Deck 19: Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/189
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation
1
A histone code is the:
A)nucleotide sequence of an individual histone protein's gene.
B)pattern of chemical modification of the DNA wrapped around an individual histone.
C)pattern of chemical modification of the histone tails.
D)number of amino acids in an individual histone that are methylated.
E)None of the other answer options is correct.
A)nucleotide sequence of an individual histone protein's gene.
B)pattern of chemical modification of the DNA wrapped around an individual histone.
C)pattern of chemical modification of the histone tails.
D)number of amino acids in an individual histone that are methylated.
E)None of the other answer options is correct.
C
2
Which of the following processes produce different proteins in different cells from the same primary transcript?
A)chromatin remodeling
B)histone modification
C)combinatorial control
D)alternative splicing
E)RNA editing
A)chromatin remodeling
B)histone modification
C)combinatorial control
D)alternative splicing
E)RNA editing
D, E
3
A researcher notices that women working in the petrochemical industry who are exposed to aromatic hydrocarbons may have a greater incidence of breast cancer than women without such exposure. The researcher undertakes a study of the BRCA1 promoter using the restriction enzymes MspI and HpaII. MspI cleaves double-stranded DNA at 5'-CCGG-3' regardless of whether the CG in the middle has cytosine methylation, whereas HpaII cleaves double-stranded DNA at 5'-CCGG-3' only when the CG in the middle lacks cytosine methylation. For a region of double-stranded DNA in the promoter region of BRCA1, tumor cells from the breasts of exposed women with breast cancer and nontumor cells from breasts from the same women show the illustrated patterns of bands produced by MspI and HpaII: 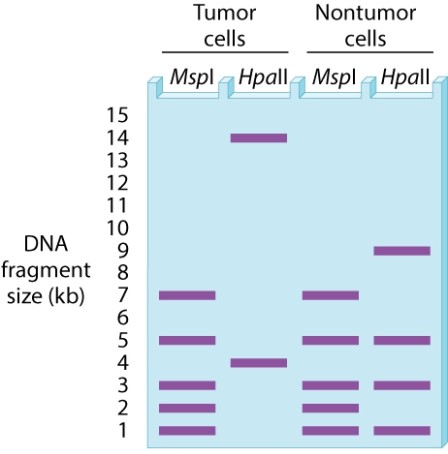 Which of the following statements are supported by this evidence?
Which of the following statements are supported by this evidence?
A)More sites are methylated in tumor cells than in nontumor cells.
B)Fewer sites are methylated in tumor cells than in nontumor cells.
C)The same sites are methylated in tumor cells as in nontumor cells.
D)No sites are methylated in nontumor cells.
E)The BRCA1 gene may be epigenetically silenced in tumor cells.
 Which of the following statements are supported by this evidence?
Which of the following statements are supported by this evidence?A)More sites are methylated in tumor cells than in nontumor cells.
B)Fewer sites are methylated in tumor cells than in nontumor cells.
C)The same sites are methylated in tumor cells as in nontumor cells.
D)No sites are methylated in nontumor cells.
E)The BRCA1 gene may be epigenetically silenced in tumor cells.
A, E
4
Transcription of a gene can be increased or decreased according to the:
A)combination of histone proteins found within the nucleosome.
B)coding sequences in the messenger RNAs for histone proteins.
C)proportion of arginine and lysine amino acids in the histone proteins.
D)combination of amino acid modifications in the histone tails.
A)combination of histone proteins found within the nucleosome.
B)coding sequences in the messenger RNAs for histone proteins.
C)proportion of arginine and lysine amino acids in the histone proteins.
D)combination of amino acid modifications in the histone tails.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
_____ is defined as the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product.
A)Gene expression
B)Gene regulation
C)Epigenetics
D)Imprinting
E)Chromatin remodeling
A)Gene expression
B)Gene regulation
C)Epigenetics
D)Imprinting
E)Chromatin remodeling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The methylation state of an individual CpG island:
A)is fixed; such genes are permanently turned off.
B)is fixed, but this has no effect on whether genes are expressed.
C)is random-sometimes the cytosines are methylated and sometimes they're not, but the state is independent of the environment or cell type.
D)can change over time in response to environmental cues, allowing genes to be turned on or off as needed.
E)can change over time in response to environmental cues, but this has no effect on gene expression.
A)is fixed; such genes are permanently turned off.
B)is fixed, but this has no effect on whether genes are expressed.
C)is random-sometimes the cytosines are methylated and sometimes they're not, but the state is independent of the environment or cell type.
D)can change over time in response to environmental cues, allowing genes to be turned on or off as needed.
E)can change over time in response to environmental cues, but this has no effect on gene expression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Chromatin remodeling refers to the process by which:
A)nucleosomes are repositioned to expose different stretches of DNA to the nuclear environment.
B)DNA strands are "straightened out" to allow access to the proteins that carry out transcription.
C)DNA strands are "unzipped" to allow access to the proteins that carry out transcription.
D)methylation occurs in CpG islands.
E)mutations change DNA structure and therefore chromatin structure.
A)nucleosomes are repositioned to expose different stretches of DNA to the nuclear environment.
B)DNA strands are "straightened out" to allow access to the proteins that carry out transcription.
C)DNA strands are "unzipped" to allow access to the proteins that carry out transcription.
D)methylation occurs in CpG islands.
