Deck 2: The Molecules of Life
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/232
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: The Molecules of Life
1
Explain why an atom that is NOT an ion is electrically neutral.
In an atom that is not an ion, the number of positively charged protons always equals the number of negatively charged electrons.
2
The designation of a magnesium ion as Mg2+ indicates an atom that has:
A)two more protons than neutrons.
B)lost two electrons and is negatively charged.
C)lost two electrons and is positively charged.
D)gained two protons and is positively charged.
E)gained two protons and is negatively charged.
A)two more protons than neutrons.
B)lost two electrons and is negatively charged.
C)lost two electrons and is positively charged.
D)gained two protons and is positively charged.
E)gained two protons and is negatively charged.
C
3
Which of the following CORRECTLY pairs the particles of an atom with their physical properties?
A)proton-positively charged; neutron-uncharged; electron-negatively charged
B)proton-negatively charged; neutron-uncharged; electron-positively charged
C)proton-positively charged; neutron-negatively charged; electron-uncharged
D)proton-uncharged; neutron-negatively charged; electron-positively charged
A)proton-positively charged; neutron-uncharged; electron-negatively charged
B)proton-negatively charged; neutron-uncharged; electron-positively charged
C)proton-positively charged; neutron-negatively charged; electron-uncharged
D)proton-uncharged; neutron-negatively charged; electron-positively charged
A
4
You discover an isotope of an element that has 6 electrons in its second and outermost shell, 8 protons, and 6 neutrons. What element is it?
A)fluorine (F)
B)carbon (C)
C)nitrogen (N)
D)oxygen (O)
A)fluorine (F)
B)carbon (C)
C)nitrogen (N)
D)oxygen (O)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
For an atom that is NOT an ion, which of the following must be TRUE?
A)The number of electrons equals the number of protons.
B)The number of electrons equals the number of neutrons.
C)The number of protons equals the number of neutrons.
A)The number of electrons equals the number of protons.
B)The number of electrons equals the number of neutrons.
C)The number of protons equals the number of neutrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What would happen to an atom's atomic mass and electric charge if it gained or lost a proton, a neutron, or an electron?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The atom:
A)is the basic unit of matter.
B)is the unit of composition for elements.
C)contains protons, neutrons, and electrons.
D)has negatively charged particles circling around a positively charged nucleus.
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)is the basic unit of matter.
B)is the unit of composition for elements.
C)contains protons, neutrons, and electrons.
D)has negatively charged particles circling around a positively charged nucleus.
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The most common isotope of oxygen has an atomic mass of 16 (16O). An isotope with an atomic mass of 18 (18O) is also stable. How many valence electrons are present in 18O?
A)fewer than in 16O
B)more than in 16O
C)the same as in 16O
D)None of the other answer options is correct.
A)fewer than in 16O
B)more than in 16O
C)the same as in 16O
D)None of the other answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
How many electron orbitals does a carbon atom possess?
A)2
B)4
C)5
D)6
E)12
A)2
B)4
C)5
D)6
E)12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
List the particles in an atom, and indicate whether each is positively charged, negatively charged, or uncharged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The basic unit of matter is referred to as a(n) _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The most common isotope of oxygen has 8 protons and an atomic mass of 16. How many electrons are present in the orbitals around an atom of oxygen?
A)2
B)4
C)6
D)8
E)10
A)2
B)4
C)6
D)8
E)10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An atom with three electrons has:
A)one occupied orbital with three electrons.
B)two occupied orbitals, one of which has two electrons and the other has one.
C)three occupied orbitals, each of which contains one electron.
D)three energy shells, each of which contains one electron.
A)one occupied orbital with three electrons.
B)two occupied orbitals, one of which has two electrons and the other has one.
C)three occupied orbitals, each of which contains one electron.
D)three energy shells, each of which contains one electron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
14C is an isotope of carbon that possesses:
A)6 protons, 6 neutrons, and 2 electrons.
B)6 protons, 8 neutrons, and 6 electrons.
C)8 protons, 6 neutrons, and 2 electrons.
D)6 protons, 2 neutrons, and 6 electrons.
E)6 protons, 8 neutrons, and 2 electrons.
