Deck 36: Animal Sensory Systems and Brain Function
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/205
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 36: Animal Sensory Systems and Brain Function
1
Mechanoreceptors present in human skin are involved in tactile sensation. Where are the cell bodies of these mechanoreceptors located?
A)in the brain
B)in ganglia near the spinal cord
C)in the spinal cord
D)in the dermal layer of the skin near the sensory endings of the mechanoreceptors
A)in the brain
B)in ganglia near the spinal cord
C)in the spinal cord
D)in the dermal layer of the skin near the sensory endings of the mechanoreceptors
B
2
Which of the following is the chemical substance that allows the transmission of an impulse from a sensory neuron across a synapse to another neuron?
A)receptor
B)hormone
C)sodium
D)neurotransmitter
A)receptor
B)hormone
C)sodium
D)neurotransmitter
D
3
Diagram A below shows a stimulus applied to a sensory cell, and diagram B is the pattern of action potentials generated in response. 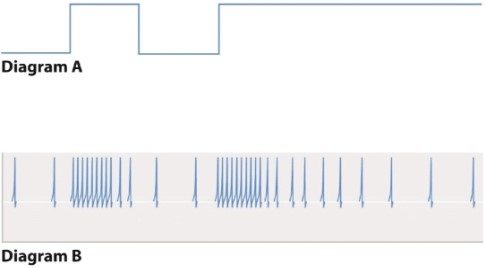 This pattern of action potentials:
This pattern of action potentials:
A)permits discrimination between different kinds of stimuli.
B)improves the simultaneous detection of two kinds of stimuli-for example, smell and taste.
C)allows an animal to constantly measure the strength of a continuing input.
D)allows an animal to detect the onset of a new stimulus. /12
 This pattern of action potentials:
This pattern of action potentials:A)permits discrimination between different kinds of stimuli.
B)improves the simultaneous detection of two kinds of stimuli-for example, smell and taste.
C)allows an animal to constantly measure the strength of a continuing input.
D)allows an animal to detect the onset of a new stimulus. /12
D
4
Nociceptors have a protective function. What is that function?
A)avoidance of cold temperatures
B)avoidance of conditions that cause pain, and thus bodily harm
C)control of emotional outbursts
D)smoothing out pressure fluctuations (as in cases of high blood pressure)
A)avoidance of cold temperatures
B)avoidance of conditions that cause pain, and thus bodily harm
C)control of emotional outbursts
D)smoothing out pressure fluctuations (as in cases of high blood pressure)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Over time, a sensory neuron will decrease its responsiveness to a specific signal. This behavior is known as:
A)accommodation.
B)appreciation.
C)adaptation.
D)alleviation.
A)accommodation.
B)appreciation.
C)adaptation.
D)alleviation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which one of the following is a type of sensory receptor that senses changes in blood pressure?
A)chemoreceptor
B)mechanoreceptor
C)proprioceptor
D)nociceptor
A)chemoreceptor
B)mechanoreceptor
C)proprioceptor
D)nociceptor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Some fish have electroreceptors that detect weak electrical signals. The function of these electroreceptors is to:
A)avoid dangerous situations.
B)identify potential mates.
C)help photosensitive species avoid excessive light.
A)avoid dangerous situations.
B)identify potential mates.
C)help photosensitive species avoid excessive light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Sensory receptors convert _____ into _____ by signal transduction.
A)neurotransmitters; synapses
B)physical or chemical stimuli; nerve impulses
C)physical stimuli; sound
D)neurons; sensory organs
A)neurotransmitters; synapses
B)physical or chemical stimuli; nerve impulses
C)physical stimuli; sound
D)neurons; sensory organs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When a nerve cell is firing rapidly, it can inhibit signal transmission by neighboring cells. This phenomenon is known as:
A)accommodation.
B)lateral inhibition
C)excitatory postsynaptic potential.
D)adaptation.
A)accommodation.
B)lateral inhibition
C)excitatory postsynaptic potential.
D)adaptation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is the firing rate of a neuron?
A)the magnitude of a depolarization
B)the magnitude of an action potential
C)the number of action potentials generated over a given period of time
D)It is related to the resting membrane potential.
