Deck 3: Gains and Losses From Trade in the Specific-Factors Model
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/148
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Gains and Losses From Trade in the Specific-Factors Model
1
Which short-run model is used to study the earnings of resources?
A) comparative advantage theory
B) absolute advantage theory
C) specific-factors model
D) production possibility frontier
A) comparative advantage theory
B) absolute advantage theory
C) specific-factors model
D) production possibility frontier
C
2
In a two-sector (manufacturing and agriculture) specific-factors model, which resource is specific to the agriculture sector?
A) labor
B) land
C) capital
D) entrepreneurs
A) labor
B) land
C) capital
D) entrepreneurs
B
3
The two-sector (manufacturing and agriculture) specific-factors model assumes:
A) that there are increasing returns to labor.
B) that there are diminishing returns to labor.
C) that there are diminishing returns to capital in the agricultural sector.
D) that there are diminishing returns to land in the manufacturing sector.
A) that there are increasing returns to labor.
B) that there are diminishing returns to labor.
C) that there are diminishing returns to capital in the agricultural sector.
D) that there are diminishing returns to land in the manufacturing sector.
B
4
In the two-sector (manufacturing and agriculture) specific-factors model, it is assumed that labor:
A) can move freely between the manufacturing and agricultural sectors.
B) can move from the manufacturing to the agriculture sector, but not from the agricultural to the manufacturing sector.
C) cannot move from one sector to the other.
D) cannot move within a sector.
A) can move freely between the manufacturing and agricultural sectors.
B) can move from the manufacturing to the agriculture sector, but not from the agricultural to the manufacturing sector.
C) cannot move from one sector to the other.
D) cannot move within a sector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What does the two-sector (agriculture and manufacturing) specific-factors model allow us to analyze?
A) the returns to all factors of production
B) only the returns to capital in agriculture
C) only the returns to land in manufacturing
D) only the allocation of land to agriculture
A) the returns to all factors of production
B) only the returns to capital in agriculture
C) only the returns to land in manufacturing
D) only the allocation of land to agriculture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In a two-sector (manufacturing and agriculture) specific-factors model:
A) land is specific to the manufacturing sector.
B) labor is specific to the manufacturing sector.
C) capital is specific to the manufacturing sector.
D) labor and capital are specific to the manufacturing sector.
A) land is specific to the manufacturing sector.
B) labor is specific to the manufacturing sector.
C) capital is specific to the manufacturing sector.
D) labor and capital are specific to the manufacturing sector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the two-sector specific-factors model, diminishing returns to labor implies:
A) that the country's production possibilities frontier is linear (a straight line).
B) that the country's production possibilities frontier is concave to the origin (bowed out from the origin).
C) that the country's production possibilities frontier is convex from the origin (bowed in toward the origin).
D) that the country's production possibilities frontier may be either concave to or convex from the origin.
A) that the country's production possibilities frontier is linear (a straight line).
B) that the country's production possibilities frontier is concave to the origin (bowed out from the origin).
C) that the country's production possibilities frontier is convex from the origin (bowed in toward the origin).
D) that the country's production possibilities frontier may be either concave to or convex from the origin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The two-sector (manufacturing and agriculture) specific-factors model is termed a "short-run" model because:
A) labor cannot move from one activity to another.
B) land resources can move from one activity to another.
C) labor can move from one activity to another.
D) land and capital cannot move from one activity to another.
A) labor cannot move from one activity to another.
B) land resources can move from one activity to another.
C) labor can move from one activity to another.
D) land and capital cannot move from one activity to another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The argument that trade generates gains for all workers may NOT be true because:
A) a more realistic assumption includes capital and land as specific factors of production and recognizes that trade will generate gains for some factors and losses for others.
B) greedy corporations exploit workers.
C) technology gains are concentrated among low-skilled workers.
D) some workers lack skills and training and cannot find jobs.
A) a more realistic assumption includes capital and land as specific factors of production and recognizes that trade will generate gains for some factors and losses for others.
B) greedy corporations exploit workers.
C) technology gains are concentrated among low-skilled workers.
D) some workers lack skills and training and cannot find jobs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In contrast to the Ricardian model, international trade in the two-sector (manufacturing and agriculture) specific-factors model:
A) will lead to gains for all resources.
B) will lead to losses for all resources.
C) will lead to gains for some resources and losses for other resources.
D) will not lead to any in the returns of any resources.
A) will lead to gains for all resources.
B) will lead to losses for all resources.
C) will lead to gains for some resources and losses for other resources.
D) will not lead to any in the returns of any resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If we assume only one factor (labor), we can demonstrate on the PPF the opportunity cost of producing less of one good and more of the other good by:
A) taking the sum of the marginal products of labor for the two goods.