A)6 protons, 6 neutrons, and 2 electrons.
B)6 protons, 8 neutrons, and 6 electrons.
C)8 protons, 6 neutrons, and 2 electrons.
D)6 protons, 2 neutrons, and 6 electrons.
E)6 protons, 8 neutrons, and 2 electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Using the periodic table in Fig. 2.3, select the element that would be found in LEAST abundance in a living cell.
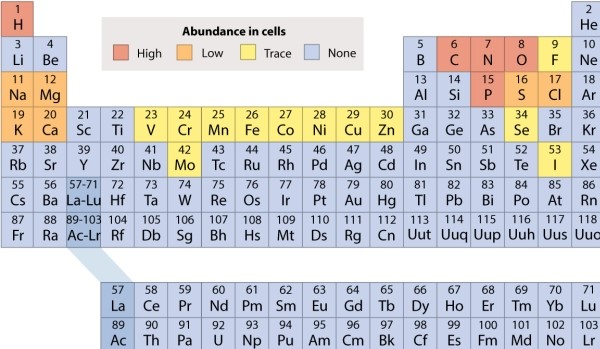
A)hydrogen (H)
B)sodium (Na)
C)phosphorous (P)
D)zinc (Zn)
E)silicon (Si)

A)hydrogen (H)
B)sodium (Na)
C)phosphorous (P)
D)zinc (Zn)
E)silicon (Si)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The most common isotope of oxygen has 8 protons and an atomic mass of 16. How many neutrons are present in the oxygen nucleus?
A)2
B)4
C)6
D)8
E)10
A)2
B)4
C)6
D)8
E)10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The negatively charged components of atoms are referred to as:
A)protons.
B)electrons.
C)anions.
D)neutrons.
E)cations.
A)protons.
B)electrons.
C)anions.
D)neutrons.
E)cations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If an atom has three electrons, how many occupied orbitals will the atom have, and how many electrons will be in each?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What differentiates isotopes of the same element?
A)protons
B)neutrons
C)electrons
D)charge
A)protons
B)neutrons
C)electrons
D)charge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Sometimes, atoms gain or lose particles. The loss of which of the following results in a change of atomic mass?
A)a neutron
B)a proton
C)an electron
D)a neutron and a proton
E)a proton and an electron
A)a neutron
B)a proton
C)an electron
D)a neutron and a proton
E)a proton and an electron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which one of the following contributes to the measurement referred to as atomic mass?
A)protons and electrons
B)electrons and neutrons
C)protons, electrons, and neutrons
D)protons and neutrons
E)neutrons only
A)protons and electrons
B)electrons and neutrons
C)protons, electrons, and neutrons
D)protons and neutrons
E)neutrons only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What percentage of carbon's orbitals is spherical in conformation?
A)0%
B)20%
C)40%
D)80%
E)100%
A)0%
B)20%
C)40%
D)80%
E)100%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
For the first three rows of the periodic table, elements in the same row have the same number and type of electron orbitals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Consider two carbon atoms, one represented as 14C and the other as 12C. Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding these two atoms?
A)These carbon atoms have the same number of protons.
B)These carbon atoms have the same number of neutrons.
C)These carbon atoms have different numbers of electrons.
D)These carbon atoms have different numbers of protons.
A)These carbon atoms have the same number of protons.
B)These carbon atoms have the same number of neutrons.
C)These carbon atoms have different numbers of electrons.
D)These carbon atoms have different numbers of protons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A pair of atoms joined by a polar covalent bond:
A)has the charge spread evenly across both atoms.
B)has a slight positive charge on one atom and a slight negative charge on the other.
C)is unlikely to form hydrogen bonds with water.
D)mixes well with nonpolar solvents.
A)has the charge spread evenly across both atoms.
B)has a slight positive charge on one atom and a slight negative charge on the other.
C)is unlikely to form hydrogen bonds with water.
D)mixes well with nonpolar solvents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Two elements within the same group:
A)occupy the same row on the periodic table of elements.
B)occupy the same column on the periodic table of elements.
C)have the same number of electrons in their outermost shell.
D)have different numbers of electrons in their outermost shell.
E)occupy the same column on the periodic table and have the same number of electrons in their outermost shell.