E)mutations change DNA structure and therefore chromatin structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In the hierarchy of levels of gene regulation, in what order do the following levels of regulation take place? (1) post-translational modification
(2) RNA processing
(3) transcription
(4) chromatin remodeling
A)(1)-(2)-(3)-(4)
B)(4)-(3)-(2)-(1)
C)(1)-(3)-(2)-(4)
D)(4)-(1)-(2)-(3)
E)(4)-(2)-(3)-(1)
(2) RNA processing
(3) transcription
(4) chromatin remodeling
A)(1)-(2)-(3)-(4)
B)(4)-(3)-(2)-(1)
C)(1)-(3)-(2)-(4)
D)(4)-(1)-(2)-(3)
E)(4)-(2)-(3)-(1)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
X-inactivation is caused by the accumulation of:
A)proteins produced by the Xist gene; these proteins induce methylation, histone modification, and other changes associated with preventing transcription.
B)coding RNA produced by the Xist gene; this RNA, in addition to coding for Xist proteins, binds to and coats the X chromosome undergoing inactivation and physically prevents it from being transcribed.
C)noncoding RNA produced by the Xist gene, which coats the X chromosome and covalenty crosslinks the DNA strands preventing them from being unwound, "unzipped," and transcribed.
D)noncoding RNA produced by the Xist gene, which coats the X chromosome and induces DNA methylation, histone modification, and other changes associated with preventing transcription.
E)None of the answer choices accurately describes the process of X-inactivation.
A)proteins produced by the Xist gene; these proteins induce methylation, histone modification, and other changes associated with preventing transcription.
B)coding RNA produced by the Xist gene; this RNA, in addition to coding for Xist proteins, binds to and coats the X chromosome undergoing inactivation and physically prevents it from being transcribed.
C)noncoding RNA produced by the Xist gene, which coats the X chromosome and covalenty crosslinks the DNA strands preventing them from being unwound, "unzipped," and transcribed.
D)noncoding RNA produced by the Xist gene, which coats the X chromosome and induces DNA methylation, histone modification, and other changes associated with preventing transcription.
E)None of the answer choices accurately describes the process of X-inactivation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which process produces multiple proteins from the same primary transcript in the same cell?
A)chromatin remodeling
B)histone modification
C)combinatorial control
D)alternative splicing
E)RNA editing
A)chromatin remodeling
B)histone modification
C)combinatorial control
D)alternative splicing
E)RNA editing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In humans and other mammals, X-inactivation takes place:
A)early in development, with each new cell inheriting the same inactivated X chromosome as its parent cell.
B)late in development, with each new cell inheriting the same inactivated X chromosome as its parent cell.
C)throughout the lifetime of an organism-with each new cell division, both X chromosomes are activated, and one is then inactivated in each new cell.
D)early in development, with all maternal X chromosomes being inactivated and cells maintaining active copies of only the paternal X chromosome.
E)early in development, with all paternal X chromosomes being inactivated and cells maintaining active copies of only the maternal X chromosome.
A)early in development, with each new cell inheriting the same inactivated X chromosome as its parent cell.
B)late in development, with each new cell inheriting the same inactivated X chromosome as its parent cell.
C)throughout the lifetime of an organism-with each new cell division, both X chromosomes are activated, and one is then inactivated in each new cell.
D)early in development, with all maternal X chromosomes being inactivated and cells maintaining active copies of only the paternal X chromosome.
E)early in development, with all paternal X chromosomes being inactivated and cells maintaining active copies of only the maternal X chromosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A CpG island is:
A)a stretch of nucleotides with many C bases adjacent to G bases in a small region near or in the promoter site of a gene.
B)a stretch of nucleotides with many C bases adjacent to G bases found anywhere along a DNA strand.
C)a stretch of nucleotides with many C bases adjacent to G bases found near bacterial operons.
A)a stretch of nucleotides with many C bases adjacent to G bases in a small region near or in the promoter site of a gene.
B)a stretch of nucleotides with many C bases adjacent to G bases found anywhere along a DNA strand.
C)a stretch of nucleotides with many C bases adjacent to G bases found near bacterial operons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The diagram shown here is part of an RNA transcript containing four open reading frames (M, H, K, and L) and three introns (1, 2, 3). The sites labeled d1-d3 are nucleotides immediately before each intron on the 5' side and those labeled a1-a3 are nucleotides immediately after each intron on the 3' side. Splicing out an intron involves cleaving the DNA at the d and a sites at either end of the intron. 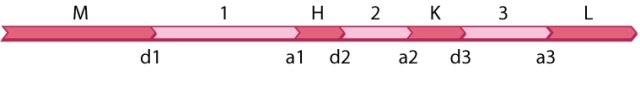 A missense mutation takes place in open reading frame K. In which possible alternative splice forms of the transcript would the missense mutation not affect the polypeptide product?
A missense mutation takes place in open reading frame K. In which possible alternative splice forms of the transcript would the missense mutation not affect the polypeptide product?
A)d1-a1 + d2-a2 + d3-a3
B)d1-a2 + d3-a3
C)d1-a1 + d2-a3
D)d1-a3
E)None of the answer options is correct.
 A missense mutation takes place in open reading frame K. In which possible alternative splice forms of the transcript would the missense mutation not affect the polypeptide product?
