Deck 6: Increasing Returns to Scale and Monopolistic Competition
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/149
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Increasing Returns to Scale and Monopolistic Competition
1
Intra-industry trade refers to:
A) imports and exports within the same industry.
B) imports and exports originating in different industries.
C) international trade patterns predicted by the Heckscher-Ohlin model.
D) Ricardian comparative advantage.
A) imports and exports within the same industry.
B) imports and exports originating in different industries.
C) international trade patterns predicted by the Heckscher-Ohlin model.
D) Ricardian comparative advantage.
A
2
"Differentiated" is another word for:
A) identical.
B) homogeneous.
C) heterogeneous.
D) None of these has the same meaning.
A) identical.
B) homogeneous.
C) heterogeneous.
D) None of these has the same meaning.
C
3
Equilibrium in a monopoly occurs when:
A) the monopolist has driven out all competitors.
B) the monopoly firm has sold the maximum number of units.
C) the monopoly firm produces the quantity that maximizes its profits (or minimizes loss) where MR = MC.
D) the monopoly firm has gotten unions to agree to wage concessions.
A) the monopolist has driven out all competitors.
B) the monopoly firm has sold the maximum number of units.
C) the monopoly firm produces the quantity that maximizes its profits (or minimizes loss) where MR = MC.
D) the monopoly firm has gotten unions to agree to wage concessions.
C
4
To analyze intra-industry trade, we change our assumptions about our trade models to allow:
A) price-conscious consumers.
B) short-run unemployment.
C) differentiated products.
D) perfect competition.
A) price-conscious consumers.
B) short-run unemployment.
C) differentiated products.
D) perfect competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What will happen when a firm raises the price of a differentiated product in an imperfectly competitive market?
A) It will see lower sales but will not lose all its sales.
B) It will lose all its sales to competitor firms.
C) It will actually get new customers from other firms.
D) It will see an increase in revenues.
A) It will see lower sales but will not lose all its sales.
B) It will lose all its sales to competitor firms.
C) It will actually get new customers from other firms.
D) It will see an increase in revenues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A monopolist maximizes its profits by selling up to the point at which:
A) its price equals its marginal cost.
B) its price equals its marginal revenue.
C) its marginal revenue equals its marginal costs.
D) the difference between its price and average cost is maximized.
A) its price equals its marginal cost.
B) its price equals its marginal revenue.
C) its marginal revenue equals its marginal costs.
D) the difference between its price and average cost is maximized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following features is characteristic of monopolistic competition?
A) only one producer
B) homogeneous products
C) differentiated products
D) No individual producer has any influence on the market price.
A) only one producer
B) homogeneous products
C) differentiated products
D) No individual producer has any influence on the market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
For a monopolistic competitor, marginal revenue at its short-run equilibrium price and quantity equals:
A) price.
B) marginal cost.
C) average cost.
D) average revenue.
A) price.
B) marginal cost.
C) average cost.
D) average revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Products that are very similar and very close substitutes, but that may be of different quality or prices, are called:
A) differentiated complements.
B) differentiated substitutes.
C) differentiated products.
D) perfect substitute products.
A) differentiated complements.
B) differentiated substitutes.
C) differentiated products.
D) perfect substitute products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The price charged by a monopoly firm is the market price (demand curve) at which:
A) MR = MC, and usually P > MR and P > MC.
B) the firm is just breaking even.
C) the firm makes a normal profit.
D) MR = MC = P.
A) MR = MC, and usually P > MR and P > MC.
B) the firm is just breaking even.
C) the firm makes a normal profit.
D) MR = MC = P.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A monopolistic competitive firm:
A) will always earn monopoly profits.
B) will never earn monopoly profits.
C) may earn monopoly profits in the short run.
D) may earn monopoly profits in the long run.
A) will always earn monopoly profits.
B) will never earn monopoly profits.
C) may earn monopoly profits in the short run.
D) may earn monopoly profits in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What term is used to describe situations in which countries specialize in and trade different varieties of the same type of product?
A) comparative advantage
B) the Heckscher-Ohlin model
C) intra-industry trade
D) increasing returns to scale
A) comparative advantage
B) the Heckscher-Ohlin model
C) intra-industry trade
D) increasing returns to scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The ____________ model best explains intra-industry trade.
