Deck 37: Animal Movement: Muscles and Skeletons
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/175
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 37: Animal Movement: Muscles and Skeletons
1
What is the function of tropomyosin in muscle cells?
A)Tropomyosin binds to actin molecules and brings about shortening of the muscles.
B)Tropomyosin covers the myosin binding sites on the actin filaments, preventing contraction from occurring.
C)Tropomyosin is the contractile unit of the muscle cell.
D)Tropomyosin stores calcium.
A)Tropomyosin binds to actin molecules and brings about shortening of the muscles.
B)Tropomyosin covers the myosin binding sites on the actin filaments, preventing contraction from occurring.
C)Tropomyosin is the contractile unit of the muscle cell.
D)Tropomyosin stores calcium.
B
2
Cnidarians, such as _____, have muscle fibers.
A)clams
B)earthworms
C)jellyfish
D)sea corals
A)clams
B)earthworms
C)jellyfish
D)sea corals
C
3
The cross-bridge power stroke corresponds to which event in muscle contraction?
A)myosin detachment from actin
B)sliding of actin with respect to myosin
C)cocking of the myosin head
D)binding of the myosin head to actin
A)myosin detachment from actin
B)sliding of actin with respect to myosin
C)cocking of the myosin head
D)binding of the myosin head to actin
B
4
Cross-bridges form between the contractile proteins of the muscle cell. The movement of cross-bridges shortens the muscle fiber. What two proteins participate in cross-bridge formation?
A)actin and myosin
B)troponin and titin
C)titin and myosin
D)titin and actin
A)actin and myosin
B)troponin and titin
C)titin and myosin
D)titin and actin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Curare is a poison that was used by South American Indians on their arrowheads. Curare blocks the action of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. How did the action of curare make hunting easier for these Indians?
A)Blocking acetylcholine shut down cellular respiration and killed organisms.
B)The prey were paralyzed.
C)The hunted animals bled to death.
D)Curare interfered with the spontaneous depolarization of heart muscle cells.
A)Blocking acetylcholine shut down cellular respiration and killed organisms.
B)The prey were paralyzed.
C)The hunted animals bled to death.
D)Curare interfered with the spontaneous depolarization of heart muscle cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which letter(s) in the diagram of a muscle refer(s) to skeletal muscle structures that are multicellular? 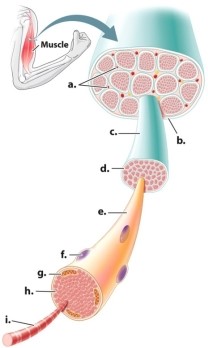
A)letter c only
B)letters a, c, e, f, and i
C)letters a, b, c, and d
D)letters f, g, h, and i
E)letter i only

A)letter c only
B)letters a, c, e, f, and i
C)letters a, b, c, and d
D)letters f, g, h, and i
E)letter i only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What event results from the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP by the myosin head?
A)cross-bridge formation
B)shortening of the muscle fiber
C)cocking of myosin head to its high-energy position
D)the power stroke
A)cross-bridge formation
B)shortening of the muscle fiber
C)cocking of myosin head to its high-energy position
D)the power stroke

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which letter(s) in the diagram of a muscle refer(s) to an individual muscle cell? 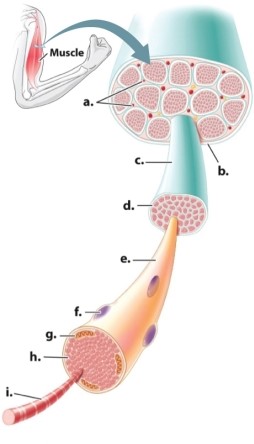
A)letter c only
B)letters c, e, f, and i
C)letter e only
D)letters f and i
E)letter i only

A)letter c only
B)letters c, e, f, and i
C)letter e only
D)letters f and i
E)letter i only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The contractile machinery of muscles is only found in the most recently diverged animal groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is the motor endplate?
A)the terminal membrane of the motor neuron where neurotransmitter is released
B)the portion of the membrane of the muscle cell that has postsynaptic receptors that respond to the neurotransmitter released by the motor neuron
C)the membrane of the sarcoplasmic reticulum where calcium is stored
D)the Z disc where two sarcomeres adjoin
A)the terminal membrane of the motor neuron where neurotransmitter is released
B)the portion of the membrane of the muscle cell that has postsynaptic receptors that respond to the neurotransmitter released by the motor neuron
C)the membrane of the sarcoplasmic reticulum where calcium is stored
D)the Z disc where two sarcomeres adjoin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Calmodulin is involved in the regulation of:
A)skeletal muscle contraction.
B)propagation of a nerve impulse across a synapse.
C)contraction of smooth muscle.
D)propagation of heart muscle contraction to the entire myocardium.
A)skeletal muscle contraction.
B)propagation of a nerve impulse across a synapse.
C)contraction of smooth muscle.
D)propagation of heart muscle contraction to the entire myocardium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When a skeletal muscle contracts, what is happening at the level of the muscle proteins?
A)Thick filaments shorten.
B)Thin filaments slide relative to thick filaments.