A missense mutation takes place in open reading frame K. In which possible alternative splice forms of the transcript would the missense mutation not affect the polypeptide product?A)d1-a1 + d2-a2 + d3-a3
B)d1-a2 + d3-a3
C)d1-a1 + d2-a3
D)d1-a3
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The diagram shown here is part of an RNA transcript containing four open reading frames (M, H, K, and L) and three introns (1, 2, 3). The sites labeled d1-d3 are nucleotides immediately before each intron on the 5' side and those labeled a1-a3 are nucleotides immediately after each intron on the 3' side. Splicing out an intron involves a spliceosome facilitating the cleavage of the DNA at the d and a sites at either end of the intron. 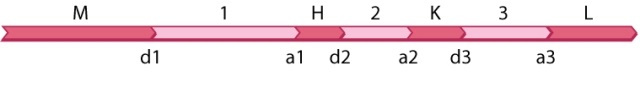 A missense mutation takes place in open reading frame H. In which possible alternative splice forms of the transcript would the missense mutation not affect the polypeptide product?
A missense mutation takes place in open reading frame H. In which possible alternative splice forms of the transcript would the missense mutation not affect the polypeptide product?
A)d1-a1 + d2-a2 + d3-a3
B)d1-a2 + d3-a3
C)d1-a1 + d2-a3
D)d1-a3
E)None of the answer options is correct.
 A missense mutation takes place in open reading frame H. In which possible alternative splice forms of the transcript would the missense mutation not affect the polypeptide product?
A missense mutation takes place in open reading frame H. In which possible alternative splice forms of the transcript would the missense mutation not affect the polypeptide product?A)d1-a1 + d2-a2 + d3-a3
B)d1-a2 + d3-a3
C)d1-a1 + d2-a3
D)d1-a3
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Modifications of histone tails can:
A)affect chromatin structure.
B)activate transcription of some genes.
C)repress transcription of some genes.
D)affect expression of some genes in response to the environment.
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)affect chromatin structure.
B)activate transcription of some genes.
C)repress transcription of some genes.
D)affect expression of some genes in response to the environment.
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Sex-specific silencing of gene expression is known as:
A)X-inactivation.
B)methylation.
C)chromatin remodeling.
D)imprinting.
E)None of the answer options is correct.
A)X-inactivation.
B)methylation.
C)chromatin remodeling.
D)imprinting.
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In mammals, dosage compensation refers to a mechanism in which:
A)the level of expression for a given gene is directly related to the number of copies of the gene.
B)genes in the Y chromosome must be expressed at higher levels than would otherwise be the case because they are not homologous with genes on the X chromosome.
C)genes in the X chromosome must be expressed at lower levels than would otherwise be the case because they are not homologous with genes on the Y chromosome.
D)X chromosome genes are regulated differently in males and females because members of one sex have two X chromosomes, whereas members of the other have only one.
E)None of the answer options is correct.
A)the level of expression for a given gene is directly related to the number of copies of the gene.
B)genes in the Y chromosome must be expressed at higher levels than would otherwise be the case because they are not homologous with genes on the X chromosome.
C)genes in the X chromosome must be expressed at lower levels than would otherwise be the case because they are not homologous with genes on the Y chromosome.
D)X chromosome genes are regulated differently in males and females because members of one sex have two X chromosomes, whereas members of the other have only one.
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In general, when cytosine bases in CpG islands are methylated:
A)transcription is active and rapid.
B)transcription is active, but slow.
C)transcription is repressed.
D)translation is active and rapid.
E)translation is repressed.
A)transcription is active and rapid.
B)transcription is active, but slow.
C)transcription is repressed.
D)translation is active and rapid.
E)translation is repressed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The diagram shown here is part of an RNA transcript containing four open reading frames (M, H, K, and L) and three introns (1, 2, 3). The sites labeled d1-d3 are nucleotides immediately before each intron on the 5' side and those labeled a1-a3 are nucleotides immediately after each intron on the 3' side. Splicing out an intron involves a spliceosome facilitating the cleavage of the DNA at the d and a sites at either end of the intron. 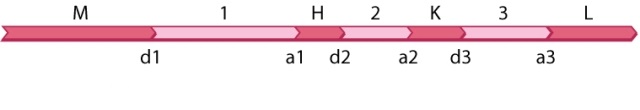 How many processed transcripts are possible in which two d sites and two a sites are cleaved?
How many processed transcripts are possible in which two d sites and two a sites are cleaved?
A)one
B)two
C)three
D)four
E)five
 How many processed transcripts are possible in which two d sites and two a sites are cleaved?
How many processed transcripts are possible in which two d sites and two a sites are cleaved?A)one
B)two
C)three
D)four
E)five

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Two related but distinct neurological disorders are Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) and Angelman syndrome (AS). Children with PWS are obese, have weak muscle tone, and delayed development. Children with AS have severe speech impairment, developmental delay, intellectual disability, and problems with movement and balance. However, both disorders are due to the deletion of the same part of chromosome 15. When the deletion is in the copy of chromosome 15 that came from the father, the child has PWS, but when the deletion is in the copy of chromosome 15 that came from the mother, the child has AS. What hypothesis can explain these observations?
A)unequal crossing over
B)parental imprinting
C)dosage compensation
D)alternative splicing
E)combinatorial control
A)unequal crossing over
B)parental imprinting
C)dosage compensation
D)alternative splicing
E)combinatorial control

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Methylation is a mechanism often used by cells to prevent the expression of:
A)genes in transposable elements.