A) Ricardian
B) Heckscher-Ohlin
C) monopolistic competition
D) specific-factors
A) Ricardian
B) Heckscher-Ohlin
C) monopolistic competition
D) specific-factors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is characteristic of a monopolistically competitive industry?
A) monopoly profits
B) few firms in the industry
C) homogeneous products
D) Individual firms can influence the market price.
A) monopoly profits
B) few firms in the industry
C) homogeneous products
D) Individual firms can influence the market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A differentiated product is one that:
A) is slightly different from the competitor's product, although it is a close substitute.
B) is very different.
C) is traded within firms and is not for sale in retail markets.
D) has a shelf life of less than a year.
A) is slightly different from the competitor's product, although it is a close substitute.
B) is very different.
C) is traded within firms and is not for sale in retail markets.
D) has a shelf life of less than a year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A feature of imperfect competition is _________, which means that as the firm expands its production, average costs of production fall. Therefore, the firm can _______ its costs of production by selling internationally.
A) increasing returns to scale; decrease
B) increasing returns to scale; increase
C) decreasing returns to scale; decrease
D) decreasing returns to scale; increase
A) increasing returns to scale; decrease
B) increasing returns to scale; increase
C) decreasing returns to scale; decrease
D) decreasing returns to scale; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is NOT characteristic of a monopolistically competitive industry?
A) monopoly profits
B) many firms in the industry
C) differentiated products
D) Individual firms can influence the market price.
A) monopoly profits
B) many firms in the industry
C) differentiated products
D) Individual firms can influence the market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which model best explains the cross-trade of very similar products exported and imported by trading partners?
A) Ricardian
B) Heckscher-Ohlin
C) specific-factors
D) monopolistic competition
A) Ricardian
B) Heckscher-Ohlin
C) specific-factors
D) monopolistic competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is the term describing very similar products being exported and imported by trading partners?
A) reciprocal trade
B) imperfect competition
C) intra-industry trade
D) inter-industry trade
A) reciprocal trade
B) imperfect competition
C) intra-industry trade
D) inter-industry trade

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Increasing returns to scale occur when a firm's:
A) average costs of production increase as its output increases.
B) average costs of production decrease as its output increases.
C) average fixed costs increase as its output increases.
D) marginal costs increase as its output increases.
A) average costs of production increase as its output increases.
B) average costs of production decrease as its output increases.
C) average fixed costs increase as its output increases.
D) marginal costs increase as its output increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In a duopoly where products are differentiated and firms charge different prices, their demand curves are _______________ than if the firms sell identical products at the same price.
A) steeper
B) farther to the right
C) more elastic
D) less elastic
A) steeper
B) farther to the right
C) more elastic
D) less elastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When average costs of production are falling, average cost:
A) is higher than marginal cost.
B) is equal to price.
C) is negative.
D) is less than marginal cost.
A) is higher than marginal cost.
B) is equal to price.
C) is negative.
D) is less than marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Firm X's total fixed costs are $1,000. Its total variable costs of producing 100 units are $2,000, and its total variable costs of producing 200 units are $4,000. What are its average costs of producing 100 and 200 units of output?
A) $30 and $25
B) $20 and $20
C) $10 and $5
D) $25 and $30
A) $30 and $25
B) $20 and $20
C) $10 and $5
D) $25 and $30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A duopoly is a market structure in which:
A) two consumers buy the product.
B) two firms sell the product.
C) one firm sells the product and one consumer buys the product.
D) two firms sell the product and two consumers buy the product.
A) two consumers buy the product.
B) two firms sell the product.
C) one firm sells the product and one consumer buys the product.
D) two firms sell the product and two consumers buy the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following will NOT cause increasing returns to scale and declining average costs?
A) focusing on a single product line and specializing
B) exporting goods to other countries
C) selling more in their home market
D) hiring more workers at the existing plant
A) focusing on a single product line and specializing
B) exporting goods to other countries
C) selling more in their home market
D) hiring more workers at the existing plant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is NOT an assumption of monopolistic competition?
A) Each firm's output is slightly different from other firms in the industry.
B) There are many firms in the industry.
C) Production occurs with increasing returns to scale technology.
D) Each firm faces a perfectly elastic demand curve.
A) Each firm's output is slightly different from other firms in the industry.
B) There are many firms in the industry.
C) Production occurs with increasing returns to scale technology.
