Deck 8: Skating to Where the Puck Is Going: Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/304
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Skating to Where the Puck Is Going: Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand
1
The short run is a period of time when
A) the economy is a full employment.
B) all prices have adjusted to equilibrium prices.
C) Adam Smith's invisible hand works well.
D) the economy is at potential GDP.
E) none of the above are true.
A) the economy is a full employment.
B) all prices have adjusted to equilibrium prices.
C) Adam Smith's invisible hand works well.
D) the economy is at potential GDP.
E) none of the above are true.
none of the above are true.
2
Which macroeconomic performance targets are not represented by long-run aggregate supply?
A) economic growth and stable prices
B) economic growth and full employment
C) economic growth and potential GDP
D) full employment and potential GDP
E) stable prices and potential GDP
A) economic growth and stable prices
B) economic growth and full employment
C) economic growth and potential GDP
D) full employment and potential GDP
E) stable prices and potential GDP
economic growth and stable prices
3
Unemployment is represented by points 1 inside the macro PPF.
2 outside the macro PPF.
3 on the macro PPF.
4 to the left of LAS.
5 to the right of LAS.
6 on LAS.
A) 1 and 4
B) 1 and 5
C) 2 and 4
D) 2 and 5
E) 3 and 6
2 outside the macro PPF.
3 on the macro PPF.
4 to the left of LAS.
5 to the right of LAS.
6 on LAS.
A) 1 and 4
B) 1 and 5
C) 2 and 4
D) 2 and 5
E) 3 and 6
1 and 4
4
Figure 6.3.1 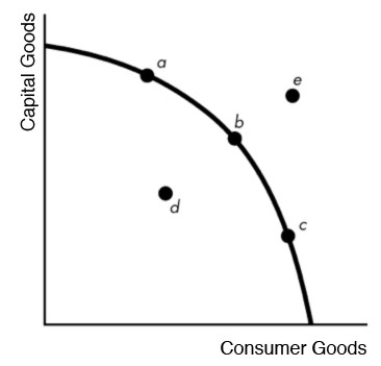
Look at the macro production possibilities frontier in Figure 6.3.1. Which point(s) represent unemployed inputs?
A) a only
B) b only
C) a, b, c
D) d only
E) e only

Look at the macro production possibilities frontier in Figure 6.3.1. Which point(s) represent unemployed inputs?
A) a only
B) b only
C) a, b, c
D) d only
E) e only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Long-run aggregate supply represents the macroeconomic performance targets of
A) economic growth and stable prices.
B) economic growth and full employment.
C) economic growth and potential GDP.
D) full employment and potential GDP.
E) stable prices and potential GDP.
A) economic growth and stable prices.
B) economic growth and full employment.
C) economic growth and potential GDP.
D) full employment and potential GDP.
E) stable prices and potential GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The long run is a period of time
A) when some input prices do not change.
B) when all prices have adjusted to equilibrium.
C) when the inflation rate is zero.
D) longer than 1 year.
E) longer than 10 years.
A) when some input prices do not change.
B) when all prices have adjusted to equilibrium.
C) when the inflation rate is zero.
D) longer than 1 year.
E) longer than 10 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The short run is a period of time
A) when all input prices have adjusted to clear markets.
B) when all input and output prices have adjusted to equilibrium prices.
C) when some input prices do not change.
D) shorter than 10 years.
E) shorter than 1 year.
A) when all input prices have adjusted to clear markets.
B) when all input and output prices have adjusted to equilibrium prices.
C) when some input prices do not change.
D) shorter than 10 years.
E) shorter than 1 year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Figure 6.3.1 
Look at the macro production possibilities frontier in Figure 6.3.1. Which point(s) represent real GDP greater than potential GDP?
A) a only
B) b only
C) a, b, c
D) d only
E) e only

Look at the macro production possibilities frontier in Figure 6.3.1. Which point(s) represent real GDP greater than potential GDP?
