) Both Finnish steel producers and steel consumers will be worse off with the tariff than without it.
B) Finnish steel producers will be better off; Finnish steel consumers will be worse off with the tariff than without it.
C) Finnish steel producers will be worse off; Finnish steel consumers will be better off with the tariff than without it.
D) Both Finnish steel producers and steel consumers will be better off with the tariff than without it.
A) Both Finnish steel producers and steel consumers will be worse off with the tariff than without it.
B) Finnish steel producers will be better off; Finnish steel consumers will be worse off with the tariff than without it.
C) Finnish steel producers will be worse off; Finnish steel consumers will be better off with the tariff than without it.
D) Both Finnish steel producers and steel consumers will be better off with the tariff than without it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The following table gives the hypothetical supply and demand of television sets in Guatemala. Guatemala is a small country that is unable to affect world prices. The world price (free-trade price) is $300 per TV set. 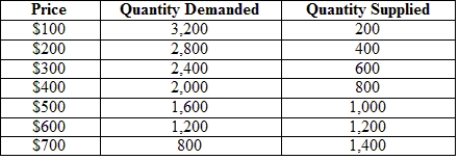 With free trade, how many TV sets will Guatemala produce?
With free trade, how many TV sets will Guatemala produce?
A) 800
B) 600
C) 400
D) 200
 With free trade, how many TV sets will Guatemala produce?
With free trade, how many TV sets will Guatemala produce?A) 800
B) 600
C) 400
D) 200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The home import demand curve is downward sloping because:
A) as the government forces the price down, consumers buy more.
B) foreign companies want to help domestic competitors.
C) as the price falls below domestic equilibrium, the shortage in demand is filled by importing more quantity from abroad.
D) consumers can control the price of the good.
A) as the government forces the price down, consumers buy more.
B) foreign companies want to help domestic competitors.
C) as the price falls below domestic equilibrium, the shortage in demand is filled by importing more quantity from abroad.
D) consumers can control the price of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
(Figure: Home's Import-Competing Industry) Based on the graph, which of the following statements is (are) correct? 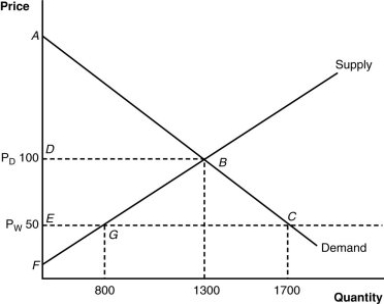
A) This nation will not produce anything if the world price is greater than $100.
B) This nation will import nothing if the world price is $50.
C) This nation would import 1,700 units if the world price is $50.
D) This nation will produce 800 units if the world price is $50.

A) This nation will not produce anything if the world price is greater than $100.
B) This nation will import nothing if the world price is $50.
C) This nation would import 1,700 units if the world price is $50.
D) This nation will produce 800 units if the world price is $50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Suppose that the free-trade price of a ton of steel is €500. (Note: € is the symbol for the euro, a common currency used in 19 European countries, including Finland.) Finland, a small country, imposes a €60 per-ton specific tariff on imported steel. With the tariff, Finland produces 300,000 tons of steel and consumes 600,000 tons of steel. How much total tariff revenue will the Finnish government collect as a result of the €60-per-ton tariff?
A) €6 million
B) €12 million
C) €18 million
D) €30 million
A) €6 million
B) €12 million
C) €18 million
D) €30 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
(Figure: Home's Import-Competing Industry) How would we measure the "gains" from trade in this diagram? 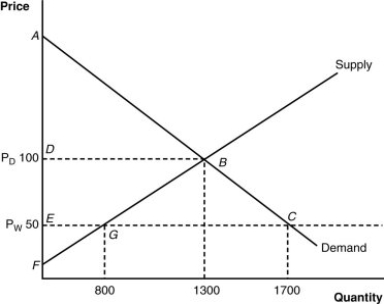
A) triangle AFB
B) triangle AEC
C) quadrangle DECB (consumer gains) - DEBG (producer losses)
D) triangle EFC