C)Thin filaments depolymerize to shorten.
D)Calcium ions bind to tropomyosin, which allows actin to bind to myosin.
E)Tropomyosin binds to troponin, which allows calcium to bind to actin.
A)Thick filaments shorten.
B)Thin filaments slide relative to thick filaments.
C)Thin filaments depolymerize to shorten.
D)Calcium ions bind to tropomyosin, which allows actin to bind to myosin.
E)Tropomyosin binds to troponin, which allows calcium to bind to actin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following can be associated with striated, multinucleated muscle tissue?
A)cardiac muscle cell
B)calmodulin
C)skeletal muscle cell
D)smooth muscle cell
A)cardiac muscle cell
B)calmodulin
C)skeletal muscle cell
D)smooth muscle cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following are roles played by calcium ions in coordinating the activation of a muscle by motor neurons?
A)Calcium ions enter the motor endplate of the muscle fiber, causing depolarization of the muscle cell.
B)Calcium ions enter the motor neuron axon terminus to stimulate vesicle fusion and neurotransmitter release into the neuromuscular synapse.
C)Calcium ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and bind with troponin to open actin binding sites for myosin, leading to force generation.
D)Calcium ions diffuse into the sarcoplasmic reticulum to open actin binding sites for myosin, leading to force generation.
E)Calcium ions are actively pumped into the sarcoplasmic reticulum to cause muscle relaxation by allowing tropomyosin to block actin binding sites.
A)Calcium ions enter the motor endplate of the muscle fiber, causing depolarization of the muscle cell.
B)Calcium ions enter the motor neuron axon terminus to stimulate vesicle fusion and neurotransmitter release into the neuromuscular synapse.
C)Calcium ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and bind with troponin to open actin binding sites for myosin, leading to force generation.
D)Calcium ions diffuse into the sarcoplasmic reticulum to open actin binding sites for myosin, leading to force generation.
E)Calcium ions are actively pumped into the sarcoplasmic reticulum to cause muscle relaxation by allowing tropomyosin to block actin binding sites.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is the function of troponin in muscle contraction?
A)Troponin slides past myosin, causing muscle shortening.
B)Troponin forms the cross-bridges between actin and myosin.
C)Troponin moves tropomyosin from actin binding sites, allowing myosin to bind to actin.
D)Troponin has no function in muscle contraction.
A)Troponin slides past myosin, causing muscle shortening.
B)Troponin forms the cross-bridges between actin and myosin.
C)Troponin moves tropomyosin from actin binding sites, allowing myosin to bind to actin.
D)Troponin has no function in muscle contraction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
You measure levels of Ca2+ in various locations within a motor neuron and a skeletal muscle fiber when the motor neuron is NOT depolarized, and the muscle fiber is at rest. Where do you expect to find high levels of Ca2+?
A)in vesicles within the motor neuron
B)in the cytosol of the motor neuron terminus
C)in the synaptic cleft
D)within the sarcoplasmic reticulum of the muscle fiber
A)in vesicles within the motor neuron
B)in the cytosol of the motor neuron terminus
C)in the synaptic cleft
D)within the sarcoplasmic reticulum of the muscle fiber

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is the neurotransmitter that is released at the neuromuscular junction?
A)epinephrine
B)dopamine
C)norepinephrine
D)acetylcholine
A)epinephrine
B)dopamine
C)norepinephrine
D)acetylcholine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Striated muscles appear striated or banded under a microscope. Striated muscle fibers include:
A)skeletal muscle cells.
B)muscle fibers that close the shells of clams.
C)smooth muscle cells.
D)cardiac muscle cells.
A)skeletal muscle cells.
B)muscle fibers that close the shells of clams.
C)smooth muscle cells.
D)cardiac muscle cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is a muscle tissue that moves one bone with respect to another, enabling movement of an organism?
A)skeletal muscle
B)cardiac muscle
C)smooth muscle
D)cartilage
A)skeletal muscle
B)cardiac muscle
C)smooth muscle
D)cartilage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The sliding filament model of muscle contraction argues that:
A)tropomyosin must be removed from the actin molecule before it can bind to myosin.
B)muscle contraction requires energy in the form of GTP.
C)the sarcomere stretches to create contraction.
D)actin filaments slide past myosin, causing the shortening of the muscle fiber.
A)tropomyosin must be removed from the actin molecule before it can bind to myosin.
B)muscle contraction requires energy in the form of GTP.
C)the sarcomere stretches to create contraction.
D)actin filaments slide past myosin, causing the shortening of the muscle fiber.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is a muscle fiber?
A)a single cell of a muscle
B)a group of muscle cells that make up the same muscle group
C)the myosin that makes up the contractile unit of a muscle cell
D)the connective tissue outer covering of a muscle
A)a single cell of a muscle
B)a group of muscle cells that make up the same muscle group
C)the myosin that makes up the contractile unit of a muscle cell
D)the connective tissue outer covering of a muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is the basic contracting unit of a skeletal muscle?