A)occupy the same row on the periodic table of elements.
B)occupy the same column on the periodic table of elements.
C)have the same number of electrons in their outermost shell.
D)have different numbers of electrons in their outermost shell.
E)occupy the same column on the periodic table and have the same number of electrons in their outermost shell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Consider the two elements, sodium (Na) and magnesium (Mg), which occupy the same row in the periodic table of elements. Sodium and magnesium atoms have:
A)a different number of orbitals.
B)the same atomic number.
C)different atomic masses.
D)the same number of electrons in their outermost orbitals.
E)different atomic masses and the same number of electrons in their outermost orbitals.
A)a different number of orbitals.
B)the same atomic number.
C)different atomic masses.
D)the same number of electrons in their outermost orbitals.
E)different atomic masses and the same number of electrons in their outermost orbitals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Nitrogen and phosphorus are in the same column of the periodic table. They have similar properties in bonding with other molecules because they have the same number of:
A)electrons.
B)paired electrons.
C)valence electrons.
D)electron shells.
A)electrons.
B)paired electrons.
C)valence electrons.
D)electron shells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Refer to the periodic table, and decide which of the following molecules is held together by nonpolar covalent bonds. 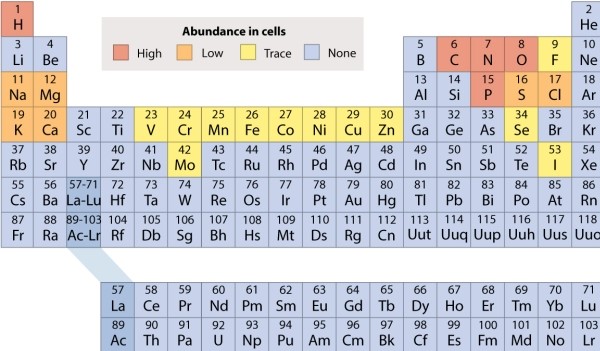
A)NH3
B)CO2
C)KCl

A)NH3
B)CO2
C)KCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Of the following types of bonds between atoms, which is the STRONGEST?
A)ionic bond
B)hydrogen bond
C)covalent bond
D)van der Waals forces
A)ionic bond
B)hydrogen bond
C)covalent bond
D)van der Waals forces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Refer to the periodic table, and decide which of the following molecules is held together by polar covalent bonds. 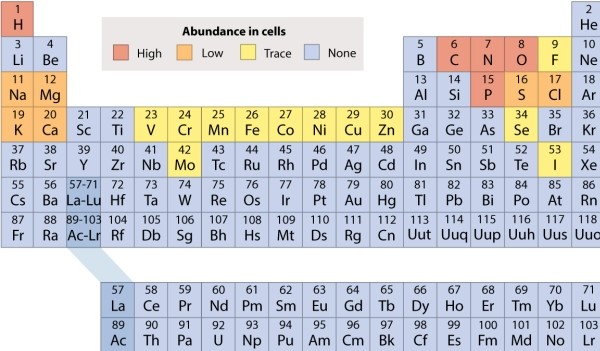
A)NH3
B)CO2
C)KCl

A)NH3
B)CO2
C)KCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding elements?
A)Elements are composed of several different types of atoms.
B)Elements are only found in nature and cannot be created by humans.
C)Elements are still categorized according to Aristotle's early classifications.
D)Elements are composed of only one type of atom.
E)Elements are only found in inorganic substances and not in living organisms.
A)Elements are composed of several different types of atoms.
B)Elements are only found in nature and cannot be created by humans.
C)Elements are still categorized according to Aristotle's early classifications.
D)Elements are composed of only one type of atom.
E)Elements are only found in inorganic substances and not in living organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which component of an atom has the SMALLEST mass?
A)proton
B)neutron
C)electron
D)isotope
E)isomer
A)proton
B)neutron
C)electron
D)isotope
E)isomer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following bonds rely on the attraction of positive and negative charges?
A)ionic bonds
B)covalent bonds
C)hydrogen bonds
D)ionic bonds and hydrogen bonds
E)ionic bonds and covalent bonds
A)ionic bonds
B)covalent bonds
C)hydrogen bonds
D)ionic bonds and hydrogen bonds
E)ionic bonds and covalent bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Where is the highest-energy electron found in an atom of hydrogen?
