Deck 35: Animal Nervous Systems
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/157
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 35: Animal Nervous Systems
1
Why are sensory organs, such as eyes, located on the surface of the body?
A)Their location is adaptive; it allows sensory organs to receive input from the environment.
B)Their location is adaptive; it allows sensory organs to receive input from the central nervous system.
C)Their location is an artifact of development; these structures are derived from mesoderm.
D)Their location is an artifact of development; these structures are derived from endoderm.
E)None of the answer options is correct; there is a better explanation that is not listed.
A)Their location is adaptive; it allows sensory organs to receive input from the environment.
B)Their location is adaptive; it allows sensory organs to receive input from the central nervous system.
C)Their location is an artifact of development; these structures are derived from mesoderm.
D)Their location is an artifact of development; these structures are derived from endoderm.
E)None of the answer options is correct; there is a better explanation that is not listed.
A
2
When a gazelle senses a predator, which action is under voluntary control?
A)running
B)faster heartbeat
C)dilation of blood vessels supplying the muscles
A)running
B)faster heartbeat
C)dilation of blood vessels supplying the muscles
A
3
An embryologist is looking at a cross-section of a mouse embryo. She notices that flanking either side of the neural tube (the rudiment of the spinal chord) are eggplant-shaped structures that contain many cell bodies. These structures are MOST likely:
A)ganglia.
B)nerve cords.
C)nerves.
D)myelin sheaths.
E)axon hillocks.
A)ganglia.
B)nerve cords.
C)nerves.
D)myelin sheaths.
E)axon hillocks.
A
4
When an environmental stimulus is received, the signal is usually transmitted through three types of nerve cells. In which order is the signal transmitted through these cells?
A)sensory neurons, motor neurons, interneurons
B)motor neurons, sensory neurons, interneurons
C)sensory neurons, interneurons, motor neurons
D)interneurons, sensory neurons, motor neurons
E)motor neurons, interneurons, sensory neurons
A)sensory neurons, motor neurons, interneurons
B)motor neurons, sensory neurons, interneurons
C)sensory neurons, interneurons, motor neurons
D)interneurons, sensory neurons, motor neurons
E)motor neurons, interneurons, sensory neurons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A)All animals have a nervous system.
B)All animals sense and respond to the environment.
C)It is necessary to have a nervous system to sense and respond to the environment.
D)All animals have a nervous system and it is necessary to have a nervous system to sense and respond to the environment, but not all animals sense and respond to the environment.
E)All animals have a nervous system, all animals sense and respond to the environment, and it is necessary to have a nervous system to sense and respond to the environment.
A)All animals have a nervous system.
B)All animals sense and respond to the environment.
C)It is necessary to have a nervous system to sense and respond to the environment.
D)All animals have a nervous system and it is necessary to have a nervous system to sense and respond to the environment, but not all animals sense and respond to the environment.
E)All animals have a nervous system, all animals sense and respond to the environment, and it is necessary to have a nervous system to sense and respond to the environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which group contains animals with a nerve net?
A)sponges
B)cnidarians
C)bilaterians
A)sponges
B)cnidarians
C)bilaterians

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Approximately how many nerve cells does a human have?
A)10 million
B)100 million
C)10 billion
D)100 billion
E)We do not have a good estimate of the number of nerve cells in a human body.
A)10 million
B)100 million
C)10 billion
D)100 billion
E)We do not have a good estimate of the number of nerve cells in a human body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Before the evolution of complex nervous systems, animals with very simple nervous systems, such as the nerve nets of cnidarians, could engage in the following behaviors EXCEPT:
A)finding a mate.
B)obtaining food.
C)choosing a suitable habitat.
D)regulating internal body functions.
E)sensing chemical cues in the environment.
A)finding a mate.
B)obtaining food.
C)choosing a suitable habitat.
D)regulating internal body functions.
E)sensing chemical cues in the environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Squid (shown in Figure 35.3) are predatory mollusks: They need to be able to detect both sedentary and highly mobile prey. Which of the following would you expect is NOT a property of this animal's nervous system? 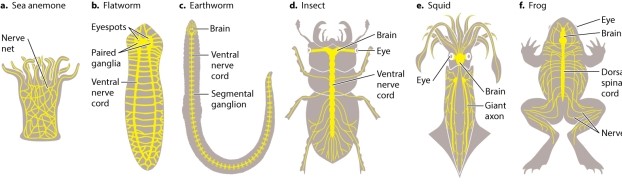
A)cephalization
B)nerve net
C)sense organs
D)bilateral symmetry

