Deck 25: Cycling Carbon
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/116
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: Cycling Carbon
1
Which of the following equations is the chemical reaction for cellular respiration?
A)C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O
B)6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 +6O2
C)CaSiO3 +CO2 CaCO3 +SiO2
D)C6H12O6 + 6CO2 6O2 + 6H2O
A)C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O
B)6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 +6O2
C)CaSiO3 +CO2 CaCO3 +SiO2
D)C6H12O6 + 6CO2 6O2 + 6H2O
C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O
2
Studies assessing the amounts of different carbon isotopes (12C, 13C, and 14C) in the atmosphere were important because they provided evidence that human activities were in fact adding CO2 to the atmosphere. This is an example of what type of relationship?
A)correlation
B)causation
C)conduction
D)antagonism
A)correlation
B)causation
C)conduction
D)antagonism
B
3
As shown in Figure 25.1 below, atmospheric CO2 levels oscillate throughout the year. 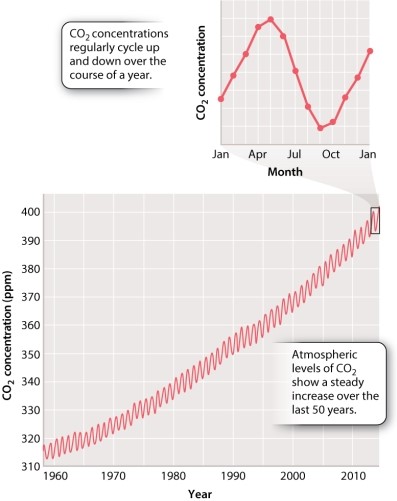 How would this trend change if it were spring for an entire year? Select the graph below that represents the atmospheric CO2 levels of an Earth with a full year of spring (assume you are in the Northern Hemisphere).
How would this trend change if it were spring for an entire year? Select the graph below that represents the atmospheric CO2 levels of an Earth with a full year of spring (assume you are in the Northern Hemisphere). 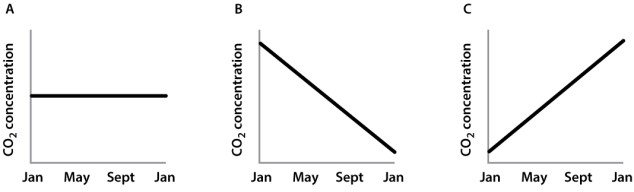
A)graph A
B)graph B
C)graph C
 How would this trend change if it were spring for an entire year? Select the graph below that represents the atmospheric CO2 levels of an Earth with a full year of spring (assume you are in the Northern Hemisphere).
How would this trend change if it were spring for an entire year? Select the graph below that represents the atmospheric CO2 levels of an Earth with a full year of spring (assume you are in the Northern Hemisphere). 
A)graph A
B)graph B
C)graph C
C
4
A positive feedback is one in which the products of a process act to increase the rate at which the process operates. Which of the following would constitute a positive feedback in the carbon cycle?
A)Increasing CO2 causing an increase in rates of photosynthesis.
B)Increasing temperature causing an increase in rates of photosynthesis.
C)Increasing temperature causing an increase in rates of respiration.
D)Increasing temperature causing an increase in rates of continental weathering.
A)Increasing CO2 causing an increase in rates of photosynthesis.
B)Increasing temperature causing an increase in rates of photosynthesis.
C)Increasing temperature causing an increase in rates of respiration.
D)Increasing temperature causing an increase in rates of continental weathering.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which correlates CLOSEST with the net increase in CO2 levels over the past two centuries?
A)volcanic gases
B)carbon dissolved in the oceans
C)respiration
D)human activities
A)volcanic gases
B)carbon dissolved in the oceans
C)respiration
D)human activities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When looking at the carbon isotopes present in the atmosphere, scientists determined that 13C and 14C levels have decreased over time. What did researchers conclude from these observations?
A)volcanic activity is responsible for increased atmospheric CO2
B)the burning of forests is responsible for increased atmospheric CO2
C)the use of fossil fuels is responsible for increased atmospheric CO2
D)increased plant/animal respiration is responsible for increased atmospheric CO2
A)volcanic activity is responsible for increased atmospheric CO2
B)the burning of forests is responsible for increased atmospheric CO2
C)the use of fossil fuels is responsible for increased atmospheric CO2
D)increased plant/animal respiration is responsible for increased atmospheric CO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If plants consume CO2 during photosynthesis, why hasn't all the atmospheric CO2 been used up?
A)Photosynthesis also produces CO2 as a product.