A) a only
B) b only
C) a, b, c
D) d only
E) e only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The long run is a period of time when
A) the economy is a full employment.
B) all prices have adjusted to equilibrium prices.
C) Adam Smith's invisible hand works well.
D) the economy is at potential GDP.
E) all of the above are true.
A) the economy is a full employment.
B) all prices have adjusted to equilibrium prices.
C) Adam Smith's invisible hand works well.
D) the economy is at potential GDP.
E) all of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The long run is a period of time
A) when the economy is at potential GDP.
B) when some input prices do not change.
C) when the inflation rate is zero.
D) longer than 1 year.
E) longer than 10 years.
A) when the economy is at potential GDP.
B) when some input prices do not change.
C) when the inflation rate is zero.
D) longer than 1 year.
E) longer than 10 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
On the graph of the macro production possibilities frontier (PPF), inputs
A) are on the horizontal axis and outputs are on the vertical axis.
B) are on the vertical axis and outputs are on the horizontal axis.
C) do not appear.
D) increase as you move down along the PPF.
E) increase as you move up along the PPF.
A) are on the horizontal axis and outputs are on the vertical axis.
B) are on the vertical axis and outputs are on the horizontal axis.
C) do not appear.
D) increase as you move down along the PPF.
E) increase as you move up along the PPF.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Figure 6.3.1 
Look at the macro production possibilities frontier in Figure 6.3.1. Which point(s) represent fully employed inputs?
A) a only
B) b only
C) a, b, c
D) d only
E) e only

Look at the macro production possibilities frontier in Figure 6.3.1. Which point(s) represent fully employed inputs?
A) a only
B) b only
C) a, b, c
D) d only
E) e only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The short run is a period of time
A) when all input prices have adjusted to clear markets.
B) when all prices have adjusted to equilibrium prices.
C) when some prices have not adjusted to clear markets.
D) shorter than 10 years.
E) shorter than 1 year.
A) when all input prices have adjusted to clear markets.
B) when all prices have adjusted to equilibrium prices.
C) when some prices have not adjusted to clear markets.
D) shorter than 10 years.
E) shorter than 1 year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Figure 6.3.1 
Look at the macro production possibilities frontier in Figure 6.3.1. Which point(s) represent real GDP less than potential GDP?
A) a only
B) b only
C) a, b, c
D) d only
E) e only

Look at the macro production possibilities frontier in Figure 6.3.1. Which point(s) represent real GDP less than potential GDP?
A) a only
B) b only
C) a, b, c
D) d only
E) e only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The long-run aggregate supply curve (LAS) is vertical because
A) the quantity of potential real GDP does not change when the price level changes.
B) real GDP can never be greater than potential GDP.
C) businesses do not have any incentive to produce more than potential GDP.
D) the price level does not change when the quantity of potential real GDP changes.
E) potential GDP never changes.
A) the quantity of potential real GDP does not change when the price level changes.
B) real GDP can never be greater than potential GDP.
C) businesses do not have any incentive to produce more than potential GDP.
D) the price level does not change when the quantity of potential real GDP changes.
E) potential GDP never changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Full employment is represented by points 1 inside the macro PPF.
2 outside the macro PPF.
3 on the macro PPF.
4 to the left of LAS.
5 to the right of LAS.
6 on LAS.
A) 1 and 4
B) 1 and 5
C) 2 and 4
D) 2 and 5
E) 3 and 6
2 outside the macro PPF.
3 on the macro PPF.
4 to the left of LAS.
5 to the right of LAS.
6 on LAS.
A) 1 and 4
B) 1 and 5
C) 2 and 4
D) 2 and 5
E) 3 and 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The targets for a macro economy that performs well are
A) stable prices.
B) full employment.
C) steady growth in living standards.
D) all of the above.
E) none of the above.
A) stable prices.
B) full employment.
C) steady growth in living standards.
D) all of the above.
E) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Potential GDP is represented by points 1 inside the macro PPF.