A)cephalization
B)nerve net
C)sense organs
D)bilateral symmetry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A young girl walking along the beach discovers a sea sponge washed up on the shore. She pokes it with her finger, and the animal contracts locally in response. Because the sea sponge reacted to her poke, the girl concludes that this animal has a brain. Is this conclusion correct?
A)Yes, if an animal responds to any type of touch or sensory signal, the animal must have a brain where such a signal is processed.
B)Yes, sea sponges are known to have brains; however, these structures are relatively simple compared to the brains of vertebrates.
C)No, sea sponges possess paired ganglia that process their responses to touch or environmental changes (much like flatworms).
D)No, sea sponges actually lack any type of nervous system-the reaction the girl observed is the result of a local population of touch-sensitive (non-neuronal)cells.
E)None of the answer options is correct.
A)Yes, if an animal responds to any type of touch or sensory signal, the animal must have a brain where such a signal is processed.
B)Yes, sea sponges are known to have brains; however, these structures are relatively simple compared to the brains of vertebrates.
C)No, sea sponges possess paired ganglia that process their responses to touch or environmental changes (much like flatworms).
D)No, sea sponges actually lack any type of nervous system-the reaction the girl observed is the result of a local population of touch-sensitive (non-neuronal)cells.
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What do all bilaterians have in common?
A)symmetrical right and left sides
B)a distinct back and front end
C)a brain instead of ganglia
A)symmetrical right and left sides
B)a distinct back and front end
C)a brain instead of ganglia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Echinoderms are descended from bilaterians, but many members of the group lack a brain, have no specialized sense organs, and have radial nerves that extend down each "arm" from a central nerve ring that surrounds the gut. What was a likely selective pressure in the evolution of this type of nervous system?
A)ability to move forward
B)role as a predator in the ecosystem
C)multicellularity
D)possession of an endoskeleton of calcium carbonate
E)None of the other answer options is correct.
A)ability to move forward
B)role as a predator in the ecosystem
C)multicellularity
D)possession of an endoskeleton of calcium carbonate
E)None of the other answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
All multicellular organisms have a nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is/are thought to be adaptive predatory characteristics?
A)cephalization
B)jaws
C)teeth
D)tongue
A)cephalization
B)jaws
C)teeth
D)tongue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is the basic functional unit of a nervous system?
A)a motor unit
B)an axon
C)a glial cell
D)a neuron
A)a motor unit
B)an axon
C)a glial cell
D)a neuron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding sea anemones?
A)Because sea anemones are "simple" organisms, these animals only possess motor neurons; sensory neurons or interneurons are never found in sea anemones.
B)Although sea anemones possess "net-like" nervous systems, these animals have brains located at their bases (near where they would attach to rocks).
C)Sponges-not sea anemones-possess what is considered to be the "simplest" nervous system found in animals.
D)Although sea anemones lack definitive brains, they do possess ganglia that serve a similar function to the paired ganglia of flatworms.
E)None of the answer options is correct.
A)Because sea anemones are "simple" organisms, these animals only possess motor neurons; sensory neurons or interneurons are never found in sea anemones.
B)Although sea anemones possess "net-like" nervous systems, these animals have brains located at their bases (near where they would attach to rocks).
C)Sponges-not sea anemones-possess what is considered to be the "simplest" nervous system found in animals.
D)Although sea anemones lack definitive brains, they do possess ganglia that serve a similar function to the paired ganglia of flatworms.
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A)All animals have a nervous system.
B)All animals sense and respond to the environment.
C)It is necessary to have a nervous system to sense and respond to the environment.
D)All animals have a nervous system and it is necessary to have a nervous system to sense and respond to the environment, but not all animals sense and respond to the environment.
E)All animals have a nervous system, all animals sense and respond to the environment, and it is necessary to have a nervous system to sense and respond to the environment.
A)All animals have a nervous system.
B)All animals sense and respond to the environment.
C)It is necessary to have a nervous system to sense and respond to the environment.
D)All animals have a nervous system and it is necessary to have a nervous system to sense and respond to the environment, but not all animals sense and respond to the environment.
E)All animals have a nervous system, all animals sense and respond to the environment, and it is necessary to have a nervous system to sense and respond to the environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is TRUE regarding cephalization?
A)Although most predatory vertebrates demonstrate cephalization, herbivores and other prey animals do not (as cephalization is thought to have evolved specifically in predators).
B)All multicellular organisms demonstrate cephalization, including both cnidarians and bilaterians.
C)The eyes of owls, the noses of bloodhounds, and the ears of bats could all be considered examples of cephalization (as each of these structures is associated with specialized sensory neurons, specific cranial ganglia and nerves).
D)Cephalization first appeared in the last common ancestor of cnidarians and bilaterians; it is not the result of convergent evolution.
E)Cephalization was initially believed to have evolved to assist in "backward" motion, as many organisms possess sensory organs at both their anterior and posterior ends.
A)Although most predatory vertebrates demonstrate cephalization, herbivores and other prey animals do not (as cephalization is thought to have evolved specifically in predators).
B)All multicellular organisms demonstrate cephalization, including both cnidarians and bilaterians.
C)The eyes of owls, the noses of bloodhounds, and the ears of bats could all be considered examples of cephalization (as each of these structures is associated with specialized sensory neurons, specific cranial ganglia and nerves).
D)Cephalization first appeared in the last common ancestor of cnidarians and bilaterians; it is not the result of convergent evolution.
E)Cephalization was initially believed to have evolved to assist in "backward" motion, as many organisms possess sensory organs at both their anterior and posterior ends.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What advantage(s) has the evolution of the brain provided over ganglia?
A)learning
B)complex behaviors
C)environmental perception
D)reaction to touch
A)learning
B)complex behaviors
C)environmental perception
D)reaction to touch