B) taking the difference of the marginal products of labor for the two goods.
C) taking the ratio of the marginal products of labor for the two goods.
D) taking the average of the marginal products of labor for the two goods.
A) taking the sum of the marginal products of labor for the two goods.
B) taking the difference of the marginal products of labor for the two goods.
C) taking the ratio of the marginal products of labor for the two goods.
D) taking the average of the marginal products of labor for the two goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When there are diminishing marginal returns to factors of production, the PPF is:
A) a negatively sloped straight line.
B) bowed out from the origin.
C) caved in toward the origin.
D) a positively sloped straight line.
A) a negatively sloped straight line.
B) bowed out from the origin.
C) caved in toward the origin.
D) a positively sloped straight line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the two-sector (manufacturing and agriculture) specific-factors model, which resource(s) is(are) transferable between sectors?
A) land
B) labor
C) capital
D) labor and capital
A) land
B) labor
C) capital
D) labor and capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Because of the "law of diminishing marginal returns" to a factor, as more labor is employed, its marginal product:
A) rises.
B) falls.
C) stays constant.
D) rises disproportionally.
A) rises.
B) falls.
C) stays constant.
D) rises disproportionally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In a two-sector (manufacturing and agriculture) specific-factors model:
A) land, labor, and capital are transferable between sectors.
B) labor is transferable between sectors.
C) land is transferable between sectors.
D) capital is transferable between sectors.
A) land, labor, and capital are transferable between sectors.
B) labor is transferable between sectors.
C) land is transferable between sectors.
D) capital is transferable between sectors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Bolivia's government attempted to solve some of its problems with inequality of outcomes due to foreign investment in its natural gas resources by:
A) taxing international firms.
B) insisting that the firms pay higher wages to workers in the industry.
C) shutting down the firms in the wake of protests.
D) nationalizing the natural gas industry.
A) taxing international firms.
B) insisting that the firms pay higher wages to workers in the industry.
C) shutting down the firms in the wake of protests.
D) nationalizing the natural gas industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A "specific" factor of production is:
A) critical to the production of the good or service.
B) not transferable to other types of production and can only be used for the product in question.
C) a set quantity for each unit produced.
D) the opposite of a general factor, meaning it must fit within certain narrow quality parameters.
A) critical to the production of the good or service.
B) not transferable to other types of production and can only be used for the product in question.
C) a set quantity for each unit produced.
D) the opposite of a general factor, meaning it must fit within certain narrow quality parameters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In the two-sector specific-factors model, as more labor is added to a sector, we will see:
A) the total product of labor decrease.
B) the marginal product of labor increase.
C) the average product of labor remains constant.
D) the marginal product of labor decrease.
A) the total product of labor decrease.
B) the marginal product of labor increase.
C) the average product of labor remains constant.
D) the marginal product of labor decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Under free trade and comparative advantage, the home country:
A) will see only benefits for its resources.
B) will see only losses for its resources.
C) will see winners and losers within its economy.
D) will be convinced that trade is not beneficial.
A) will see only benefits for its resources.
B) will see only losses for its resources.
C) will see winners and losers within its economy.
D) will be convinced that trade is not beneficial.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Diminishing returns to labor means:
A) that the marginal product of labor declines as the amount of labor used in a sector increases.
B) that the marginal product of labor declines as the amount of capital combined with labor in a sector increases.
C) that the marginal product of labor declines as the amount of land combined with labor in a sector increases.
D) that the marginal product of capital declines as the amount of labor used in a sector increases.
A) that the marginal product of labor declines as the amount of labor used in a sector increases.
B) that the marginal product of labor declines as the amount of capital combined with labor in a sector increases.
C) that the marginal product of labor declines as the amount of land combined with labor in a sector increases.
D) that the marginal product of capital declines as the amount of labor used in a sector increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A microeconomic analysis shows that in a competitive economy in which labor is homogenous and mobile, the ratio of the prices of the products in equilibrium is inversely proportional to:
A) the ratio of the capital used in production.
B) the ratio of the marginal products of labor.
C) the geographical region of the country in which the factory is located.
D) the strength of bargaining power of the workers.
A) the ratio of the capital used in production.
B) the ratio of the marginal products of labor.
C) the geographical region of the country in which the factory is located.
D) the strength of bargaining power of the workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which term below describes a situation in which a nation engages in no trade and produces everything it consumes?