A)in the spherical orbital closest to the nucleus
B)in the second spherical orbital, a little farther from the nucleus
C)in the dumbbell-shaped orbital of the y-axis
D)in the dumbbell-shaped orbital of the x-axis
E)in the dumbbell-shaped orbital of the z-axis
A)in the spherical orbital closest to the nucleus
B)in the second spherical orbital, a little farther from the nucleus
C)in the dumbbell-shaped orbital of the y-axis
D)in the dumbbell-shaped orbital of the x-axis
E)in the dumbbell-shaped orbital of the z-axis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Refer to the periodic table, and decide which of the following molecules is held together by ionic bonds. 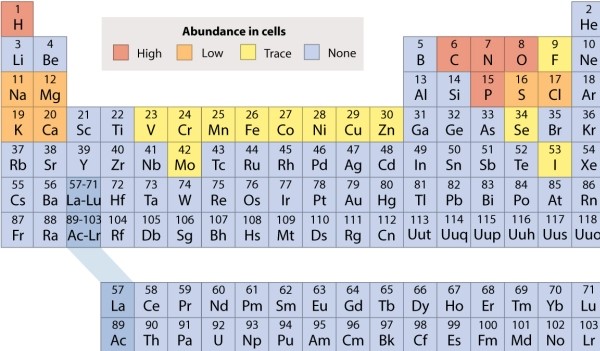
A)NH3
B)CO2
C)KCl

A)NH3
B)CO2
C)KCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which one of the following pairs would be classified as isotopes of each other?
A)H and H+
B)Na + and Cl-
C)C and Si
D)12C and 13C
E)H and H+, Na+ and Cl-, C and Si, 12C and 13C
A)H and H+
B)Na + and Cl-
C)C and Si
D)12C and 13C
E)H and H+, Na+ and Cl-, C and Si, 12C and 13C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding atomic mass?
A)The atomic mass is defined as the sum of electrons and neutrons in an atom.
B)The atomic mass can be used to differentiate between different isotopes of the same element.
C)The atomic mass is synonymous with the atomic number.
D)The atomic mass is calculated by adding the total number of electrons, protons, and neutrons in an atom.
A)The atomic mass is defined as the sum of electrons and neutrons in an atom.
B)The atomic mass can be used to differentiate between different isotopes of the same element.
C)The atomic mass is synonymous with the atomic number.
D)The atomic mass is calculated by adding the total number of electrons, protons, and neutrons in an atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Imagine that you have two different carbon atoms, one identified as 14C and the other as 13C. These two carbon atoms:
A)are two different carbon isotopes.
B)have a different number of neutrons.
C)have a different number of protons.
D)are two different carbon isotopes and have a different number of protons.
E)are two different carbon isotopes and have a different number of neutrons.
A)are two different carbon isotopes.
B)have a different number of neutrons.
C)have a different number of protons.
D)are two different carbon isotopes and have a different number of protons.
E)are two different carbon isotopes and have a different number of neutrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The ability of atoms to form bonds is due largely to electrons farthest from the nucleus. These electrons are called _____ electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A molecule of common table salt, or NaCl, is the result of _____ bond forming between a sodium (Na) atom and a chlorine (Cl) atom.
A)an ionic
B)a covalent
C)a polar covalent
D)a hydrogen
E)either an ionic or a polar covalent
A)an ionic
B)a covalent
C)a polar covalent
D)a hydrogen
E)either an ionic or a polar covalent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The ability of atoms to attract electrons is referred to as:
A)van der Waals attraction.
B)potential energy.
C)hydrophobicity.
D)cohesion.
E)electronegativity.
A)van der Waals attraction.
B)potential energy.
C)hydrophobicity.
D)cohesion.
E)electronegativity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The _____ of a chemical reaction are transformed into different molecules called _____.
A)reactants; products
B)reactants; isomers
C)products; compounds
D)products; reactants
E)compounds; products
A)reactants; products
B)reactants; isomers
C)products; compounds
D)products; reactants
E)compounds; products

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following accurately describes a polar covalent bond?