D) Each firm faces a perfectly elastic demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In a duopoly, each firm faces:
A) a more elastic demand curve if it raises its price.
B) a more elastic demand curve if it lowers its price.
C) a perfectly elastic demand curve.
D) a perfectly inelastic demand curved.
A) a more elastic demand curve if it raises its price.
B) a more elastic demand curve if it lowers its price.
C) a perfectly elastic demand curve.
D) a perfectly inelastic demand curved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
At its current production level, a monopolist's marginal revenue is $20 and its marginal cost is $10. Which of the following is correct?
A) The monopolist should produce and sell more output.
B) The monopolist should produce and sell less output.
C) The monopolist is maximizing its profits at its current level of output.
D) The monopolist should cease production.
A) The monopolist should produce and sell more output.
B) The monopolist should produce and sell less output.
C) The monopolist is maximizing its profits at its current level of output.
D) The monopolist should cease production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Whenever a firm's marginal costs are less than its average costs, its average costs must be:
A) falling.
B) rising.
C) constant.
D) falling, then rising.
A) falling.
B) rising.
C) constant.
D) falling, then rising.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When there are increasing returns to scale, average costs must be:
A) falling.
B) rising.
C) constant.
D) falling, then rising.
A) falling.
B) rising.
C) constant.
D) falling, then rising.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
To analyze monopolistic competition in trade, we make several assumptions about the market. Which of the following is an assumption of monopolistic competition?
A) few firms in the industry
B) difficult entry and exit
C) increasing long-run average cost
D) increasing returns to scale
A) few firms in the industry
B) difficult entry and exit
C) increasing long-run average cost
D) increasing returns to scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The demand curve facing a monopolistic competitor:
A) is perfectly inelastic.
B) is perfectly elastic.
C) slopes downward to the right.
D) has a positive slope.
A) is perfectly inelastic.
B) is perfectly elastic.
C) slopes downward to the right.
D) has a positive slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is NOT an assumption for monopolistic competition?
A) Firms produce goods using a technology with increasing returns to scale.
B) There are many firms in the industry.
C) Firms are price takers.
D) Each firm produces a good that is similar to, but differentiated from, the goods that other firms in the industry produce.
A) Firms produce goods using a technology with increasing returns to scale.
B) There are many firms in the industry.
C) Firms are price takers.
D) Each firm produces a good that is similar to, but differentiated from, the goods that other firms in the industry produce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Consider the following cost information for a monopolist: its MR = $15, its MC = $23, and it is producing nine units of output. Which of the following statements is correct?
A) The monopolist should produce and sell nine units of output.
B) The monopolist should increase production of output.
C) We need more information to decide if the firm needs to produce.
D) The monopolist should not produce this output because MR < MC.
A) The monopolist should produce and sell nine units of output.
B) The monopolist should increase production of output.
C) We need more information to decide if the firm needs to produce.
D) The monopolist should not produce this output because MR < MC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If there is a duopoly and the products are identical (homogeneous), the firm selling the product for a lower price will:
A) earn less revenue.
B) get 100% of the sales.
C) have a hard time being profitable.
D) be perceived to have lower-quality products.
A) earn less revenue.
B) get 100% of the sales.
C) have a hard time being profitable.
D) be perceived to have lower-quality products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of monopolistic competition?
A) Firms have some control over their markets.
B) Firms produce an identical product.
C) Firms retain some ability to control prices.
D) The average cost for firms declines as they produce more output.
A) Firms have some control over their markets.
B) Firms produce an identical product.
C) Firms retain some ability to control prices.
D) The average cost for firms declines as they produce more output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
To analyze monopolistic competition in trade, we make several assumptions about the market. Which of the following is NOT an assumption of monopolistic competition?
A) many firms in the industry
B) easy entry and exit
C) constant long-run average cost
D) increasing returns to scale
A) many firms in the industry
B) easy entry and exit
C) constant long-run average cost
D) increasing returns to scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A firm's average costs will be falling whenever its marginal costs are:
A) positive.
B) negative.
C) less than average costs.
D) less than fixed costs.
A) positive.
B) negative.
C) less than average costs.
D) less than fixed costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Firm X's total fixed costs are $1,000. Its total variable costs of producing 100 units are $2,000, and its total variable costs of producing 200 units are $4,000. Which of the following will happen to firm X's average costs as it increases output from 100 to 200 units?
