Deck 31: Plant Growth and Development
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/187
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 31: Plant Growth and Development
1
Cells directly beneath the shoot apical meristem begin to elongate and form the stem. Which of the following events or structures contribute to the elongation of these cells?
A)the formation of a large vacuole in these cells
B)the orientation of cellulose molecules around these cells
C)the presence of meristem identity genes in these cells
D)the loss of cytoplasm from these cells
A)the formation of a large vacuole in these cells
B)the orientation of cellulose molecules around these cells
C)the presence of meristem identity genes in these cells
D)the loss of cytoplasm from these cells
A, B
2
Within each "unit" composing a shoot of a vascular plant, you would observe leaves attached at the _____, and a large stretch of stem without leaves at the _____.
A)node; shoot apical meristem
B)node; internode
C)shoot apical meristem; node
D)internode; node
A)node; shoot apical meristem
B)node; internode
C)shoot apical meristem; node
D)internode; node
B
3
Plant growth results from actively dividing cells called:
A)nodes.
B)primordial cells.
C)meristem cells.
D)vascular cells.
E)bundle sheath cells.
A)nodes.
B)primordial cells.
C)meristem cells.
D)vascular cells.
E)bundle sheath cells.
C
4
De-differentiation and the taking on of new cellular identities by previously mature cells is a common theme in plant development. Why might this behavior be much more prevalent in plants than animals? All of the responses provided are true. Select the response that BEST answers the question posed.
A)Due to their cell walls, plant cells cannot migrate as animal cells do
B)plants are in a state of continual growth and development throughout their lives
C)plants are rooted in place and so react to their environment by modifying their growth
D)plant meristems need to be able to take on different identities to produce different types of organs
A)Due to their cell walls, plant cells cannot migrate as animal cells do
B)plants are in a state of continual growth and development throughout their lives
C)plants are rooted in place and so react to their environment by modifying their growth
D)plant meristems need to be able to take on different identities to produce different types of organs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Recall that leaves form in distinct arrangements (whorled, opposite, or alternate) on the stems of vascular plants. How might chemical factors cause new leaves to form in these particular patterns?
A)Leaf primordia drain auxin from neighboring cells, with new primordia forming where auxin in the meristem surface is at the highest concentration.
B)Leaf primordia secrete chemical activators that promote the formation of leaves nearby.
C)Mature leaves secrete chemical inhibitors that prevent the formation of leaves nearby.
D)Mature leaves secrete chemical activators that promote the formation of leaves nearby.
A)Leaf primordia drain auxin from neighboring cells, with new primordia forming where auxin in the meristem surface is at the highest concentration.
B)Leaf primordia secrete chemical activators that promote the formation of leaves nearby.
C)Mature leaves secrete chemical inhibitors that prevent the formation of leaves nearby.
D)Mature leaves secrete chemical activators that promote the formation of leaves nearby.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
How do the meristems of leaves compare to those of stems?
A)Leaves do not have discrete populations of meristem cells.
B)Meristem cells in leaves do not form persistent populations that have the potential to produce new cells for the lifetime of the plant.
C)Meristem cells in leaves are only ever located at the leaf margin.
D)Meristems in leaves do not produce auxin.
A)Leaves do not have discrete populations of meristem cells.
B)Meristem cells in leaves do not form persistent populations that have the potential to produce new cells for the lifetime of the plant.
C)Meristem cells in leaves are only ever located at the leaf margin.
D)Meristems in leaves do not produce auxin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
You are growing plants hydroponically (rooted in an aqueous solution rather than soil). For one group of plants, the solution for the "control group" contains normal levels of salts and nutrients, while the solution for the "treatment group" has a high concentration of large molecular weight solutes that are excluded by roots. You find that the plants in the treatment group are on average smaller than those in the control group, but there is no significant difference between the groups in the amount of CO2 being fixed by the average plant. What differences at the cellular level between groups would you expect to make an important contribution to the difference in size of the shoots?
A)the total number of cells in the treatment group shoots would be smaller
B)the girth of cells in the elongation and mature zones would be larger in the control group
C)the length of cells in the elongation and mature zones would be larger in the control group
D)cellulose molecules would be more randomly oriented in mature cell walls in the treatment group
E)auxin levels and cell wall extensibility would be lower in the treatment group
A)the total number of cells in the treatment group shoots would be smaller
B)the girth of cells in the elongation and mature zones would be larger in the control group
C)the length of cells in the elongation and mature zones would be larger in the control group
D)cellulose molecules would be more randomly oriented in mature cell walls in the treatment group
E)auxin levels and cell wall extensibility would be lower in the treatment group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following were key events in the evolution of vascular plant leaves?