B)Respiration produces CO2 as a product.
C)Both photosynthesis and respiration produce CO2 as products.
D)Plants actually don't use CO2 during photosynthesis; they use O2.
E)Photosynthesis and respiration use one another's products as reactants.
A)Photosynthesis also produces CO2 as a product.
B)Respiration produces CO2 as a product.
C)Both photosynthesis and respiration produce CO2 as products.
D)Plants actually don't use CO2 during photosynthesis; they use O2.
E)Photosynthesis and respiration use one another's products as reactants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What can Antarctic ice core samples tell us about atmospheric CO2 levels?
A)Nothing, because ice is made of H2O and not CO2.
B)CO2 ice core data confirm CO2 measurements taken directly from the atmosphere.
C)Ice cores can help scientists estimate atmospheric CO2 levels from centuries ago.
D)Ice cores can tell scientists exactly what plants lived on Earth centuries ago.
A)Nothing, because ice is made of H2O and not CO2.
B)CO2 ice core data confirm CO2 measurements taken directly from the atmosphere.
C)Ice cores can help scientists estimate atmospheric CO2 levels from centuries ago.
D)Ice cores can tell scientists exactly what plants lived on Earth centuries ago.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following processes are typically associated with the short-term carbon cycle?
A)respiration
B)plate tectonics
C)photosynthesis
D)chemical weathering
A)respiration
B)plate tectonics
C)photosynthesis
D)chemical weathering

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In reviewing historical records and ice core data, researchers noted that atmospheric CO2 levels started to rise as humans began to burn fossil fuels. This is an example of what type of relationship?
A)correlation
B)contradiction
C)causation
D)antagonism
E)conduction
A)correlation
B)contradiction
C)causation
D)antagonism
E)conduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The process of cellular respiration consumes _____ and produces _____.
A)CO2; O2
B)O2; CO2
C)O2; H2O
D)CO2; H2O
A)CO2; O2
B)O2; CO2
C)O2; H2O
D)CO2; H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The CO2 level is _____ during winter in the northern hemisphere compared to levels in the summer.
A)lower
B)higher
C)the same
A)lower
B)higher
C)the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Consider the Keeling curve, which shows a steady increase in CO2 levels over the past 50+ years. This steady rise has been attributed to both natural and human activity. Imagine if everyone in the world planted a fast-growing vine that was an annual (i.e., it grows large and fast, but dies after one year). Predict the effect this would hypothetically have on the level of CO2 in the atmosphere over the next 20 years.
A)The level of CO2 in the atmosphere will steadily decrease because of increased rates of photosynthesis.
B)The level of CO2 in the atmosphere will steadily increase because decomposition of the annuals simply returns the CO2 back into the atmosphere.
C)The level of CO2 in the atmosphere will stay the same because the growing annuals will remove the extra CO2 from human activity.
A)The level of CO2 in the atmosphere will steadily decrease because of increased rates of photosynthesis.
B)The level of CO2 in the atmosphere will steadily increase because decomposition of the annuals simply returns the CO2 back into the atmosphere.
C)The level of CO2 in the atmosphere will stay the same because the growing annuals will remove the extra CO2 from human activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the below statements is true regarding the movement of carbon between organisms in a food web and the transfer of energy between organisms in different trophic levels?
A)Both energy and carbon can be continuously cycled.
B)Neither energy nor carbon can be continuously cycled.
C)Energy can be continuously cycled, but carbon cannot.
D)Carbon can be continuously cycled, but energy cannot.
A)Both energy and carbon can be continuously cycled.
B)Neither energy nor carbon can be continuously cycled.
C)Energy can be continuously cycled, but carbon cannot.
D)Carbon can be continuously cycled, but energy cannot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Over the last several decades, what have researchers discovered about atmospheric CO2 levels?
A)They have decreased.
B)They have increased.
C)They have remained the same.
D)They increased for a period, but have now stabilized.
A)They have decreased.
B)They have increased.
C)They have remained the same.
D)They increased for a period, but have now stabilized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
CO2 is added to the atmosphere by:
A)respiration.
B)photosynthesis.
C)deforestation.
D)the weathering of rocks.
A)respiration.
B)photosynthesis.
C)deforestation.