A)the interaction of a hydrogen atom connected to an atom with a high electronegativity, and an electronegative atom of another molecule
B)the interaction of an atom with very high electronegativity, and an atom with very low electronegativity
C)the unequal sharing of electrons between an atom with a partial positive charge, and an atom with a partial negative charge
D)the equal sharing of electrons between atoms of identical or similar electronegativities
E)None of the other answer options is correct.
A)the interaction of a hydrogen atom connected to an atom with a high electronegativity, and an electronegative atom of another molecule
B)the interaction of an atom with very high electronegativity, and an atom with very low electronegativity
C)the unequal sharing of electrons between an atom with a partial positive charge, and an atom with a partial negative charge
D)the equal sharing of electrons between atoms of identical or similar electronegativities
E)None of the other answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Hydrogen bonding is ultimately due to differences in _____ between two atoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When two atoms form a covalent bond, they share electrons from all of their orbitals. All of their orbitals, in turn, combine to form a single molecular orbital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A polar bond is due to:
A)equal sharing of valence electrons.
B)an attraction of opposite charges.
C)uneven sharing of electrons in a covalent bond.
D)the interaction between an ion and a non-ionic atom.
E)None of the other answer options is correct
A)equal sharing of valence electrons.
B)an attraction of opposite charges.
C)uneven sharing of electrons in a covalent bond.
D)the interaction between an ion and a non-ionic atom.
E)None of the other answer options is correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A(n) _____ is a substance composed of two or more atoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A young girl is staring at the raindrops running down her window. She notices that the raindrops remain more or less intact, even as they cascade down the windowpane. This is a result of:
A)covalent bonds between water molecules.
B)oxygen bonds between water molecules.
C)polar covalent bonds between water molecules.
D)hydrogen bonds between water molecules.
E)ionic bonds between water molecules.
A)covalent bonds between water molecules.
B)oxygen bonds between water molecules.
C)polar covalent bonds between water molecules.
D)hydrogen bonds between water molecules.
E)ionic bonds between water molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
An ionic bond is really a modified polar covalent bond, because two atoms "share" electrons when one atom steals a valence electron from the other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is an example of a hydrogen bond?
A)the bond that forms between a hydrogen and oxygen atom within the same water molecule
B)the bond that forms between two hydrogen atoms within the same water molecule
C)the bond that forms between hydrogen and oxygen atoms within different water molecules
D)the bond that forms between two hydrogen atoms within different water molecules
E)the bond that forms between two oxygen atoms within different water molecules
A)the bond that forms between a hydrogen and oxygen atom within the same water molecule
B)the bond that forms between two hydrogen atoms within the same water molecule
C)the bond that forms between hydrogen and oxygen atoms within different water molecules
D)the bond that forms between two hydrogen atoms within different water molecules
E)the bond that forms between two oxygen atoms within different water molecules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A pair of shared valence electrons is referred to as a(n):
A)ionic bond.
B)hydrogen bond.
C)van der Waals interaction.
D)covalent bond.
E)hydrophobic effect.
A)ionic bond.
B)hydrogen bond.
C)van der Waals interaction.
D)covalent bond.
E)hydrophobic effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A woman's doctor tells her to gargle with salt water. She stirs a tablespoon of salt into a cup of warm water and watches it dissolve. Why does the salt dissolve in water?
A)The positive hydrogen atoms in water molecules are attracted to chlorine ions.
B)The positive hydrogen atoms in water molecules are attracted to sodium ions.
C)The negative oxygen atoms in water molecules are attracted to chlorine ions.
D)The negative oxygen atoms in water molecules are attracted to sodium ions.
E)The positive hydrogen atoms in water molecules are attracted to chlorine ions, and the negative oxygen atoms in water molecules are attracted to sodium ions.
A)The positive hydrogen atoms in water molecules are attracted to chlorine ions.
B)The positive hydrogen atoms in water molecules are attracted to sodium ions.
C)The negative oxygen atoms in water molecules are attracted to chlorine ions.
D)The negative oxygen atoms in water molecules are attracted to sodium ions.