A) anarchy
B) oligarchy
C) autarky
D) embargo
A) anarchy
B) oligarchy
C) autarky
D) embargo

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
(Table: Home and Foreign Prices for Manufacturing and Agriculture) Consider the information provided about the price of agriculture and manufacturing goods in two countries (Home and Foreign). Under the condition of no trade, what is the relative price of manufacturing goods? 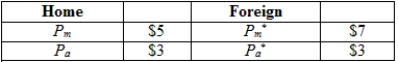
A) 1.66 of the agricultural good in Home
B) 0.40 of the agricultural good in Foreign
C) 0.60 of the agricultural good in Home
D) 0.40 of the agricultural good in Foreign and 0.60 of the agricultural good in Home

A) 1.66 of the agricultural good in Home
B) 0.40 of the agricultural good in Foreign
C) 0.60 of the agricultural good in Home
D) 0.40 of the agricultural good in Foreign and 0.60 of the agricultural good in Home

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In an economy in which labor is mobile and homogeneous, the wages between industries will be:
A) equal.
B) very unequal.
C) less in the export industry.
D) unequal because in some firms the management is fairer to its workers.
A) equal.
B) very unequal.
C) less in the export industry.
D) unequal because in some firms the management is fairer to its workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In equilibrium, with diminishing marginal products, the slope of the PPF is equal to:
A) the ratio of prices for the products.
B) the marginal product of labor.
C) the marginal product of capital.
D) the ratio of prices to the marginal product of labor.
A) the ratio of prices for the products.
B) the marginal product of labor.
C) the marginal product of capital.
D) the ratio of prices to the marginal product of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Suppose that wages in the agricultural and manufacturing sectors are $10 and $20 per hour, respectively, and that the prices of both the agricultural and manufactured good are both $50 per unit. What is the marginal productivity of labor in the manufacturing sector?
A) $1,000
B) 0.4 units per hour
C) 2.5 units per hour
D) $0.40
A) $1,000
B) 0.4 units per hour
C) 2.5 units per hour
D) $0.40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which term below describes a situation in which a nation prohibits trade with one or more trading partner nations?
A) anarchy
B) oligarchy
C) autarky
D) embargo
A) anarchy
B) oligarchy
C) autarky
D) embargo

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Suppose that the home country in the two-sector (manufacturing and agriculture) specific-factors model has a comparative advantage in manufacturing output. What will happen to the relative price of manufactured output when trade occurs?
A) It will fall.
B) It will rise.
C) It will not change.
D) It will first rise, then fall.
A) It will fall.
B) It will rise.
C) It will not change.
D) It will first rise, then fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
(Table: Home and Foreign Prices for Manufacturing and Agriculture) Consider the information provided about the price of agriculture and manufacturing goods in two countries (Home and Foreign). If the two countries open their markets for trade, then: 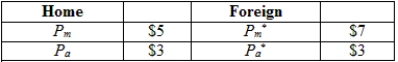
A) Home has the comparative advantage in agriculture.
B) Home has the comparative advantage in manufacturing.
C) Foreign has absolute advantage in both goods.
D) Foreign has a comparative advantage in manufacturing.

A) Home has the comparative advantage in agriculture.
B) Home has the comparative advantage in manufacturing.
C) Foreign has absolute advantage in both goods.
D) Foreign has a comparative advantage in manufacturing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
(Table: Home and Foreign Prices for Manufacturing and Agriculture) Consider the information provided about the price of agriculture and manufacturing goods in two countries (Home and Foreign). Under free trade conditions, Foreign will export ________ goods and Home will export ___________ goods. 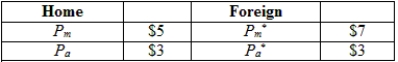
A) manufactured; agricultural
B) manufactured; manufactured
C) agricultural; manufactured
D) agricultural, agricultural

A) manufactured; agricultural
B) manufactured; manufactured
C) agricultural; manufactured
D) agricultural, agricultural

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If a nation begins to trade, it will be able to sell (export) the product for which its own relative price is:
A) lower than other nations.
B) higher than other nations.
C) the same as other nations.
D) less than 10% of the value of other nations.
A) lower than other nations.
B) higher than other nations.
C) the same as other nations.
D) less than 10% of the value of other nations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
As a nation begins to export, its own relative price of exported goods will ______, and as it imports other goods, the relative price of those will ______ , thus ___________ its standard of living.
A) fall; rise; lowering
B) rise; fall; lowering
C) rise; fall; raising
D) fall; rise; raising
A) fall; rise; lowering
B) rise; fall; lowering
C) rise; fall; raising
D) fall; rise; raising

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If a nation begins to trade, it will wish to buy (import) the product for which its own relative price is:
A) lower than other nations.
B) higher than other nations.
C) the same as other nations.
D) less than 10% of the value of other nations.
A) lower than other nations.
B) higher than other nations.
C) the same as other nations.
D) less than 10% of the value of other nations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Consider the following information for a hypothetical economy: If the price per bicycle is $20 and the wage per worker is $40, then what is the marginal product of labor?