D)the weathering of rocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
It is thought that approximately 90% of plant species went extinct during the Carboniferous Period (~320-290 mya). Which of the following graphs represent the changes that likely occurred in carbon dioxide and oxygen levels? (The solid black line depicts CO2 levels, the dashed line represents O2 levels) The left side of the x-axis represents the time of the extinction event. 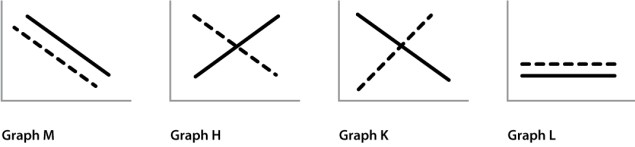
A)graph M
B)graph H
C)graph K
D)graph L

A)graph M
B)graph H
C)graph K
D)graph L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The Keeling curve in Figure 25.1, below, shows that while CO2 levels oscillate on an annual basis, overall CO2 levels increase from year to year. 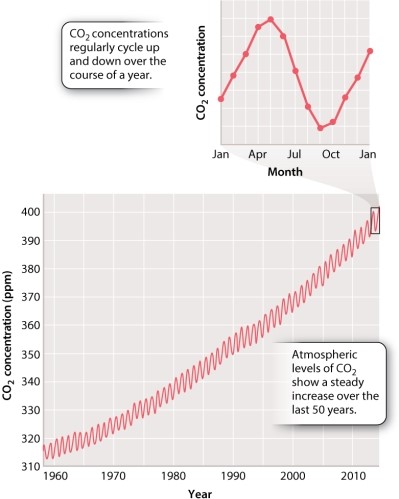 Why has this trend continued in the last 50 years?
Why has this trend continued in the last 50 years?
A)increasing rates of aerobic respiration associated with the rise in world population
B)decreasing rates of oxygenic photosynthesis by plants and algae
C)clearing of forests to create agricultural land outside the tropics
D)combustion of fossil fuels
 Why has this trend continued in the last 50 years?
Why has this trend continued in the last 50 years?A)increasing rates of aerobic respiration associated with the rise in world population
B)decreasing rates of oxygenic photosynthesis by plants and algae
C)clearing of forests to create agricultural land outside the tropics
D)combustion of fossil fuels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Why are carbon-based organic compounds, such as C6H12O6 (glucose), often referred to as "energy molecules"?
A)Energy is released when carbon-containing compounds are broken down.
B)Energy is stored in carbon-containing organic compounds.
C)Energy is required to build carbon-containing organic compounds.
D)None of the answer options is correct.
A)Energy is released when carbon-containing compounds are broken down.
B)Energy is stored in carbon-containing organic compounds.
C)Energy is required to build carbon-containing organic compounds.
D)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The levels of CO2 in the atmosphere have been:
A)increasing.
B)decreasing.
C)staying the same.
A)increasing.
B)decreasing.
C)staying the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The equation 6CO2 + 6H2O+ C2H12O6 + 6O2 represents the process of:
A)photosynthesis.
B)respiration.
C)None of the answer options is correct.
A)photosynthesis.
B)respiration.
C)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Photosynthesis and respiration both play a major role in the _____ carbon cycle, and can affect atmospheric CO2 levels on a seasonal or annual basis.
A)short-term
B)long-term
C)None of the answer options is correct.
A)short-term
B)long-term
C)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The equation C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O represents the process of:
A)photosynthesis.
B)respiration.
C)None of the answer options is correct.
A)photosynthesis.
B)respiration.
C)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Cellular respiration is a process unique to animals, and is not undertaken by plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Photosynthesis _____ the atmosphere, whereas respiration _____ the atmosphere.
A)removes CO2 from; introduces CO2 to
B)introduces CO2 to; removes CO2 from
A)removes CO2 from; introduces CO2 to
B)introduces CO2 to; removes CO2 from

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Measuring the isotopic composition of atmospheric CO2 shows that the burning of fossil fuels has led to _____ CO2 levels over the last 200 years.
A)increasing
B)decreasing
A)increasing
B)decreasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The rate of respiration _____ throughout the year.
A)remains more or less constant
B)varies significantly
A)remains more or less constant
B)varies significantly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Imagine that a time traveler was able to successfully travel 2 billion years back in time and modified the environment so that photosynthesis and respiration were completely coupled (i.e., there was no "leakage" of products from respiration or photosynthesis). How would this affect Earth's present-day atmosphere, if at all?
A)Earth's atmosphere would be unaffected.
B)Atmospheric O2 levels would increase.
C)Atmospheric O2 levels would decrease.
D)Atmospheric CO2 levels would increase, but O2 levels would be unaffected.
E)Atmospheric O2 levels would increase, but CO2 levels would be unaffected.
A)Earth's atmosphere would be unaffected.
B)Atmospheric O2 levels would increase.