A)sarcomere
B)myofibril
C)actin filament
D)myosin
A)sarcomere
B)myofibril
C)actin filament
D)myosin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The binding of neurotransmitter to receptors on a vertebrate muscle cell causes:
A)an influx of sodium ions, causing a spike in depolarization.
B)an influx of potassium ions.
C)an efflux of sodium ions.
D)a graded depolarization of the muscle cell.
A)an influx of sodium ions, causing a spike in depolarization.
B)an influx of potassium ions.
C)an efflux of sodium ions.
D)a graded depolarization of the muscle cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Striated muscles include:
A)skeletal muscles.
B)cardiac muscles.
C)smooth muscles.
D)skeletal muscles and cardiac muscles.
A)skeletal muscles.
B)cardiac muscles.
C)smooth muscles.
D)skeletal muscles and cardiac muscles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
You measure levels of Ca2+ in various locations within a motor neuron and a skeletal muscle fiber when the motor neuron is NOT depolarized, and the muscle fiber is at rest. Where do you expect to find high levels of Ca2+?
A)binding to the receptors at the motor endplate of the muscle cell
B)diffusing into the motor neuron through specialized channels in the plasma membrane
C)within the T-tubules
D)within the sarcoplasmic reticulum of the muscle fiber
E)bound to troponin
A)binding to the receptors at the motor endplate of the muscle cell
B)diffusing into the motor neuron through specialized channels in the plasma membrane
C)within the T-tubules
D)within the sarcoplasmic reticulum of the muscle fiber
E)bound to troponin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The hormone oxytocin stimulates contraction of:
A)the smooth muscles in the walls of blood vessels.
B)the muscles of the stomach wall.
C)uterine muscles.
D)skeletal muscles.
A)the smooth muscles in the walls of blood vessels.
B)the muscles of the stomach wall.
C)uterine muscles.
D)skeletal muscles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following curves in the figure labeled below would represent a single uterine contraction in response to oxytocin? 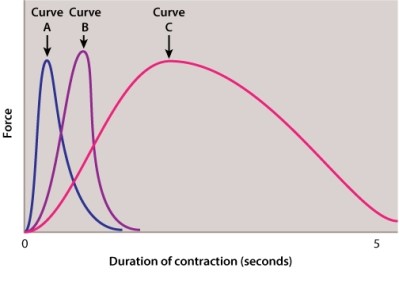
A)curve A
B)curve B
C)curve C

A)curve A
B)curve B
C)curve C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If a skeletal muscle is no longer able to make enough ATP, then:
A)the muscle will be unable to shorten.
B)actin and myosin in the sarcomeres are in the unbound state.
C)there will be low levels of acetylcholine at the motor endplate.
D)actin and myosin in the sarcomeres will remain bound.
A)the muscle will be unable to shorten.
B)actin and myosin in the sarcomeres are in the unbound state.
C)there will be low levels of acetylcholine at the motor endplate.
D)actin and myosin in the sarcomeres will remain bound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following are muscle cells that are active in vasoconstriction and vasodilation of blood vessels?
A)skeletal muscle cells
B)cardiac muscle cells
C)endocardium cells
D)smooth muscle cells
A)skeletal muscle cells
B)cardiac muscle cells
C)endocardium cells
D)smooth muscle cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is a muscle tissue that pumps blood throughout the body?
A)skeletal muscle
B)cardiac muscle
C)smooth muscle
A)skeletal muscle
B)cardiac muscle
C)smooth muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What stimulates a skeletal muscle cell to contract?
A)an impulse from a sensory neuron
B)an impulse from a motor neuron
C)auto-depolarizing cells in the membrane of muscle cells
D)hormones
A)an impulse from a sensory neuron
B)an impulse from a motor neuron
C)auto-depolarizing cells in the membrane of muscle cells
D)hormones

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the function of the protein titin?
A)It binds to myosin heads, enabling shortening of the muscle fiber.
B)It attaches the myosin thick filament to the Z disk at the end of the sarcomere.
C)It transports calcium into and out of the cell.
D)It regulates contraction of muscle cells.
A)It binds to myosin heads, enabling shortening of the muscle fiber.
B)It attaches the myosin thick filament to the Z disk at the end of the sarcomere.
C)It transports calcium into and out of the cell.
D)It regulates contraction of muscle cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
ATP hydrolysis allows for what component of skeletal muscle contraction?
A)the myosin head to bind to actin
B)the actin head to bind to tropomyosin
C)calcium levels in the cytoplasm to rise
D)the reorientation of tropomyosin and troponin
E)cocking of the myosin head to its high-energy position
A)the myosin head to bind to actin
B)the actin head to bind to tropomyosin
C)calcium levels in the cytoplasm to rise
D)the reorientation of tropomyosin and troponin
E)cocking of the myosin head to its high-energy position

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Myosin from a rabbit will bind to actin from an amoeba. What does this suggest about the evolution of the structures of actin and myosin?
A)The binding sites of actin and myosin are strongly conserved.
B)The binding sites of actin and myosin are highly variable.
C)The binding sites of actin and myosin are not subject to evolution.
D)There is no genetic basis to the structure of actin and myosin.
E)None of the answer options is correct.
A)The binding sites of actin and myosin are strongly conserved.