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Cephalization is thought to be an adaptation for:
A)taste perception.
B)forward locomotion.
C)predation.
D)organ function.
A)taste perception.
B)forward locomotion.
C)predation.
D)organ function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Where on the neuron are nerve impulses summed? 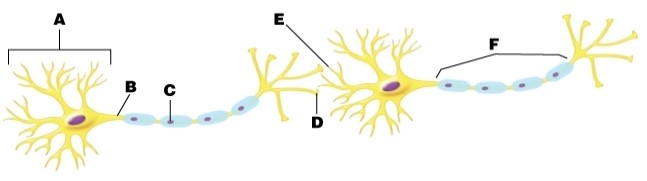
A)at letter A
B)at letter B
C)at letter C
D)at letter D
E)at letter E

A)at letter A
B)at letter B
C)at letter C
D)at letter D
E)at letter E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is NOT the role of an interneuron?
A)relaying information from sensory to motor neurons
B)conveying information from the internal environment of an animal
C)stimulating a muscle to contract
D)maintaining homeostasis
A)relaying information from sensory to motor neurons
B)conveying information from the internal environment of an animal
C)stimulating a muscle to contract
D)maintaining homeostasis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Sensory neurons are involved in all of the following EXCEPT:
A)taste.
B)vision.
C)muscle contraction.
D)hearing.
A)taste.
B)vision.
C)muscle contraction.
D)hearing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following animals possesses a brain?
A)earthworm
B)flatworm
C)sponge
D)cnidarian
A)earthworm
B)flatworm
C)sponge
D)cnidarian

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The earliest nervous system likely resembled a:
A)nerve cord.
B)ganglia.
C)simple brain and nerve cord.
D)nerve net.
A)nerve cord.
B)ganglia.
C)simple brain and nerve cord.
D)nerve net.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Cephalization is: the
A)development of a "head end" in an organism.
B)concentration of sensory organs within the head end of an animal.
C)development of a brain within the head of an animal.
D)All of these choices are correct.
A)development of a "head end" in an organism.
B)concentration of sensory organs within the head end of an animal.
C)development of a brain within the head of an animal.
D)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What character state distinguishes cnidarians from bilaterians in the phylogenetic tree in Figure 35.2? 
A)presence or absence of ganglia
B)presence or absence of sensory neurons
C)presence or absence of interneurons
D)presence or absence of motor neurons

A)presence or absence of ganglia
B)presence or absence of sensory neurons
C)presence or absence of interneurons
D)presence or absence of motor neurons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is NOT an advantage of cephalization?
A)ability to better detect and capture prey
B)ability to sense stimuli from the environment toward which an organism is moving
C)ability to quickly produce a suitable behavioral response to stimuli
D)ability to sense changes in environmental temperature
A)ability to better detect and capture prey
B)ability to sense stimuli from the environment toward which an organism is moving
C)ability to quickly produce a suitable behavioral response to stimuli
D)ability to sense changes in environmental temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Although animal nervous systems differ in complexity, their nerve cells are still remarkably similar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An important function of myelin is to:
A)increase the size of the synaptic cleft.
B)decrease the size of the synaptic cleft.
C)increase the speed of nerve signal transmission along the axon.
D)decrease the speed of nerve signal transmission along the axon.
E)None of the answer options is correct.
A)increase the size of the synaptic cleft.
B)decrease the size of the synaptic cleft.
C)increase the speed of nerve signal transmission along the axon.
D)decrease the speed of nerve signal transmission along the axon.
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Ligand-gated ion channels are found within the postsynaptic neuron's cell membrane. Why are ligand-gated ion channels critical to how synapses communicate information?
A)Ligand-gated ion channels enable specific neurotransmitters released by presynaptic neurons to exert either excitatory or inhibitory effects on the postsynaptic cell.
B)Ligand-gated ion channels open more rapidly than voltage-gated ion channels.
C)Ligand-gated ion channels allow the postsynaptic cell to control, through intracellular signaling, to which neurotransmitters the postsynaptic cell responds.
D)Ligand-gated ion channels are found within a neuron's dendrites but not its axon.
A)Ligand-gated ion channels enable specific neurotransmitters released by presynaptic neurons to exert either excitatory or inhibitory effects on the postsynaptic cell.
B)Ligand-gated ion channels open more rapidly than voltage-gated ion channels.
C)Ligand-gated ion channels allow the postsynaptic cell to control, through intracellular signaling, to which neurotransmitters the postsynaptic cell responds.
D)Ligand-gated ion channels are found within a neuron's dendrites but not its axon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Consider the figure of a motor neuron shown below. Which areas of the motor neuron are myelinated? 
A)the dendrites
B)the axon terminals
C)the axon before (to the left of)the cell body
D)the axon after (to the right of)the cell body
E)the entire axon