A) triangle AFB
B) triangle AEC
C) quadrangle DECB (consumer gains) - DEBG (producer losses)
D) triangle EFC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The following table gives the hypothetical supply and demand of television sets in Guatemala. Guatemala is a small country that is unable to affect world prices. The world price (free-trade price) is $300 per TV set. 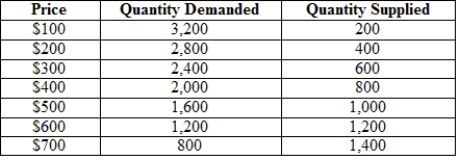 How much total tariff revenue will Guatemala collect when it imposes the 100% tariff on imported TVs?
How much total tariff revenue will Guatemala collect when it imposes the 100% tariff on imported TVs?
A) $300
B) $0
C) $240,000
D) $360,000
 How much total tariff revenue will Guatemala collect when it imposes the 100% tariff on imported TVs?
How much total tariff revenue will Guatemala collect when it imposes the 100% tariff on imported TVs?A) $300
B) $0
C) $240,000
D) $360,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If S = 1P represents a country's home supply curve and D = 100 - 1P represents its home demand curve, then the equation representing its import demand curve is:
A) 100 - 2P.
B) 50 - 1P.
C) 100 - 1P.
D) 50 - 2P.
A) 100 - 2P.
B) 50 - 1P.
C) 100 - 1P.
D) 50 - 2P.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The following table gives the hypothetical supply and demand of television sets in Guatemala. Guatemala is a small country that is unable to affect world prices. The world price (free-trade price) is $300 per TV set. 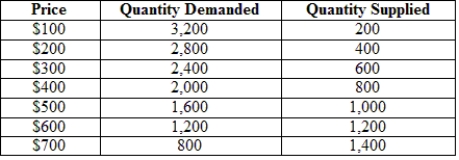 With free trade, how many TV sets will Guatemala import?
With free trade, how many TV sets will Guatemala import?
A) 1,800
B) 1,200
C) 800
D) 600
 With free trade, how many TV sets will Guatemala import?
With free trade, how many TV sets will Guatemala import?A) 1,800
B) 1,200
C) 800
D) 600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Suppose that the equations S = 2P and D = 6 - P represent a small country's home supply and home demand curves. Which of the following is the equilibrium price in autarky?
A) $2
B) $4
C) $6
D) $8
A) $2
B) $4
C) $6
D) $8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The following table gives the hypothetical supply and demand of television sets in Guatemala. Guatemala is a small country that is unable to affect world prices. The world price (free-trade price) is $300 per TV set. 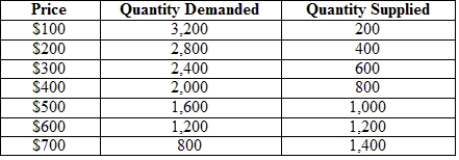 Suppose that Guatemala now imposes a 100% tariff on imported TVs. How many TVs will it now import?
Suppose that Guatemala now imposes a 100% tariff on imported TVs. How many TVs will it now import?
A) 0
B) 200
C) 400
D) 600
 Suppose that Guatemala now imposes a 100% tariff on imported TVs. How many TVs will it now import?
Suppose that Guatemala now imposes a 100% tariff on imported TVs. How many TVs will it now import?A) 0
B) 200
C) 400
D) 600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Suppose that the equations S = 2P and D = 6 - P represent a small country's home supply and home demand curves, and the free-trade world price is $1. If the government imposed a 50% tariff on imports, how much revenue would it collect as a result of the tariff? (Note: It is possible to consume partial units of this product, such as 2.5 units.)
A) $1.50
B) $2.75
C) $0.50
D) $0.75
A) $1.50
B) $2.75
C) $0.50
D) $0.75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Suppose that the equations S = 2P and D = 6 - P represent a small country's home supply and home demand curves. If the world price is $1, which of the following is the increase in the country's welfare when it trades compared with autarky?
A) $6.00
B) $4.50
C) $1.50
D) $0.50
A) $6.00
B) $4.50
C) $1.50
D) $0.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Suppose that the world price of radios is above the no-trade domestic price. In that case, the country:
A) imports radios at the world price.
B) imports radios at the no-trade domestic price.
C) exports radios at the world price.
D) exports radios at the no-trade domestic price.
A) imports radios at the world price.
B) imports radios at the no-trade domestic price.
C) exports radios at the world price.
D) exports radios at the no-trade domestic price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The following table gives the hypothetical supply and demand of television sets in Guatemala. Guatemala is a small country that is unable to affect world prices. The world price (free-trade price) is $300 per TV set. 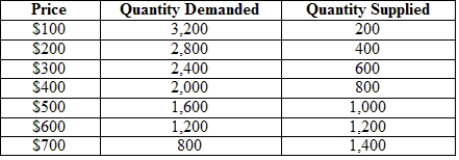 In the absence of trade, how many TV sets will Guatemala produce?
In the absence of trade, how many TV sets will Guatemala produce?
A) 1,400
B) 1,200
C) 1,000
D) 800
 In the absence of trade, how many TV sets will Guatemala produce?
In the absence of trade, how many TV sets will Guatemala produce?A) 1,400
B) 1,200
C) 1,000
D) 800

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