A)the conversion of stems (or branches)to flattened structures
B)the development of apical meristem identity genes
C)the development of leaf meristem cells
D)the development of leaf identity genes
A)the conversion of stems (or branches)to flattened structures
B)the development of apical meristem identity genes
C)the development of leaf meristem cells
D)the development of leaf identity genes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
It is the production and elongation of cells at the shoot tip that lead to an increase in shoot length.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If a researcher discovered a new tulip mutant that never produces flowers, the production of what compound might be affected in this mutant?
A)gibberellic acid
B)cytokinins
C)auxin
D)florigen
A)gibberellic acid
B)cytokinins
C)auxin
D)florigen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Flowering is often delayed in plants whose leaves have been eaten by herbivores You do an experiment in the lab where you remove leaves of different ages as different plants approach the day length that triggers flowering. You find that only stems with at least some mature leaves flower at the usual time. You conclude that:
A)only mature leaves can sense photoperiod.
B)plants without mature leaves lack the nutritional resources to flower.
C)florigen cannot reach the shoot apical meristem from leaves that are still importing sugar.
D)a reduction in auxin transport resulting from leaf removal promotes vegetative meristem identity.
A)only mature leaves can sense photoperiod.
B)plants without mature leaves lack the nutritional resources to flower.
C)florigen cannot reach the shoot apical meristem from leaves that are still importing sugar.
D)a reduction in auxin transport resulting from leaf removal promotes vegetative meristem identity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Plants have collections of totipotent stem cells called _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An axillary bud can develop into which of the following?
A)a leaf
B)a flower
C)a branch
D)a root
E)None of the answer options is correct.
A)a leaf
B)a flower
C)a branch
D)a root
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Meristem identity genes within plants:
A)confer totipotency.
B)are expressed within the "cell elongation zone."
C)cause cells to differentiate.
D)influence vacuole size.
E)encode for chitin.
A)confer totipotency.
B)are expressed within the "cell elongation zone."
C)cause cells to differentiate.
D)influence vacuole size.
E)encode for chitin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In which of the following structures of a vascular plant would you expect to find totipotent cells?
A)mature leaves
B)shoot apical meristem
C)cell elongation zone
D)axillary buds
A)mature leaves
B)shoot apical meristem
C)cell elongation zone
D)axillary buds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Within the stem of a vascular plant, where would you expect to find the cells that are the MOST mature?
A)within the shoot apical meristem at the tip of the stem
B)within the zone of elongation directly beneath the shoot apical meristem
C)at the base of the stem near the soil
A)within the shoot apical meristem at the tip of the stem
B)within the zone of elongation directly beneath the shoot apical meristem
C)at the base of the stem near the soil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
_____ are meristems in gymnosperms and angiosperms that are often dormant. Upon activation, these structures will go on to form lateral branches.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements about axillary, floral, and shoot apical meristems is TRUE?
A)When a shoot apical meristem (but not an axillary bud)converts to a floral meristem, further development of the whole plant ceases.
B)Axillary buds can only grow out to become new shoots once the shoot apical meristem has been converted into a floral meristem.
C)Shoot apical meristems can revert to vegetative meristem identity after having converted to a floral meristem and producing a flower, but axillary buds that give rise to flowers cannot.
D)In shoot apical meristems that develop into flowers, the arrangement of floral organs is the same as that of the leaves produced earlier, while the floral organs of flowers that develop from axillary buds are free to follow a different arrangement.
E)None of the answer options is correct.
A)When a shoot apical meristem (but not an axillary bud)converts to a floral meristem, further development of the whole plant ceases.
B)Axillary buds can only grow out to become new shoots once the shoot apical meristem has been converted into a floral meristem.
C)Shoot apical meristems can revert to vegetative meristem identity after having converted to a floral meristem and producing a flower, but axillary buds that give rise to flowers cannot.
D)In shoot apical meristems that develop into flowers, the arrangement of floral organs is the same as that of the leaves produced earlier, while the floral organs of flowers that develop from axillary buds are free to follow a different arrangement.
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is TRUE regarding the cells in a flower meristem?
A)Cells in a flower meristem will divide mitotically throughout the life of the plant.
B)A subpopulation of cells in the flower meristem will remain totipotent, even after the flower has formed.
C)The flower meristem only loses its identity as a continuous population of totipotent cells after fruit development
D)All the cells of the flower meristem differentiate as the flower is formed.
A)Cells in a flower meristem will divide mitotically throughout the life of the plant.
B)A subpopulation of cells in the flower meristem will remain totipotent, even after the flower has formed.