C)Atmospheric O2 levels would decrease.
D)Atmospheric CO2 levels would increase, but O2 levels would be unaffected.
E)Atmospheric O2 levels would increase, but CO2 levels would be unaffected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Recall that photosynthetic rates remain relatively constant in regions near the equator. Imagine that tropical environments persisted throughout Earth's northern and southern hemispheres (i.e., Earth's entire climate mirrored that near the equator). If Keeling had collected his atmospheric CO2 data on such an Earth, what would you expect the Keeling Curve to look like?
A)a straight line sloping upward (atmospheric CO2 levels would not seasonally oscillate, but would have increased over time)
B)a straight line sloping downward (atmospheric CO2 levels would not seasonally oscillate, but would have decreased over time)
C)a sinusoidal curve sloping upward (atmospheric CO2 levels would fluctuate seasonally, but would increase over time)
D)a sinusoidal curve sloping downward (atmospheric CO2 levels would fluctuate seasonally, but would have decreased over time)
E)a straight line without a slope (atmospheric CO2 levels would have remained constant over time)
A)a straight line sloping upward (atmospheric CO2 levels would not seasonally oscillate, but would have increased over time)
B)a straight line sloping downward (atmospheric CO2 levels would not seasonally oscillate, but would have decreased over time)
C)a sinusoidal curve sloping upward (atmospheric CO2 levels would fluctuate seasonally, but would increase over time)
D)a sinusoidal curve sloping downward (atmospheric CO2 levels would fluctuate seasonally, but would have decreased over time)
E)a straight line without a slope (atmospheric CO2 levels would have remained constant over time)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Photosynthesis and respiration affect atmospheric CO2 levels on a _____ timescale, whereas volcanic eruptions affect atmospheric CO2 levels on a _____ timescale.
A)yearly; century
B)century; yearly
A)yearly; century
B)century; yearly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Hans Suess's work (and subsequent studies carried out by other researchers) determined that the amount of 13C in Earth's atmosphere has _____, and the amount of 14C in the atmosphere has _____.
A)decreased; increased
B)increased; decreased
C)decreased; also decreased
D)increased; also increased
A)decreased; increased
B)increased; decreased
C)decreased; also decreased
D)increased; also increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In the northern and southern hemispheres, the rate of photosynthesis is _____ in the summer and _____ in the winter.
A)highest; lowest
B)lowest; highest
A)highest; lowest
B)lowest; highest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following processes is responsible for the changes scientists observed in atmospheric concentrations of 12C, 13C, and 14C over the last 200 years?
A)the burning of fossil fuels
B)volcanism
C)the clearing of forests
D)chemical weathering
E)subduction
A)the burning of fossil fuels
B)volcanism
C)the clearing of forests
D)chemical weathering
E)subduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is NOT considered a photosynthetic organism, and so would not remove atmospheric CO2?
A)kelp
B)elm tree
C)human
D)moss
E)phytoplankton
A)kelp
B)elm tree
C)human
D)moss
E)phytoplankton

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The ocean, much like the atmosphere, can serve as a sink for man-made CO2. In fact, both Earth's atmosphere and the ocean store roughly equal amounts of man-made CO2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Because the products of photosynthesis are used as the reactants of respiration, these two processes are said to be:
A)antagonistic.
B)complementary.
C)supplementary.
D)symbiotic.
E)tangential.
A)antagonistic.
B)complementary.
C)supplementary.
D)symbiotic.
E)tangential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A researcher is measuring atmospheric CO2 levels on cloudy and sunny days. He notices that on sunny days, CO2 levels appear slightly higher compared to levels on cloudy days. This is an example of:
A)causation.
B)fluxation.
C)correlation.
D)conjugation.
E)assimilation.
A)causation.
B)fluxation.
C)correlation.
D)conjugation.
E)assimilation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Scientists can gain information about ancient atmospheric CO2 levels through ice core data. This is primarily the result of sediments being trapped in glaciers, which scientists can subsequently assess for different carbon isotopes (13C, 12C, 14C).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Recall that in the northern hemisphere, atmospheric CO2 levels are highest in early spring and lowest in early fall. What accounts for this seasonal fluctuation in atmospheric CO2 levels?
A)photosynthesis
B)human activities
C)respiration
D)biomineralization
E)plate tectonics
A)photosynthesis
B)human activities
C)respiration
D)biomineralization
E)plate tectonics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If researchers never evaluated the amount of 14C in the atmosphere, they could still use 13C levels to demonstrate causation between human activities and increased atmospheric CO2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding CO2?