A) 20 bicycles
B) 2 bicycles
C) 0.5 bicycle
D) 1 bicycle
A) 20 bicycles
B) 2 bicycles
C) 0.5 bicycle
D) 1 bicycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Suppose that the wage is $20 per hour in a two-sector (manufacturing and agriculture) specific-factors model. Currently, the prices of manufactured and agricultural outputs are $5 and $1, respectively; the marginal product of labor in the manufactured sector is 6 units per hour; and the marginal product of labor in the agricultural sector is 10 units per hour. What will happen to the distribution of labor between the two sectors?
A) Nothing will happen. The current allocation of labor between the two sectors is ideal.
B) The manufacturing sector will demand more labor, and the agricultural sector will demand less labor at the current wage.
C) The agricultural sector will demand more labor, and the manufacturing sector will demand less labor at the current wage.
D) Both the agricultural and the manufacturing sector will demand more labor at the current wage.
A) Nothing will happen. The current allocation of labor between the two sectors is ideal.
B) The manufacturing sector will demand more labor, and the agricultural sector will demand less labor at the current wage.
C) The agricultural sector will demand more labor, and the manufacturing sector will demand less labor at the current wage.
D) Both the agricultural and the manufacturing sector will demand more labor at the current wage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If the price per bushel of wheat is $3 and the marginal product of labor is four bushels per hour, then what is the hourly wage?
A) $0.75
B) $1.33
C) $12
D) four bushels
A) $0.75
B) $1.33
C) $12
D) four bushels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In the two-sector (manufacturing and agriculture) specific-factors model, the slope of the production possibilities curve equals:
A) the ratio of marginal products of capital in the two sectors.
B) the ratio of marginal products of labor utilized in the two sectors.
C) the ratio of outputs produced in the two sectors.
D) the ratio of land and capital utilized in the two sectors.
A) the ratio of marginal products of capital in the two sectors.
B) the ratio of marginal products of labor utilized in the two sectors.
C) the ratio of outputs produced in the two sectors.
D) the ratio of land and capital utilized in the two sectors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
As a nation opens up to free trade:
A) the relative prices of the traded products do not change.
B) the absolute prices measured in the domestic currency do not change.
C) the relative price rises in the export sector and falls in the import sector.
D) the export sector experiences a decline in demand.
A) the relative prices of the traded products do not change.
B) the absolute prices measured in the domestic currency do not change.
C) the relative price rises in the export sector and falls in the import sector.
D) the export sector experiences a decline in demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When there are diminishing returns to labor, the production possibility frontier is _______ sloping and ________.
A) downward; convex (bowed in toward the origin)
B) downward; concave (bowed out from the origin)
C) upward; concave (bowed out from the origin)
D) upward; convex (bowed in toward the origin)
A) downward; convex (bowed in toward the origin)
B) downward; concave (bowed out from the origin)
C) upward; concave (bowed out from the origin)
D) upward; convex (bowed in toward the origin)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Suppose that a country has a comparative advantage in agricultural products. When trade occurs, the nominal and real prices of the agricultural good will:
A) both fall.
B) both rise.
C) both remain constant.
D) The nominal price will fall and the real price will rise.
A) both fall.
B) both rise.
C) both remain constant.
D) The nominal price will fall and the real price will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A change in the relative price of one good versus another will cause a change in marginal product and the allocation of labor resources. When the price of good A increases relative to the price of good B and labor is mobile, the equilibrium real wage in industry A will:
A) rise in terms of good B.
B) fall in terms of good B.
C) remain the same.
D) rise in terms of good A.
A) rise in terms of good B.
B) fall in terms of good B.
C) remain the same.
D) rise in terms of good A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
An increase in demand for resources specific to an industry will cause their earnings to _____ because those resources cannot be released from other industries.
A) fall
B) rise by the same rate as for all resources
C) rise disproportionally
D) fall disproportionally
A) fall
B) rise by the same rate as for all resources
C) rise disproportionally
D) fall disproportionally

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The absence of trade is known as:
A) aristocracy.
B) oligarchy.
C) autarky.
D) embargo.
A) aristocracy.
B) oligarchy.
C) autarky.
D) embargo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In the two-sector (manufacturing and agriculture) specific-factors model, an increase in the price of the manufactured good will cause:
A) an increase in the wage in the manufacturing sector.
B) capital to move from the agricultural to the manufacturing sector.
C) land to move from the manufacturing to the agricultural sector.
D) a decrease in the wage in the agricultural sector.
A) an increase in the wage in the manufacturing sector.
B) capital to move from the agricultural to the manufacturing sector.
C) land to move from the manufacturing to the agricultural sector.
D) a decrease in the wage in the agricultural sector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
As a nation opens trade, the relative prices of products it imports will __________ and the relative prices of products it exports will ___________.