A)the magnitude of a depolarization
B)the magnitude of an action potential
C)the number of action potentials generated over a given period of time
D)It is related to the resting membrane potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What do spatial and temporal summation have in common?
A)Both lead to lateral inhibition.
B)Both lead to adaptation to continuous stimuli.
C)Both increase the firing rate of neighboring neurons.
A)Both lead to lateral inhibition.
B)Both lead to adaptation to continuous stimuli.
C)Both increase the firing rate of neighboring neurons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Chemoreceptor is to taste as mechanoreceptor is to:
A)smell.
B)pain.
C)temperature.
D)sound.
A)smell.
B)pain.
C)temperature.
D)sound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The charge difference between the inside of the cell membrane and the outside of the cell membrane is known as:
A)an action potential.
B)the membrane potential.
C)depolarization.
D)repolarization.
A)an action potential.
B)the membrane potential.
C)depolarization.
D)repolarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
How is a nerve impulse generated when most sensory receptors are activated?
A)The action potential is converted to a binary code.
B)The membrane becomes hyperpolarized.
C)The membrane becomes repolarized.
D)The membrane becomes depolarized.
A)The action potential is converted to a binary code.
B)The membrane becomes hyperpolarized.
C)The membrane becomes repolarized.
D)The membrane becomes depolarized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Under conditions of resting membrane potential, the inside of the cell is _____ charged with respect to the outside, and when an action potential is generated, the inside becomes _____ with respect to the outside of the cell.
A)negatively; even more negative
B)negatively; positive
C)positively; negative
D)positively; hyperpolarized
A)negatively; even more negative
B)negatively; positive
C)positively; negative
D)positively; hyperpolarized

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Three different cells-A1, A2, and A3-are activated to different extents by a sensory input, as shown in the graph below.  If lateral inhibition from neurons A1-3 to B1-3 were added to the network below, which pattern of activity is expected in cells B1, B2, and B3?
If lateral inhibition from neurons A1-3 to B1-3 were added to the network below, which pattern of activity is expected in cells B1, B2, and B3? 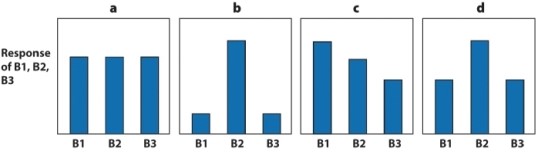
A)graph a
B)graph b
C)graph c
D)graph d
 If lateral inhibition from neurons A1-3 to B1-3 were added to the network below, which pattern of activity is expected in cells B1, B2, and B3?
If lateral inhibition from neurons A1-3 to B1-3 were added to the network below, which pattern of activity is expected in cells B1, B2, and B3? 
A)graph a
B)graph b
C)graph c
D)graph d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An interneuron may receive multiple stimuli from the same sensory neuron over a very short period of time. The firing rate of the receiving neuron is proportional to the number of signals received from the sensory neuron over time. Of which of the following is this an example?
A)temporal summation
B)spatial summation
C)action potential
D)hyperpolarization
A)temporal summation
B)spatial summation
C)action potential
D)hyperpolarization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A microelectrode (an electrically conducting glass pipette) is inserted into an olfactory receptor cell to measure the cell's response to a stimulus. The cell is continuously exposed to an odorant molecule. Initially the cell responds by firing action potentials, but over time, the response decreases. This decrease in response is known as:
A)sensory adaptation.
B)sensory integration.
C)sensory transduction.
D)sensory enhancement.
A)sensory adaptation.
B)sensory integration.
C)sensory transduction.
D)sensory enhancement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Sensory cells and sensory neurons allow multicellular animals to sense physical and chemical cues from their environment. What key properties of these cells enable them to perform this function?
A)Sensory cells and sensory neurons have electrically excitable membranes that change in charge potential in response to binding an environmental signaling molecule.
B)Sensory neurons have myelinated dendrites that serve as nerve endings.
C)All sensory cells and sensory neurons fire action potentials when they bind a signaling molecule.
D)Sensory cells and sensory neurons have protein receptors linked to intracellular or membrane-based signaling pathways that alter ion channel permeability.
A)Sensory cells and sensory neurons have electrically excitable membranes that change in charge potential in response to binding an environmental signaling molecule.