B)The binding sites of actin and myosin are highly variable.
C)The binding sites of actin and myosin are not subject to evolution.
D)There is no genetic basis to the structure of actin and myosin.
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Movement of multicellular animals is dependent on:
A)a mucous coating.
B)the action of muscle cells.
C)cilia and flagella.
D)the movement of mitochondria.
A)a mucous coating.
B)the action of muscle cells.
C)cilia and flagella.
D)the movement of mitochondria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Calcium is necessary to initiate muscle contraction. Which of the following molecules binds calcium?
A)myosin
B)actin
C)troponin
D)tropomyosin
A)myosin
B)actin
C)troponin
D)tropomyosin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The combination of a nerve impulse, neurotransmitter release at the neuromuscular junction, calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, and subsequent muscle contraction is known as:
A)an action potential.
B)threshold potential.
C)a motor event.
D)excitation-contraction coupling.
A)an action potential.
B)threshold potential.
C)a motor event.
D)excitation-contraction coupling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The functional unit of a muscle cell is:
A)a muscle fiber.
B)the sarcomere.
C)myosin.
D)actin.
A)a muscle fiber.
B)the sarcomere.
C)myosin.
D)actin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Skeletal muscle contraction is largely dependent on calcium ions that exit the:
A)extracellular space.
B)sarcoplasmic reticulum.
C)T-tubule.
D)Z disc.
A)extracellular space.
B)sarcoplasmic reticulum.
C)T-tubule.
D)Z disc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
You take a human smooth muscle cell and block the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. What effect does that have on contraction of that smooth muscle cell, and why?
A)Contraction is completely blocked because calcium binding to troponin is required for contraction.
B)Contraction is completely blocked because calcium binding to calmodulin is required for contraction.
C)Contraction still occurs because Ca2+ can enter the cell directly through Ca2+ channels in the plasma membrane and bind to troponin.
D)Contraction still occurs because Ca2+ can enter the cell directly through Ca2+ channels in the plasma membrane and bind to calmodulin.
E)Contraction still occurs because contraction in smooth muscle is completely independent of Ca2+ levels.
A)Contraction is completely blocked because calcium binding to troponin is required for contraction.
B)Contraction is completely blocked because calcium binding to calmodulin is required for contraction.
C)Contraction still occurs because Ca2+ can enter the cell directly through Ca2+ channels in the plasma membrane and bind to troponin.
D)Contraction still occurs because Ca2+ can enter the cell directly through Ca2+ channels in the plasma membrane and bind to calmodulin.
E)Contraction still occurs because contraction in smooth muscle is completely independent of Ca2+ levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What role does ATP play in the cross-bridge cycle?
A)The binding of ATP to myosin causes myosin to detach from actin.
B)The binding of ATP to myosin causes myosin to bind to actin.
C)The binding of ATP to myosin causes the myosin head to cock.
D)The binding of ATP to myosin produces the power stroke.
E)The binding of ATP to myosin forms a cross-bridge.
A)The binding of ATP to myosin causes myosin to detach from actin.
B)The binding of ATP to myosin causes myosin to bind to actin.
C)The binding of ATP to myosin causes the myosin head to cock.
D)The binding of ATP to myosin produces the power stroke.
E)The binding of ATP to myosin forms a cross-bridge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following graphs best depicts the relationship between the amount of isometric force (y-axis) produced by a muscle fiber and sarcomere length (x-axis)? 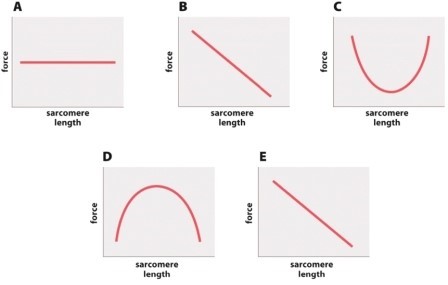
A)graph A
B)graph B
C)graph C
D)graph D
E)graph E

A)graph A
B)graph B
C)graph C
D)graph D
E)graph E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following is NOT a correct pairing of structure and function?
A)motor endplate: region of the motor neuron axon that releases acetylcholine
B)sarcoplasmic reticulum: modified endoplasmic reticulum that stores Ca2+
C)T-tubules: infoldings of the plasma membrane that conduct electrical signals deep into the muscle fiber
D)troponin: protein that moves tropomyosin when activated by Ca2+
E)tropomyosin: protein that lies between the helices in actin and blocks myosin-binding sites when the muscle is at rest
A)motor endplate: region of the motor neuron axon that releases acetylcholine
B)sarcoplasmic reticulum: modified endoplasmic reticulum that stores Ca2+
C)T-tubules: infoldings of the plasma membrane that conduct electrical signals deep into the muscle fiber
D)troponin: protein that moves tropomyosin when activated by Ca2+
E)tropomyosin: protein that lies between the helices in actin and blocks myosin-binding sites when the muscle is at rest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following statements regarding smooth muscle versus striated muscle is FALSE?
A)Calcium for skeletal muscle contraction enters the cell from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and through voltage-gated calcium channels in the plasma membrane, whereas the calcium for smooth muscle contraction enters the cell from the sarcoplasmic reticulum only.