A) Average costs increase.
B) Average costs decrease.
C) Average costs remain constant.
D) Average costs increase slightly.
A) Average costs increase.
B) Average costs decrease.
C) Average costs remain constant.
D) Average costs increase slightly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is an assumption of monopolistic competition?
A) Firms produce identical (homogeneous) outputs.
B) There are many firms in the industry.
C) Production occurs with decreasing returns to scale technology.
D) Each firm faces a perfectly elastic demand curve.
A) Firms produce identical (homogeneous) outputs.
B) There are many firms in the industry.
C) Production occurs with decreasing returns to scale technology.
D) Each firm faces a perfectly elastic demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A monopolistic competitor has fixed costs of $100 and marginal costs of $10 per unit. What is its average cost of producing 100 units?
A) $10
B) $11
C) $1,100
D) $2,000
A) $10
B) $11
C) $1,100
D) $2,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
(Figure: Costs and Demand for a Monopolistic Competitor) The profits for the firm are: 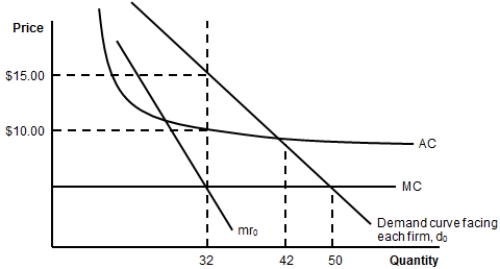
A) $320.
B) $480.
C) $160.
D) $420.

A) $320.
B) $480.
C) $160.
D) $420.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
(Figure: Costs and Demand for a Monopolistic Competitor) What price should the firm charge? 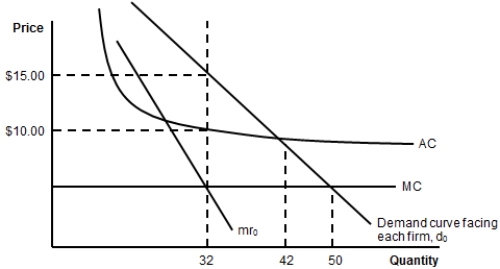
A) $15
B) $10
C) a price greater than $15
D) The firm cannot be profitable, so the price is zero.

A) $15
B) $10
C) a price greater than $15
D) The firm cannot be profitable, so the price is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If a firm has an average total cost of $55 and an average fixed cost of $10 for producing five units of output, then the total variable cost will be:
A) $550.
B) $525.
C) $225.
D) $65.
A) $550.
B) $525.
C) $225.
D) $65.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The demand equation for a good produced by a monopolistically competitive firm is P = 10 - Q. If the firm's marginal cost is a constant $2 per unit, what price will it charge and how many units will it produce if it maximizes its profits?
A) $8 and two units
B) $7 and three units
C) $6 and four units
D) $5 and five units
A) $8 and two units
B) $7 and three units
C) $6 and four units
D) $5 and five units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
(Figure: Costs and Demand for a Monopolistic Competitor) The total cost of producing the profit-maximizing output is: 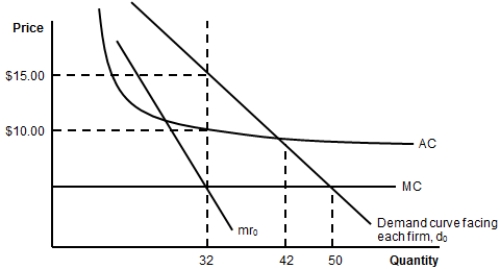
A) $320.
B) $480.
C) $420.
D) $500.

A) $320.
B) $480.
C) $420.
D) $500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If a firm has a total cost of $150 and a total variable cost of $100 for producing five units of output, then the fixed cost is:
A) $35.
B) $50.
C) $250.
D) $100.
A) $35.
B) $50.
C) $250.
D) $100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If a firm has a total fixed cost of $75 and an average variable cost of $35 for producing 10 units of output, the average total cost would be:
A) $425.
B) $42.50.
C) $110.
D) $350.
A) $425.
B) $42.50.
C) $110.
D) $350.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm will:
A) earn normal monopoly profits.
B) earn excess monopoly profits.
C) earn no monopoly profits.
D) produce where marginal cost equals price.