C)The flower meristem only loses its identity as a continuous population of totipotent cells after fruit development
D)All the cells of the flower meristem differentiate as the flower is formed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A researcher discovers a mutant carnation plant that lacks any A-class homeotic genes. Which of the following structures would be malformed (or absent) in this mutant?
A)stamens
B)carpels
C)petals
D)sepals
A)stamens
B)carpels
C)petals
D)sepals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Recall that in many plants, if the shoot apical meristem is removed, axillary buds become active and new lateral branches form. What is this an example of?
A)auxin dominance
B)axillary dominance
C)meristem dominance
D)apical dominance
A)auxin dominance
B)axillary dominance
C)meristem dominance
D)apical dominance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Fossils show that leaves MOST likely evolved from:
A)algal cells.
B)endosymbiotic cyanobacterium.
C)vascular tissue.
D)photosynthetic stems.
E)lateral meristems.
A)algal cells.
B)endosymbiotic cyanobacterium.
C)vascular tissue.
D)photosynthetic stems.
E)lateral meristems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In plants, cell division and increase in size generally occur in different growth zones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
_____ are cells that lay the framework for new phloem and xylem in vascular plants. Prior to the differentiation of these cells, their precursors transported auxin out of immature leaves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A researcher creates a mutant pea plant in which cytokinins are overexpressed and gibberellic acid is underexpressed. What is the MOST likely phenotype of this mutant pea plant?
A)The pea plant would be shorter with more branches compared to wild-type plants.
B)The pea plant would be taller with more branches compared to wild-type plants.
C)The pea plant would be shorter with fewer branches compared to wild-type plants.
D)The pea plant would be taller with fewer branches compared to wild-type plants.
A)The pea plant would be shorter with more branches compared to wild-type plants.
B)The pea plant would be taller with more branches compared to wild-type plants.
C)The pea plant would be shorter with fewer branches compared to wild-type plants.
D)The pea plant would be taller with fewer branches compared to wild-type plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Flower organs:
A)occur in whorls.
B)arise in the same pattern as leaf primordia.
C)are randomly arranged.
D)None of the answer options is correct.
A)occur in whorls.
B)arise in the same pattern as leaf primordia.
C)are randomly arranged.
D)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Plant growth that elongates stems occurs in the:
A)shoot apical meristem.
B)root apical meristem.
C)shoot lateral meristem.
D)root lateral meristem.
E)internode.
A)shoot apical meristem.
B)root apical meristem.
C)shoot lateral meristem.
D)root lateral meristem.
E)internode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following statements describes the hypothesis proposed to explain the regular arrangement of leaves around the stem?
A)Primordia are genetically preprogrammed to grow in a regular pattern.
B)Primordia secrete growth inhibitors that block new primordia from forming near them; where these signals are at a minimum, farthest from existing primordia, a new primordia can form.
C)New primordia initiate where auxin accumulates, while existing primordia efficiently drain auxin from the meristem surface. This ensures that new primordia form in the location farthest from existing primordia.
D)Developing leaf primordia physically block new primordia near them, such that new primordia initiate in the largest space not currently occupied by existing primordia.
E)We do not currently have a hypothesis to explain this growth pattern.
A)Primordia are genetically preprogrammed to grow in a regular pattern.
B)Primordia secrete growth inhibitors that block new primordia from forming near them; where these signals are at a minimum, farthest from existing primordia, a new primordia can form.
C)New primordia initiate where auxin accumulates, while existing primordia efficiently drain auxin from the meristem surface. This ensures that new primordia form in the location farthest from existing primordia.
D)Developing leaf primordia physically block new primordia near them, such that new primordia initiate in the largest space not currently occupied by existing primordia.
E)We do not currently have a hypothesis to explain this growth pattern.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is NOT a function that can be fulfilled by modified leaves?
A)protection
B)attachment for climbing
C)trapping insects
D)None of the answer options is correct.
E)insulation
A)protection
B)attachment for climbing
C)trapping insects
D)None of the answer options is correct.
E)insulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The highly productive varieties of wheat and rice that were developed in the Green Revolution produce lots of seeds. Given that evolutionary fitness is measured in terms of reproductive success (for which total seed production is a good proxy), why might natural selection have failed to produce these highly productive varieties on its own, without the work of human plant breeders?
A)Green Revolution crops require too much nitrogen to develop normally without added fertilizer.
B)Green Revolution crops require too much water to develop normally without irrigation.
C)Green Revolution crops have reduced root elongation and thus are sensitive to natural droughts.
D)Green Revolution crops have reduced stem elongation and thus are poor competitors for sunlight compared to wild plants.
A)Green Revolution crops require too much nitrogen to develop normally without added fertilizer.
