Deck 43: Animal Immune Systems
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/169
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 43: Animal Immune Systems
1
Some forms of diabetes and arthritis are examples of:
A)immunodeficiency.
B)autoimmune disease.
C)adaptive immunity.
D)innate immunity.
A)immunodeficiency.
B)autoimmune disease.
C)adaptive immunity.
D)innate immunity.
B
2
Lupus is an autoimmune disorder. Which of the following would you expect to be a symptom of lupus?
A)an increase in ciliary action of the esophagus
B)increased phagocytosis of bacterial pathogens in the body
C)B cells binding to antigens on host cells and targeting their degradation
D)increased blood clotting if the skin is cut.
A)an increase in ciliary action of the esophagus
B)increased phagocytosis of bacterial pathogens in the body
C)B cells binding to antigens on host cells and targeting their degradation
D)increased blood clotting if the skin is cut.
C
3
Immunological memory is a feature of which of the following?
A)the innate immune system
B)the adaptive immune system
C)both the innate and adaptive immune systems
D)neither the innate and adaptive immune systems
A)the innate immune system
B)the adaptive immune system
C)both the innate and adaptive immune systems
D)neither the innate and adaptive immune systems
B
4
Immunodeficiency can occur in all of the following EXCEPT:
A)the elderly.
B)HIV-infected individuals.
C)newborns.
D)All of these choices are correct.
A)the elderly.
B)HIV-infected individuals.
C)newborns.
D)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The immune system is composed of all the following EXCEPT:
A)cells.
B)organs.
C)proteins.
D)organelles.
A)cells.
B)organs.
C)proteins.
D)organelles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A small child enters a clinic for the third time in one month with another bad skin infection filled with pus (tissue fluid combined with large numbers of bacteria growing in the fluid). Decreased numbers, or loss of function, in which of the following cell types could account for these symptoms?
A)eosinophils
B)neutrophils
C)T cells
D)B cells
A)eosinophils
B)neutrophils
C)T cells
D)B cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
You are a doctor who examines a swollen and warm puncture wound on the hand of a patient. Next door, a vet examines a puncture wound on the foot of a dog. Do you and the vet expect to see the same response in the dog and human patient?
A)Yes, because dogs have innate immune systems but not adaptive immune systems.
B)Yes, because dogs have adaptive immune systems but not innate immune systems.
C)No, because the immune response is completely unique to humans.
D)Yes, because vertebrates have both adaptive immune systems and innate immune systems.
E)No, because the foot of a dog is a completely different structure than the hand of a patient.
A)Yes, because dogs have innate immune systems but not adaptive immune systems.
B)Yes, because dogs have adaptive immune systems but not innate immune systems.
C)No, because the immune response is completely unique to humans.
D)Yes, because vertebrates have both adaptive immune systems and innate immune systems.
E)No, because the foot of a dog is a completely different structure than the hand of a patient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following describes innate immunity?
A)It is a response to a specific pathogen.
B)It is the basis for the use of vaccines.
C)It reacts to a wide variety of pathogens.
D)It is a response to a specific pathogen and is the basis for the use of vaccines.
A)It is a response to a specific pathogen.
B)It is the basis for the use of vaccines.
C)It reacts to a wide variety of pathogens.
D)It is a response to a specific pathogen and is the basis for the use of vaccines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Innate immunity activation depends on:
A)previous exposure to a foreign antigen.
B)diversity of antibodies in the blood stream.
C)MHC class II proteins.
D)memory B cells.
E)None of the answer options is correct.
A)previous exposure to a foreign antigen.
B)diversity of antibodies in the blood stream.
C)MHC class II proteins.
D)memory B cells.
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The ability to react more strongly to a subsequent infection is a feature of which of the following?
A)the innate immune system
B)the adaptive immune system
C)both the innate and adaptive immune systems
D)neither the innate nor the adaptive immune systems
A)the innate immune system
B)the adaptive immune system
C)both the innate and adaptive immune systems
D)neither the innate nor the adaptive immune systems

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following describes adaptive immunity?
A)It is a general response to pathogens.
B)It does not change over time.
C)It is the basis for vaccines.
D)It is a general response to pathogens and does not change over time.