A)CO2 is a greenhouse gas.
B)CO2 plays a vital role in maintaining Earth's temperature.
C)CO2 is released as a product of respiration.
D)CO2 can be produced by natural and man-made processes.
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)CO2 is a greenhouse gas.
B)CO2 plays a vital role in maintaining Earth's temperature.
C)CO2 is released as a product of respiration.
D)CO2 can be produced by natural and man-made processes.
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is considered a carbon reservoir?
A)the Atlantic Ocean
B)Redwood National Park
C)the Great Barrier Reef
D)all the organisms on Earth
A)the Atlantic Ocean
B)Redwood National Park
C)the Great Barrier Reef
D)all the organisms on Earth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Recall that over the last 400,000 years, atmospheric CO2 levels have fluctuated, with the lowest levels occurring during glacial periods and the highest levels occurring during interglacial periods. Why might atmospheric CO2 levels be lower during glacial periods?
A)During glacial periods, there are more volcanic eruptions.
B)During glacial periods, there are fewer photosynthesizing plants.
C)During glacial periods, more carbon is stored in ocean reservoirs.
D)During glacial periods, chemical weathering stops.
A)During glacial periods, there are more volcanic eruptions.
B)During glacial periods, there are fewer photosynthesizing plants.
C)During glacial periods, more carbon is stored in ocean reservoirs.
D)During glacial periods, chemical weathering stops.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A scientist studying a material has determined that 12C, 13C, and 14C occur in the material in a ratio of 1000:10:1. How did he MOST likely differentiate between these forms of carbon?
A)by the number of protons in 12C, 13C, and 14C
B)by the number of electrons in 12C, 13C, and 14C
C)by the number of neutrons in 12C, 13C, and 14C
D)by the biomasses of 12C, 13C, and 14C
E)by the number of positrons in 12C, 13C, and 14C
A)by the number of protons in 12C, 13C, and 14C
B)by the number of electrons in 12C, 13C, and 14C
C)by the number of neutrons in 12C, 13C, and 14C
D)by the biomasses of 12C, 13C, and 14C
E)by the number of positrons in 12C, 13C, and 14C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What would be the environmental consequences if Earth's volcanoes all shut down tomorrow?
A)CO2 levels in the atmosphere would slowly rise.
B)Continental weathering would decrease.
C)Rates of continental weathering would slowly increase.
D)Temperature would slowly increase.
A)CO2 levels in the atmosphere would slowly rise.
B)Continental weathering would decrease.
C)Rates of continental weathering would slowly increase.
D)Temperature would slowly increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The movement of carbon from CO2 in the atmosphere to HCO3-(a byproduct of chemical weathering) on rocks to CaCO3 in coral skeletons and finally CaCO3 in limestone are all steps in the _____ cycle.
A)short-term carbon
B)nitrogen
C)sulfur
D)long-term carbon
A)short-term carbon
B)nitrogen
C)sulfur
D)long-term carbon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Charles Keeling's work demonstrated that, over the last five decades, atmospheric CO2 levels have increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Nearly 150 years ago, man-made CO2 was introduced into the atmosphere primarily through _____. Currently, _____ is the main contributing factor to increased levels of human-produced CO2 in the atmosphere.
A)the burning of fossil fuels; deforestation
B)deforestation; the burning of fossil fuels
C)respiration; deforestation
D)deforestation; respiration
E)the burning of fossil fuels; the burning of fossil fuels
A)the burning of fossil fuels; deforestation
B)deforestation; the burning of fossil fuels
C)respiration; deforestation
D)deforestation; respiration
E)the burning of fossil fuels; the burning of fossil fuels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
How has Earth's atmosphere been influenced by the fact that, as part of the carbon cycle, some amount of organic carbon is stored in sedimentary rocks and is not immediately re-introduced back into the atmosphere?
A)The storing of organic carbon in sedimentary rocks allowed for Earth's atmosphere to remain the same for the last 4 billion years.
B)The storing of organic carbon in sedimentary rocks allowed for oxygen to become a main component of Earth's atmosphere.
C)The storing of organic carbon in sedimentary rocks resulted in carbon not becoming an integral part of Earth's atmosphere.
D)The carbon cycle is not related to the composition of Earth's atmosphere.
A)The storing of organic carbon in sedimentary rocks allowed for Earth's atmosphere to remain the same for the last 4 billion years.
B)The storing of organic carbon in sedimentary rocks allowed for oxygen to become a main component of Earth's atmosphere.