B)Green Revolution crops require too much water to develop normally without irrigation.
C)Green Revolution crops have reduced root elongation and thus are sensitive to natural droughts.
D)Green Revolution crops have reduced stem elongation and thus are poor competitors for sunlight compared to wild plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A plant has undergone a robust phase of growth; however, the roots can no longer provide enough nutrients to the plant. What signal(s) can the roots send to the rest of the plant that will prevent new branches from forming?
A)cytokinins
B)gibberellic acid
C)strigolactone
D)ethylene
A)cytokinins
B)gibberellic acid
C)strigolactone
D)ethylene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Cells at shoot tips maintain their totipotency due to the expression of _____ genes.
A)meristem identity
B)growth regulation
C)lateral growth
D)S-regulation
E)nodal expression
A)meristem identity
B)growth regulation
C)lateral growth
D)S-regulation
E)nodal expression

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
You are studying a mutant in which cellulose molecules are always deposited in the walls with random orientations, and in which giberellic acid is over-expressed. You find that the:
A)two mutations have opposing effects on cell elongation and so the plant appears similar to the wild type.
B)plants become long and spindly as the effects on elongation of the two mutations are additive.
C)plants are small in stature but with an overproliferation of branches.
D)stem internodes are larger in diameter but compressed in length relative to wild type.
A)two mutations have opposing effects on cell elongation and so the plant appears similar to the wild type.
B)plants become long and spindly as the effects on elongation of the two mutations are additive.
C)plants are small in stature but with an overproliferation of branches.
D)stem internodes are larger in diameter but compressed in length relative to wild type.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The primary site of photosynthesis in MOST plants is the:
A)stems.
B)roots.
C)shoots.
D)buds.
E)leaves.
A)stems.
B)roots.
C)shoots.
D)buds.
E)leaves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
At the tip of each branch, the _____ surround(s) the shoot apical meristem.
A)bundle sheath
B)leaf primordia
C)flower bud
D)node
E)internode
A)bundle sheath
B)leaf primordia
C)flower bud
D)node
E)internode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Flowering is triggered by the production of _____, which triggers the transition from apical meristem to floral meristem identity.
A)meristemogen
B)florigen
C)auxin
D)gibberellin
E)ethylene
A)meristemogen
B)florigen
C)auxin
D)gibberellin
E)ethylene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In seed plants, branches grow out from _____, which are meristems that form at the base of each leaf.
A)apical buds
B)bud scales
C)axillary buds
D)augmented buds
E)flower buds
A)apical buds
B)bud scales
C)axillary buds
D)augmented buds
E)flower buds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Consider the following excerpt of Fig. 31.9 from your text. What phenotypic effects would you expect to observe if a mutation leads to the loss of the plant cell's ability to control where PIN proteins are inserted in the plasma membrane? 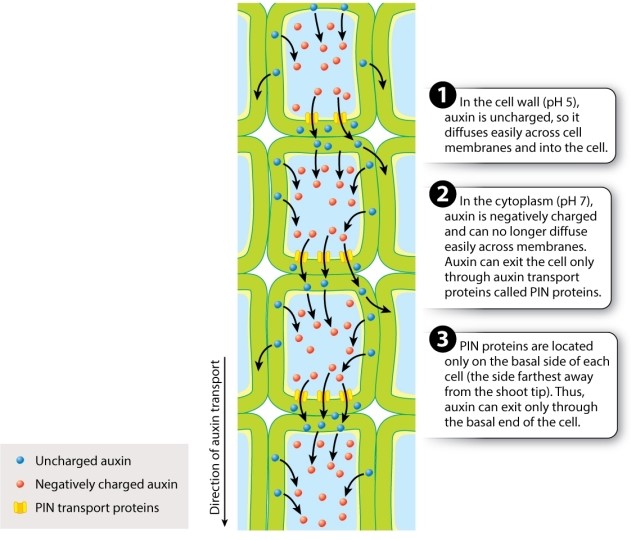
A)an irregular pattern of leaf primordia initiation
B)a disruption of the pattern of veins in the leaves
C)reduced branching
D)all cells elongating more than usual

A)an irregular pattern of leaf primordia initiation
B)a disruption of the pattern of veins in the leaves
C)reduced branching
D)all cells elongating more than usual

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Suppose the pH in the cell walls of an apical meristem became highly basic ( > pH 7), but traffic through PIN proteins in the membrane remained normal. Where would you expect most auxin molecules to be concentrated-in the cell wall or cytoplasm? Would the auxin molecules be in the charged or uncharged form?