A)the dendrites
B)the axon terminals
C)the axon before (to the left of)the cell body
D)the axon after (to the right of)the cell body
E)the entire axon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is consistent about the structure of all four types of neurons shown in the figure? 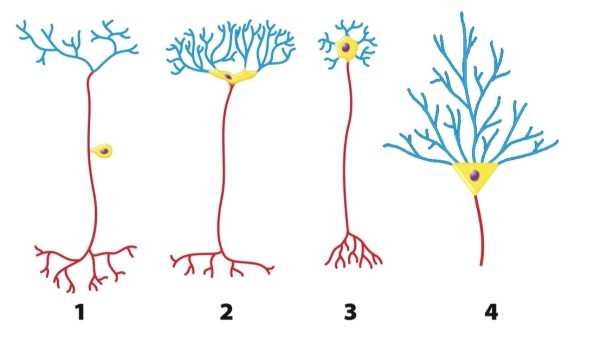
A)Each type has a region, called the cell body, that contains the nucleus.
B)Each type has a series of projections, called the dendrites, specialized for receiving information.
C)Each type has a region, called the axon, specialized for transmitting information.
D)All aspects of neuronal structure are completely consistent in the diagrams shown above.
E)Each type has a region, called the cell body, that contains the nucleus; each type has a series of projections, called the dendrites, specialized for receiving information; each type has a region, called the axon, specialized for transmitting information, but not all aspects of neuronal structure are completely consistent in the diagrams shown above.

A)Each type has a region, called the cell body, that contains the nucleus.
B)Each type has a series of projections, called the dendrites, specialized for receiving information.
C)Each type has a region, called the axon, specialized for transmitting information.
D)All aspects of neuronal structure are completely consistent in the diagrams shown above.
E)Each type has a region, called the cell body, that contains the nucleus; each type has a series of projections, called the dendrites, specialized for receiving information; each type has a region, called the axon, specialized for transmitting information, but not all aspects of neuronal structure are completely consistent in the diagrams shown above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In the figure, arrow B is pointing at the _____ in the _____. 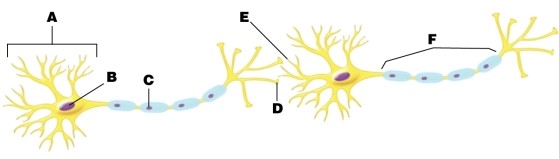
A)nucleus; glial cell
B)nucleus; cell body
C)vesicle; dendrite
D)neurotransmitter; synaptic cleft
E)synaptic cleft; neuron

A)nucleus; glial cell
B)nucleus; cell body
C)vesicle; dendrite
D)neurotransmitter; synaptic cleft
E)synaptic cleft; neuron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The functional relationship between glial cells and neurons is analogous to the functional relationship between what cell types in plants?
A)cork cambium cells and primary meristem
B)tracheids and vessel elements.
C)parenchyma and schlerenchyma
D)companion cells and sieve tube elements
E)epidermal cells and companion cells
A)cork cambium cells and primary meristem
B)tracheids and vessel elements.
C)parenchyma and schlerenchyma
D)companion cells and sieve tube elements
E)epidermal cells and companion cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Neuron _____ in the figure is a motor neuron; its function is _____. 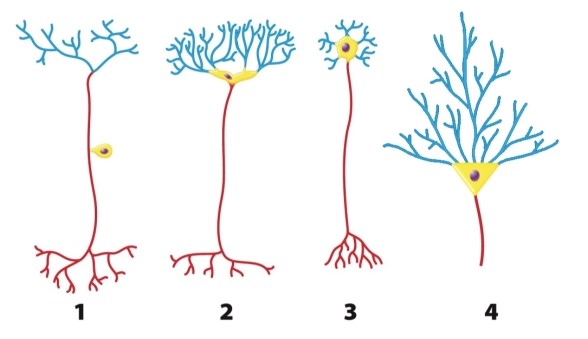
A)1; connecting different types of neurons
B)2; receiving incoming information or "sensing"
C)2; stimulating muscles or glands
D)3; stimulating muscles or glands
E)3; connecting different types of neurons

A)1; connecting different types of neurons
B)2; receiving incoming information or "sensing"
C)2; stimulating muscles or glands
D)3; stimulating muscles or glands
E)3; connecting different types of neurons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following types of animals lacks a nervous system?
A)spiders
B)sponges
C)squid
D)sea anemones
A)spiders
B)sponges
C)squid
D)sea anemones

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In the accompanying diagram, why does the pyramidal cell, neuron 4, illustrate the concept of information integration in the nervous system? 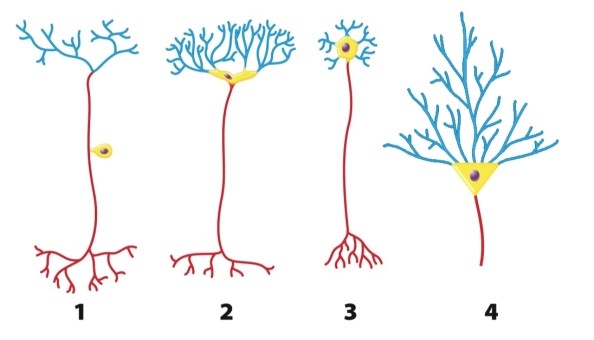
A)It has many dendrites and a single axon.
B)It has a cell membrane.
C)It is an excitable cell.
D)It has a nucleus, in which transcription and translation occur.
E)All of these are features of the pyramidal cell that illustrate the concept of information integration.