B)genes from viruses that have been integrated into the genome.
C)harmful (mutant)genes such as those responsible for cystic fibrosis.
A)genes in transposable elements.
B)genes from viruses that have been integrated into the genome.
C)harmful (mutant)genes such as those responsible for cystic fibrosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The diagram shown here is part of an RNA transcript containing four open reading frames (M, H, K, and L) and three introns (1, 2, 3).  Splicing out an intron involves a spliceosome facilitating the cleavage of the DNA at nucleotides on either side of the intron. How many processed transcripts are possible if all three 5' nucleotides (immediately before each intron) and all three 3' nucleotides (immediately after each intron) are cleaved?
Splicing out an intron involves a spliceosome facilitating the cleavage of the DNA at nucleotides on either side of the intron. How many processed transcripts are possible if all three 5' nucleotides (immediately before each intron) and all three 3' nucleotides (immediately after each intron) are cleaved?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5
 Splicing out an intron involves a spliceosome facilitating the cleavage of the DNA at nucleotides on either side of the intron. How many processed transcripts are possible if all three 5' nucleotides (immediately before each intron) and all three 3' nucleotides (immediately after each intron) are cleaved?
Splicing out an intron involves a spliceosome facilitating the cleavage of the DNA at nucleotides on either side of the intron. How many processed transcripts are possible if all three 5' nucleotides (immediately before each intron) and all three 3' nucleotides (immediately after each intron) are cleaved?A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In the type of RNA editing in which C is converted to U, which codons could be converted to a stop codon? 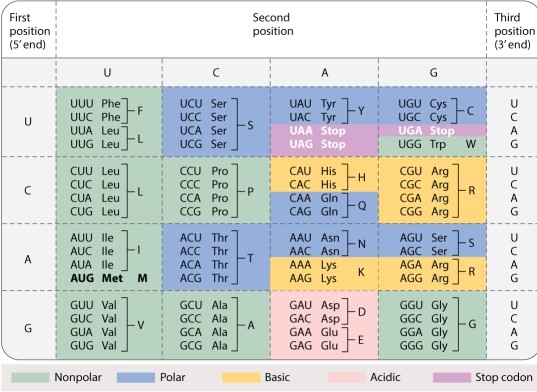
A)ACG
B)CAA
C)ACC
D)CAG
E)CGA

A)ACG
B)CAA
C)ACC
D)CAG
E)CGA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The human body contains approximately 200 major cell types. They look and function differently from one another because each:
A)has a slightly different genome.
B)expresses a different set of genes.
C)expresses the same set of genes, but in different orders at different times.
D)has a slightly different genome and each expresses a different set of genes.
A)has a slightly different genome.
B)expresses a different set of genes.
C)expresses the same set of genes, but in different orders at different times.
D)has a slightly different genome and each expresses a different set of genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Chromatin may be remodeled by:
A)chemical modification of the nucleotide bases of the DNA.
B)mutations affecting the structure of the chromosome's nonhistone proteins.
C)chemical modification of the chromosome's histone proteins.
A)chemical modification of the nucleotide bases of the DNA.
B)mutations affecting the structure of the chromosome's nonhistone proteins.
C)chemical modification of the chromosome's histone proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
RNA splicing provides an opportunity for regulating gene expression because:
A)the same exons may be spliced together in different sequences to produce different proteins from the same primary transcript.
B)the same introns may be spliced together in different sequences to produce different proteins from the same primary transcript.
C)a spliceosome in one cell can "see" as an intron what another spliceosome in another cell "sees" as an exon, allowing different proteins to be produced from the same primary transcript.
D)methylation of spliceosomes controls how rapidly primary transcripts are processed and sent to the cytoplasm.
E)methylation of the poly(A)tail controls how rapidly the primary transcript can be broken up and spliced back together again.
A)the same exons may be spliced together in different sequences to produce different proteins from the same primary transcript.
B)the same introns may be spliced together in different sequences to produce different proteins from the same primary transcript.
C)a spliceosome in one cell can "see" as an intron what another spliceosome in another cell "sees" as an exon, allowing different proteins to be produced from the same primary transcript.
D)methylation of spliceosomes controls how rapidly primary transcripts are processed and sent to the cytoplasm.
E)methylation of the poly(A)tail controls how rapidly the primary transcript can be broken up and spliced back together again.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Epigenetic modifications can:
A)be inherited.
B)be reversed.
C)alter gene expression.
D)change the sequence of the DNA.
A)be inherited.
B)be reversed.
C)alter gene expression.
D)change the sequence of the DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Combinatorial control refers to a regulatory mechanism in which:
A)transcription is initiated by a combination of sites in the promoter.
B)transcription is terminated by a combination of sites in the terminator.
C)each alternatively spliced transcript has a different combination of exons.
D)transcription requires a specific combination of transcription factors.
E)None of the answer options is correct.
A)transcription is initiated by a combination of sites in the promoter.
B)transcription is terminated by a combination of sites in the terminator.
C)each alternatively spliced transcript has a different combination of exons.
D)transcription requires a specific combination of transcription factors.
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
X-inactivation is an example of:
A)post-transcriptional modification.
B)epigenetic gene regulation.
C)dosage compensation.
D)positive regulation by CRP-cAMP.
E)miRNA-induced silencing.
A)post-transcriptional modification.
B)epigenetic gene regulation.
C)dosage compensation.