A)cell wall; charged form
B)cell wall; uncharged form
C)cytoplasm; charged form
D)cytoplasm; uncharged form
A)cell wall; charged form
B)cell wall; uncharged form
C)cytoplasm; charged form
D)cytoplasm; uncharged form

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Flowers may develop from:
A)an apical meristem.
B)a leaf meristem.
C)an axillary bud.
D)a lateral meristem.
E)either apical meristem or an axillary bud.
A)an apical meristem.
B)a leaf meristem.
C)an axillary bud.
D)a lateral meristem.
E)either apical meristem or an axillary bud.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
You are surveying a crop and find that insects have eaten the shoot apical meristems of all the plants, but none of the axillary buds have started to grow out. In addition, you noticed many of the plants are showing signs of nitrogen deficiency and/or wilting. You sample axillary buds from these plants for analysis and hypothesize that you will find:
A)low levels of both cytokinin and strigolactone.
B)high levels of both cytokinin and strigolactone.
C)high levels of cytokinin but low levels of strigolactone.
D)low levels of cytokinin but high levels of strigolactone.
A)low levels of both cytokinin and strigolactone.
B)high levels of both cytokinin and strigolactone.
C)high levels of cytokinin but low levels of strigolactone.
D)low levels of cytokinin but high levels of strigolactone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is NOT one of the major plant hormones?
A)auxin
B)ethylene
C)calcitonin
D)gibberellic acid
E)abscisic acid
A)auxin
B)ethylene
C)calcitonin
D)gibberellic acid
E)abscisic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Why was finding varieties with reduced internode elongation a key step in the breeding of "green revolution" varieties?
A)The resulting reduction in stem biomass allowed the plant to allocate more resources to the grain.
B)Less stem made the plants more palatable to livestock.
C)It reduced the need for the root growth required to support a tall plant.
D)It kept the stems from falling over under the weight of larger seed heads.
A)The resulting reduction in stem biomass allowed the plant to allocate more resources to the grain.
B)Less stem made the plants more palatable to livestock.
C)It reduced the need for the root growth required to support a tall plant.
D)It kept the stems from falling over under the weight of larger seed heads.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Hormones play a role in which of the following plant processes?
A)branch development
B)root development
C)fruit ripening
D)gravitropism
A)branch development
B)root development
C)fruit ripening
D)gravitropism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
_____ are chemical signaling molecules that influence physiology and development.
A)Genes
B)Hormones
C)Meristems
D)Lipids
E)Mitochondria
A)Genes
B)Hormones
C)Meristems
D)Lipids
E)Mitochondria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The condition in which shoot apical meristems suppress the growth of axillary buds is called:
A)repression.
B)apical dominance.
C)shoot-root ratio.
D)optimum growth pattern.
E)primary growth.
A)repression.
B)apical dominance.
C)shoot-root ratio.
D)optimum growth pattern.
E)primary growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Auxin has no net charge under the _____ conditions _____ a cell.
A)acidic; inside
B)basic; outside
C)acidic; outside
D)basic; inside
A)acidic; inside
B)basic; outside
C)acidic; outside
D)basic; inside

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Where in a growing plant would you expect to find the highest concentration of auxin?
A)in the leaf margins of mature leaves
B)in axillary buds that are not growing
C)in the apical meristem
D)in the floral meristem
A)in the leaf margins of mature leaves
B)in axillary buds that are not growing
C)in the apical meristem
D)in the floral meristem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Gibberellic acid:
A)stimulates fruit formation.
B)inhibits photosynthesis.
C)stimulates stem elongation.
D)maintains seed dormancy.
E)is overexpressed in semidwarf varieties of plants.
A)stimulates fruit formation.
B)inhibits photosynthesis.
C)stimulates stem elongation.
D)maintains seed dormancy.
E)is overexpressed in semidwarf varieties of plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A researcher discovers a pea plant mutant having PIN proteins that are located on the apical (not basal) sides of cells in the shoot apical meristem. What processes would this affect?
A)polar transport of auxin
B)the development of new xylem
C)the development of new phloem
D)the establishment of procambial cells
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)polar transport of auxin
B)the development of new xylem
C)the development of new phloem
D)the establishment of procambial cells
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following hormones is NOT matched with the proper function?
A)gibberellic acid-mobilizes seed resources for the developing embryo
B)auxin-promotes increases in cell size
C)cytokinins-stimulates cell division
D)ethylene-inhibits fruit ripening
E)abscisic acid-promotes root elongation
A)gibberellic acid-mobilizes seed resources for the developing embryo
B)auxin-promotes increases in cell size
C)cytokinins-stimulates cell division
D)ethylene-inhibits fruit ripening
E)abscisic acid-promotes root elongation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The growth of axillary buds is promoted by:
A)high auxin, low cytokinin, and low strigolactone.