B)Sensory neurons have myelinated dendrites that serve as nerve endings.
C)All sensory cells and sensory neurons fire action potentials when they bind a signaling molecule.
D)Sensory cells and sensory neurons have protein receptors linked to intracellular or membrane-based signaling pathways that alter ion channel permeability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Photoreceptors respond to light energy. When activated, vertebrate photoreceptors cause Na+ channels to close, resulting in:
A)an action potential.
B)depolarization of the cell membrane.
C)repolarization of the cell membrane.
D)hyperpolarization of the cell membrane.
A)an action potential.
B)depolarization of the cell membrane.
C)repolarization of the cell membrane.
D)hyperpolarization of the cell membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The conversion of physical or chemical stimuli into nerve impulses is known as:
A)sensory transduction.
B)sensory reception.
C)motor response.
D)cellular response.
A)sensory transduction.
B)sensory reception.
C)motor response.
D)cellular response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Changes in membrane potential are a direct result of:
A)changes in a G protein activity.
B)changes in the activity of ion pumps.
C)reaching threshold.
D)summation of impulses
E)changes in the permeability of the membrane to ions.
A)changes in a G protein activity.
B)changes in the activity of ion pumps.
C)reaching threshold.
D)summation of impulses
E)changes in the permeability of the membrane to ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Mechanoreceptors respond to:
A)changes in pressure.
B)temperature changes.
C)wet and/or dry environmental conditions.
D)light.
A)changes in pressure.
B)temperature changes.
C)wet and/or dry environmental conditions.
D)light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Some people can detect PTC, a bitter compound found in broccoli and Brussels sprouts, whereas others cannot. Which of the following is the MOST likely explanation for this observation?
A)The G protein pathway that alters the conformation of the sodium channels is defective.
B)Chemoreceptors specific for PTC are not expressed.
C)Too few sodium channels are present in the taste receptors.
D)Neurotransmitter release from these taste receptors is impaired.
A)The G protein pathway that alters the conformation of the sodium channels is defective.
B)Chemoreceptors specific for PTC are not expressed.
C)Too few sodium channels are present in the taste receptors.
D)Neurotransmitter release from these taste receptors is impaired.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Multiple excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) from temporal summation and spatial summation can result in:
A)an action potential.
B)filtering out of unimportant background signals.
C)adaptation.
D)hyperpolarization.
A)an action potential.
B)filtering out of unimportant background signals.
C)adaptation.
D)hyperpolarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Multiple sensory receptors can synapse on a single neuron. The receiving neuron has a firing rate proportional to the number of signals received. Of which of the following is this an example?
A)temporal summation
B)spatial summation
C)action potential
D)hyperpolarization
A)temporal summation
B)spatial summation
C)action potential
D)hyperpolarization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
After wearing a watch for a period of time you are no longer as aware of its presence on your wrist. This is an example of:
A)lateral inhibition.
B)adaptation.
C)temporal summation.
D)desensitization.
A)lateral inhibition.
B)adaptation.
C)temporal summation.
D)desensitization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Sensory receptors respond to a novel stimulus with a(n) _____ firing rate.
A)constant
B)low
C)initially high
D)initially low
A)constant
B)low
C)initially high
D)initially low

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following carries out sensory transduction?
A)a CO2 chemoreceptor in a mosquito
B)a pheromone receptor in a moth's antennae
C)hair cell in the ear of a gazelle
D)thermoreceptors in the skin of vertebrates
A)a CO2 chemoreceptor in a mosquito
B)a pheromone receptor in a moth's antennae
C)hair cell in the ear of a gazelle
D)thermoreceptors in the skin of vertebrates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A young girl places her hand on a hot stove, but she does not immediately remove it. This girl likely carries a mutation in genes encoding:
A)mechanoreceptors.
B)chemoreceptors.
C)electroreceptors.
D)nociceptors.
E)photoreceptors.
A)mechanoreceptors.
B)chemoreceptors.
C)electroreceptors.
D)nociceptors.
E)photoreceptors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is a sensory receptor?