A) rise; fall
B) fall; rise
C) remain constant; fall
D) rise; remain constant
A) rise; fall
B) fall; rise
C) remain constant; fall
D) rise; remain constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
From 1807 to 1809, a trade embargo imposed by the United States resulted in:
A) a rise in real GDP, as residents turned toward domestic production.
B) a fall in real GDP of about 5%.
C) a lower unemployment rate in the United States.
D) a rise in the U.S. standard of living from lower prices as a result of lowered demand.
A) a rise in real GDP, as residents turned toward domestic production.
B) a fall in real GDP of about 5%.
C) a lower unemployment rate in the United States.
D) a rise in the U.S. standard of living from lower prices as a result of lowered demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The term real wages refers to:
A) a worker's hourly wage in dollars.
B) the purchasing power of a worker's wage.
C) the productivity of a worker's labor.
D) the productivity of a worker's capital.
A) a worker's hourly wage in dollars.
B) the purchasing power of a worker's wage.
C) the productivity of a worker's labor.
D) the productivity of a worker's capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If the wage rate in the agriculture sector is lower than the manufacturing sector, then labor will migrate to the manufacturing sector. This will cause:
A) both the wage and the marginal product of labor in the manufacturing sector to decrease.
B) both the wage and the marginal product of labor in the agriculture sector to decrease.
C) the nation to import more goods.
D) There will be no effect on either sector.
A) both the wage and the marginal product of labor in the manufacturing sector to decrease.
B) both the wage and the marginal product of labor in the agriculture sector to decrease.
C) the nation to import more goods.
D) There will be no effect on either sector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
When Japan opened its borders to trade with the United States in 1854:
A) the prices of Japanese exports to the United States rose.
B) the terms of trade for Japan deteriorated.
C) there were no gains from trade for the United States.
D) the prices of Japanese imports from the United States rose.
A) the prices of Japanese exports to the United States rose.
B) the terms of trade for Japan deteriorated.
C) there were no gains from trade for the United States.
D) the prices of Japanese imports from the United States rose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Many examples in this chapter indicate that there are substantial __________ as a result of competition and trade.
A) environmental disasters
B) labor shortages and strikes
C) gains to the economy
D) losses to consumers and workers
A) environmental disasters
B) labor shortages and strikes
C) gains to the economy
D) losses to consumers and workers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In the two-sector (manufacturing and agriculture) specific-factors model, an increase in the price of the manufactured good will cause:
A) a decrease in nominal wages in both the agricultural and manufacturing sectors.
B) an increase in real wages in both the agricultural and manufacturing sectors.
C) an increase in both nominal and real wages in both the agricultural and manufacturing sectors.
D) an increase in nominal wages in both the agricultural and manufacturing sectors.
A) a decrease in nominal wages in both the agricultural and manufacturing sectors.
B) an increase in real wages in both the agricultural and manufacturing sectors.
C) an increase in both nominal and real wages in both the agricultural and manufacturing sectors.
D) an increase in nominal wages in both the agricultural and manufacturing sectors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Suppose that the home country in the two-sector (manufacturing and agriculture) specific-factors model has a comparative advantage in agricultural output. Will workers be better or worse off following the opening of trade with other countries?
A) Workers will be better off because the nominal wage increases.
B) Workers will be worse off because the nominal wage decreases.
C) Workers may be better off or worse off because the real wage in terms of the agricultural good rises and the real wage in terms of the manufactured good falls.
D) Workers may be better off or worse off because the real wage in terms of the agricultural good falls and the real wage in terms of the manufactured good rises.
A) Workers will be better off because the nominal wage increases.
B) Workers will be worse off because the nominal wage decreases.
C) Workers may be better off or worse off because the real wage in terms of the agricultural good rises and the real wage in terms of the manufactured good falls.
D) Workers may be better off or worse off because the real wage in terms of the agricultural good falls and the real wage in terms of the manufactured good rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
As a nation increases its production of exports, demand for specific or fixed factors (such as capital and land) used in the exporting sector will:
A) rise.
B) fall.
C) remain the same.
D) decrease but only slightly.
A) rise.
B) fall.
C) remain the same.
D) decrease but only slightly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
As a nation increases its production of exports, demand for all factors of production used in the exporting sector will:
A) rise.
B) fall.
C) remain the same.
D) decrease but only slightly.
A) rise.
B) fall.
C) remain the same.
D) decrease but only slightly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
As relative prices in various industries change due to trade, the marginal product of the mobile resources used in the expanding industry __________, and the marginal product of the mobile resources used in the contracting industry __________.