B)low auxin, high cytokinin, and high strigolactone.
C)low auxin and low strigolactone, but high cytokinin.
D)high auxin and high cytokinin, but low strigolactone.
A)high auxin, low cytokinin, and low strigolactone.
B)low auxin, high cytokinin, and high strigolactone.
C)low auxin and low strigolactone, but high cytokinin.
D)high auxin and high cytokinin, but low strigolactone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The "dwarfing genes" that played an important role in the green revolution targeted the production of or sensitivity to:
A)auxin.
B)giberellic acid.
C)cytokinin.
D)ethylene.
A)auxin.
B)giberellic acid.
C)cytokinin.
D)ethylene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
If auxin failed to lose a proton (and so never became negatively charged) in a cell's cytoplasm, how would its failure to lose a proton affect auxin transport and the development of new xylem and phloem?
A)Auxin would remain sequestered in the cells where it was produced.
B)Auxin may move between cells (via diffusion), but not in a directed manner.
C)New xylem and phloem would continue to form normally.
D)New xylem and phloem would be malformed or not form at all.
A)Auxin would remain sequestered in the cells where it was produced.
B)Auxin may move between cells (via diffusion), but not in a directed manner.
C)New xylem and phloem would continue to form normally.
D)New xylem and phloem would be malformed or not form at all.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The development of axillary buds is under the control of a single hormone, cytokinin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Auxin:
A)prevents cell elongation.
B)is transported from developing leaves to differentiated vascular tissue.
C)has a net positive charge in the cytoplasm of cells.
D)inhibits cellular production of PIN proteins.
E)inhibits fruit ripening.
A)prevents cell elongation.
B)is transported from developing leaves to differentiated vascular tissue.
C)has a net positive charge in the cytoplasm of cells.
D)inhibits cellular production of PIN proteins.
E)inhibits fruit ripening.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Roots are thought to load strigolactones into the xylem to _____ when soils are _____.
A)suppress the production of branches and so new leaf area; dry
B)promote the production of branches and so new leaf area; wet
C)promote the conversion of apical meristems to floral meristems; dry
D)suppress the conversion of apical meristems to floral meristems; wet
A)suppress the production of branches and so new leaf area; dry
B)promote the production of branches and so new leaf area; wet
C)promote the conversion of apical meristems to floral meristems; dry
D)suppress the conversion of apical meristems to floral meristems; wet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The movement of auxin from the apical to basal sides of immature leaf cells-and toward the xylem and phloem of the stem-is an example of _____ transport.
A)trophic
B)polar
C)bidirectional
D)paraxial
A)trophic
B)polar
C)bidirectional
D)paraxial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following statements is NOT true of hormone actions in plants?
A)Most plant hormones are effective in extremely low concentrations.
B)Plant hormones influence cell growth and differentiation.
C)Plant hormones may alter patterns of gene expression and rates of cell division.
D)Plant hormones act independently and do not affect one another's actions.
E)Plant hormones play a central role in plant development.
A)Most plant hormones are effective in extremely low concentrations.
B)Plant hormones influence cell growth and differentiation.
C)Plant hormones may alter patterns of gene expression and rates of cell division.
D)Plant hormones act independently and do not affect one another's actions.
E)Plant hormones play a central role in plant development.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In experiments to test apical dominance, researchers found that:
A)if the shoot tip is cut off and auxin is applied, the axillary branch will grow.
B)if the shoot tip is cut off, the axillary branch will grow.
C)if the shoot tip is cut off and cytokinins are applied, the axillary branch will grow.
D)if the shoot tip is cut off and treated with something that inhibits cytokinin transport, the axillary branch will grow.
E)branching is enhanced by the movement of auxin from the shoot tip toward the root.
A)if the shoot tip is cut off and auxin is applied, the axillary branch will grow.
B)if the shoot tip is cut off, the axillary branch will grow.
C)if the shoot tip is cut off and cytokinins are applied, the axillary branch will grow.
D)if the shoot tip is cut off and treated with something that inhibits cytokinin transport, the axillary branch will grow.
E)branching is enhanced by the movement of auxin from the shoot tip toward the root.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
There are three giant redwoods in California that a person can actually drive through. Imagine that you look up right when you are in the middle of driving through the tree and continue looking up until you exit out the other side. What order of structures would you see as you were driving through the tree starting at the middle?