A) earn normal monopoly profits.
B) earn excess monopoly profits.
C) earn no monopoly profits.
D) produce where marginal cost equals price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A monopolistically competitive firm faces demand given by this equation: P = 50 - Q. It has no fixed costs and its marginal cost is $20 per unit. What is the value of the firm's monopoly profits when it sets a price that maximizes its monopoly profits?
A) $125
B) $300
C) $425
D) $225
A) $125
B) $300
C) $425
D) $225

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following describes the long-run situation for a firm in a monopolistically competitive market?
A) Competition drives out firms until there is only one left.
B) New firms enter the market because of monopoly profits, the firm's demand curve shifts to the left and becomes flatter, and monopoly profits disappear.
C) New firms enter the market and eventually there is only one kind of product, and each firm agrees to share the profits.
D) Consumers are left with no choices and no close substitutes, and firms make higher profits.
A) Competition drives out firms until there is only one left.
B) New firms enter the market because of monopoly profits, the firm's demand curve shifts to the left and becomes flatter, and monopoly profits disappear.
C) New firms enter the market and eventually there is only one kind of product, and each firm agrees to share the profits.
D) Consumers are left with no choices and no close substitutes, and firms make higher profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The demand equation for a good produced by a monopolistically competitive firm is P = 10 - Q. At what price is the firm's total revenue maximized?
A) $9
B) $7
C) $5
D) $3
A) $9
B) $7
C) $5
D) $3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
When firms charge different prices for differentiated products in imperfect competition, each firm faces a demand curve that is ___________ than would be the case if the market was perfectly competitive.
A) flatter
B) farther to the left
C) farther to the right
D) less elastic
A) flatter
B) farther to the left
C) farther to the right
D) less elastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm will produce where:
A) average cost equals price.
B) average cost equals marginal revenue.
C) marginal revenue equals price.
D) marginal cost equals price.
A) average cost equals price.
B) average cost equals marginal revenue.
C) marginal revenue equals price.
D) marginal cost equals price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The demand equation for a good produced by a monopolistically competitive firm is P = 10 - Q. If the firm has no fixed costs and variable costs of $2 per unit, what is the value of the firm's monopoly profits when it sets a price that maximizes its monopoly profits?
A) $7
B) $12
C) $15
D) $16
A) $7
B) $12
C) $15
D) $16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A monopolistic competitor has fixed costs of $100 and marginal costs of $10 per unit. What is its marginal revenue at its equilibrium price and quantity?
A) $10
B) $11
C) $1,100
D) $2,000
A) $10
B) $11
C) $1,100
D) $2,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A monopolistically competitive firm faces demand given by this equation: P = 50 - Q. It has no fixed costs and its marginal cost is $20 per unit. What quantity will the firm produce when it is maximizing its profits?
A) 10
B) 15
C) 20
D) 25
A) 10
B) 15
C) 20
D) 25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In the long run, profits in a monopolistically competitive market are zero because:
A) of government regulations.
B) of collusion.
C) firms are free to enter and exit the market.
D) firms produce a differentiated product.
A) of government regulations.
B) of collusion.
C) firms are free to enter and exit the market.
D) firms produce a differentiated product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A monopolistically competitive firm faces demand given by this equation: P = 50 - Q. It has no fixed costs and its marginal cost is $20 per unit. What price will the firm charge when it is maximizing its profits?
A) $20
B) $25
C) $30
D) $35
A) $20
B) $25
C) $30
D) $35

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In the short run, in equilibrium, firms that operate in a monopolistically competitive market face a downward sloping demand curve and will charge a price where _____ and ______.
A) quantity produced is maximized; costs are minimized
B) sales revenue is maximized; costs are falling
C) MR = MC; P > average cost
D) average costs are rising; sales are rising
A) quantity produced is maximized; costs are minimized
B) sales revenue is maximized; costs are falling
C) MR = MC; P > average cost
D) average costs are rising; sales are rising

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In the long run, international trade allows a monopolistically competitive firm an opportunity to produce:
A) more output and earn monopoly profits.
B) less output and earn monopoly profits.
C) more output and reduce its average costs.
D) less output and increase its average costs.
A) more output and earn monopoly profits.
B) less output and earn monopoly profits.
C) more output and reduce its average costs.