A)a nerve cell specialized to detect particular stimuli
B)a membrane protein that binds to a sensory ligand
C)the dendritic field of a sensory neuron
D)a specialized tissue like the eye
A)a nerve cell specialized to detect particular stimuli
B)a membrane protein that binds to a sensory ligand
C)the dendritic field of a sensory neuron
D)a specialized tissue like the eye

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Sensory transduction requires:
A)a change in membrane potential.
B)reaction of a receptor protein with a stimulus.
C)alteration of the conformation of a channel protein.
D)All of these choices are correct.
A)a change in membrane potential.
B)reaction of a receptor protein with a stimulus.
C)alteration of the conformation of a channel protein.
D)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A thermoreceptor responds to:
A)wet and/or dry environmental conditions.
B)temperature.
C)physical force.
D)pain.
A)wet and/or dry environmental conditions.
B)temperature.
C)physical force.
D)pain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following types of sensory receptors do NOT generate an action potential in response to its stimulus?
A)thermoreceptors
B)nociceptors
C)photoreceptors
D)chemoreceptors
A)thermoreceptors
B)nociceptors
C)photoreceptors
D)chemoreceptors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
How are thermoreceptors involved in homeostasis?
A)They have a role in blood pressure regulation.
B)They play a role in regulating body temperature.
C)They control electrolyte balance of the body.
D)Once these signals are processed, the brain sends signals to avoid the pain.
A)They have a role in blood pressure regulation.
B)They play a role in regulating body temperature.
C)They control electrolyte balance of the body.
D)Once these signals are processed, the brain sends signals to avoid the pain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which receptor is associated with the perception of pain?
A)thermoreceptor
B)chemoreceptor
C)nociceptor
D)photoreceptor
A)thermoreceptor
B)chemoreceptor
C)nociceptor
D)photoreceptor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Lateral inhibition requires:
A)production of an EPSP on the center interneuron.
B)production of an IPSP on the adjacent interneurons.
C)hyperpolarization of adjacent interneurons.
D)All of these choices are correct.
A)production of an EPSP on the center interneuron.
B)production of an IPSP on the adjacent interneurons.
C)hyperpolarization of adjacent interneurons.
D)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
On a phylogenetic tree, which of the following would you expect to have evolved first?
A)mechanoreceptors
B)chemoreceptors
C)thermoreceptors
D)nociceptors
E)photoreceptors
A)mechanoreceptors
B)chemoreceptors
C)thermoreceptors
D)nociceptors
E)photoreceptors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is TRUE regarding sensory receptors in a dog?
A)A dog's sense of smell is equivalent to a human's.
B)If properly stimulated, all of a dog's sensory receptors would fire action potentials.
C)If properly stimulated, the membranes of all of a dog's sensory receptors would become depolarized.
D)None of the answer options is correct.
A)A dog's sense of smell is equivalent to a human's.
B)If properly stimulated, all of a dog's sensory receptors would fire action potentials.
C)If properly stimulated, the membranes of all of a dog's sensory receptors would become depolarized.
D)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What are sensory receptors?
A)integral membrane proteins that respond to signal molecules
B)integral membrane proteins that open channels in response to signal molecules
C)sensory neurons or cells that are able to respond to environmental stimuli
D)interneurons that transmit sensory information
A)integral membrane proteins that respond to signal molecules
B)integral membrane proteins that open channels in response to signal molecules
C)sensory neurons or cells that are able to respond to environmental stimuli
D)interneurons that transmit sensory information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When mosquitoes search for their next blood meal, their sensory receptors respond to CO2 levels. Which of the following types of receptor is functioning?
A)a mechanoreceptor
B)a thermoreceptor
C)a nociceptor
D)a chemoreceptor
A)a mechanoreceptor
B)a thermoreceptor
C)a nociceptor
D)a chemoreceptor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
How many different types of chemoreceptors can be found in the taste buds?
A)hundreds
B)thousands
C)40 to 50
D)five
A)hundreds
B)thousands
C)40 to 50
D)five

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What type of sensory receptor is present in taste buds?
A)mechanoreceptors
B)nociceptors
C)chemoreceptors
D)thermoreceptors
A)mechanoreceptors
B)nociceptors
C)chemoreceptors
D)thermoreceptors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following structures would NOT contain sensory receptors?