2 outside the macro PPF.
3 on the macro PPF.
4 to the left of LAS.
5 to the right of LAS.
6 on LAS.
A) 1 and 4
B) 1 and 5
C) 2 and 4
D) 2 and 5
E) 3 and 6
2 outside the macro PPF.
3 on the macro PPF.
4 to the left of LAS.
5 to the right of LAS.
6 on LAS.
A) 1 and 4
B) 1 and 5
C) 2 and 4
D) 2 and 5
E) 3 and 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Figure 6.3.1 
Look at the macro production possibilities frontier in Figure 6.3.1. Which point(s) correspond to points on the long-run aggregate supply (LAS) curve?
A) a only
B) b only
C) a, b, c
D) d only
E) e only

Look at the macro production possibilities frontier in Figure 6.3.1. Which point(s) correspond to points on the long-run aggregate supply (LAS) curve?
A) a only
B) b only
C) a, b, c
D) d only
E) e only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Unemployment is represented by points 1 inside the macro PPF.
2 outside the macro PPF.
3 to the left of LAS.
4 to the right of LAS.
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4
E) 1 only
2 outside the macro PPF.
3 to the left of LAS.
4 to the right of LAS.
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4
E) 1 only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Long-run aggregate supply represents the macroeconomic performance targets of full employment and potential GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The long run is a period of time when the inflation rate equals zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The long run is a period of time when all prices have adjusted to equilibrium prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Long-run aggregate supply represents the macroeconomic performance targets of economic growth and full employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The long run is a period of time longer than 1 year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The short run is a period of time when all prices have adjusted to equilibrium prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Inputs do not appear on the graph of the macro production possibilities frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Unemployment is represented by points on the macro production possibilities frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Long-run aggregate supply represents the macroeconomic performance targets of full employment and stable prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The long run is a period of time when the price level equals 100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Inputs decrease as you move down along the macro production possibilities frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The short run is a period of time when all prices have adjusted to equilibrium prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The long run is a period of time when some input prices do not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The short run is a period of time when some input prices do not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Inputs increase as you move down along the macro production possibilities frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Long-run aggregate supply represents the macroeconomic performance targets of potential GDP and stable prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Long-run aggregate supply represents the macroeconomic performance targets of economic growth and stable prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The short run is a period of time shorter than 10 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The long run is a period of time longer than 10 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The short run is a period of time shorter than 1 year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
According to the law of short-run aggregate supply, as the price level rises, short-run aggregate
A) quantity supplied is not affected.
B) supply decreases.
C) quantity supplied decreases.
D) supply increases.
E) quantity supplied increases.
A) quantity supplied is not affected.
B) supply decreases.
C) quantity supplied decreases.
D) supply increases.
E) quantity supplied increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Full employment is represented by points on the macro production possibilities frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Higher world oil prices
A) decrease short-run aggregate supply.
B) decrease aggregate demand.
C) increase aggregate quantity demanded.
D) increase short-run aggregate supply.
E) increase aggregate quantity supplied.
A) decrease short-run aggregate supply.
B) decrease aggregate demand.
C) increase aggregate quantity demanded.
D) increase short-run aggregate supply.
E) increase aggregate quantity supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Higher world oil prices
A) shift both SAS and LAS leftward.
B) shift SAS leftward only.
C) shift both SAS and LAS rightward.
D) shift SAS rightward only.
E) increase aggregate quantity supplied.
A) shift both SAS and LAS leftward.
B) shift SAS leftward only.
C) shift both SAS and LAS rightward.
D) shift SAS rightward only.
E) increase aggregate quantity supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Government investments to improve the quality of public infrastructure like roads, transit and sewers
A) decreases both long-run and short-run aggregate supply.
B) increases aggregate quantity supplied.
C) increases only long-run aggregate supply.
D) increases both long-run and short-run aggregate supply.
E) decreases aggregate quantity supplied.