A) rises; falls
B) falls; rises
C) remains the same; remains the same
D) changes by exactly the same percentage; changes by exactly the same percentage
A) rises; falls
B) falls; rises
C) remains the same; remains the same
D) changes by exactly the same percentage; changes by exactly the same percentage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If the relative price of one product rises and labor is mobile, then:
A) the percentage increase in the equilibrium real wage will be exactly the same as the percentage increase in the relative price.
B) the percentage increase in the equilibrium real wage will be lower than the percentage increase in the relative price.
C) the percentage increase in the equilibrium real wage will be higher than the percentage increase in the relative price.
D) the equilibrium real wage will not change.
A) the percentage increase in the equilibrium real wage will be exactly the same as the percentage increase in the relative price.
B) the percentage increase in the equilibrium real wage will be lower than the percentage increase in the relative price.
C) the percentage increase in the equilibrium real wage will be higher than the percentage increase in the relative price.
D) the equilibrium real wage will not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In a competitive market, what happens to the equilibrium wage?
A) It differs among industries.
B) It is equal to the marginal product of the labor..
C) It is determined by the intersection of curves representing the demand for and the supply of imports.
D) It is the same in all industries.
A) It differs among industries.
B) It is equal to the marginal product of the labor..
C) It is determined by the intersection of curves representing the demand for and the supply of imports.
D) It is the same in all industries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In the two-sector (manufacturing and agriculture) specific-factors model, suppose that a country has a comparative advantage in manufacturing output. Will workers be better or worse off following the opening of trade with other countries?
A) Workers will be better off because the nominal wage increases.
B) Workers will be better off because both nominal and real wages increase.
C) Workers may be better off or worse off because the real wage in terms of the agricultural good rises and the real wage in terms of the manufactured good falls.
D) Workers may be better off or worse off because the real wage in terms of the agricultural good falls and the real wage in terms of the manufactured good rises.
A) Workers will be better off because the nominal wage increases.
B) Workers will be better off because both nominal and real wages increase.
C) Workers may be better off or worse off because the real wage in terms of the agricultural good rises and the real wage in terms of the manufactured good falls.
D) Workers may be better off or worse off because the real wage in terms of the agricultural good falls and the real wage in terms of the manufactured good rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
As relative prices in various industries change due to trade, the marginal product of fixed resources used in the expanding industry __________, and the marginal product of fixed resources used in the contracting industry __________.
A) rises; falls
B) remains the same; remains the same
C) changes by exactly the same percentage; changes by exactly the same percentage
D) falls; rises
A) rises; falls
B) remains the same; remains the same
C) changes by exactly the same percentage; changes by exactly the same percentage
D) falls; rises

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
When the demand for products competing with imports falls, demand for the specific factors used in their production falls and:
A) the relative prices (earnings) of these specific factors will fall disproportionally.
B) the relative prices (earnings) of these specific factors will rise disproportionally.
C) the relative prices (earnings) of these specific factors will fall by the same rate as for all resources.
D) the employment of these specific factors will rise disproportionally.
A) the relative prices (earnings) of these specific factors will fall disproportionally.
B) the relative prices (earnings) of these specific factors will rise disproportionally.
C) the relative prices (earnings) of these specific factors will fall by the same rate as for all resources.
D) the employment of these specific factors will rise disproportionally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In an industrialized country, the amount of labor employed in the agriculture sector is:
A) larger than labor employed in the manufacturing sector.
B) larger than labor employed in the service sector.
C) lower than labor employed in either the manufacturing or the service sector.
D) is about the same as labor employed in the service sector.
A) larger than labor employed in the manufacturing sector.
B) larger than labor employed in the service sector.
C) lower than labor employed in either the manufacturing or the service sector.
D) is about the same as labor employed in the service sector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In the United States, which workers displaced by trade between 2011 and 2014 were more likely to be reemployed?
A) those in the service industries
B) those in the manufacturing industries
C) Evidence indicates that there is no difference across industries.
D) There is no available evidence on this topic.
A) those in the service industries
B) those in the manufacturing industries
C) Evidence indicates that there is no difference across industries.
D) There is no available evidence on this topic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In the two-sector (manufacturing and agriculture) specific-factors model, an increase in the price of the agricultural good will cause:
A) a decrease in nominal wages in both the agricultural and manufacturing sectors.
B) an increase in nominal wages in both the agricultural and manufacturing sectors.
C) an increase in both nominal and real wages in both the agricultural and manufacturing sectors.
D) an increase in the nominal wage in the agricultural sector and a decrease in nominal wage in the manufacturing sector.
A) a decrease in nominal wages in both the agricultural and manufacturing sectors.
B) an increase in nominal wages in both the agricultural and manufacturing sectors.
C) an increase in both nominal and real wages in both the agricultural and manufacturing sectors.