A)It is a general response to pathogens.
B)It does not change over time.
C)It is the basis for vaccines.
D)It is a general response to pathogens and does not change over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The immune system sometimes attacks cells of its own body, resulting in:
A)immunodeficiency.
B)autoimmune disease.
C)adaptive immunity.
D)innate immunity.
A)immunodeficiency.
B)autoimmune disease.
C)adaptive immunity.
D)innate immunity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Skin is an important part of the immune response because:
A)it is relatively porous.
B)the presence of white blood cells on the surface provides protection to the host.
C)it acts as a barrier to keep out pathogens.
D)bacteria on the surface kill viruses that touch the skin.
A)it is relatively porous.
B)the presence of white blood cells on the surface provides protection to the host.
C)it acts as a barrier to keep out pathogens.
D)bacteria on the surface kill viruses that touch the skin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What type of pathogen causes AIDS?
A)virus
B)bacterium
C)protist
D)fungus
E)worm
A)virus
B)bacterium
C)protist
D)fungus
E)worm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What type of pathogen causes cholera?
A)virus
B)bacterium
C)protist
D)fungus
E)worm
A)virus
B)bacterium
C)protist
D)fungus
E)worm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The ability to distinguish self from nonself is a feature of which of the following?
A)the innate immune system
B)the adaptive immune system
C)both the innate and adaptive immune systems
D)neither the innate nor the adaptive immune systems
A)the innate immune system
B)the adaptive immune system
C)both the innate and adaptive immune systems
D)neither the innate nor the adaptive immune systems

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Specificity is a feature of which of the following?
A)the innate immune system
B)the adaptive immune system
C)both the innate and adaptive immune systems
D)neither the innate nor the adaptive immune systems
A)the innate immune system
B)the adaptive immune system
C)both the innate and adaptive immune systems
D)neither the innate nor the adaptive immune systems

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Phagocytic cells are an important part of the innate immune system because of their ability to:
A)engulf many different pathogens.
B)present foreign antigens that stimulate adaptive immune responses.
C)attack cells infected by a virus.
D)produce multiple antibodies.
A)engulf many different pathogens.
B)present foreign antigens that stimulate adaptive immune responses.
C)attack cells infected by a virus.
D)produce multiple antibodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Innate immunity is different from adaptive immunity in that innate immunity:
A)only works after exposure to foreign antigens.
B)only stimulates responses through mast cells.
C)does not require prior exposure to a pathogen.
D)does not stimulate cell-mediated immunity pathways.
A)only works after exposure to foreign antigens.
B)only stimulates responses through mast cells.
C)does not require prior exposure to a pathogen.
D)does not stimulate cell-mediated immunity pathways.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A flu virus infects a human. Where will the "self" molecules of the infected individual be found?
A)on the viral coat
B)in the viral coat
C)on human cells
D)on human cells and on the viral coat
A)on the viral coat
B)in the viral coat
C)on human cells
D)on human cells and on the viral coat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following cells act as phagocytes?
A)macrophages
B)natural killer cells
C)neutrophils
D)mast cells
E)plasma cells
A)macrophages
B)natural killer cells
C)neutrophils
D)mast cells
E)plasma cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following statements is(are) true regarding bacteria in the human body?
A)Human bodies may contain pathogenic bacteria, but these are often kept in check by other (nonpathogenic)species.
B)Human bodies contain bacteria that are beneficial to certain processes (for example, digestion).
C)Cholera is caused by a bacterium that infects and disables part of the immune system.
A)Human bodies may contain pathogenic bacteria, but these are often kept in check by other (nonpathogenic)species.
B)Human bodies contain bacteria that are beneficial to certain processes (for example, digestion).
C)Cholera is caused by a bacterium that infects and disables part of the immune system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A man is scratched by his cat. A phagocyte near the scratch site recognizes and engulfs a bacterium. Shortly thereafter, more phagocytes arrive in the tissue surrounding the scratch. How are the additional phagocytes recruited to the site of the scratch?
A)by antigens secreted by the bacteria
B)by cytokines produced by the bacteria
C)by antigens secreted by the initial phagocyte
D)by cytokines secreted by the initial phagocyte
A)by antigens secreted by the bacteria
B)by cytokines produced by the bacteria
C)by antigens secreted by the initial phagocyte
D)by cytokines secreted by the initial phagocyte

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following processes are considered components of the complement system?