A)It has many dendrites and a single axon.
B)It has a cell membrane.
C)It is an excitable cell.
D)It has a nucleus, in which transcription and translation occur.
E)All of these are features of the pyramidal cell that illustrate the concept of information integration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Voltage-gated ion channels underlie the function of electrically excitable cells, such as nerve and muscle cells. Which of the following statements is TRUE about voltage-gated ion channels?
A)Voltage-gated ion channels open and close in response to changes in membrane potential.
B)Voltage-gated ion channels vary in terms of how rapidly they respond to changes in membrane potential.
C)Voltage-gated ion channels involve a conformational change of the transmembrane protein in response to membrane voltage that changes the channel's permeability to ion flow through the channel.
D)All of these choices are correct.
A)Voltage-gated ion channels open and close in response to changes in membrane potential.
B)Voltage-gated ion channels vary in terms of how rapidly they respond to changes in membrane potential.
C)Voltage-gated ion channels involve a conformational change of the transmembrane protein in response to membrane voltage that changes the channel's permeability to ion flow through the channel.
D)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following BEST outlines the evolution of a brain?
A)interneuron ganglia brain
B)nerve cord ganglia brain
C)nerve cord interneuron brain
D)nerve cord nerve net brain
A)interneuron ganglia brain
B)nerve cord ganglia brain
C)nerve cord interneuron brain
D)nerve cord nerve net brain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Different types of neurons tend to differ in their:
A)function.
B)size and shape.
C)number of extensions.
A)function.
B)size and shape.
C)number of extensions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In the figure, which arrow points at the axon hillock? 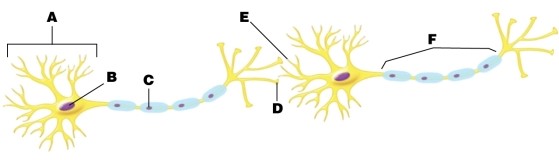
A)arrow A
B)arrow C
C)arrow E
D)arrow F
E)None of the answer options is correct.

A)arrow A
B)arrow C
C)arrow E
D)arrow F
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What aspect(s) of a neuron is/are consistent in the diagram? 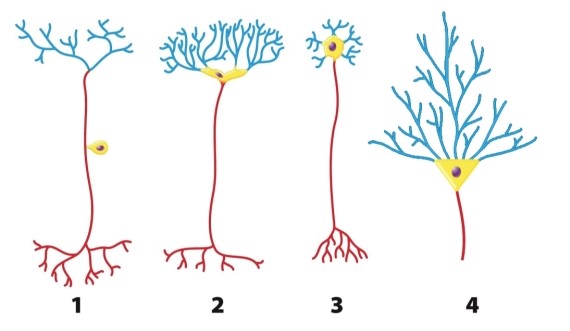
A)the shape of the cell body
B)the branching patterns of dendrites and axon terminals
C)the presence of axons and dendrites
D)the length of the axon
E)the number of potential connections between that neuron and its neighbors

A)the shape of the cell body
B)the branching patterns of dendrites and axon terminals
C)the presence of axons and dendrites
D)the length of the axon
E)the number of potential connections between that neuron and its neighbors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Membrane potential is determined by the:
A)number and types of ion-channel proteins present in the plasma membrane of a cell.
B)difference in concentration of ions and charged molecules on the two sides of a cell's plasma membrane.
C)number and type of phospholipids present in a membrane.
D)concentration of cholesterol in a membrane.
A)number and types of ion-channel proteins present in the plasma membrane of a cell.
B)difference in concentration of ions and charged molecules on the two sides of a cell's plasma membrane.
C)number and type of phospholipids present in a membrane.
D)concentration of cholesterol in a membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The action potential travels down:
A)the dendrite.
B)the synapse.
C)the axon.
D)both the dendrite and axon.
A)the dendrite.
B)the synapse.
C)the axon.
D)both the dendrite and axon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Neurons can synapse with many different types of cells, including muscle cells, secretory cells, and other neurons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Where on a neuron would you expect to find myelin?
A)around the dendrites
B)at the axon hillock
C)around and along the axon
D)around the dendrites and axon, and along the axon
A)around the dendrites
B)at the axon hillock
C)around and along the axon
D)around the dendrites and axon, and along the axon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The decision to initiate an action potential in a neuron is made at the:
A)synapse.
B)axon hillock.
C)cell body.
D)dendrite.
A)synapse.
B)axon hillock.
C)cell body.
D)dendrite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What happens when a ligand binds to a ligand-gated Na+ channel?
A)Sodium ions flow passively from high concentration to low concentration.
B)Sodium ions are pumped from low concentration to high concentration.
C)Sodium ions flow passively from low concentration to high concentration.
D)There is no net flow of sodium ions.
A)Sodium ions flow passively from high concentration to low concentration.
B)Sodium ions are pumped from low concentration to high concentration.
C)Sodium ions flow passively from low concentration to high concentration.
D)There is no net flow of sodium ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Neuronal stimuli are received by:
A)dendrites.
B)axons.
C)neurotransmitters.
D)cell nuclei.
A)dendrites.
B)axons.
C)neurotransmitters.
D)cell nuclei.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is TRUE of astrocytes?
A)They are a specific type of glial cell.
B)They surround blood vessels in the brain.
C)They contribute to the blood-brain barrier.
A)They are a specific type of glial cell.
B)They surround blood vessels in the brain.
C)They contribute to the blood-brain barrier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which part of a neuron is associated with receiving information?
A)dendrite
B)cell body
C)axon
D)synapse
A)dendrite
B)cell body
C)axon
D)synapse