D)positive regulation by CRP-cAMP.
E)miRNA-induced silencing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Enhancer sequences are bound by:
A)RNA splicing complexes.
B)RNA editing complexes.
C)histone-modifying complexes.
D)cytosine methylation enzymes.
E)transcription factors.
A)RNA splicing complexes.
B)RNA editing complexes.
C)histone-modifying complexes.
D)cytosine methylation enzymes.
E)transcription factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Gene regulation can occur through:
A)DNA modification.
B)histone modification.
C)RNA modification.
D)All of these choices are correct.
A)DNA modification.
B)histone modification.
C)RNA modification.
D)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The diagram shown here is part of an RNA transcript containing four open reading frames (M, H, K, and L) and three introns (1, 2, 3). 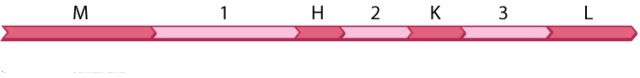 How many cuts would a spliceosome have to make in order to result in a transcript containing only open reading frames M, K, and L?
How many cuts would a spliceosome have to make in order to result in a transcript containing only open reading frames M, K, and L?
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)3
E)4
 How many cuts would a spliceosome have to make in order to result in a transcript containing only open reading frames M, K, and L?
How many cuts would a spliceosome have to make in order to result in a transcript containing only open reading frames M, K, and L?A)0
B)1
C)2
D)3
E)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Epigenetic mechanisms can include:
A)chromatin remodeling.
B)histone modification.
C)cytosine methylation.
D)X-inactivation.
E)combinatorial control.
A)chromatin remodeling.
B)histone modification.
C)cytosine methylation.
D)X-inactivation.
E)combinatorial control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Many genes have multiple enhancer sequences. The multiple enhancer sequences allow multiple:
A)options for alternative splicing of the RNA transcript.
B)options for RNA editing of the RNA transcript.
C)transcription factors to control gene expression.
D)proteins to be made from the same protein-coding gene.
E)None of the answer options is correct.
A)options for alternative splicing of the RNA transcript.
B)options for RNA editing of the RNA transcript.
C)transcription factors to control gene expression.
D)proteins to be made from the same protein-coding gene.
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Humans with hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia have defects in the formation and function of their sweat glands. Males with the condition have reduced ability to sweat over their entire body. Females with the condition lose the ability to sweat only in patches of skin. Where must the gene that encodes this trait be located?
A)in the Y chromosome
B)in the X chromosome
C)in an autosome
A)in the Y chromosome
B)in the X chromosome
C)in an autosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Alternative splicing may be considered a mechanism of gene regulation because it:
A)results in DNA rearrangements.
B)enhances RNA editing.
C)results in different protein products.
D)is mutagenic.
A)results in DNA rearrangements.
B)enhances RNA editing.
C)results in different protein products.
D)is mutagenic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Lifestyle choices that can affect levels of gene expression include:
A)diet.
B)exercise.
C)drug abuse.
D)meditation.
E)inherited mutation.
A)diet.
B)exercise.
C)drug abuse.
D)meditation.
E)inherited mutation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
One type of RNA editing converts Cs to Us. In how many codons in the genetic code would such a change NOT affect what amino acid is translated? 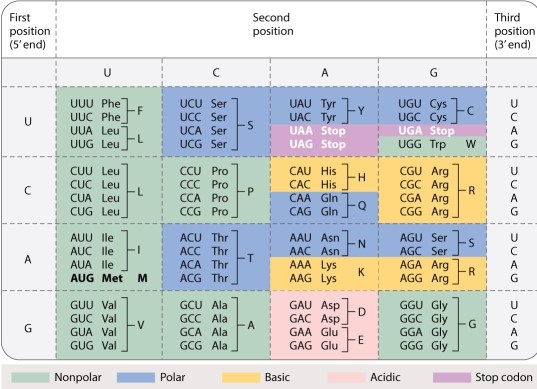
A)20
B)22
C)24
D)25
E)27

A)20
B)22
C)24
D)25
E)27

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A single gene can produce different proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A woman is heterozygous for a recessive allele that causes X-linked hemophilia. This recessive allele has a mutation that makes a gene for a blood-clotting factor nonfunctional. Considering the implications of X-inactivation, the level of clotting factor in her blood is likely to be approximately _____ that of a homozygous nonmutant woman.
A)1)0
B)3/4
C)1/2
D)1/4
E)None of the answer options is correct.
A)1)0
B)3/4
C)1/2
D)1/4
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Histone modification:
A)is fixed; once a histone is modified, it stays that way and the genes with which it is associated are turned on or off permanently.
B)is fixed, but this has no effect on whether genes are expressed.
C)is random-sometimes the lysines are modified and sometimes they're not, but the state is independent of the environment or cell type.
D)can change over time in response to environmental cues, allowing genes to be turned on or off as needed.
E)can change over time in response to environmental cues, but this has no effect on gene expression.
A)is fixed; once a histone is modified, it stays that way and the genes with which it is associated are turned on or off permanently.
B)is fixed, but this has no effect on whether genes are expressed.
C)is random-sometimes the lysines are modified and sometimes they're not, but the state is independent of the environment or cell type.
D)can change over time in response to environmental cues, allowing genes to be turned on or off as needed.
E)can change over time in response to environmental cues, but this has no effect on gene expression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In humans and other mammals, genes in the inactivated X chromosome:
A)are not transcribed at all.