D) an increase in the nominal wage in the agricultural sector and a decrease in nominal wage in the manufacturing sector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Economists believe that layoffs and wage declines due to increased imports:
A) are the most critical problem facing the economy today.
B) may be caused by factors such as changing technology and changing demands for workers rather than by increased imports.
C) should be addressed by the WTO, which usually ignores such issues.
D) are so minor that we may safely ignore them.
A) are the most critical problem facing the economy today.
B) may be caused by factors such as changing technology and changing demands for workers rather than by increased imports.
C) should be addressed by the WTO, which usually ignores such issues.
D) are so minor that we may safely ignore them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the people losing jobs in the manufacturing sector between 2011 and 2014 were:
A) more likely to find higher paying jobs than service sector workers.
B) less likely to find higher paying jobs than service sector workers.
C) more likely to work in a foreign country.
D) more likely to be reemployed than those in the service sector.
A) more likely to find higher paying jobs than service sector workers.
B) less likely to find higher paying jobs than service sector workers.
C) more likely to work in a foreign country.
D) more likely to be reemployed than those in the service sector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which federal government program provides additional benefits to workers who are laid off because of import competition?
A) Trade Unemployment Insurance
B) Import Unemployment Insurance
C) Trade Adjustment Assistance
D) Unemployment Insurance
A) Trade Unemployment Insurance
B) Import Unemployment Insurance
C) Trade Adjustment Assistance
D) Unemployment Insurance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The Trade Adjustment Assistance program is:
A) an unemployment insurance program regardless of the reason for job loss.
B) an unemployment insurance program that pays for job loss due to import competition.
C) a subsidy program for the producers.
D) a tax on importers of foreign goods.
A) an unemployment insurance program regardless of the reason for job loss.
B) an unemployment insurance program that pays for job loss due to import competition.
C) a subsidy program for the producers.
D) a tax on importers of foreign goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The United States maintains a program to help workers affected by trade relocation. This is called:
A) the North American Free Trade Alliance.
B) the Worker Retraining and Education Act.
C) Trade Adjustment Assistance.
D) Supplemental Security Income (SSI).
A) the North American Free Trade Alliance.
B) the Worker Retraining and Education Act.
C) Trade Adjustment Assistance.
D) Supplemental Security Income (SSI).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Suppose that the home country in the two-sector (manufacturing and agriculture) specific-factors model has a comparative advantage in manufactured output. Will workers be better or worse off following the opening of trade with other countries?
A) Workers will be better off because the nominal wage increases.
B) Workers will be worse off because the nominal wage decreases.
C) Workers may be better off or worse off because the real wage in terms of the agricultural good rises and the real wage in terms of the manufactured good falls.
D) Workers may be better off or worse off because the real wage in terms of the agricultural good falls and the real wage in terms of the manufactured good rises.
A) Workers will be better off because the nominal wage increases.
B) Workers will be worse off because the nominal wage decreases.
C) Workers may be better off or worse off because the real wage in terms of the agricultural good rises and the real wage in terms of the manufactured good falls.
D) Workers may be better off or worse off because the real wage in terms of the agricultural good falls and the real wage in terms of the manufactured good rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which statement below is correct?
A) Between 2011 and 2014, there were more manufacturing workers displaced by trade than service workers displaced by trade.
B) Between 2011 and 2014, younger workers displaced by trade had larger losses than older workers displaced by trade.
C) Between 2011 and 2014, about 60% of manufacturing and service workers displaced by trade were reemployed.
D) Between 2011 and 2014, most service workers displaced by trade were reemployed in higher paying jobs.
A) Between 2011 and 2014, there were more manufacturing workers displaced by trade than service workers displaced by trade.
B) Between 2011 and 2014, younger workers displaced by trade had larger losses than older workers displaced by trade.
C) Between 2011 and 2014, about 60% of manufacturing and service workers displaced by trade were reemployed.
D) Between 2011 and 2014, most service workers displaced by trade were reemployed in higher paying jobs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If we consider the two-sector (manufacturing and agriculture) specific-factors model, the effect of an increase in exports on the real wages of workers:
A) is inconclusive because some goods' prices will be higher compared with the wage, and some will be lower.
B) absolutely increases the buying power of the real wage.
C) absolutely decreases the buying power of the real wage.
D) will encourage foreign workers to emigrate to the United States.
A) is inconclusive because some goods' prices will be higher compared with the wage, and some will be lower.
B) absolutely increases the buying power of the real wage.
C) absolutely decreases the buying power of the real wage.
D) will encourage foreign workers to emigrate to the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Suppose that labor is mobile between sectors but that capital and land are specific. Then labor is more likely to benefit from trade when:
A) it spends a large amount of its income on the imported good.
B) it spends a large amount of its income on the exported good.
C) wages do not change much in percentage terms.