A)MHC molecules on the surface of cells
B)membrane attack complexes (MACs)
C)histamine produced by mast cells
A)MHC molecules on the surface of cells
B)membrane attack complexes (MACs)
C)histamine produced by mast cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Cholera causes disease by which of the following?
A)proliferation in body tissues
B)destroying cells
C)production of a toxin
D)compromising the immune system
A)proliferation in body tissues
B)destroying cells
C)production of a toxin
D)compromising the immune system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What are possible mechanisms of action for phagocytes?
A)They engulf and digest pathogens with lysosome-enclosed enzymes.
B)They destroy pathogens by the production of reactive nitrogen species.
C)They specifically target and kill virus-infected cells.
D)They form membrane attack complexes (MACs).
A)They engulf and digest pathogens with lysosome-enclosed enzymes.
B)They destroy pathogens by the production of reactive nitrogen species.
C)They specifically target and kill virus-infected cells.
D)They form membrane attack complexes (MACs).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The adaptive immune system does NOT include:
A)memory cells.
B)plasma cells.
C)mast cells.
D)T cells.
E)B cells.
A)memory cells.
B)plasma cells.
C)mast cells.
D)T cells.
E)B cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Allergies result when the immune system:
A)responds to self molecules and cells.
B)does not respond to self molecules and cells.
C)responds to harmless nonself molecules and cells.
D)responds to harmful nonself molecules and cells.
A)responds to self molecules and cells.
B)does not respond to self molecules and cells.
C)responds to harmless nonself molecules and cells.
D)responds to harmful nonself molecules and cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Phagocytes produce transmembrane proteins called toll-like receptors (TLR). The structure of a TLR is represented below. The gray structure indicated by the bracket is _____, which is held together by _____ bonding and is an example of _____. 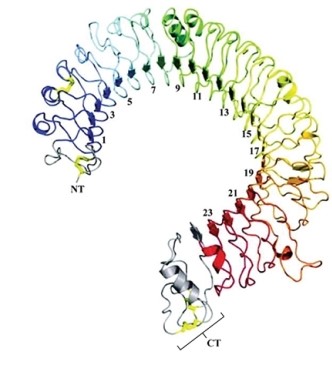
A)an amino acid; covalent; primary structure
B)beta sheet; hydrogen; secondary structure
C)an alpha helix; hydrogen; secondary structure
D)tRNA; covalent; translation
E)rRNA; covalent; ribosome formation

A)an amino acid; covalent; primary structure
B)beta sheet; hydrogen; secondary structure
C)an alpha helix; hydrogen; secondary structure
D)tRNA; covalent; translation
E)rRNA; covalent; ribosome formation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
How would a rapid evolutionary change in cell-surface proteins in bacteria affect the innate immune system?
A)Helper T cells would not develop in the thymus.
B)TLRs of phagocytes would be unable to recognize the proteins.
C)Histamine concentrations in the blood would increase.
D)Cytokine release from memory B cells would increase.
A)Helper T cells would not develop in the thymus.
B)TLRs of phagocytes would be unable to recognize the proteins.
C)Histamine concentrations in the blood would increase.
D)Cytokine release from memory B cells would increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
You are a doctor who examines a swollen and warm puncture wound on the hand of a patient. Which was NOT a response of the patient's immune system to this injury when it occurred?
A)Antibodies were produced as part of the adaptive immune response.
B)Phagocytes attacked foreign cells that entered the wound.
C)The innate immune system triggered an inflammation response.
D)Cell division was inhibited at the wound site.
A)Antibodies were produced as part of the adaptive immune response.
B)Phagocytes attacked foreign cells that entered the wound.
C)The innate immune system triggered an inflammation response.
D)Cell division was inhibited at the wound site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Immunodeficiency is a general term that refers to the loss of:
A)one or more components of the immune system.
B)functional T cells in the body.
C)immune system function with age.
D)immune system function because of genetic mutations.
A)one or more components of the immune system.
B)functional T cells in the body.
C)immune system function with age.