B)may be transcribed at a low level.
C)are expressed at exactly half the level of an autosomal gene.
D)are transcribed but not translated.
A)are not transcribed at all.
B)may be transcribed at a low level.
C)are expressed at exactly half the level of an autosomal gene.
D)are transcribed but not translated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In humans and other mammals, dosage compensation is achieved by:
A)males transcribing twice the normal amount of copies of X-chromosome genes.
B)females decreasing transcription of both X chromosomes by half.
C)females eliminating one X chromosome in each cell.
D)females inactivating the paternal X chromosome in each cell.
E)females randomly inactivating one X chromosome in each cell.
A)males transcribing twice the normal amount of copies of X-chromosome genes.
B)females decreasing transcription of both X chromosomes by half.
C)females eliminating one X chromosome in each cell.
D)females inactivating the paternal X chromosome in each cell.
E)females randomly inactivating one X chromosome in each cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Epigenetic mechanisms of gene regulation include:
A)changes to DNA sequences.
B)the way in which DNA is packaged within chromosomes.
C)the way in which chromosomes are organized into genomes.
D)repression by binding of repressor proteins.
E)chemical modifications to DNA.
A)changes to DNA sequences.
B)the way in which DNA is packaged within chromosomes.
C)the way in which chromosomes are organized into genomes.
D)repression by binding of repressor proteins.
E)chemical modifications to DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Insulin is needed to regulate sugar levels in the blood. While every cell in the body contains genes for the production of insulin, it is only produced by a specialized subset of cells in the pancreas. Therefore:
A)every cell must regulate its own sugar production.
B)the genes for insulin production must be mutated except in the specialized cells of the pancreas.
C)there must be mechanisms of gene regulation that promote insulin expression in the specialized pancreatic cells and prevent insulin expression in all other cells.
D)only the specialized cells of the pancreas have functional genes for insulin production.
E)insulin production is not regulated because the genes for it are present in every cell.
A)every cell must regulate its own sugar production.
B)the genes for insulin production must be mutated except in the specialized cells of the pancreas.
C)there must be mechanisms of gene regulation that promote insulin expression in the specialized pancreatic cells and prevent insulin expression in all other cells.
D)only the specialized cells of the pancreas have functional genes for insulin production.
E)insulin production is not regulated because the genes for it are present in every cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The process by which a single primary RNA transcript is used to make multiple proteins is called:
A)combinatorial control.
B)alternative splicing.
C)regulatory splicing.
D)translational control.
E)polymerization control.
A)combinatorial control.
B)alternative splicing.
C)regulatory splicing.
D)translational control.
E)polymerization control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In RNA editing:
A)spliceosomes change the base sequence of the primary transcript and therefore the protein for which it codes.
B)different spliceosomes in different cells create different RNA sequences from the same primary transcript.
C)enzymes change the base sequence of the primary transcript and therefore the protein for which it codes.
D)microRNAs in different cells create different primary RNA transcripts from the same DNA sequence.
E)a combination of spliceosomes and enzymes creates different primary RNA transcripts from the same DNA sequence.
A)spliceosomes change the base sequence of the primary transcript and therefore the protein for which it codes.
B)different spliceosomes in different cells create different RNA sequences from the same primary transcript.
C)enzymes change the base sequence of the primary transcript and therefore the protein for which it codes.
D)microRNAs in different cells create different primary RNA transcripts from the same DNA sequence.
E)a combination of spliceosomes and enzymes creates different primary RNA transcripts from the same DNA sequence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Gene regulation by means of epigenetic mechanisms is useful to the organism because it:
A)does not require new mutations.
B)can quickly be reversed.
C)can respond rapidly to environmental change.
D)can differ between the sexes.
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)does not require new mutations.
B)can quickly be reversed.
C)can respond rapidly to environmental change.
D)can differ between the sexes.
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Epigenetic mechanisms of gene regulation _____ inherited by daughter cells and are _____.
A)can be; permanent
B)can be; often reversible and responsive to environmental change
C)can be; random with respect to the environment
D)are not; reversible and responsive to environmental change
E)are not; permanent
A)can be; permanent
B)can be; often reversible and responsive to environmental change
C)can be; random with respect to the environment
D)are not; reversible and responsive to environmental change
E)are not; permanent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Regulatory transcription factors:
A)bind to DNA sequences in or near gene enhancers.
B)recruit the components of the general transcriptional factors.
C)recruit the components of the RNA polymerase complex.
A)bind to DNA sequences in or near gene enhancers.
B)recruit the components of the general transcriptional factors.
C)recruit the components of the RNA polymerase complex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In domestic cats, the coat-color pattern known as calico is an example of:
A)gene regulation at the level of the chromosome.
B)dosage compensation.
C)epigenetic regulation.
D)X-inactivation.
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)gene regulation at the level of the chromosome.
B)dosage compensation.
C)epigenetic regulation.
D)X-inactivation.
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A woman is heterozygous for X-linked color blindness. Considering the implications of X-inactivation, her phenotype is:
A)likely to be color blind.
B)likely to be color blind in one eye.
C)likely to be normal color vision.
D)unpredictable.
A)likely to be color blind.
B)likely to be color blind in one eye.
C)likely to be normal color vision.
D)unpredictable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Although lifestyle choices cannot, in general, change our genomes, they can:
A)change the physiological states of our cells, which in turn affects post-translational gene regulation.