D) less output and increase its average costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In the long run, after trade occurs, the equilibrium number of monopolistically competitive firms:
A) is less than the total number of firms worldwide in autarky.
B) is the same as the total number of firms worldwide in autarky.
C) is greater than the total number of firms worldwide in autarky.
D) may be less than, the same as, or greater than the total number of firms worldwide in autarky.
A) is less than the total number of firms worldwide in autarky.
B) is the same as the total number of firms worldwide in autarky.
C) is greater than the total number of firms worldwide in autarky.
D) may be less than, the same as, or greater than the total number of firms worldwide in autarky.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The costs identified with opening trade are called:
A) short-run costs.
B) adjustment costs.
C) variable costs.
D) overhead costs.
A) short-run costs.
B) adjustment costs.
C) variable costs.
D) overhead costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
When trade occurs among nations with similar tastes, technology, products, and costs, monopolistically competitive firms will have an incentive to:
A) lower prices to get new customers and increase market share.
B) raise prices to take advantage of a lucrative situation.
C) cut corners in manufacturing to boost profits.
D) raise quality, so they can charge a higher price than the competition.
A) lower prices to get new customers and increase market share.
B) raise prices to take advantage of a lucrative situation.
C) cut corners in manufacturing to boost profits.
D) raise quality, so they can charge a higher price than the competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Suppose that there are 50 firms in a monopolistically competitive industry in country A and 50 firms in the same monopolistically competitive industry in country B. If country A and country B engage in international trade, we expect that the total number of firms in this industry:
A) will increase.
B) will decrease.
C) will remain unchanged.
D) will first decrease, then increase.
A) will increase.
B) will decrease.
C) will remain unchanged.
D) will first decrease, then increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
How do consumers benefit from trade among monopolistically competitive firms?
A) Prices are the same as in autarky, but the wider choice of goods increases consumer surplus.
B) Consumer surplus increases because prices are lower than in autarky, and there is a wider choice of goods.
C) Prices are higher than in autarky, but the wider choice of goods increases consumer surplus.
D) The government provides cash subsidies to consumers.
A) Prices are the same as in autarky, but the wider choice of goods increases consumer surplus.
B) Consumer surplus increases because prices are lower than in autarky, and there is a wider choice of goods.
C) Prices are higher than in autarky, but the wider choice of goods increases consumer surplus.
D) The government provides cash subsidies to consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Consumers gain from trade within a monopolistically competitive industry because:
A) prices fall and product varieties decrease.
B) prices rise and product varieties increase.
C) prices rise and product varieties decrease.
D) prices fall and product varieties increase.
A) prices fall and product varieties decrease.
B) prices rise and product varieties increase.
C) prices rise and product varieties decrease.
D) prices fall and product varieties increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
With increasing returns (falling average costs), international trade will cause the demand curves of monopolistically competitive firms to become _______________ because of foreign competition and firms must _______________to meet foreign competition.
A) steeper; raise prices
B) flatter; lower prices
C) flatter; raise prices
D) steeper; lower prices
A) steeper; raise prices
B) flatter; lower prices
C) flatter; raise prices
D) steeper; lower prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What is the expected outcome when trade occurs in a monopolistically competitive industry if the nations have similar tastes, technology, products, and costs?
A) No trade is possible.
B) Consumers are left with no choices.
C) Each firm has a larger market in which to sell, and consumers have more choices of sellers and products.
D) Transportation costs become the driving factor.
A) No trade is possible.
B) Consumers are left with no choices.
C) Each firm has a larger market in which to sell, and consumers have more choices of sellers and products.
D) Transportation costs become the driving factor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following was NOT a reason for Canada to join NAFTA?
A) Canadian firms could expand their markets by selling to the United States and Mexico.
B) Canadian firms could enjoy lower average costs by producing more.
C) Canada did not want U.S. products to dominate its domestic market.
D) Canada would experience an increase in income and employment by joining NAFTA.
A) Canadian firms could expand their markets by selling to the United States and Mexico.
B) Canadian firms could enjoy lower average costs by producing more.
C) Canada did not want U.S. products to dominate its domestic market.
D) Canada would experience an increase in income and employment by joining NAFTA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In long-run equilibrium with trade, losses from import competition will force some firms to ______________, increasing demand for the remaining firms' output, which will then cause their demand curves to become ______________, due to the increased variety of products from _______________.