A)pith, phloem, xylem, vascular cambium, cork
B)pith, vascular cambium, phloem, xylem, cork
C)pith, xylem, phloem, vascular cambium, cork
D)pith, xylem, vascular cambium, phloem, cork
E)pith, phloem, vascular cambium, xylem, cork
A)pith, phloem, xylem, vascular cambium, cork
B)pith, vascular cambium, phloem, xylem, cork
C)pith, xylem, phloem, vascular cambium, cork
D)pith, xylem, vascular cambium, phloem, cork
E)pith, phloem, vascular cambium, xylem, cork

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A botanist is studying the growth rings of a redwood tree. She notices that three concentric rings are very thin compared to the surrounding growth rings. What can she deduce from the presence of these thin growth rings?
A)The tree developed more apical shoot meristems during that time period.
B)The tree may have experienced a drought or had limited access to nutrients during that time period.
C)The tree developed more secondary xylem during that time period.
D)The tree had ample access to water and other resources during that time period.
A)The tree developed more apical shoot meristems during that time period.
B)The tree may have experienced a drought or had limited access to nutrients during that time period.
C)The tree developed more secondary xylem during that time period.
D)The tree had ample access to water and other resources during that time period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Auxin can freely diffuse _____ a cell but can only _____ via a PIN channel.
A)out of; enter
B)into; exit
C)inside and outside; enter or exit
D)within; enter into an adjacent cell
A)out of; enter
B)into; exit
C)inside and outside; enter or exit
D)within; enter into an adjacent cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A researcher examines a piece of oak tree bark under a microscope. He notices many small holes or spaces within his bark sample. What are these areas?
A)stomata
B)suberins
C)pericycles
D)lenticels
A)stomata
B)suberins
C)pericycles
D)lenticels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
MOST of the height growth of a plant is due to:
A)changes in cell number but not cell dimension in the apical meristem.
B)changes in cell dimension but not cell number in the elongation zone.
C)both changes in cell number and cell dimension, roughly equally.
D)thickening of the cell walls in the zone of maturation.
A)changes in cell number but not cell dimension in the apical meristem.
B)changes in cell dimension but not cell number in the elongation zone.
C)both changes in cell number and cell dimension, roughly equally.
D)thickening of the cell walls in the zone of maturation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Suppose you invented a way to genetically transform all of the cells expressing meristematic identity in a plant so that they would fluoresce green. Suppose too that this transformation was heritable by daughter cells, such that they would also fluoresce as long as they continued to express meristematic identity, but would lose the ability to fluoresce irreversibly upon differentiating to a nonmeristematic cell type. You then genetically transform all the cells of a tree, and soon after examine a cross section of a branch stem. A few years later, you examine a cross section of another branch stem. What should you expect to see in comparing the two stem cross sections?
A)a continuous green ring in the first sample, but multiple discontinuous rings in the later sample
B)a discontinuous green ring surrounding a continuous green ring in the first sample, but multiple continuous green rings in the later sample
C)multiple discontinuous green rings in the first sample, but multiple continuous green rings surrounding a discontinuous green ring in the later sample
D)a continuous green ring surrounded by multiple discontinuous green rings in the first sample, but a single continuous green ring in the later sample
A)a continuous green ring in the first sample, but multiple discontinuous rings in the later sample
B)a discontinuous green ring surrounding a continuous green ring in the first sample, but multiple continuous green rings in the later sample
C)multiple discontinuous green rings in the first sample, but multiple continuous green rings surrounding a discontinuous green ring in the later sample
D)a continuous green ring surrounded by multiple discontinuous green rings in the first sample, but a single continuous green ring in the later sample

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
As trees get larger and the number of leaves increases, transpiration rates rise and demand for water increases. How do mature plant stems meet this added demand for water?
A)Cells of the xylem continue to divide and produce more cells that transport water.
B)Vascular cambium continues to divide, and cells of its inner surface differentiate to form additional secondary xylem cells.
C)Cells of secondary phloem adjacent to the vascular cambium differentiate into xylem cells.
D)Cells present in the pith closest to the xylem differentiate into xylem cells.
A)Cells of the xylem continue to divide and produce more cells that transport water.
B)Vascular cambium continues to divide, and cells of its inner surface differentiate to form additional secondary xylem cells.
C)Cells of secondary phloem adjacent to the vascular cambium differentiate into xylem cells.
D)Cells present in the pith closest to the xylem differentiate into xylem cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Vascular cambium is capable of producing:
A)primary xylem only.
B)primary phloem only.
C)secondary xylem only.
D)secondary phloem only.
E)secondary xylem and phloem.
A)primary xylem only.
B)primary phloem only.
C)secondary xylem only.
D)secondary phloem only.
E)secondary xylem and phloem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following cell types can become the meristem cells of a vascular cambium?