B)increase the rate at which some genes are transcribed.
C)decrease the rate at which some genes are transcribed.
D)change the genetic code for translation.
E)change the metabolic pathways of glycolysis.
A)change the physiological states of our cells, which in turn affects post-translational gene regulation.
B)increase the rate at which some genes are transcribed.
C)decrease the rate at which some genes are transcribed.
D)change the genetic code for translation.
E)change the metabolic pathways of glycolysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Gene regulation in multicellular organisms leads to differential gene expression and specialized cell functions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Gene regulation can occur at which of the following steps in the path from DNA to protein?
A)during transcription from a chromosome
B)during translation from DNA to RNA
C)after protein synthesis
D)during transcription from a chromosome and during translation from DNA to RNA
E)during transcription from a chromosome, during translation from DNA to RNA, and after protein synthesis
A)during transcription from a chromosome
B)during translation from DNA to RNA
C)after protein synthesis
D)during transcription from a chromosome and during translation from DNA to RNA
E)during transcription from a chromosome, during translation from DNA to RNA, and after protein synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In the type of RNA editing in which C is converted to U, which of the codons listed below could be converted to AUG?
A)AGC
B)GCA
C)AUG
D)ACG
A)AGC
B)GCA
C)AUG
D)ACG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following questions is about gene regulation?
A)Why do all eukaryotes share a common genetic code?
B)Where are genes for hemoglobin expressed?
C)How much insulin is produced after a meal?
A)Why do all eukaryotes share a common genetic code?
B)Where are genes for hemoglobin expressed?
C)How much insulin is produced after a meal?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A cell could potentially regulate transcription by adjusting the number and kinds of:
A)regulatory transcription factors present.
B)general transcription factors present.
C)components of the RNA polymerase complex present.
A)regulatory transcription factors present.
B)general transcription factors present.
C)components of the RNA polymerase complex present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Methylation, acetylation, and other histone modifications are important because they are associated with:
A)chromatin remodeling and affect gene transcription.
B)CpG island methylation and affect gene transcription.
C)cancer genes and their regulation.
D)the environmental and developmental cues that determine whether viral genes and genes in transposable elements are turned off or on.
A)chromatin remodeling and affect gene transcription.
B)CpG island methylation and affect gene transcription.
C)cancer genes and their regulation.
D)the environmental and developmental cues that determine whether viral genes and genes in transposable elements are turned off or on.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which one of the following statements about gene regulation is INCORRECT?
A)Gene regulation occurs at the level of the chromosome.
B)Gene regulation occurs at the level of transcription.
C)Gene regulation occurs only in prokaryotes.
D)Gene regulation occurs at the translational level.
E)Gene regulation occurs at the post-translational level.
A)Gene regulation occurs at the level of the chromosome.
B)Gene regulation occurs at the level of transcription.
C)Gene regulation occurs only in prokaryotes.
D)Gene regulation occurs at the translational level.
E)Gene regulation occurs at the post-translational level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which one of the following statements MOST accurately describes methylation?
A)Methyl groups are most often added to cytosines adjacent to guanine bases in or near the promoter sequence, increasing the probability of gene expression.
B)Methyl groups are most often added to cytosines adjacent to guanine bases in or near the promoter sequence, decreasing the probability of gene expression.
C)Methyl groups are most often added to adenine-thymine base pairs because they are held by only two hydrogen bonds, and this increases the probability of gene expression.
D)Methyl groups are most often added to guanine-cytosine base pairs because they are held by three hydrogen bonds, and this decreases the probability of gene expression.
E)Methyl groups are added to most bases in the promoter region of a specific gene so that RNA polymerase and its associated proteins will bind more efficiently.
A)Methyl groups are most often added to cytosines adjacent to guanine bases in or near the promoter sequence, increasing the probability of gene expression.
B)Methyl groups are most often added to cytosines adjacent to guanine bases in or near the promoter sequence, decreasing the probability of gene expression.
C)Methyl groups are most often added to adenine-thymine base pairs because they are held by only two hydrogen bonds, and this increases the probability of gene expression.
D)Methyl groups are most often added to guanine-cytosine base pairs because they are held by three hydrogen bonds, and this decreases the probability of gene expression.
E)Methyl groups are added to most bases in the promoter region of a specific gene so that RNA polymerase and its associated proteins will bind more efficiently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The type of gene regulation in which transcription of a gene depends on the presence of a particular combination of enhancers and other regulatory transcription factors is known as _____ control.
A)histone
B)epigenetic
C)polynomial
D)combinatorial
E)recombinational
A)histone
B)epigenetic
C)polynomial
D)combinatorial
E)recombinational

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Nucleosomes occupy fixed positions along the DNA that remain the same over time and in each cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which one of the following describes an event that takes place during gene regulation at the level of the chromosome?
A)Chromatin becomes condensed in order for transcription to begin.
B)Chromatin coils so it can become more accessible to the proteins that carry out transcription.
C)RNA polymerase and associated proteins bind to nucleosomes.
D)Chromatin is remodeled and nucleosomes are repositioned so that specific regions of the DNA are made available for transcription.
E)Cytosine bases in the sequence near the promoter of a gene become methylated in order to stimulate transcription.
A)Chromatin becomes condensed in order for transcription to begin.
B)Chromatin coils so it can become more accessible to the proteins that carry out transcription.