D) wages increase only in industries competing with imports.
A) it spends a large amount of its income on the imported good.
B) it spends a large amount of its income on the exported good.
C) wages do not change much in percentage terms.
D) wages increase only in industries competing with imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
(Table: Production and Prices in Two Industries) Using the information from the table, we can expect which of the following to happen in the economy? 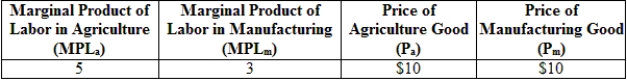
A) Labor will migrate from the agriculture to the manufacturing sector.
B) Labor will migrate from the manufacturing to the agriculture sector.
C) The marginal product of labor in the agriculture sector will increase.
D) The marginal product of labor in the manufacturing sector will decrease.

A) Labor will migrate from the agriculture to the manufacturing sector.
B) Labor will migrate from the manufacturing to the agriculture sector.
C) The marginal product of labor in the agriculture sector will increase.
D) The marginal product of labor in the manufacturing sector will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
If trade causes some workers to be laid off, most economists conclude that:
A) all other workers will be better off because their wages will rise.
B) we should not allow imports to take U.S. jobs.
C) we should expect wages to fall.
D) most of the workers laid off will be reemployed.
A) all other workers will be better off because their wages will rise.
B) we should not allow imports to take U.S. jobs.
C) we should expect wages to fall.
D) most of the workers laid off will be reemployed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following best describes changes in U.S. manufacturing employment between 1973 and 2014?
A) Manufacturing employment fell, but manufacturing employment as a share of total U.S. employment rose.
B) Manufacturing employment rose, but manufacturing employment as a share of total U.S. employment fell.
C) Both manufacturing employment and manufacturing employment as a share of total U.S. employment fell.
D) Both manufacturing employment and manufacturing employment as a share of total U.S. employment rose.
A) Manufacturing employment fell, but manufacturing employment as a share of total U.S. employment rose.
B) Manufacturing employment rose, but manufacturing employment as a share of total U.S. employment fell.
C) Both manufacturing employment and manufacturing employment as a share of total U.S. employment fell.
D) Both manufacturing employment and manufacturing employment as a share of total U.S. employment rose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
(Table: Production and Prices in Two Industries) According to the information provided in the table, the wage rate in the agriculture sector is: 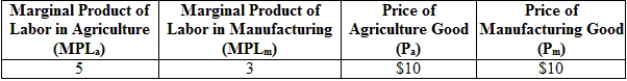
A) $50.
B) $15.
C) $30.
D) $10.

A) $50.
B) $15.
C) $30.
D) $10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If trade causes shifts in production so that some workers are laid off, most economists conclude:
A) that the nation should extend unemployment benefits for a longer period.
B) that the situation is usually temporary because there are jobs created in export industries.
C) that we should expect wages to fall and therefore should not allow imports to take U.S. jobs.
D) that all workers will be better off because overall the equilibrium wage will rise.
A) that the nation should extend unemployment benefits for a longer period.
B) that the situation is usually temporary because there are jobs created in export industries.
C) that we should expect wages to fall and therefore should not allow imports to take U.S. jobs.
D) that all workers will be better off because overall the equilibrium wage will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
(Table: Production and Prices in Two Industries) According to the information provided in the table, the wage rate in the manufacturing sector is: 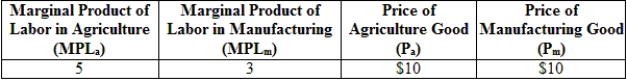
A) $50.
B) $10.
C) $100.
D) $30.

A) $50.
B) $10.
C) $100.
D) $30.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following is NOT a possible explanation for wage differences across sectors?
A) Demand for products affects demand for resources.
B) Changes in technology affect demand for resources.
C) The government mandates a $15 per hour minimum wage for service workers.
D) Import competition in a sector leads to lower wages.
A) Demand for products affects demand for resources.
B) Changes in technology affect demand for resources.
C) The government mandates a $15 per hour minimum wage for service workers.
D) Import competition in a sector leads to lower wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
(Table: Production and Prices in Two Industries) According to the information provided in the table, if the price of the agriculture good decreases to $5, then: 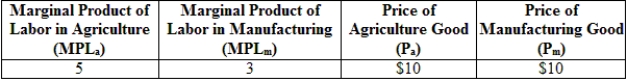
A) wages in the manufacturing sector will be $25.
B) the wage rate in the agriculture sector will be $25.
C) the marginal product of both sectors will decline.
D) more agriculture goods should be imported.

A) wages in the manufacturing sector will be $25.
B) the wage rate in the agriculture sector will be $25.
C) the marginal product of both sectors will decline.
D) more agriculture goods should be imported.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