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
An astrocyte is a type of:
A)glial cell.
B)sensory neuron.
C)interneuron.
D)motor neuron.
A)glial cell.
B)sensory neuron.
C)interneuron.
D)motor neuron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Ganglia were the evolutionary precursor to the centralized concentration of neurons that we now call a brain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is found in the synapse?
A)nucleus
B)neurotransmitter
C)cell body
D)myelin sheath
A)nucleus
B)neurotransmitter
C)cell body
D)myelin sheath

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What is consistent about the structure of all four types of neurons shown in the figure? 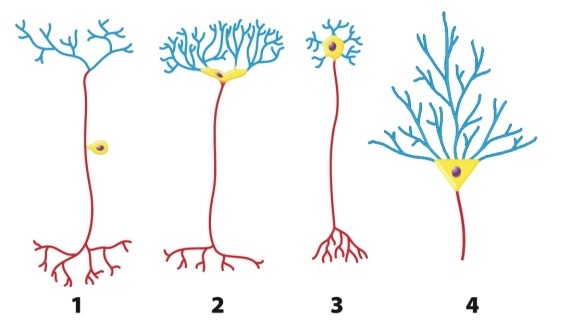
A)Each type has a region, called the cell body, that contains the nucleus.
B)Each type has a series of projections, called the dendrites, specialized for receiving information.
C)Each type has a region, called the axon, specialized for transmitting information.
D)All aspects of neuronal structure are completely consistent in the diagrams.
E)Each type has a region, called the cell body, that contains the nucleus; each type has a series of projections, called the dendrites, specialized for receiving information; each type has a region, called the axon, specialized for transmitting information, but not all aspects of neuronal structure are completely consistent in the diagrams.