A)the feet of a fruit fly
B)the bill of a platypus
C)the tongue of a dog
D)the skin of a human
E)None of the answer options is correct.
A)the feet of a fruit fly
B)the bill of a platypus
C)the tongue of a dog
D)the skin of a human
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is true of olfaction and gustation?
A)Gustation is chemosensory, whereas olfaction is not.
B)Humans have more olfactory receptor proteins than gustation receptor proteins.
C)Gustation and olfaction signals are processed by the same cranial nerves supplying the brain.
D)Gustation is more sensitive to stimuli than olfaction.
A)Gustation is chemosensory, whereas olfaction is not.
B)Humans have more olfactory receptor proteins than gustation receptor proteins.
C)Gustation and olfaction signals are processed by the same cranial nerves supplying the brain.
D)Gustation is more sensitive to stimuli than olfaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When you actually perceive the "taste" of something you are eating, it means that:
A)a single sensory cell has been depolarized and the signal has been transmitted to the area of the brain that perceives the taste.
B)a single taste bud has been depolarized and the signal has been transmitted to the area of the brain that perceives the taste.
C)multiple sensory cells have been depolarized by a sufficient amount of a food item and their combined EPSPs have been summed to transmit a signal to the brain.
D)multiple sensory cells have been depolarized by a variety of food items.
A)a single sensory cell has been depolarized and the signal has been transmitted to the area of the brain that perceives the taste.
B)a single taste bud has been depolarized and the signal has been transmitted to the area of the brain that perceives the taste.
C)multiple sensory cells have been depolarized by a sufficient amount of a food item and their combined EPSPs have been summed to transmit a signal to the brain.
D)multiple sensory cells have been depolarized by a variety of food items.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What part of a taste sensory neuron is directly involved with receiving stimuli?
A)microvilli
B)supporting cells
C)axons
D)papillae
A)microvilli
B)supporting cells
C)axons
D)papillae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The nose, your sensory organ of smell, contains which type of sensory neurons?
A)chemoreceptors
B)mechanoreceptors
C)baroreceptors
D)tactile receptors
A)chemoreceptors
B)mechanoreceptors
C)baroreceptors
D)tactile receptors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Many television chefs will season their food, somewhat liberally, with salt and pepper. On occasion you will even hear the remark, "Salt wakes up the flavor of the food." Why would the addition of salt help to heighten the "taste" of the food?
A)The salt changes the ion concentration in the mouth, activating salt-sensitive taste bud receptors and increasing the number of cells that depolarize and transduce other flavor signals to the brain.
B)It does not heighten the taste of the food; everything just tastes salty.
C)The salt can combine with the taste molecules so they bind more strongly to their receptors.
D)The salt causes more saliva to be produced, and that results in more taste molecules reaching the taste cells in the mouth.
A)The salt changes the ion concentration in the mouth, activating salt-sensitive taste bud receptors and increasing the number of cells that depolarize and transduce other flavor signals to the brain.
B)It does not heighten the taste of the food; everything just tastes salty.
C)The salt can combine with the taste molecules so they bind more strongly to their receptors.
D)The salt causes more saliva to be produced, and that results in more taste molecules reaching the taste cells in the mouth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Taste bud sensory cells synapse with:
A)the brain.
B)interneurons.
C)motor neurons.
D)memory cells.
A)the brain.
B)interneurons.
C)motor neurons.
D)memory cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
When an appropriate odor molecule (odorant) binds to its receptor, depolarization of the membrane occurs. Does this mean a signal goes directly to the brain and the odor is perceived by the brain?
A)Yes, because if an EPSP is generated, then the cell was depolarized and the signal was sent to the brain.
B)Yes, because if an EPSP is generated, then the match between the molecule and its receptor was appropriate and the signal was sent to the brain.
C)No, because although each EPSP is sent to the brain, the brain doesn't perceive the odor or taste unless an appropriate number of EPSPs are sent by the odor sensory cells.
D)No, because enough of the appropriate molecules must bind to the receptors for a summed response from all the EPSPs to generate an action potential that is transmitted to the brain.
A)Yes, because if an EPSP is generated, then the cell was depolarized and the signal was sent to the brain.
B)Yes, because if an EPSP is generated, then the match between the molecule and its receptor was appropriate and the signal was sent to the brain.