C)The storing of organic carbon in sedimentary rocks resulted in carbon not becoming an integral part of Earth's atmosphere.
D)The carbon cycle is not related to the composition of Earth's atmosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Of the processes that release CO2 to the atmosphere, which are influenced by human technology?
A)increased volcanic activity because of local earthquakes
B)wild fires set by lightning strikes in remote areas of forests
C)burning organic carbon that has been stored in sediments and sedimentary rocks
D)respiration rates dropping because of increased temperatures at the poles
A)increased volcanic activity because of local earthquakes
B)wild fires set by lightning strikes in remote areas of forests
C)burning organic carbon that has been stored in sediments and sedimentary rocks
D)respiration rates dropping because of increased temperatures at the poles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
CO2 is an example of a _____, a gas in the atmosphere that is transparent to solar radiation but can absorb heat emitted from Earth's surface.
A)photosynthesis product
B)synthetic carbon cycle product
C)greenhouse gas
D)None of the answer options is correct.
A)photosynthesis product
B)synthetic carbon cycle product
C)greenhouse gas
D)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What would be the environmental consequences if Earth's volcanoes all shut down tomorrow?
A)CO2 levels in the atmosphere would slowly rise.
B)CO2 levels in the atmosphere would slowly fall.
C)Rates of continental weathering would slowly increase.
D)Temperature would slowly increase.
A)CO2 levels in the atmosphere would slowly rise.
B)CO2 levels in the atmosphere would slowly fall.
C)Rates of continental weathering would slowly increase.
D)Temperature would slowly increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following processes are typically associated with the long-term carbon cycle?
A)respiration
B)burial of carbon in sediments
C)photosynthesis
D)volcanic eruptions
A)respiration
B)burial of carbon in sediments
C)photosynthesis
D)volcanic eruptions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the processes listed below naturally release CO2 into the atmosphere?
A)volcanism
B)chemical weathering
C)subduction
D)biomineralization
E)oxidation of fossil fuels (by bacteria)
A)volcanism
B)chemical weathering
C)subduction
D)biomineralization
E)oxidation of fossil fuels (by bacteria)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
How is atmospheric oxygen linked to the carbon cycle?
A)More burial of organic carbon in sediments results in more oxygen in the atmosphere and oceans.
B)More photosynthesis leads to more oxygen in the atmosphere and oceans.
C)More volcanic CO2 emission leads to more oxygen in the atmosphere and oceans.
D)Longer food chains with more consumers lead to more oxygen in the atmosphere and oceans.
A)More burial of organic carbon in sediments results in more oxygen in the atmosphere and oceans.
B)More photosynthesis leads to more oxygen in the atmosphere and oceans.
C)More volcanic CO2 emission leads to more oxygen in the atmosphere and oceans.
D)Longer food chains with more consumers lead to more oxygen in the atmosphere and oceans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Seasonal respiration rates fluctuate in a similar manner as seasonal photosynthesis rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A researcher is comparing atmospheric CO2 levels in Earth's northern and southern hemispheres during June and August. Since more terrestrial plants are present in the northern hemisphere, what do you expect she will find?
A)Atmospheric CO2 measurements will be greater in the northern hemisphere.
B)Atmospheric CO2 measurements will be greater in the southern hemisphere
C)Because atmospheric CO2 measurements represent global amounts, measurements in the northern and southern hemispheres will be (approximately)the same.
A)Atmospheric CO2 measurements will be greater in the northern hemisphere.
B)Atmospheric CO2 measurements will be greater in the southern hemisphere
C)Because atmospheric CO2 measurements represent global amounts, measurements in the northern and southern hemispheres will be (approximately)the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Over the last 400,000 years, how have atmospheric CO2 levels changed?
A)Atmospheric CO2 levels have remained the same.
B)Atmospheric CO2 levels have been steadily increasing overall.
C)Atmospheric CO2 levels have been steadily decreasing overall.
D)Atmospheric CO2 levels have fluctuated periodically.
A)Atmospheric CO2 levels have remained the same.
B)Atmospheric CO2 levels have been steadily increasing overall.
C)Atmospheric CO2 levels have been steadily decreasing overall.
D)Atmospheric CO2 levels have fluctuated periodically.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following statements is TRUE about photosynthesis and chemical weathering?
A)Both processes release CO2 as a product (i.e., increase atmospheric CO2 levels).
B)Both processes use CO2 as a reactant (i.e., decrease atmospheric CO2 levels).
C)Both processes are typically associated with the long-term carbon cycle.
D)Both processes are typically associated with the short-term carbon cycle.