B)Smooth muscle contraction is regulated by the binding of calcium to calmodulin, whereas skeletal muscle contraction is regulated by calcium interacting with the troponin-tropomyosin system.
C)Smooth muscle is activated by the autonomic nervous system, whereas skeletal muscle is activated by the somatic nervous system.
D)Separate enzymes mediate the binding of myosin to actin through phosphorylation and dephosphorylation in smooth muscle, whereas the myosin heads of skeletal muscle function as enzymes themselves to hydrolyze ATP.
E)Smooth muscle contracts longer and relaxes more slowly compared to skeletal muscle.
A)Calcium for skeletal muscle contraction enters the cell from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and through voltage-gated calcium channels in the plasma membrane, whereas the calcium for smooth muscle contraction enters the cell from the sarcoplasmic reticulum only.
B)Smooth muscle contraction is regulated by the binding of calcium to calmodulin, whereas skeletal muscle contraction is regulated by calcium interacting with the troponin-tropomyosin system.
C)Smooth muscle is activated by the autonomic nervous system, whereas skeletal muscle is activated by the somatic nervous system.
D)Separate enzymes mediate the binding of myosin to actin through phosphorylation and dephosphorylation in smooth muscle, whereas the myosin heads of skeletal muscle function as enzymes themselves to hydrolyze ATP.
E)Smooth muscle contracts longer and relaxes more slowly compared to skeletal muscle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following statements about muscle proteins is FALSE?
A)Actin filaments have globular heads.
B)Thick filaments consist of parallel bundles of myosin molecules.
C)Tropomyosin lies in a groove formed by the actin helices.
D)Titin connects myosin filaments to the Z disc.
E)Z discs are protein backbones that mark the boundaries of sarcomeres.
A)Actin filaments have globular heads.
B)Thick filaments consist of parallel bundles of myosin molecules.
C)Tropomyosin lies in a groove formed by the actin helices.
D)Titin connects myosin filaments to the Z disc.
E)Z discs are protein backbones that mark the boundaries of sarcomeres.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Muscles can produce forces when shortening and when lengthening.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Imagine that a researcher has dissected out a single muscle bundle from a triceps muscle biopsy. She sections this bundle and stains it for a variety of muscle-associated proteins. After this staining, when she zooms in on a sarcomere, she notices that a certain protein always dots the periphery along the length of the thin filaments. This protein is MOST likely:
A)actin.
B)myosin.
C)titin.
D)tropomyosin.
E)Z protein.
A)actin.
B)myosin.
C)titin.
D)tropomyosin.
E)Z protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A researcher is comparing the size of sarcomeres in mice to those in elephants. What will he find?
A)Sarcomere size is proportional to the size of the animal; sarcomeres of elephants will be much larger than sarcomeres in mice.
B)Sarcomere size is inversely proportional to animal size; sarcomeres in mice will be much larger than sarcomeres in elephants.
C)Sarcomere size is relatively constant in vertebrates. As a result, mouse and elephant sarcomeres will likely be equal in size.
D)It is impossible to determine sarcomere size in elephants and mice, given that sarcomeres are dynamic and are constantly changing in length and diameter.
A)Sarcomere size is proportional to the size of the animal; sarcomeres of elephants will be much larger than sarcomeres in mice.
B)Sarcomere size is inversely proportional to animal size; sarcomeres in mice will be much larger than sarcomeres in elephants.
C)Sarcomere size is relatively constant in vertebrates. As a result, mouse and elephant sarcomeres will likely be equal in size.
D)It is impossible to determine sarcomere size in elephants and mice, given that sarcomeres are dynamic and are constantly changing in length and diameter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following statements about muscles is CORRECT?
A)Smooth muscles contract more slowly than skeletal muscles.
B)Actin and myosin are arranged irregularly in cardiac and smooth muscles.
C)Skeletal muscles are striated, whereas cardiac muscles are not.
D)Striated muscles use actin and myosin to generate force, whereas smooth muscles do not.
E)Cardiac muscles are found in the heart and the walls of the arteries.
A)Smooth muscles contract more slowly than skeletal muscles.
B)Actin and myosin are arranged irregularly in cardiac and smooth muscles.
C)Skeletal muscles are striated, whereas cardiac muscles are not.
D)Striated muscles use actin and myosin to generate force, whereas smooth muscles do not.
E)Cardiac muscles are found in the heart and the walls of the arteries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The basic contractile unit of a muscle is called the:
A)sarcomere.
B)myofibril.
C)muscle fiber.
D)thick filament.
E)Z disc.
A)sarcomere.
B)myofibril.
C)muscle fiber.
D)thick filament.
E)Z disc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Why is calcium necessary for muscle contraction?
A)Calcium is needed to activate troponin so that tropomyosin can be moved to expose the myosin-binding sites on the actin filament.
B)Calcium is needed to allow the muscle fiber to become depolarized.
C)Calcium functions as a neurotransmitter and is released from the motor neuron.
D)Calcium is needed to cock the myosin head so that it can form a cross-bridge with actin.