D)immune system function because of genetic mutations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Your phagocytes have transmembrane proteins called toll-like receptors (TLR) on their surface, but your mast cells do not because:
A)your phagocytes carry the genetic information to make TLRs but your mast cells do not.
B)your phagocytes run transcription and translation but your mast cells only run transcription.
C)some of your body's cells contain ribosomes but most do not.
D)your phagocytes express some genes that are not expressed in your mast cells (and vice versa).
A)your phagocytes carry the genetic information to make TLRs but your mast cells do not.
B)your phagocytes run transcription and translation but your mast cells only run transcription.
C)some of your body's cells contain ribosomes but most do not.
D)your phagocytes express some genes that are not expressed in your mast cells (and vice versa).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The complement system refers to:
A)proteins present on macrophages that recognize foreign proteins.
B)proteins circulating in the blood that are activated by opsonization.
C)proteins circulating in the blood that are activated by antibodies or molecules on pathogens.
D)proteins that are activated when histamine levels increase.
A)proteins present on macrophages that recognize foreign proteins.
B)proteins circulating in the blood that are activated by opsonization.
C)proteins circulating in the blood that are activated by antibodies or molecules on pathogens.
D)proteins that are activated when histamine levels increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
An individual is born with a mutation such that they cannot form MAC proteins that associate with one another in a plasma membrane. This is an example of:
A)immunodeficiency.
B)failure of the cell-mediated response system.
C)a mutation in one of the classes of antibodies.
D)clonal selection.
A)immunodeficiency.
B)failure of the cell-mediated response system.
C)a mutation in one of the classes of antibodies.
D)clonal selection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
_____ describes the process whereby a phagocyte exits a blood vessel and moves into an infected region of tissue.
A)Extravasation
B)Opsonization
C)Phagocytosis
D)Clonal selection
E)Antigen presentation
A)Extravasation
B)Opsonization
C)Phagocytosis
D)Clonal selection
E)Antigen presentation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following statements are TRUE regarding histamine?
A)It can be produced by granulocytes.
B)It indirectly causes swelling.
C)It contributes to inflammation.
D)It causes blood vessels to dilate.
E)It changes the permeability of blood vessels.
A)It can be produced by granulocytes.
B)It indirectly causes swelling.
C)It contributes to inflammation.
D)It causes blood vessels to dilate.
E)It changes the permeability of blood vessels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The immune system usually responds to _____ cells and molecules, but not _____ cells and molecules.
A)nonself; self
B)host; self
C)self; nonself
D)host; foreign
A)nonself; self
B)host; self
C)self; nonself
D)host; foreign

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A person inhales a potentially pathogenic bacterium. What defenses will the bacterium encounter as it travels through the human body?
A)hairs in the nasal cavity
B)mucus and cilia in the respiratory tract (if the bacterium enters the respiratory tract)
C)digestive enzymes in the stomach (if the bacterium enters the gastrointestinal tract)
D)phagocytes (if the bacterium enters the bloodstream)
A)hairs in the nasal cavity
B)mucus and cilia in the respiratory tract (if the bacterium enters the respiratory tract)
C)digestive enzymes in the stomach (if the bacterium enters the gastrointestinal tract)
D)phagocytes (if the bacterium enters the bloodstream)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
How does the adaptive immune system differ from the innate immune system?
A)in the ability to distinguish self from nonself
B)in having memory
C)in the ability to target a specific pathogen
D)both in having memory and in the ability to target a specific pathogen
A)in the ability to distinguish self from nonself
B)in having memory
C)in the ability to target a specific pathogen
D)both in having memory and in the ability to target a specific pathogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The cytoskeleton is involved in which of the following cellular responses?
A)phagocytosis
B)toll-like receptor binding
C)extravasation
D)phagocytosis and extravasation
A)phagocytosis
B)toll-like receptor binding
C)extravasation
D)phagocytosis and extravasation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is NOT a type of phagocytic cell?
A)mast cell
B)neutrophil
C)dendritic cell
D)macrophage
A)mast cell
B)neutrophil
C)dendritic cell
D)macrophage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Cytokine signaling of phagocytes is an example of _____ signaling.