A) decreases both long-run and short-run aggregate supply.
B) increases aggregate quantity supplied.
C) increases only long-run aggregate supply.
D) increases both long-run and short-run aggregate supply.
E) decreases aggregate quantity supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which is a supply plan with existing inputs?
A) a couple's decision to have more children.
B) BlackBerry's decision to fund research and development for improved Blackberries.
C) a restaurant's decision to extend closing time from 10 pm to midnight.
D) a high school student's choice to go to college.
E) Rogers Wireless training new employees to work at its outlets in Saskatoon.
A) a couple's decision to have more children.
B) BlackBerry's decision to fund research and development for improved Blackberries.
C) a restaurant's decision to extend closing time from 10 pm to midnight.
D) a high school student's choice to go to college.
E) Rogers Wireless training new employees to work at its outlets in Saskatoon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Unemployment is represented by points inside the macro production possibilities frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Lower world coal prices
A) decrease short-run aggregate supply.
B) decrease aggregate quantity demanded.
C) decrease aggregate quantity supplied.
D) increase aggregate quantity supplied.
E) increase short-run aggregate supply.
A) decrease short-run aggregate supply.
B) decrease aggregate quantity demanded.
C) decrease aggregate quantity supplied.
D) increase aggregate quantity supplied.
E) increase short-run aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Price stability is represented by points on the long-run aggregate supply curve (LAS).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The 2011 tsunami caused Japan's
A) SAS and LAS curves to both shift leftward.
B) SAS curve to shift leftward, but Japan's LAS curve was unchanged.
C) SAS and LAS curves to both shift rightward.
D) SAS curve to shift rightward, but Japan's LAS curve was unchanged.
E) aggregate quantity supplied to decrease.
A) SAS and LAS curves to both shift leftward.
B) SAS curve to shift leftward, but Japan's LAS curve was unchanged.
C) SAS and LAS curves to both shift rightward.
D) SAS curve to shift rightward, but Japan's LAS curve was unchanged.
E) aggregate quantity supplied to decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Full employment is represented by points on the long-run aggregate supply curve (LAS).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The long-run aggregate supply curve (LAS) is a vertical line at potential GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Government investments to improve the quality of public infrastructure like roads, transit and sewers
A) shifts both LAS and SAS leftward.
B) increases aggregate quantity supplied.
C) shifts only LAS rightward.
D) shifts both LAS and SAS rightward.
E) decreases aggregate quantity supplied.
A) shifts both LAS and SAS leftward.
B) increases aggregate quantity supplied.
C) shifts only LAS rightward.
D) shifts both LAS and SAS rightward.
E) decreases aggregate quantity supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which is a negative supply shock?
A) a lower world price for oil.
B) a lower world price for copper.
C) a drought on the Prairies that reduces wheat production.
D) a scientific discovery that lowers costs for solar energy.
E) all of the above are negative supply shocks.
A) a lower world price for oil.
B) a lower world price for copper.
C) a drought on the Prairies that reduces wheat production.
D) a scientific discovery that lowers costs for solar energy.
E) all of the above are negative supply shocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which is a supply plan to increase inputs?
A) a government plan to allow more logging on Crown land in British Columbia.
B) a snow-removal business's decision to buy another plow to expand capacity.
C) a baby-boomer's decision not to retire but keep working.
D) a shoe factory's choice to increase output from its factory in Manitoba.
E) a worker's choice to accept more overtime shifts in order to pay off a big VISA bill.
A) a government plan to allow more logging on Crown land in British Columbia.
B) a snow-removal business's decision to buy another plow to expand capacity.
C) a baby-boomer's decision not to retire but keep working.
D) a shoe factory's choice to increase output from its factory in Manitoba.
E) a worker's choice to accept more overtime shifts in order to pay off a big VISA bill.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The long-run aggregate supply curve (LAS) is a horizontal line at potential GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which is a supply plan with existing inputs?