E)Calcium is needed to detach the myosin from the actin.
A)Calcium is needed to activate troponin so that tropomyosin can be moved to expose the myosin-binding sites on the actin filament.
B)Calcium is needed to allow the muscle fiber to become depolarized.
C)Calcium functions as a neurotransmitter and is released from the motor neuron.
D)Calcium is needed to cock the myosin head so that it can form a cross-bridge with actin.
E)Calcium is needed to detach the myosin from the actin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following statements about muscle contraction is FALSE?
A)Actin and myosin filaments shorten during muscle contraction.
B)Sarcomere length is variable in invertebrates, but uniform in vertebrates.
C)Longer sarcomeres allow for a greater degree of shortening.
D)Actin and myosin filaments overlap more when a muscle is contracted than when it is relaxed.
E)Rapidly contracting muscles express myosin molecules that have higher rates of ATP hydrolysis.
A)Actin and myosin filaments shorten during muscle contraction.
B)Sarcomere length is variable in invertebrates, but uniform in vertebrates.
C)Longer sarcomeres allow for a greater degree of shortening.
D)Actin and myosin filaments overlap more when a muscle is contracted than when it is relaxed.
E)Rapidly contracting muscles express myosin molecules that have higher rates of ATP hydrolysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Striated muscles include:
A)cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle.
B)skeletal muscle.
C)cardiac muscle.
D)smooth muscle.
E)smooth muscle and skeletal muscle.
A)cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle.
B)skeletal muscle.
C)cardiac muscle.
D)smooth muscle.
E)smooth muscle and skeletal muscle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Vertebrate smooth muscle cells are activated when Ca+ binds to:
A)calmodulin.
B)troponin.
C)tropomyosin.
D)myosin kinase.
E)myosin.
A)calmodulin.
B)troponin.
C)tropomyosin.
D)myosin kinase.
E)myosin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The power stroke describes the:
A)pivoting of the myosin head, which causes actin and myosin to slide relative to each other.
B)binding of the myosin head to actin.
C)cocking of the myosin head by hydrolysis of ATP.
D)cycle of events involved in muscle contraction.
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)pivoting of the myosin head, which causes actin and myosin to slide relative to each other.
B)binding of the myosin head to actin.
C)cocking of the myosin head by hydrolysis of ATP.
D)cycle of events involved in muscle contraction.
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The five steps listed below are part of the cross-bridge cycle.
1) The myosin head binds to actin.
2) The myosin head is cocked back through the hydrolysis of ATP.
3) The actin filament slides relative to the myosin filament.
4) The myosin head binds ATP.
"5) The myosin head detaches from the actin.
Which of the following lists the steps in the CORRECT order?"
A)4, 5, 2, 1, 3
B)1, 4, 2, 3, 5
C)1, 2, 3, 4, 5
D)5, 4, 1, 2, 3
E)2, 1, 3, 5, 4
1) The myosin head binds to actin.
2) The myosin head is cocked back through the hydrolysis of ATP.
3) The actin filament slides relative to the myosin filament.
4) The myosin head binds ATP.
"5) The myosin head detaches from the actin.
Which of the following lists the steps in the CORRECT order?"
A)4, 5, 2, 1, 3
B)1, 4, 2, 3, 5
C)1, 2, 3, 4, 5
D)5, 4, 1, 2, 3
E)2, 1, 3, 5, 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The five steps listed below are involved in excitation-contraction coupling.
1) A wave of depolarization passes through the T-tubules.
2) Ca2+ binds to and causes a conformational change in troponin.
3) Tropomyosin moves to expose myosin-binding sites on the actin.
4) Ca2+ is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
"5) Cross-bridges form and produce a contraction.
Which of the following lists the steps in the CORRECT order of events?"
A)1, 4, 2, 3, 5
B)4, 5, 2, 1, 3
C)1, 2, 4, 3, 5
D)5, 4, 1, 2, 3
E)2, 1, 3, 5, 4
1) A wave of depolarization passes through the T-tubules.
2) Ca2+ binds to and causes a conformational change in troponin.
3) Tropomyosin moves to expose myosin-binding sites on the actin.
4) Ca2+ is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
"5) Cross-bridges form and produce a contraction.
Which of the following lists the steps in the CORRECT order of events?"
A)1, 4, 2, 3, 5
B)4, 5, 2, 1, 3
C)1, 2, 4, 3, 5
D)5, 4, 1, 2, 3
E)2, 1, 3, 5, 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Smooth muscles can be activated by all of the following EXCEPT:
A)the somatic nervous system.
B)hormones.
C)nitric oxide.
D)pH.
E)stretch of the muscle.
A)the somatic nervous system.
B)hormones.
C)nitric oxide.
D)pH.
E)stretch of the muscle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
At the level of actin and myosin molecules, what is producing force when a skeletal muscle contracts?
A)The binding of calcium to troponin.
B)The binding of ATP to the myosin head.
C)The hydrolysis of ATP to ADP + Pi.
D)The binding of myosin to actin.
E)None of the answer options is correct.
A)The binding of calcium to troponin.
B)The binding of ATP to the myosin head.