A)autocrine
B)endocrine
C)paracrine
D)contact-dependent
A)autocrine
B)endocrine
C)paracrine
D)contact-dependent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Probiotics are foods, like yogurt, or dietary supplements that contain living bacteria. Why would someone want to knowingly consume bacteria?
A)to populate their gut with "good" bacteria
B)to reduce the ability of pathogens to populate the gut
C)to reduce or eliminate gastrointestinal problems
D)All of these choices are correct.
A)to populate their gut with "good" bacteria
B)to reduce the ability of pathogens to populate the gut
C)to reduce or eliminate gastrointestinal problems
D)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The adhesion step in extravasation is MOST likely to be mediated by:
A)integrin proteins.
B)cell wall proteins.
C)collagen.
D)keratin.
A)integrin proteins.
B)cell wall proteins.
C)collagen.
D)keratin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is the function of a toll-like receptor?
A)to bind to surface molecules present on phagocytes
B)to bind to cytokines
C)to bind to surface molecules present on pathogens
D)to facilitate the extravasation of phagocytes
A)to bind to surface molecules present on phagocytes
B)to bind to cytokines
C)to bind to surface molecules present on pathogens
D)to facilitate the extravasation of phagocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
How does a macrophage destroy a pathogen?
A)production of antibodies
B)phagocytosis
C)secretion of histamine
D)production of antigens
A)production of antibodies
B)phagocytosis
C)secretion of histamine
D)production of antigens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
How can a pathogen be destroyed once a phagocyte internalizes it?
A)exposure to reactive oxygen species
B)encapsulation
C)degradation by lysosomes
D)exposure to reactive oxygen species and degradation by lysosomes.
A)exposure to reactive oxygen species
B)encapsulation
C)degradation by lysosomes
D)exposure to reactive oxygen species and degradation by lysosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following is NOT part of the innate immune system?
A)a cell wall
B)a helper T cell
C)cilia
D)skin
A)a cell wall
B)a helper T cell
C)cilia
D)skin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Where would toll-like receptors be synthesized in a phagocyte?
A)on the rough endoplasmic reticulum
B)in the cytosol
C)in the nucleus
D)on the smooth endoplasmic reticulum
A)on the rough endoplasmic reticulum
B)in the cytosol
C)in the nucleus
D)on the smooth endoplasmic reticulum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
How does the release of histamine by mast cells help the innate immune response?
A)It signals neutrophils to migrate to the site of infection.
B)It makes it easier for neutrophils to move from the bloodstream to the site of infection.
C)It increases the volume of blood flow in the area of the infection.
D)It makes it easier for neutrophils to move from the bloodstream to the site of infection and it increases the volume of blood flow in the area of the infection.
A)It signals neutrophils to migrate to the site of infection.
B)It makes it easier for neutrophils to move from the bloodstream to the site of infection.
C)It increases the volume of blood flow in the area of the infection.
D)It makes it easier for neutrophils to move from the bloodstream to the site of infection and it increases the volume of blood flow in the area of the infection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The job of a natural killer cell is to:
A)release histamine.
B)destroy invading pathogens through phagocytosis.
C)destroy infected or abnormal host cells.
D)trigger inflammation.
A)release histamine.
B)destroy invading pathogens through phagocytosis.
C)destroy infected or abnormal host cells.
D)trigger inflammation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What does the process of extravasation involve?
A)movement of phagocytes from the bloodstream into infected tissue
B)the engulfing of a pathogen by a phagocyte
C)release of chemical signals such as histamines or cytokines
D)coating of a pathogen with C-reactive protein
A)movement of phagocytes from the bloodstream into infected tissue
B)the engulfing of a pathogen by a phagocyte
C)release of chemical signals such as histamines or cytokines
D)coating of a pathogen with C-reactive protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Cilia are part of the protective barrier located in the:
A)respiratory tract.
B)skin.
C)stomach.
D)genitourinary tract.
A)respiratory tract.
B)skin.
C)stomach.
D)genitourinary tract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Two of the classic signs of infection, swelling and redness, are a result of:
A)the increase in cell density due to migration of phagocytes.
B)the effect of histamines on blood vessels.
C)changes in osmotic balance due to the presence of cytokines.
D)All of the answer options are correct.