A) an oil company's investment in new tar sands oil extraction technology.
B) a baby-boomer's decision not to retire but keep working.
C) a snow-removal business's decision to buy another plow to expand capacity.
D) a shoe factory's plan to install new, improved robots in its factory in Manitoba.
E) Toronto's plan to extend the subway system.
A) an oil company's investment in new tar sands oil extraction technology.
B) a baby-boomer's decision not to retire but keep working.
C) a snow-removal business's decision to buy another plow to expand capacity.
D) a shoe factory's plan to install new, improved robots in its factory in Manitoba.
E) Toronto's plan to extend the subway system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Lower world coal prices
A) shift both SAS and LAS leftward.
B) shift SAS leftward only.
C) shift both SAS and LAS rightward.
D) shift SAS rightward only.
E) decrease aggregate quantity supplied.
A) shift both SAS and LAS leftward.
B) shift SAS leftward only.
C) shift both SAS and LAS rightward.
D) shift SAS rightward only.
E) decrease aggregate quantity supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which is a supply plan to increase inputs?
A) a worker's choice about how many hours to work each week.
B) a father's choice to take a paying job or take care of the kids at home.
C) a business's plan to increase output from its Hamilton, Ontario factory.
D) a government plan to allow more logging on Crown land in British Columbia.
E) a new government policy allowing more immigrants into Canada.
A) a worker's choice about how many hours to work each week.
B) a father's choice to take a paying job or take care of the kids at home.
C) a business's plan to increase output from its Hamilton, Ontario factory.
D) a government plan to allow more logging on Crown land in British Columbia.
E) a new government policy allowing more immigrants into Canada.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Unemployment is represented by points outside the macro production possibilities frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Short-run aggregate supply increases if
A) the price level falls.
B) prices for resource inputs fall.
C) prices for resource inputs rise.
D) the price level rises.
E) government transfer payments decrease.
A) the price level falls.
B) prices for resource inputs fall.
C) prices for resource inputs rise.
D) the price level rises.
E) government transfer payments decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which changes Canada's short-run aggregate supply?
A) the Government of Canada legalizes the cultivation of marijuana
B) a senior citizen decides to keep working instead of retiring
C) a working mother decides to quite her job and go back to school full-time
D) American consumers stop buying Canadian beef during an outbreak of Mad Cow Disease
E) Canadian manufacturers want to increase their sales as prices rise
A) the Government of Canada legalizes the cultivation of marijuana
B) a senior citizen decides to keep working instead of retiring
C) a working mother decides to quite her job and go back to school full-time
D) American consumers stop buying Canadian beef during an outbreak of Mad Cow Disease
E) Canadian manufacturers want to increase their sales as prices rise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A positive supply shock from falling input prices shifts
A) both the SAS and AD curves rightward.
B) both the SAS and LAS curves leftward.
C) the SAS curve rightward but leaves the LAS curve unchanged.
D) the LAS curve rightward but leaves the SAS curve unchanged.
E) both the SAS and LAS curves rightward.
A) both the SAS and AD curves rightward.
B) both the SAS and LAS curves leftward.
C) the SAS curve rightward but leaves the LAS curve unchanged.
D) the LAS curve rightward but leaves the SAS curve unchanged.
E) both the SAS and LAS curves rightward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What shifts the short-run aggregate supply (SAS) curve but not the long-run aggregate supply (LAS) curve?
A) a change in input prices.
B) a change in the quantity of capital.
C) an improved technology.
D) an increase in population.
E) none of the above.
A) a change in input prices.
B) a change in the quantity of capital.
C) an improved technology.
D) an increase in population.
E) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The short-run aggregate supply (SAS) curve shifts rightward if
A) wage rates rise.
B) aggregate demand increases.
C) the population increases.
D) input prices rise.
E) the quantity of capital decreases.
A) wage rates rise.
B) aggregate demand increases.
C) the population increases.
D) input prices rise.