A)Each type has a region, called the cell body, that contains the nucleus.
B)Each type has a series of projections, called the dendrites, specialized for receiving information.
C)Each type has a region, called the axon, specialized for transmitting information.
D)All aspects of neuronal structure are completely consistent in the diagrams.
E)Each type has a region, called the cell body, that contains the nucleus; each type has a series of projections, called the dendrites, specialized for receiving information; each type has a region, called the axon, specialized for transmitting information, but not all aspects of neuronal structure are completely consistent in the diagrams.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A neuron that responds to the environment is a(n):
A)interneuron.
B)motor neuron.
C)homeostatic neuron.
D)sensory neuron.
A)interneuron.
B)motor neuron.
C)homeostatic neuron.
D)sensory neuron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What type of cells produce myelin for sensory neurons?
A)melanocytes
B)astrocytes
C)glial cells
D)pyramidal neurons
A)melanocytes
B)astrocytes
C)glial cells
D)pyramidal neurons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The resting membrane potential of a neuron is determined by:
A)movement of potassium ions relative to other ions.
B)negatively charged proteins on the outside of the cell.
C)activation of voltage-gated sodium channels.
D)diffusion of potassium ions through sodium ion channels.
A)movement of potassium ions relative to other ions.
B)negatively charged proteins on the outside of the cell.
C)activation of voltage-gated sodium channels.
D)diffusion of potassium ions through sodium ion channels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The area within the neuron where stimuli are summed is called the:
A)dendrites.
B)cell body.
C)axon terminal.
D)axon hillock.
E)synapse.
A)dendrites.
B)cell body.
C)axon terminal.
D)axon hillock.
E)synapse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The ability of a postsynaptic cell to respond to a neurotransmitter depends on:
A)an action potential in the presynaptic cell.
B)release of neurotransmitter from the presynaptic cell.
C)presence of ligand-gated ion channel receptors on the postsynaptic cell.
D)All of these choices are correct.
A)an action potential in the presynaptic cell.
B)release of neurotransmitter from the presynaptic cell.
C)presence of ligand-gated ion channel receptors on the postsynaptic cell.
D)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What part of a cell's cytoplasm is responsible for the diversity of nerve cell shape?
A)the cytoskeleton
B)the endomembrane system
C)the nucleus
D)All of these choices are correct.
A)the cytoskeleton
B)the endomembrane system
C)the nucleus
D)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Imagine that a researcher is examining the positioning of synaptic clefts in a region of the nervous system of adult mice. In one of his mice, he notices that synaptic clefts are about 100 nm wide. What can be said of this mouse?
A)This is a normal or wild-type mouse; synaptic clefts are generally 100 to 500 nm wide.
B)This is likely a mutant mouse (as synaptic clefts are typically 10 to 20 nm wide); however, as neurotransmitters function better over long distances, this mouse will respond quicker to stimuli.
C)This is likely a mutant mouse (as synaptic clefts are typically 10 to 20 nm wide). Given that neurotransmitters act over short distances, this mouse may demonstrate delayed and diminished responses to stimuli.
D)This is likely a mutant mouse, as synaptic clefts directly connect the cytoplasm of presynaptic and postsynaptic cells (there is no space in between these cells). However, the width of this synaptic cleft will not affect the response of the mouse to stimuli.
E)None of the answer options is correct.
A)This is a normal or wild-type mouse; synaptic clefts are generally 100 to 500 nm wide.
B)This is likely a mutant mouse (as synaptic clefts are typically 10 to 20 nm wide); however, as neurotransmitters function better over long distances, this mouse will respond quicker to stimuli.
C)This is likely a mutant mouse (as synaptic clefts are typically 10 to 20 nm wide). Given that neurotransmitters act over short distances, this mouse may demonstrate delayed and diminished responses to stimuli.
D)This is likely a mutant mouse, as synaptic clefts directly connect the cytoplasm of presynaptic and postsynaptic cells (there is no space in between these cells). However, the width of this synaptic cleft will not affect the response of the mouse to stimuli.
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Neurotransmitters are stored in vesicles at the axon terminal. Assuming a neurotransmitter is a protein, where was it synthesized?
A)the cytoplasm
B)the rough endoplasmic reticulum
C)the Golgi apparatus
D)the lysosome
A)the cytoplasm
B)the rough endoplasmic reticulum
C)the Golgi apparatus
D)the lysosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Where are postsynaptic cell receptor proteins synthesized?
A)the Golgi apparatus
B)the cytoplasm
C)the rough endoplasmic reticulum
D)the lysosome
A)the Golgi apparatus
B)the cytoplasm
C)the rough endoplasmic reticulum
D)the lysosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Where in the plasma membrane of these cells would you find voltage-gated Ca2+ channels? 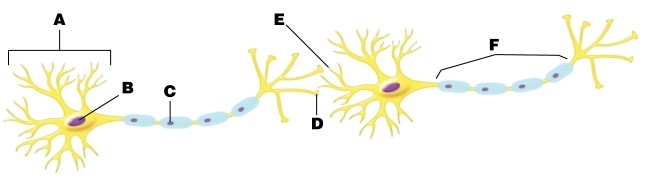
A)at letter A
B)at letter B
C)at letter C
D)at letter D
E)at letter E

A)at letter A
B)at letter B
C)at letter C
D)at letter D
E)at letter E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What cellular component of a sensory neuron would account for its specialization in response to physical or chemical cues?
A)the phospholipid composition of its plasma membrane
B)the shape of the neuron
C)the proteins present in its cytosol or on its plasma membrane
D)both the shape of the cell and the proteins in its cytosol or membrane
A)the phospholipid composition of its plasma membrane
B)the shape of the neuron
C)the proteins present in its cytosol or on its plasma membrane
D)both the shape of the cell and the proteins in its cytosol or membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following is TRUE of chemical synapses?
A)They are more common than electrical synapses.
B)Vesicles fuse with the presynaptic membrane to release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft.
C)Once released from postsynaptic membrane receptors, neurotransmitter molecules may be actively returned to the presynaptic cell.
A)They are more common than electrical synapses.
B)Vesicles fuse with the presynaptic membrane to release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft.
C)Once released from postsynaptic membrane receptors, neurotransmitter molecules may be actively returned to the presynaptic cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which excitatory neurotransmitter is directly responsible for muscle contraction in vertebrates?
A)dopamine
B)norepinephrine
C)nitrous oxide
D)glutamate
E)acetylcholine
A)dopamine
B)norepinephrine
C)nitrous oxide
D)glutamate
E)acetylcholine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Myelination of neurons in the brain is the product of:
A)glandular cells.
B)glial cells.
C)astrocytes.
D)interneurons.
A)glandular cells.
B)glial cells.
C)astrocytes.
D)interneurons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Imagine you created a toxin such that when a neuron fired an action potential, the toxin would bind immediately to the sodium-potassium pump at the top of the action potential, but the sodium and potassium channels would still function. What process(es) would be affected?
A)maintaining resting potential
B)returning to resting potential after the hyperpolarization phase of an action potential
C)the depolarization phase of an action potential
D)the hyperpolarization phase of an action potential
E)maintaining resting potential and returning to resting potential after the hyperpolarization phase of an action potential
A)maintaining resting potential
B)returning to resting potential after the hyperpolarization phase of an action potential
C)the depolarization phase of an action potential
D)the hyperpolarization phase of an action potential
E)maintaining resting potential and returning to resting potential after the hyperpolarization phase of an action potential