A)the increase in cell density due to migration of phagocytes.
B)the effect of histamines on blood vessels.
C)changes in osmotic balance due to the presence of cytokines.
D)All of the answer options are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What cellular process is involved in the release of histamine or cytokines?
A)receptor binding
B)signaling cascade
C)amplification
D)exocytosis
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)receptor binding
B)signaling cascade
C)amplification
D)exocytosis
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
You are a doctor and have a patient who has been injured by a rusty nail. As a precaution, you vaccinate her against tetanus. In response to the vaccine, how does her body produce antibodies against C. tetani and prevent future illness due to tetanus?
A)Every B cell in her body produces antibodies against C. tetani.
B)Every cell in her immune system produces antibodies against C. tetani.
C)The B cell with appropriate antibody is stimulated to divide, producing plasma cells that make antibodies to C. tetani, and memory cells that "remember" C. tetani.
D)The B cell that produces the appropriate antibody undergoes genomic rearrangement in order to produce other cells that produce the same antibody.
A)Every B cell in her body produces antibodies against C. tetani.
B)Every cell in her immune system produces antibodies against C. tetani.
C)The B cell with appropriate antibody is stimulated to divide, producing plasma cells that make antibodies to C. tetani, and memory cells that "remember" C. tetani.
D)The B cell that produces the appropriate antibody undergoes genomic rearrangement in order to produce other cells that produce the same antibody.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The efficient phagocytosis of protein-coated pathogens is called:
A)extravasation.
B)opsonization.
C)inflammation.
D)complementation.
A)extravasation.
B)opsonization.
C)inflammation.
D)complementation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following is a possible outcome of activation of the complement system?
A)inflammation
B)enhanced phagocytosis
C)cell lysis
D)All of these choices are correct.
A)inflammation
B)enhanced phagocytosis
C)cell lysis
D)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What accounts for the lysis of a bacterial cell in the presence of a membrane attack complex?
A)loss of cytoplasm due to the presence of large channels in the membrane
B)unregulated signaling due to the addition of novel proteins to the cell's membrane
C)osmosis leading to swelling and rupture of the cell
D)apoptosis due to the loss of DNA
A)loss of cytoplasm due to the presence of large channels in the membrane
B)unregulated signaling due to the addition of novel proteins to the cell's membrane
C)osmosis leading to swelling and rupture of the cell
D)apoptosis due to the loss of DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following type of cell produces antibodies?
A)helper T cells
B)cytotoxic T cells
C)mast cells
D)B cells
E)natural killer cells
A)helper T cells
B)cytotoxic T cells
C)mast cells
D)B cells
E)natural killer cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following statements is/are TRUE regarding the secondary immune response?
A)It occurs more slowly than the primary immune response.
B)It occurs faster than the primary immune response.
C)It produces more antibodies than the primary immune response.
D)It produces fewer antibodies than the primary immune response.
A)It occurs more slowly than the primary immune response.
B)It occurs faster than the primary immune response.
C)It produces more antibodies than the primary immune response.
D)It produces fewer antibodies than the primary immune response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
You are a doctor who examines a swollen and warm puncture wound on the hand of a patient. Because the wound was made by a rusty nail, you are concerned about infection by Clostridium tetani bacteria, which cause tetanus. You are relieved to see that the patient received a tetanus vaccine at her last checkup a year ago. The vaccine:
A)exposed the patient to C. tetani so that she contracted a mild version of tetanus.
B)exposed the patient to deactivated C. tetani, so that her B cells would produce antibodies to the bacteria with no risk of contracting the disease.
C)stimulated the production of mast cells by her bone marrow.
D)exposed the patient to other types of bacteria, so that her immune system would be prepared for infection by prokaryotes.
A)exposed the patient to C. tetani so that she contracted a mild version of tetanus.
B)exposed the patient to deactivated C. tetani, so that her B cells would produce antibodies to the bacteria with no risk of contracting the disease.
C)stimulated the production of mast cells by her bone marrow.
D)exposed the patient to other types of bacteria, so that her immune system would be prepared for infection by prokaryotes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
After clonal selection, B cells become either _____ cells that secrete _____, or _____ cells with membrane-bound antibodies.