E) the quantity of capital decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A positive supply shock from improving technology shifts
A) both the SAS and AD curves rightward.
B) both the SAS and LAS curves leftward.
C) the SAS curve rightward but leaves the LAS curve unchanged.
D) the LAS curve rightward but leaves the SAS curve unchanged.
E) both the SAS and LAS curves rightward.
A) both the SAS and AD curves rightward.
B) both the SAS and LAS curves leftward.
C) the SAS curve rightward but leaves the LAS curve unchanged.
D) the LAS curve rightward but leaves the SAS curve unchanged.
E) both the SAS and LAS curves rightward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which media headline describes a shift of the SAS curve only?
A) "Decreased consumer spending may lead to recession."
B) "Increased consumer spending is expected to lead to inflation, with no change in real GDP."
C) "Higher wage settlements may lead to inflation."
D) "Faster growth may be due to more women entering the labour force."
E) "Recent tornadoes destroyed factories in Edmonton and Calgary."
A) "Decreased consumer spending may lead to recession."
B) "Increased consumer spending is expected to lead to inflation, with no change in real GDP."
C) "Higher wage settlements may lead to inflation."
D) "Faster growth may be due to more women entering the labour force."
E) "Recent tornadoes destroyed factories in Edmonton and Calgary."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The short-run aggregate supply (SAS) curve is the relationship between the quantity of real GDP that macroeconomic players plan to supply and the
A) quantity of real GDP demanded.
B) exchange rate.
C) inflation rate.
D) unemployment rate.
E) price level.
A) quantity of real GDP demanded.
B) exchange rate.
C) inflation rate.
D) unemployment rate.
E) price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A negative supply shock from rising input prices shifts
A) both the SAS and AD curves leftward.
B) both the SAS and LAS curves leftward.
C) the SAS curve leftward but leaves the LAS curve unchanged.
D) the LAS curve leftward but leaves the SAS curve unchanged.
E) both the SAS and LAS curves rightward.
A) both the SAS and AD curves leftward.
B) both the SAS and LAS curves leftward.
C) the SAS curve leftward but leaves the LAS curve unchanged.
D) the LAS curve leftward but leaves the SAS curve unchanged.
E) both the SAS and LAS curves rightward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which media headline describes a rightward shift of the LAS curve?
A) "Decreased consumer spending may lead to recession."
B) "Increased consumer spending is expected to lead to inflation, with no change in real GDP."
C) "Higher wage settlements may lead to inflation."
D) "Faster growth may be due to more women entering the labour force."
E) "Recent tornadoes destroyed factories in Edmonton and Calgary."
A) "Decreased consumer spending may lead to recession."
B) "Increased consumer spending is expected to lead to inflation, with no change in real GDP."
C) "Higher wage settlements may lead to inflation."
D) "Faster growth may be due to more women entering the labour force."
E) "Recent tornadoes destroyed factories in Edmonton and Calgary."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Short-run aggregate supply decreases if
A) the price level falls.
B) prices for resource inputs fall.
C) prices for resource inputs rise.
D) the price level rises.
E) government transfer payments decrease.
A) the price level falls.
B) prices for resource inputs fall.
C) prices for resource inputs rise.
D) the price level rises.
E) government transfer payments decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A rise in the price level
A) increases short-run aggregate supply.
B) decreases short-run aggregate supply.
C) increases aggregate quantity supplied.
D) decreases aggregate quantity supplied.
E) decreases aggregate demand.
A) increases short-run aggregate supply.
B) decreases short-run aggregate supply.
C) increases aggregate quantity supplied.
D) decreases aggregate quantity supplied.
E) decreases aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Increases in the quality of inputs that do not affect the quantity of those inputs, increase
A) long-run aggregate supply but not short-run aggregate supply
B) aggregate quantity supplied.
C) both long-run aggregate supply and short-run aggregate supply.
D) short-run aggregate supply but not long-run aggregate supply.