C)The hydrolysis of ATP to ADP + Pi.
D)The binding of myosin to actin.
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The power stroke corresponds to which event in muscle contraction?
A)detachment of myosin from actin
B)sliding of actin relative to myosin filaments
C)cocking of the myosin head
D)binding of the myosin head to actin
A)detachment of myosin from actin
B)sliding of actin relative to myosin filaments
C)cocking of the myosin head
D)binding of the myosin head to actin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A fast-twitch muscle would:
A)consume more ATP than slow-twitch fibers, but have fewer mitochondria.
B)obtain energy mainly through glycolysis.
C)have less resistance to fatigue than slow-twitch fibers.
D)All of these choices are correct.
A)consume more ATP than slow-twitch fibers, but have fewer mitochondria.
B)obtain energy mainly through glycolysis.
C)have less resistance to fatigue than slow-twitch fibers.
D)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Rattlesnakes contract their tail shaker muscles at frequencies up to 90 hertz (90 times a second) to create their rattling sound; they move their body muscles much more slowly (about 5 hertz) to slither around. Do you expect the tail shaker muscles to have a faster, slower, or the same type of myosin as the body muscles? Why?
A)faster, because contraction speed is correlated with rates of myosin binding and release from actin
B)the same, because there is no relationship between contraction speed and myosin properties
C)slower, because there is a negative relationship between contraction speed and rates of myosin binding and release from actin
D)slower, because there is a positive relationship between contraction speed and rates of myosin binding and release from actin
E)More information is needed, because there is no generalized relationship between contraction speed and force production.
A)faster, because contraction speed is correlated with rates of myosin binding and release from actin
B)the same, because there is no relationship between contraction speed and myosin properties
C)slower, because there is a negative relationship between contraction speed and rates of myosin binding and release from actin
D)slower, because there is a positive relationship between contraction speed and rates of myosin binding and release from actin
E)More information is needed, because there is no generalized relationship between contraction speed and force production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Maximum force is generated by a muscle contraction when:
A)overlap between actin and myosin is low.
B)there is excessive overlap between actin and myosin.
C)the sarcomere is at intermediate length before contraction begins.
D)intracellular calcium levels are low.
A)overlap between actin and myosin is low.
B)there is excessive overlap between actin and myosin.
C)the sarcomere is at intermediate length before contraction begins.
D)intracellular calcium levels are low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A muscle can exert force while remaining the same length (e.g., when you hold a heavy bucket of cattle feed in a fixed position). This is known as:
A)isometric contraction.
B)geometric contraction.
C)isometric relaxation.
D)shortening contraction.
A)isometric contraction.
B)geometric contraction.
C)isometric relaxation.
D)shortening contraction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Consider the figure below. Which of the points represents the ratio of shortening velocity to load at which the load on the muscle is equal to the force, or tension, the muscle is able to achieve? 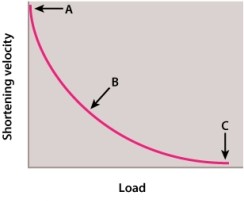
A)point A
B)point B
C)point C

A)point A
B)point B
C)point C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Rattlesnakes contract their tail shaker muscles at frequencies up to 90 hertz (90 times a second) to create their rattling sound. You compare the contraction frequency of rattlesnake tail muscles at 20°C and 35°C. Do you expect to see an effect of temperature on contraction frequency in this experiment? Why or why not?
A)no, because protein structure is not affected by temperature
B)no, because neither of these temperatures is seen in the natural environment of a rattlesnake
C)maybe, it would depend on whether the snakes are male or female
D)yes, because muscle contraction is an enzymatic process, and thus will be temperature dependent
E)yes, because all biological structures show changes when the temperature changes from 20°C to 35°C
A)no, because protein structure is not affected by temperature
B)no, because neither of these temperatures is seen in the natural environment of a rattlesnake
C)maybe, it would depend on whether the snakes are male or female
D)yes, because muscle contraction is an enzymatic process, and thus will be temperature dependent
E)yes, because all biological structures show changes when the temperature changes from 20°C to 35°C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What happens when action potentials stimulate a muscle at a rate that does NOT allow relaxation between individual action potentials?
A)The strength of contraction decreases with subsequent stimuli.
B)The strength of contraction increases with subsequent stimuli and reaches a steady plateau.
C)The strength of contraction does not change.
D)More motor units are recruited.
A)The strength of contraction decreases with subsequent stimuli.
B)The strength of contraction increases with subsequent stimuli and reaches a steady plateau.
C)The strength of contraction does not change.
D)More motor units are recruited.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following graphs best depicts the relationship between the amount of overlap between actin and myosin (y-axis) and sarcomere length (x-axis)? 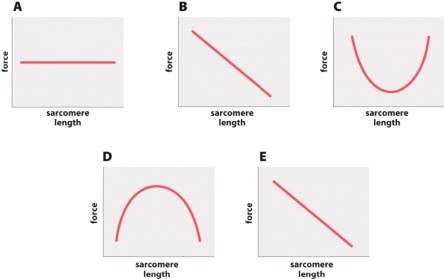
A)graph A
B)graph B
C)graph C
D)graph D
E)graph E

A)graph A
B)graph B
C)graph C
D)graph D
E)graph E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Muscle groups that produce similar motion, or work synergistically, at a joint are known as:
A)agonists.