A)shoot apical meristem cells
B)procambial cells
C)epidermal cells
D)parenchymal cells
A)shoot apical meristem cells
B)procambial cells
C)epidermal cells
D)parenchymal cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Growth rings may be used to determine the age of trees in seasonal climates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
An increase in a plant's diameter resulting from the addition of new xylem and phloem is called _____ growth.
A)primary
B)secondary
C)longitudinal
D)apical
E)herbaceous
A)primary
B)secondary
C)longitudinal
D)apical
E)herbaceous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In general, when a cell or tissue type has to serve multiple functions that each contribute to fitness, natural selection is constrained from optimizing that tissue of cell type for any one function. With this concept in mind, fill in the blanks in the sentence below with the appropriate term: poor, positive, negative. The terms may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
"In angiosperms you would expect a _____ correlation between the diameter of the water conducting conduits and the mechanical strength of the wood. In gymnoperms you would expect the correlation to be _____."
"In angiosperms you would expect a _____ correlation between the diameter of the water conducting conduits and the mechanical strength of the wood. In gymnoperms you would expect the correlation to be _____."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following is produced by the vascular cambium?
A)secondary xylem
B)cork
C)secondary phloem
D)wood
E)bark
A)secondary xylem
B)cork
C)secondary phloem
D)wood
E)bark

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The wood of gymnosperms is composed of _____, and the wood of angiosperms (e.g., a cherry tree) can consist of _____.
A)tracheids; fibers and vessel elements
B)fibers and tracheids; vessel elements
C)vessel elements and fibers; tracheids
D)tracheids and vessel elements; fibers
A)tracheids; fibers and vessel elements
B)fibers and tracheids; vessel elements
C)vessel elements and fibers; tracheids
D)tracheids and vessel elements; fibers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Vascular cambium is one of two lateral meristems; the other is cork cambium. A plant grows in diameter primarily through divisions of the vascular cambium. If you pull a small piece of bark off a tree, and then look at the bark's inside surface, what tissue are you looking at (ignore any remaining cells of vascular cambium that may be left)?
A)cork cambium
B)cork
C)xylem
D)phloem
A)cork cambium
B)cork
C)xylem
D)phloem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
When a redwood tree trunk increases in diameter (not height), this is a result of:
A)shoot apical meristems.
B)axillary buds.
C)floral meristems.
D)lateral meristems.
A)shoot apical meristems.
B)axillary buds.
C)floral meristems.
D)lateral meristems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Fibers in angiosperm wood can support large mechanical loads because:
A)their cell walls are very dense compared to vessels or tracheids.
B)their cell walls are very thick, almost filling the cell.
C)their diameter is much larger than their length.
D)they can make up a large fraction of the wood due to the efficiency with which vessels can conduct water.
A)their cell walls are very dense compared to vessels or tracheids.
B)their cell walls are very thick, almost filling the cell.
C)their diameter is much larger than their length.
D)they can make up a large fraction of the wood due to the efficiency with which vessels can conduct water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Angiosperm trees can support large diameter branches that extend far from their main stems due to the mechanical strength of their wood, a strength conferred by:
A)tracheids.
B)fibers.
C)vessels.
D)living cells.
A)tracheids.
B)fibers.
C)vessels.
D)living cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding secondary growth in vascular plants?
A)Secondary growth depends only on the vascular cambium.
B)Secondary growth depends only on the cork cambium.
C)Secondary growth depends on both the vascular and cork cambia.
D)Secondary growth causes a plant to grow in diameter (not height).
E)Secondary growth causes a plant to grow in height (not diameter).
A)Secondary growth depends only on the vascular cambium.
B)Secondary growth depends only on the cork cambium.
C)Secondary growth depends on both the vascular and cork cambia.
D)Secondary growth causes a plant to grow in diameter (not height).
E)Secondary growth causes a plant to grow in height (not diameter).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Looking out your window, you may notice that the bark of a nearby oak tree has a mosaic appearance, consisting of deep fissures and relatively flat areas. What accounts for this mosaic appearance?
A)the formation of new cork cambia as old cork cambia grow away from the phloem
B)the formation of new secondary phloem in distinct, discontinuous patches
C)the formation of new cork cambia in distinct, discontinuous patches
D)the formation of new vascular cambia as old cork cambia grow away from the phloem
A)the formation of new cork cambia as old cork cambia grow away from the phloem
B)the formation of new secondary phloem in distinct, discontinuous patches
C)the formation of new cork cambia in distinct, discontinuous patches
D)the formation of new vascular cambia as old cork cambia grow away from the phloem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 187 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