A)Both processes release CO2 as a product (i.e., increase atmospheric CO2 levels).
B)Both processes use CO2 as a reactant (i.e., decrease atmospheric CO2 levels).
C)Both processes are typically associated with the long-term carbon cycle.
D)Both processes are typically associated with the short-term carbon cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The observation that atmospheric CO2 levels were typically low during glacial periods in Earth's history is an example of:
A)causation.
B)correlation.
C)communication.
D)confusion.
A)causation.
B)correlation.
C)communication.
D)confusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The movement of the Earth's crust, plate tectonics, contributes to the long-term carbon cycle through all of the following EXCEPT:
A)subduction.
B)mountain lifting.
C)photosynthesis.
D)volcanic activity.
E)None of the answer options is correct.
A)subduction.
B)mountain lifting.
C)photosynthesis.
D)volcanic activity.
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The term that describes the movement of Earth's crust and includes the process of subduction is _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following relationships BEST depicts the amount of carbon stored in the atmosphere, sedimentary rocks, living organisms, and soil?
A)soil < the atmosphere < sedimentary rocks < living organisms
B)the atmosphere < soil < living organisms < sedimentary rocks
C)sedimentary rocks < soil < living organisms < the atmosphere
D)soil < living organisms < sedimentary rocks < the atmosphere
E)living organisms < the atmosphere < soil < sedimentary rocks
A)soil < the atmosphere < sedimentary rocks < living organisms
B)the atmosphere < soil < living organisms < sedimentary rocks
C)sedimentary rocks < soil < living organisms < the atmosphere
D)soil < living organisms < sedimentary rocks < the atmosphere
E)living organisms < the atmosphere < soil < sedimentary rocks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Because CO2 is a greenhouse gas, a rise in CO2 levels correlates with a(n):
A)rise in respiration.
B)rise in temperature.
C)increase in the size of glaciers.
D)rise in photosynthesis.
A)rise in respiration.
B)rise in temperature.
C)increase in the size of glaciers.
D)rise in photosynthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following processes INCREASES the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere?
A)photosynthesis
B)volcanic eruptions
C)subduction
D)chemical weathering
E)respiration
A)photosynthesis
B)volcanic eruptions
C)subduction
D)chemical weathering
E)respiration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding atmospheric CO2 levels during the last 400,000 years?
A)Atmospheric CO2 levels have remained relatively constant, and have only increased since the 1800s.
B)Atmospheric CO2 levels fluctuate periodically, with the highest levels occurring during interglacial periods.
C)Atmospheric CO2 levels fluctuate periodically, with the highest levels occurring during glacial periods.
D)Correlation exists between low levels of atmospheric CO2 and high temperatures.
E)Causation exists between low levels of atmospheric CO2 and high temperatures.
A)Atmospheric CO2 levels have remained relatively constant, and have only increased since the 1800s.
B)Atmospheric CO2 levels fluctuate periodically, with the highest levels occurring during interglacial periods.
C)Atmospheric CO2 levels fluctuate periodically, with the highest levels occurring during glacial periods.
D)Correlation exists between low levels of atmospheric CO2 and high temperatures.
E)Causation exists between low levels of atmospheric CO2 and high temperatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Recall that during the Paleozoic Era, atmospheric CO2 levels decreased. Why?
A)New, extensive mountain ranges formed and chemical weathering decreased.
B)Earth's plate tectonics changed dramatically, and subduction increased.
C)Photosynthetic, woody plants first appeared during this period.
D)Volcanism decreased during this period.
A)New, extensive mountain ranges formed and chemical weathering decreased.
B)Earth's plate tectonics changed dramatically, and subduction increased.
C)Photosynthetic, woody plants first appeared during this period.
D)Volcanism decreased during this period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The long-term and short-term carbon cycles are connected by the fact that some of the carbon contained in C6H12O6 (or other organic molecules) in plants is incorporated into sedimentary rocks or oil; it is not immediately reintroduced back into the atmosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding chemical weathering?
A)It plays a major role in the short-term carbon cycle.
B)It releases CO2 into the atmosphere.
C)It relies on the acid SiO2.
D)It contributes to the accumulation of CaCO3 in oceans.
E)It relies on bacteria to break down rocks.
A)It plays a major role in the short-term carbon cycle.
B)It releases CO2 into the atmosphere.
C)It relies on the acid SiO2.
D)It contributes to the accumulation of CaCO3 in oceans.
E)It relies on bacteria to break down rocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
When we think about the carbon cycle and human activities, it is important to differentiate between facts and hypotheses. Which of the following can be considered a fact?