A)memory; antibodies; plasma
B)plasma; antibodies; memory
C)memory; antigens; plasma
D)plasma; antigens; memory
A)memory; antibodies; plasma
B)plasma; antibodies; memory
C)memory; antigens; plasma
D)plasma; antigens; memory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A researcher purifying antibodies in patients' blood samples discovers that one patient has an abnormally high level of IgE. He goes back to check the patient's chart. What are the likely symptoms of this patient?
A)persistent infections of the mucous membranes
B)persistent viral infections
C)severe allergies
D)severe asthma
A)persistent infections of the mucous membranes
B)persistent viral infections
C)severe allergies
D)severe asthma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
You are a doctor who examines a swollen and warm puncture wound on the hand of a patient, which was caused by a rusty nail. You vaccinate her for tetanus. In her body's response to the vaccine, how does one of her B cells produce antibodies against C. tetani?
A)Each antigen is coded for by a unique gene in the human genome; the correct gene is expressed to produce the antigens against C. tetani.
B)Rearrangement of different gene segments in B cells after exposure to C. tetani creates a unique gene. The cell then produces lots of that specific antibody.
C)Post-translational modification of a generic antibody protein changes it from a generic form to a specific form against C. tetani.
D)Rearrangement of different gene segments in maturing B cells creates a unique gene. Upon exposure to C. tetani, the cell is stimulated to produce lots of that specific antibody.
A)Each antigen is coded for by a unique gene in the human genome; the correct gene is expressed to produce the antigens against C. tetani.
B)Rearrangement of different gene segments in B cells after exposure to C. tetani creates a unique gene. The cell then produces lots of that specific antibody.
C)Post-translational modification of a generic antibody protein changes it from a generic form to a specific form against C. tetani.
D)Rearrangement of different gene segments in maturing B cells creates a unique gene. Upon exposure to C. tetani, the cell is stimulated to produce lots of that specific antibody.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following statements is/are TRUE regarding heavy (H) chains?
A)Antibodies contain two heavy chains.
B)Heavy chains contain variable and constant regions.
C)Heavy chains are formed by the recombination of V, J, C, and D gene segments.
D)Heavy chains contain only one hypervariable region.
E)T cell receptors contain two heavy chains.
A)Antibodies contain two heavy chains.
B)Heavy chains contain variable and constant regions.
C)Heavy chains are formed by the recombination of V, J, C, and D gene segments.
D)Heavy chains contain only one hypervariable region.
E)T cell receptors contain two heavy chains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The large number of antibodies that can be produced in a single individual is a result of a single B cell:
A)producing multiple unique antibodies by genomic rearrangement.
B)being able to produce unique antibodies from both the maternal and paternal alleles.
C)producing a unique antibody from all other B cells by genomic rearrangement.
D)secreting multiple antibodies that will be presented on the surface of other B cells.
A)producing multiple unique antibodies by genomic rearrangement.
B)being able to produce unique antibodies from both the maternal and paternal alleles.
C)producing a unique antibody from all other B cells by genomic rearrangement.
D)secreting multiple antibodies that will be presented on the surface of other B cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A hypervariable region is part of a(n):
A)antibody.
B)antigen.
C)complement.
D)mast cell.
A)antibody.
B)antigen.
C)complement.
D)mast cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Genomic rearrangement in B cells occurs:
A)during clonal selection after antigen binding.
B)in the bone marrow when B cells divide and produce daughter B cells.
C)in the gamete-producing cells of an individual.
D)after clonal selection when antibodies are required for immune response.
A)during clonal selection after antigen binding.
B)in the bone marrow when B cells divide and produce daughter B cells.
C)in the gamete-producing cells of an individual.
D)after clonal selection when antibodies are required for immune response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
At which point on the curve below would you expect circulating novel viral concentrations to be HIGHEST? 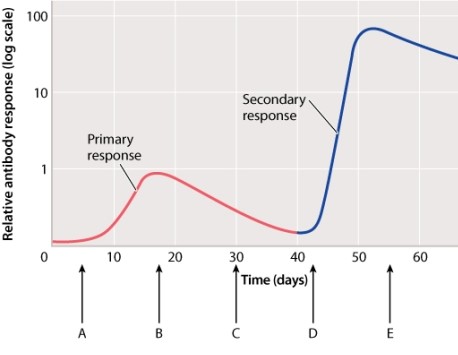


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A researcher discovers a new antibody. Upon evaluating its sequence, she determines that the antibody is not the result of genomic rearrangement alone. What other processes could have produced this specific antibody?