A) raise prices; steeper; new firms entering the industry
B) leave the industry; flatter; foreign firms
C) lower prices; more inelastic; new firms entering the industry
D) lay off workers; more elastic; the research and development departments in firms
A) raise prices; steeper; new firms entering the industry
B) leave the industry; flatter; foreign firms
C) lower prices; more inelastic; new firms entering the industry
D) lay off workers; more elastic; the research and development departments in firms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In the long run, prices in a monopolistically competitive industry will be ________ prices without trade.
A) higher than
B) lower than
C) equal to
D) the same as
A) higher than
B) lower than
C) equal to
D) the same as

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In what two ways does trade benefit consumers when firms are monopolistically competitive?
A) better quality products, increased information
B) higher incomes, more dependable products
C) lots of bells and whistles, higher wages
D) lower prices, more variety
A) better quality products, increased information
B) higher incomes, more dependable products
C) lots of bells and whistles, higher wages
D) lower prices, more variety

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following is likely under free trade and monopolistic competition?
A) Domestic firms will always be provided cash subsidies.
B) Some domestic firms will shut down.
C) Consumers will not benefit at all from trade.
D) Foreign firms will sell the product at a higher price in the export market.
A) Domestic firms will always be provided cash subsidies.
B) Some domestic firms will shut down.
C) Consumers will not benefit at all from trade.
D) Foreign firms will sell the product at a higher price in the export market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Adjustment costs include:
A) dealing with child labor issues.
B) human rights.
C) getting used to foreign products.
D) short-term unemployment.
A) dealing with child labor issues.
B) human rights.
C) getting used to foreign products.
D) short-term unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
NAFTA benefited Canadian consumers because of:
A) higher wages and more travel opportunity.
B) lower wages but also lower taxes.
C) lower prices but lower quality.
D) lower prices and increased variety.
A) higher wages and more travel opportunity.
B) lower wages but also lower taxes.
C) lower prices but lower quality.
D) lower prices and increased variety.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following is NOT a short-run opportunity that international trade provides for a monopolistically competitive firm?
A) International trade provides an opportunity for it to produce more output.
B) International trade provides an opportunity to for it to earn monopoly profits.
C) International trade provides an opportunity for it to reduce its average costs.
D) International trade provides an opportunity for it to reduce its fixed costs.
A) International trade provides an opportunity for it to produce more output.
B) International trade provides an opportunity to for it to earn monopoly profits.
C) International trade provides an opportunity for it to reduce its average costs.
D) International trade provides an opportunity for it to reduce its fixed costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Using a model of imperfect competition, economist Daniel Trefler concluded that the North American Free Trade Agreement:
A) cost Canada more than 100,000 jobs that were never replaced.
B) caused no job loss in Canada.
C) caused Canada to lose 5% of jobs in manufacturing because Canadian tariffs had to be cut, but over time the trade agreement created higher productivity and more jobs to offset losses.
D) created new jobs in Canada from day one, as firms sold across the border and undercut U.S. firms.
A) cost Canada more than 100,000 jobs that were never replaced.
B) caused no job loss in Canada.
C) caused Canada to lose 5% of jobs in manufacturing because Canadian tariffs had to be cut, but over time the trade agreement created higher productivity and more jobs to offset losses.
D) created new jobs in Canada from day one, as firms sold across the border and undercut U.S. firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If a firm in monopolistic competition lowers its price, what will happen to the quantity of products it sells?
A) The quantity of products sold will increase and sales revenue will fall.
B) The quantity of products sold will decrease because this is not perfect competition.
C) The quantity of products sold will increase slightly-and in some cases not at all.
D) The quantity of products sold and sales revenues will increase as the firm lures customers from its competitors and attracts new customers.
A) The quantity of products sold will increase and sales revenue will fall.
B) The quantity of products sold will decrease because this is not perfect competition.
C) The quantity of products sold will increase slightly-and in some cases not at all.
D) The quantity of products sold and sales revenues will increase as the firm lures customers from its competitors and attracts new customers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm that trades internationally will ____________than it would in autarky.
A) produce more output
B) earn more monopoly profits
C) have higher average costs
D) produce more output and earn more monopoly profits
A) produce more output
B) earn more monopoly profits
C) have higher average costs
D) produce more output and earn more monopoly profits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