C)No, because although each EPSP is sent to the brain, the brain doesn't perceive the odor or taste unless an appropriate number of EPSPs are sent by the odor sensory cells.
D)No, because enough of the appropriate molecules must bind to the receptors for a summed response from all the EPSPs to generate an action potential that is transmitted to the brain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What type of sensory receptor is responsible for olfaction?
A)photoreceptor
B)electroreceptor
C)chemoreceptor
D)nociceptor
A)photoreceptor
B)electroreceptor
C)chemoreceptor
D)nociceptor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Another term that could be used to describe the chemosensitive hairs of an olfactory sensory neuron would be:
A)dendrites.
B)axons.
C)axon collaterals.
D)the cell body.
A)dendrites.
B)axons.
C)axon collaterals.
D)the cell body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When someone detects a specific odor, a signal is sent to the brain through the olfactory nerve. Which of the following describes how the brain is able to perceive the smell?
A)The odorant molecule has to bind to more than 50% of olfactory neuron dendrites in order for the smell to be perceived.
B)The odorant molecule binds specifically to its receptor to generate an EPSP that is transmitted through the olfactory nerve to the brain.
C)The odorant molecule binds to specific receptors; summed EPSPs transmit an action potential to general interneurons; and the signal is transmitted to the brain.
D)The odorant molecules bind to specific receptors; summed EPSPs transmit an action potential to the odorant-specific interneuron; and the signal is transmitted to the brain.
A)The odorant molecule has to bind to more than 50% of olfactory neuron dendrites in order for the smell to be perceived.
B)The odorant molecule binds specifically to its receptor to generate an EPSP that is transmitted through the olfactory nerve to the brain.
C)The odorant molecule binds to specific receptors; summed EPSPs transmit an action potential to general interneurons; and the signal is transmitted to the brain.
D)The odorant molecules bind to specific receptors; summed EPSPs transmit an action potential to the odorant-specific interneuron; and the signal is transmitted to the brain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A fisherman senses a fish on his line, and briefly tightens his hold on the pole as he reels the fish in. During this time, the mechanoreceptors in his hands:
A)demonstrate high firing rates.
B)demonstrate low firing rates.
C)have a firing rate of zero.
A)demonstrate high firing rates.
B)demonstrate low firing rates.
C)have a firing rate of zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The perceived flavor of food depends on both the sense of taste and the sense of smell. The sensory receptors of olfaction are _____ and those of taste buds are _____.
A)chemoreceptors; thermoreceptors
B)mechanoreceptors; chemoreceptors
C)nociceptors; thermoreceptors
D)chemoreceptors; chemoreceptors.
A)chemoreceptors; thermoreceptors
B)mechanoreceptors; chemoreceptors
C)nociceptors; thermoreceptors
D)chemoreceptors; chemoreceptors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
With the proper stimuli, chemoreceptors and mechanoreceptors are depolarized. This is a result of:
A)potassium channels opening.
B)sodium channels opening.
C)chloride channels opening.
D)sodium channels closing.
E)potassium channels closing.
A)potassium channels opening.
B)sodium channels opening.
C)chloride channels opening.
D)sodium channels closing.
E)potassium channels closing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A taste bud is made up of:
A)chemoreceptors.
B)thermoreceptors.
C)mechanoreceptors.
D)gustoreceptors.
A)chemoreceptors.
B)thermoreceptors.
C)mechanoreceptors.
D)gustoreceptors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A researcher is studying a mouse strain having the characteristic that exposure to light results in the depolarization of photoreceptors. Mice of this strain have normally functioning photoreceptors, and would respond to changes in light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Both olfactory and taste receptors bind to specific stimulatory compounds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What part of the olfactory sensory neuron is located in the olfactory epithelium?
A)dendrites
B)the cell body
C)axons
D)interneurons
A)dendrites
B)the cell body
C)axons
D)interneurons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding the microvilli of taste buds?
A)They contain the cell bodies of gustatory sensory neurons.
B)They house membrane receptors that recognize chemicals in food.
C)They limit the surface area of the tongue.
D)They are extensions of supporting cells rather than gustatory sensory neurons.
E)None of the answer options is correct.
A)They contain the cell bodies of gustatory sensory neurons.