A)The amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has increased since 1950.
B)Increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide will cause mean global temperature to increase by 2 degrees Celsius over the next century.
C)The burning of fossil fuels contributes substantially to the ongoing rise of atmospheric CO2.
D)In the past, atmospheric CO2 levels reached levels higher than those observed today.
A)The amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has increased since 1950.
B)Increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide will cause mean global temperature to increase by 2 degrees Celsius over the next century.
C)The burning of fossil fuels contributes substantially to the ongoing rise of atmospheric CO2.
D)In the past, atmospheric CO2 levels reached levels higher than those observed today.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Increased rate of photosynthesis is the most likely explanation as to why atmospheric CO2 levels appear lowest during glacial periods of Earth's history.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Currently, atmospheric CO2 levels are the highest they have ever been in Earth's 4.6-billion-year history.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Of the processes involved in the long-term carbon cycle, which removes CO2 from the atmosphere?
A)chemical weathering
B)volcanism
C)respiration
D)photosynthesis
E)bacteria-based oxidation
A)chemical weathering
B)volcanism
C)respiration
D)photosynthesis
E)bacteria-based oxidation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following are NOT geological processes that drive the long-term carbon cycle?
A)volcanism and plate tectonics
B)subduction and volcanism
C)photosynthesis and respiration
D)chemical weathering and plate tectonics
E)subduction and chemical weathering
A)volcanism and plate tectonics
B)subduction and volcanism
C)photosynthesis and respiration
D)chemical weathering and plate tectonics
E)subduction and chemical weathering

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Imagine that a researcher has discovered a 500-million-year-old leaf fossil from the Cambrian Period. He notices that the leaf had very few stomata compared to present-day leaves. What does this tell the researcher about atmospheric CO2 levels during the Cambrian Period?
A)Atmospheric CO2 levels were higher during the Cambrian Period compared to today.
B)Atmospheric CO2 levels were lower during the Cambrian Period compared to today.
C)Atmospheric CO2 levels during the Cambrian Period were equal to present-day levels.
D)Atmospheric CO2 levels are not correlated with numbers of stomata.
A)Atmospheric CO2 levels were higher during the Cambrian Period compared to today.
B)Atmospheric CO2 levels were lower during the Cambrian Period compared to today.
C)Atmospheric CO2 levels during the Cambrian Period were equal to present-day levels.
D)Atmospheric CO2 levels are not correlated with numbers of stomata.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Carbon is incorporated into the skeletons of corals and other marine organisms through the process of _____. The CaCO3 making up these skeletons, in turn, becomes a major component of sedimentary rocks after these organisms die.
A)chemical weathering
B)subduction
C)biomineralization
D)inorganic mineralization
E)bacterial oxidation
A)chemical weathering
B)subduction
C)biomineralization
D)inorganic mineralization
E)bacterial oxidation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
How can scientists determine what atmospheric CO2 levels were like hundreds or thousands of years ago?
A)They can examine ice core samples from Antarctica.
B)They can examine CO2 levels in the outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere.
C)They can examine the number of stomata in fossilized leaves.
D)They can examine the number of fossilized dinosaur skeletons from different eras.
A)They can examine ice core samples from Antarctica.
B)They can examine CO2 levels in the outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere.
C)They can examine the number of stomata in fossilized leaves.
D)They can examine the number of fossilized dinosaur skeletons from different eras.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The _____ cycle deals with geological processes and carbon reservoirs, some of which have been built up (or take place) over a period of millennia. In contrast, the _____ cycle involves biological processes that are carried out on a daily and/or seasonal basis.
A)short-term carbon; long-term carbon
B)long-term carbon; short-term carbon
C)short-term carbon; rapid carbon
D)long-term carbon; intermediate carbon
A)short-term carbon; long-term carbon
B)long-term carbon; short-term carbon
C)short-term carbon; rapid carbon
D)long-term carbon; intermediate carbon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The majority of carbon stored in reservoirs is in the form of:
A)CO2.
B)C6H12O6.
C)H2CO3.
D)CaCO3.
E)CH4.
A)CO2.
B)C6H12O6.
C)H2CO3.
D)CaCO3.
E)CH4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Of the processes involved in the long-term carbon cycle, which introduces CO2 back into the atmosphere?
A)chemical weathering
B)carbonate precipitation
C)volcanism
D)respiration
E)photosynthesis
A)chemical weathering
B)carbonate precipitation
C)volcanism
D)respiration
E)photosynthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