C)RNA polymerase and associated proteins bind to nucleosomes.
D)Chromatin is remodeled and nucleosomes are repositioned so that specific regions of the DNA are made available for transcription.
E)Cytosine bases in the sequence near the promoter of a gene become methylated in order to stimulate transcription.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Amino acid sequences that are rich in lysine and protrude from the histone proteins in the nucleosome are called "tails."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In gene expression in eukaryotes, the primary transcript is transported directly to the cytoplasm and prepared for translation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Modifications of bases, changes to histones, and alterations in chromatin structure that regulate gene expression are said to be:
A)nonheritable.
B)post-translational.
C)supragenetic.
D)epigenetic.
E)synchrogenetic.
A)nonheritable.
B)post-translational.
C)supragenetic.
D)epigenetic.
E)synchrogenetic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Methylated cytosines are often observed in CpG islands near genes that are repressed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The first level of gene regulation occurs along the chromosome, through chemical modifications of the DNA or histones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which one of the following statements about the methylation state of CpG islands is INCORRECT?
A)Cells can heavily methylate CpG islands of viral DNA sequences in order to restrict their expression.
B)Cells can heavily methylate CpG islands of genes in transposable elements in order to restrict their expression.
C)The methylation state of CpG islands provides a way to turn genes on or off.
D)The methylation state of CpG islands is static and will not change over time.
E)The methylation state of CpG islands can change in response to the environment.
A)Cells can heavily methylate CpG islands of viral DNA sequences in order to restrict their expression.
B)Cells can heavily methylate CpG islands of genes in transposable elements in order to restrict their expression.
C)The methylation state of CpG islands provides a way to turn genes on or off.
D)The methylation state of CpG islands is static and will not change over time.
E)The methylation state of CpG islands can change in response to the environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Heavy methylation of CpG islands is usually associated with repression of transcription.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Transcriptional regulation in eukaryotic cells requires the coordinated action of many proteins that interact with one another and with DNA sequences near the gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
All CpG sites located near the promoter region of protein coding genes are methylated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Histone modification occurs only during early development.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Patterns of histone methylation and acetylation that affect chromatin structure and gene transcription constitute a _____ code.
A)genetic
B)DNA
C)histone
D)protein
A)genetic
B)DNA
C)histone
D)protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
RNA splicing joins together the coding regions of messenger RNA in their original linear order after the removal of introns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In female humans and other mammals, dosage compensation is achieved by the inactivation of one of the two X chromosomes in each cell. Which one of the following does NOT occur in the X-inactivation mechanism of female mammals?
A)X-inactivation begins with a small region of the X chromosome that contains a gene for an X- inactivation specific transcript (Xist).
B)Xist is expressed in low levels except when an X chromosome is about to be inactivated.
C)When an X chromosome is about to be inactivated, Xist RNA transcripts increase markedly and undergo splicing, but do not encode a protein.
D)Xist RNA is attracted to and associates with a protein called the X-chromosome inactivation center (XIC), which becomes entirely coated with Xist.
E)Xist RNA recruits factors that promote DNA methylation, histone modification, and other changes associated with transcriptional silencing.
A)X-inactivation begins with a small region of the X chromosome that contains a gene for an X- inactivation specific transcript (Xist).
B)Xist is expressed in low levels except when an X chromosome is about to be inactivated.
C)When an X chromosome is about to be inactivated, Xist RNA transcripts increase markedly and undergo splicing, but do not encode a protein.
D)Xist RNA is attracted to and associates with a protein called the X-chromosome inactivation center (XIC), which becomes entirely coated with Xist.
E)Xist RNA recruits factors that promote DNA methylation, histone modification, and other changes associated with transcriptional silencing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following statements about transcriptional regulation is INCORRECT?
A)Regulatory transcription factors are proteins that bind to enhancer DNA sequences and then recruit one or more general transcription factors.
B)A typical gene contains only one enhancer sequence.
C)General transcription factors are required to initiate the process of transcription.
D)General transcription factors bind to the TATA box in the promoter region of a gene.
E)RNA polymerase components are recruited to the promoter region by the general transcription factors bound to the TATA box.
A)Regulatory transcription factors are proteins that bind to enhancer DNA sequences and then recruit one or more general transcription factors.
B)A typical gene contains only one enhancer sequence.
C)General transcription factors are required to initiate the process of transcription.
D)General transcription factors bind to the TATA box in the promoter region of a gene.
E)RNA polymerase components are recruited to the promoter region by the general transcription factors bound to the TATA box.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The complex of DNA, RNA, and associated proteins that gives shape to the chromosome is called:
A)chromatin.
B)histones.
C)an operon.
D)a scaffold.
A)chromatin.
B)histones.
C)an operon.
D)a scaffold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
What happens when the Xist gene from an X chromosome is inserted into an autosome?
A)Gene activity in the autosome remains normal.
B)The autosome with Xist is inactivated like an X chromosome.
C)The autosome with Xist is inactivated in half the cells, and the homologous autosome is inactivated in the other half.
D)Both the autosome and its homologous chromosome are inactivated.
A)Gene activity in the autosome remains normal.
B)The autosome with Xist is inactivated like an X chromosome.
C)The autosome with Xist is inactivated in half the cells, and the homologous autosome is inactivated in the other half.
D)Both the autosome and its homologous chromosome are inactivated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