B)They house membrane receptors that recognize chemicals in food.
C)They limit the surface area of the tongue.
D)They are extensions of supporting cells rather than gustatory sensory neurons.
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The sense of olfaction is able to detect lower concentrations of stimuli than gustation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The three bones of the mammalian inner ear function:
A)in the sense of balance.
B)to amplify sound waves that strike the tympanic membrane.
C)to detect motion.
D)in proprioception.
A)in the sense of balance.
B)to amplify sound waves that strike the tympanic membrane.
C)to detect motion.
D)in proprioception.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Fish and sharks sense vibrations in the water that may be caused by prey. The lateral line system of these fish and sharks detects this motion through the action of mechanoreceptors known as:
A)hair cells.
B)statocysts.
C)semicircular canals.
D)stereocilia.
A)hair cells.
B)statocysts.
C)semicircular canals.
D)stereocilia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The steps necessary for hearing include (1) amplification of sound waves, (2) transfer of sound vibrations to fluid pressure waves, and (3) mechanoreception by hair cells of the cochlea. How are the sound vibrations transferred to fluid pressure waves?
A)by the bones of the middle ear
B)through the oval window
C)by the tympanic membrane
D)by the action of the vestibular system
A)by the bones of the middle ear
B)through the oval window
C)by the tympanic membrane
D)by the action of the vestibular system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A(n) _____ is another name for the ligand that binds to an olfactory sensory neuron.
A)smell
B)odorant molecule
C)volatile molecule
D)aromatic molecule
A)smell
B)odorant molecule
C)volatile molecule
D)aromatic molecule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Sensory receptors involved in olfaction and gustation would be classified as chemoreceptors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What type of sensory receptors function in balance and sensing gravity?
A)mechanoreceptors
B)photoreceptors
C)nociceptors
D)chemoreceptors
A)mechanoreceptors
B)photoreceptors
C)nociceptors
D)chemoreceptors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Refer to the figure if needed to complete the following: The transduction of sound waves to changes in membrane potential takes place: 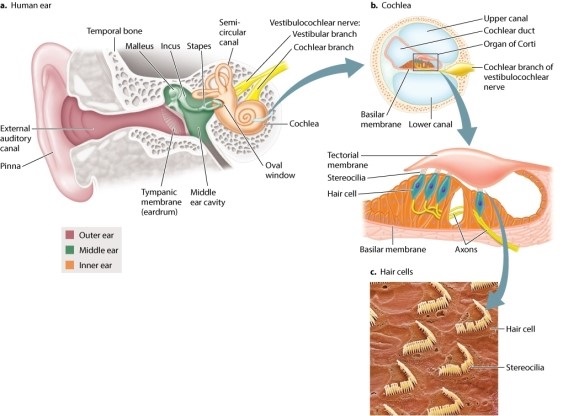
A)within the tectorial membrane as it is stimulated by the hair cells.
B)when stereocilia bend against the tectorial membrane, causing hair cell depolarization.
C)in the basilar membrane as it vibrates at different locations.
D)in the oval window, which vibrates at the same frequency as the original sound.
E)as the vibrations received by the outer ear cause the eardrum to vibrate.

A)within the tectorial membrane as it is stimulated by the hair cells.
B)when stereocilia bend against the tectorial membrane, causing hair cell depolarization.
C)in the basilar membrane as it vibrates at different locations.
D)in the oval window, which vibrates at the same frequency as the original sound.
E)as the vibrations received by the outer ear cause the eardrum to vibrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The olfactory nerve is made up of:
A)chemosensitive hairs.
B)axons of interneurons from the olfactory bulb.
C)axons of olfactory sensory neurons.
D)dendrites of olfactory sensory neurons.
A)chemosensitive hairs.
B)axons of interneurons from the olfactory bulb.
C)axons of olfactory sensory neurons.
D)dendrites of olfactory sensory neurons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Bats are able to hear frequencies of 100,000 cycles per second. The maximum firing rate of action potentials is a few hundred per second. How is this possible?
A)Action potentials are not used to transmit auditory information. The output of the sensory neuron to the brain is a graded potential.
B)The auditory system is special. Its neurons conduct signals very quickly and have no refractory period.