E) both long-run aggregate supply and aggregate quantity supplied.
A) long-run aggregate supply but not short-run aggregate supply
B) aggregate quantity supplied.
C) both long-run aggregate supply and short-run aggregate supply.
D) short-run aggregate supply but not long-run aggregate supply.
E) both long-run aggregate supply and aggregate quantity supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Aggregate quantity supplied decreases if
A) the price level rises.
B) prices for resource inputs fall.
C) technology improves.
D) the price level falls.
E) prices for resource inputs rise.
A) the price level rises.
B) prices for resource inputs fall.
C) technology improves.
D) the price level falls.
E) prices for resource inputs rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A fall in the price level
A) increases short-run aggregate supply.
B) decreases short-run aggregate supply.
C) increases aggregate quantity supplied.
D) decreases aggregate quantity supplied.
E) increases aggregate demand.
A) increases short-run aggregate supply.
B) decreases short-run aggregate supply.
C) increases aggregate quantity supplied.
D) decreases aggregate quantity supplied.
E) increases aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Increases in the quality of inputs that do not affect the quantity of those inputs,
A) shift LAS rightward but not SAS.
B) increase aggregate quantity supplied.
C) shift both LAS and SAS rightward.
D) shift SAS rightward but not LAS.
E) shift LAS rightward and increase aggregate quantity supplied.
A) shift LAS rightward but not SAS.
B) increase aggregate quantity supplied.
C) shift both LAS and SAS rightward.
D) shift SAS rightward but not LAS.
E) shift LAS rightward and increase aggregate quantity supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which does not change Canada's short-run aggregate supply?
A) Prince Edward Island is submerged by an offshore earthquake.
B) Perfect weather all across Canada improves crop yields for all farmers.
C) People around the country upgrade their human capital by reading Economics for Life.
D) The Government of Canada passes new regulations reducing the imports of advanced Japanese robots by Canadian businesses.
E) American consumers stop buying Canadian beef during an outbreak of Mad Cow Disease.
A) Prince Edward Island is submerged by an offshore earthquake.
B) Perfect weather all across Canada improves crop yields for all farmers.
C) People around the country upgrade their human capital by reading Economics for Life.
D) The Government of Canada passes new regulations reducing the imports of advanced Japanese robots by Canadian businesses.
E) American consumers stop buying Canadian beef during an outbreak of Mad Cow Disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Suppose there is an increase in the quantity of capital. As a result, the SAS
A) and the LAS curves both shift leftward.
B) and the LAS curves both shift rightward.
C) curve does not shift but the LAS curve shifts rightward.
D) curve does not shift but the LAS curve shifts leftward.
E) shifts rightward, but the LAS curve does not shift.
A) and the LAS curves both shift leftward.
B) and the LAS curves both shift rightward.
C) curve does not shift but the LAS curve shifts rightward.
D) curve does not shift but the LAS curve shifts leftward.
E) shifts rightward, but the LAS curve does not shift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which media headline describes a leftward shift of the LAS curve?
A) "Decreased consumer spending may lead to recession."
B) "Increased consumer spending is expected to lead to inflation, with no change in real GDP."
C) "Higher wage settlements may lead to inflation."
D) "Faster growth may be due to more women entering the labour force."
E) "Recent tornadoes destroyed factories in Edmonton and Calgary."
A) "Decreased consumer spending may lead to recession."
B) "Increased consumer spending is expected to lead to inflation, with no change in real GDP."
C) "Higher wage settlements may lead to inflation."
D) "Faster growth may be due to more women entering the labour force."
E) "Recent tornadoes destroyed factories in Edmonton and Calgary."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Aggregate quantity supplied increases if
A) the price level rises.
B) prices for resource inputs fall.
C) technology improves.
D) the price level falls.
E) prices for resource inputs rise.
A) the price level rises.
B) prices for resource inputs fall.
C) technology improves.
D) the price level falls.
E) prices for resource inputs rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 304 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