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Where would you expect to find ligand-gated ion channels in the plasma membranes of these cells? 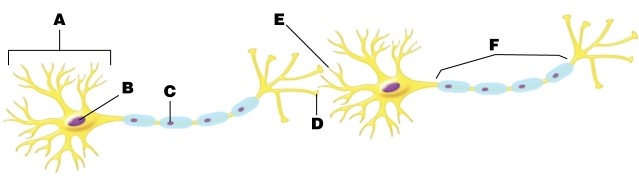
A)at letter C
B)at letter D
C)at letter E
D)at letter F
E)at letter C, letter D, letter E, and letter F

A)at letter C
B)at letter D
C)at letter E
D)at letter F
E)at letter C, letter D, letter E, and letter F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following are TRUE about the resting membrane potential?
A)It results from the sodium-potassium pump moving more Na+ ions out of the cell than K+ ions into the cell.
B)It results from K+ ions diffusing out of the cell.
C)It results from voltage-gated sodium channels remaining open for long periods of time.
A)It results from the sodium-potassium pump moving more Na+ ions out of the cell than K+ ions into the cell.
B)It results from K+ ions diffusing out of the cell.
C)It results from voltage-gated sodium channels remaining open for long periods of time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The release of neurotransmitter from the presynaptic cell is an example of:
A)phagocytosis.
B)endocytosis.
C)transcytosis.
D)exocytosis.
A)phagocytosis.
B)endocytosis.
C)transcytosis.
D)exocytosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding axons and dendrites?
A)In a neuron, axons typically receive signals and dendrites typically transmit or send signals.
B)Neurons generally possess more axons than dendrites.
C)The dendrite terminal is the site where neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic cleft.
D)Action potentials travel along neuron axons.
E)None of the answer options is correct.
A)In a neuron, axons typically receive signals and dendrites typically transmit or send signals.
B)Neurons generally possess more axons than dendrites.
C)The dendrite terminal is the site where neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic cleft.
D)Action potentials travel along neuron axons.
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Atropine is a poison that blocks nerve action by binding to ACh receptors. Where would you expect to find atropine bound on the figure? 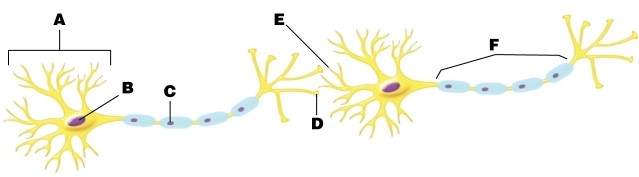
A)at letter C
B)at letter D
C)at letter E
D)at letter F
E)at letter C, letter D, letter E, and letter F

A)at letter C
B)at letter D
C)at letter E
D)at letter F
E)at letter C, letter D, letter E, and letter F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The magnitude of the action potential is correlated with the strength of the stimulating input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Imagine you genetically engineered a neuron to produce voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels that opened at the same time in response to a change in voltage. How would that change the recording shown in the figure? 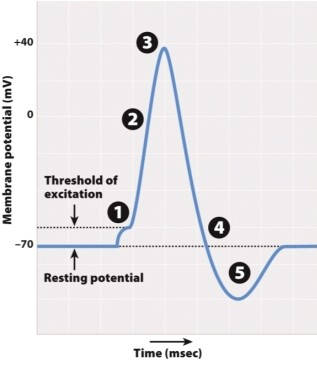
A)The peak voltage would be higher.
B)The peak would occur over a longer period of time.
C)The period of hyperpolarization would be longer.
D)No action potential would be generated.
E)Threshold values would increase.

A)The peak voltage would be higher.
B)The peak would occur over a longer period of time.
C)The period of hyperpolarization would be longer.
D)No action potential would be generated.
E)Threshold values would increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What cell type contributes to the formation of the blood-brain barrier?
A)epithelial
B)interneurons
C)neurons
D)astrocytes
A)epithelial
B)interneurons
C)neurons
D)astrocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following scenarios will MOST likely trigger an action potential?
A)multiple EPSPs arriving close in time at a single synapse (temporal summation)on the postsynaptic cell
B)single EPSPs arriving simultaneously at several different synapses (spatial summation)on the postsynaptic cell
C)an EPSP and an IPSP arriving simultaneously on the postsynaptic cell (cancellation)
A)multiple EPSPs arriving close in time at a single synapse (temporal summation)on the postsynaptic cell
B)single EPSPs arriving simultaneously at several different synapses (spatial summation)on the postsynaptic cell
C)an EPSP and an IPSP arriving simultaneously on the postsynaptic cell (cancellation)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