C)Sound wave frequency information is coded by differences in the location of vibrations along the basilar membrane, not in action potential frequency.
A)Action potentials are not used to transmit auditory information. The output of the sensory neuron to the brain is a graded potential.
B)The auditory system is special. Its neurons conduct signals very quickly and have no refractory period.
C)Sound wave frequency information is coded by differences in the location of vibrations along the basilar membrane, not in action potential frequency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The category of "savory" is a recent addition to the classic sweet, sour, bitter, and salty categories in human taste. Which of the following BEST describes the basic requirement for the identification of a new taste?
A)identification of a different type of taste bud
B)identification of a new set of interneurons
C)isolation of a novel chemoreceptor
D)isolation of a novel chemical compound in a food
A)identification of a different type of taste bud
B)identification of a new set of interneurons
C)isolation of a novel chemoreceptor
D)isolation of a novel chemical compound in a food

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A woman drinks a cup of hot tea, and burns her tongue. This incident briefly affects her ability to taste certain foods. The absence of taste is MOST likely the result of the:
A)microvilli of the woman's taste buds being damaged by the hot tea.
B)supporting cells of the woman's taste buds being damaged by the hot tea.
C)axons of the woman's taste buds being damaged by the hot tea.
D)olfactory sensory neurons being damaged by the hot tea.
A)microvilli of the woman's taste buds being damaged by the hot tea.
B)supporting cells of the woman's taste buds being damaged by the hot tea.
C)axons of the woman's taste buds being damaged by the hot tea.
D)olfactory sensory neurons being damaged by the hot tea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Recall that a "taste" signal is only relayed to the brain once a certain number of gustatory sensory receptors are stimulated. This is referred to as temporal summation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A woman carries a mutation in one of the genes encoding olfactory sensory receptors; however, her gustatory sensory receptors appear normal. What would you predict regarding this woman's senses of taste and smell?
A)The woman would have a normal sense of taste, but poor sense of smell.
B)The woman would have a normal sense of smell, but poor sense of taste.
C)Due to compensation, the woman would have a normal sense of taste and smell.
D)Given how these signals are processed, the woman would have a poor sense of smell and limited sense of taste.
A)The woman would have a normal sense of taste, but poor sense of smell.
B)The woman would have a normal sense of smell, but poor sense of taste.
C)Due to compensation, the woman would have a normal sense of taste and smell.
D)Given how these signals are processed, the woman would have a poor sense of smell and limited sense of taste.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A man complains to his doctor that he has a very hard time smelling things. What could be the cause of this patient's poor sense of smell?
A)His olfactory sensory neurons lack chemosensitive hairs.
B)He has insufficient mucus production in his nasal cavity.
C)His olfactory-associated interneurons cannot fire action potentials.
D)Connections may not have developed between his olfactory-associated interneurons and sensory neurons.
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)His olfactory sensory neurons lack chemosensitive hairs.
B)He has insufficient mucus production in his nasal cavity.
C)His olfactory-associated interneurons cannot fire action potentials.
D)Connections may not have developed between his olfactory-associated interneurons and sensory neurons.
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The function of the vestibular system of humans is:
A)to detect the head's orientation with respect to gravity.
B)in hearing.
C)to sense angular rotation of the head.
D)to sense the position of the appendages.
A)to detect the head's orientation with respect to gravity.
B)in hearing.
C)to sense angular rotation of the head.
D)to sense the position of the appendages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Variation in taste is the product of combining signals from different categories of taste buds. What cell type is MOST likely to be involved in this integration?
A)supporting cells
B)taste sensory neurons
C)sensory microvilli
D)interneurons
A)supporting cells
B)taste sensory neurons
C)sensory microvilli
D)interneurons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Your sense of taste and smell are similar in that:
A)the action potentials generated after stimulation go directly to the brain.
B)the ligands that bind to receptors must move through a fluid interface.
C)stimulus of either sense produces some stimulation in the other.
D)stimulus of either sense is done through large molecules.
A)the action potentials generated after stimulation go directly to the brain.
B)the ligands that bind to receptors must move through a fluid interface.
C)stimulus of either sense produces some stimulation in the other.
D)stimulus of either sense is done through large molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 205 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