B)antagonists.
C)synergists.
D)pro-agonists.
A)agonists.
B)antagonists.
C)synergists.
D)pro-agonists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Motion that causes two bones to move further apart from each other is known as:
A)flexion.
B)extension.
C)lengthening.
D)rotation.
A)flexion.
B)extension.
C)lengthening.
D)rotation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If a muscle contracts, all of the muscle fibers within that muscle must be contracting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Why isn't there a large muscle on the front of your tibia (your shin bone)?
A)Muscles are arranged in antagonistic pairs. The calf muscles, on the back of the tibia, are wide enough to act as an antagonistic pair for extension and flexion of the tibia.
B)Muscles are arranged in antagonistic pairs. Movement of the foot upwards requires less force than the force required to push against the ground when moving and standing.
C)Muscles are arranged in agonistic pairs. The calf muscles, on the back of the tibia, are wide enough to act as an agonistic pair for extension and flexion of the tibia.
D)Muscles are arranged in agonistic pairs. The knee joint has limited motion, and flexion of the tibia towards the front of the body is not possible.
A)Muscles are arranged in antagonistic pairs. The calf muscles, on the back of the tibia, are wide enough to act as an antagonistic pair for extension and flexion of the tibia.
B)Muscles are arranged in antagonistic pairs. Movement of the foot upwards requires less force than the force required to push against the ground when moving and standing.
C)Muscles are arranged in agonistic pairs. The calf muscles, on the back of the tibia, are wide enough to act as an agonistic pair for extension and flexion of the tibia.
D)Muscles are arranged in agonistic pairs. The knee joint has limited motion, and flexion of the tibia towards the front of the body is not possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The interaction of two proteins-actin and myosin-allows the muscles of diverse animal species to generate force and produce movement. Given this, which of the following are TRUE statements?
A)The evolution of muscle contractile function is a highly conserved process.
B)The evolution of muscle contractile function shows great diversity in a number of different animal groups.
C)The force that animal muscles can produce depends on the amount of overlap between actin and myosin protein filaments because this overlap affects the number of actin cross-bridges that can form with myosin binding sites.
D)The force that animal muscles can produce depends on the amount of overlap between actin and myosin protein filaments, because this overlap affects the number of myosin cross-bridges that can form with actin binding sites.
A)The evolution of muscle contractile function is a highly conserved process.
B)The evolution of muscle contractile function shows great diversity in a number of different animal groups.
C)The force that animal muscles can produce depends on the amount of overlap between actin and myosin protein filaments because this overlap affects the number of actin cross-bridges that can form with myosin binding sites.
D)The force that animal muscles can produce depends on the amount of overlap between actin and myosin protein filaments, because this overlap affects the number of myosin cross-bridges that can form with actin binding sites.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Muscles that contract slowly and use less ATP to generate their force:
A)contain primarily small motor units.
B)contain primarily fast-twitch fibers.
C)contain primarily slow-twitch fibers.
D)obtain their energy primarily through anaerobic glycolytic processes.
A)contain primarily small motor units.
B)contain primarily fast-twitch fibers.
C)contain primarily slow-twitch fibers.
D)obtain their energy primarily through anaerobic glycolytic processes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Muscle force is increased by increasing:
A)motor neuron firing rate.
B)the number of activated motor units.
C)the distance between muscle fibers.
D)the motor neuron firing rate and the number of activated motor units.
A)motor neuron firing rate.
B)the number of activated motor units.
C)the distance between muscle fibers.
D)the motor neuron firing rate and the number of activated motor units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Muscles do not produce any force unless they are shortening or lengthening.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following is the type of skeletal muscle fiber associated with stamina and endurance?
A)smooth muscle
B)glycolytic fast-twitch fibers
C)oxidative slow-twitch fibers
D)isometric motor units
A)smooth muscle
B)glycolytic fast-twitch fibers
C)oxidative slow-twitch fibers
D)isometric motor units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Usain Bolt, a world champion sprinter, can run a 10 m split in 0.82 s. Say you obtain a quadriceps muscle sample from Usain Bolt and compare it to one from a 25-year-old male long-distance runner. What differences do you expect to observe between those two muscle samples?
A)more fast-twitch fibers in Usain Bolt's leg muscles
B)more mitochondria in Usain Bolt's leg muscles
C)red and white muscle fibers of larger cross-sectional area in Usain Bolt's leg muscles
A)more fast-twitch fibers in Usain Bolt's leg muscles
B)more mitochondria in Usain Bolt's leg muscles
C)red and white muscle fibers of larger cross-sectional area in Usain Bolt's leg muscles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Muscle contractions have _____ force at slower shortening contraction velocities compared to higher shortening contraction velocities.
A)increased
B)decreased
C)equal
D)less stable
A)increased
B)decreased
C)equal
D)less stable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
You control your posture with fast-twitch muscles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