A)germ cell hypomutation
B)RNA editing
C)alternative mRNA splicing
D)hybridization
A)germ cell hypomutation
B)RNA editing
C)alternative mRNA splicing
D)hybridization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The specific region of an antibody to which an antigen binds is called a(n):
A)hypervariable region.
B)MHC class I.
C)MHC class II.
D)light chain.
E)heavy chain.
A)hypervariable region.
B)MHC class I.
C)MHC class II.
D)light chain.
E)heavy chain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
All antibodies in a single individual are similar in that they all contain the same:
A)C segment but different V segments.
B)C segments on their heavy and light chains.
C)V segments on their heavy and light chains.
D)C segments on their heavy chains, but different C segments on their light chains.
E)None of the answer options is correct.
A)C segment but different V segments.
B)C segments on their heavy and light chains.
C)V segments on their heavy and light chains.
D)C segments on their heavy chains, but different C segments on their light chains.
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
In order for a vaccine to be effective over the lifetime of an individual, there should be:
A)low levels of antigenic shift in the pathogen.
B)high levels of memory B cells.
C)high levels of circulating MAC proteins.
D)low levels of circulating neutrophils.
A)low levels of antigenic shift in the pathogen.
B)high levels of memory B cells.
C)high levels of circulating MAC proteins.
D)low levels of circulating neutrophils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Antibodies are formed by which cells of the immune system?
A)phagocytes
B)B cells
C)natural killer cells
D)T cells
E)mast cells
A)phagocytes
B)B cells
C)natural killer cells
D)T cells
E)mast cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Where do B cells mature in mammals?
A)bone marrow
B)blood
C)lymph nodes
D)thymus
A)bone marrow
B)blood
C)lymph nodes
D)thymus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Recall Edward Jenner's experiment, where a boy was inoculated with cowpox and, as a result, did not contract smallpox when he was exposed to the virus. Why didn't the boy get smallpox?
A)because of immune "memory" provided by plasma cells
B)because of immune "memory" provided by memory cells
C)because of a primary immune response
D)because of a secondary immune response
A)because of immune "memory" provided by plasma cells
B)because of immune "memory" provided by memory cells
C)because of a primary immune response
D)because of a secondary immune response

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Tetanus is a bacterial infection that is commonly acquired from puncture wounds. Why do you need to be vaccinated against the flu every year, but you only need a virus booster against tetanus every 10 years?
A)Antibody production against viruses drops off about 10 times faster than antibody production against bacterial infections, so you need to be vaccinated 10 times more frequently against the flu.
B)The flu is everywhere but bacterial infections are incredibly rare, so you don't need to be as careful in maintaining your immunity against them.
C)There is a higher rate of mutation in viruses than in bacteria, so you need to change the antibodies you are producing (through vaccination)every year for the flu.
D)Infections that enter the body through the bloodstream (like tetanus)are much less toxic than infections that enter the body through binding to epithelial cells (like the flu).
A)Antibody production against viruses drops off about 10 times faster than antibody production against bacterial infections, so you need to be vaccinated 10 times more frequently against the flu.
B)The flu is everywhere but bacterial infections are incredibly rare, so you don't need to be as careful in maintaining your immunity against them.
C)There is a higher rate of mutation in viruses than in bacteria, so you need to change the antibodies you are producing (through vaccination)every year for the flu.
D)Infections that enter the body through the bloodstream (like tetanus)are much less toxic than infections that enter the body through binding to epithelial cells (like the flu).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
_____ are produced by B cells and possess antibodies attached to their cell surfaces. The cells play a pivotal role in the secondary immune response.
A)Memory cells
B)Plasma cells
C)Phagocytes
D)Cytotoxic T cells
E)Helper T cells
A)Memory cells
B)Plasma cells
C)Phagocytes
D)Cytotoxic T cells
E)Helper T cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