E)The positive hydrogen atoms in water molecules are attracted to chlorine ions, and the negative oxygen atoms in water molecules are attracted to sodium ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which one of the following is maintained during a chemical reaction?
A)the number of atoms present in the reactants
B)the identity of the atoms present in the reactants
C)the arrangement of chemical bonds present in the reactants
D)the number and identity of the atoms present in the reactants
E)the number and identity of the atoms, and the arrangement of chemical bonds present in the reactants.
A)the number of atoms present in the reactants
B)the identity of the atoms present in the reactants
C)the arrangement of chemical bonds present in the reactants
D)the number and identity of the atoms present in the reactants
E)the number and identity of the atoms, and the arrangement of chemical bonds present in the reactants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following statements regarding an atom with high electronegativity is TRUE?
A)It will have fewer protons than an atom with low electronegativity.
B)It will have a tendency not to attract electrons.
C)It will most likely be located on the left-most side of the periodic table of elements.
D)None of the other answer options is correct.
A)It will have fewer protons than an atom with low electronegativity.
B)It will have a tendency not to attract electrons.
C)It will most likely be located on the left-most side of the periodic table of elements.
D)None of the other answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The valence electrons of an atom are at the lowest energy level because their increased distance from the nucleus reduces their attraction to the atom's protons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
An ionic interaction, such as the interaction between Na+ and Cl-, is considered a covalent bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which one of the following elements is likely to form exactly three non-ionic interactions with hydrogen?
A)phosphorus
B)oxygen
C)carbon
D)sulfur
E)chlorine
A)phosphorus
B)oxygen
C)carbon
D)sulfur
E)chlorine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The structural formula for hydrogen gas (H2) is represented as H-H. Here, the dash (-) represents a(n):
A)product.
B)reactant.
C)chemical reaction.
D)chemical bond.
E)electronegative bond.
A)product.
B)reactant.
C)chemical reaction.
D)chemical bond.
E)electronegative bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What is the chemical basis for water's role as the universal solvent?
A)Because water is polar, it disrupts most covalent bonds.
B)Because water is polar, it disrupts hydrogen bonds.
C)Because water is polar, it disrupts ionic bonds.
D)Because water is polar, it disrupts both covalent and hydrogen bonds.
E)Because water is polar, it disrupts both hydrogen and ionic bonds.
A)Because water is polar, it disrupts most covalent bonds.
B)Because water is polar, it disrupts hydrogen bonds.
C)Because water is polar, it disrupts ionic bonds.
D)Because water is polar, it disrupts both covalent and hydrogen bonds.
E)Because water is polar, it disrupts both hydrogen and ionic bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The unique properties of water are due to the _____ of water molecules and the ability of water to form _____ with other water molecules and with other polar molecules.
A)electronegativity; polar covalent bonds
B)polarity; polar covalent bonds
C)polarity; hydrogen bonds
D)hydrophobicity; hydrogen bonds
A)electronegativity; polar covalent bonds
B)polarity; polar covalent bonds
C)polarity; hydrogen bonds
D)hydrophobicity; hydrogen bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Water is able to dissolve many compounds as a result of which of the following?
A)the fact that water molecules are polar
B)the fact that water molecules are nonpolar
C)the fact that the hydrogen atoms in water molecules have a slight negative charge
D)the fact that most nonwater molecules are hydrophobic
E)the fact that water molecules are polar, and that the hydrogen atoms in water molecules have a slight negative charge
A)the fact that water molecules are polar
B)the fact that water molecules are nonpolar
C)the fact that the hydrogen atoms in water molecules have a slight negative charge
D)the fact that most nonwater molecules are hydrophobic
E)the fact that water molecules are polar, and that the hydrogen atoms in water molecules have a slight negative charge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
You have an aqueous solution with a pH of exactly 7.0. What would you add to make the solution more acidic?
A)hydrogen chloride (HCl)
B)sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
C)sodium chloride (NaCl)
D)deionized water (dH2O)
A)hydrogen chloride (HCl)
B)sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
C)sodium chloride (NaCl)
D)deionized water (dH2O)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
You have an aqueous solution with a pH of 8.0. You add sodium chloride to a concentration of 1 gram per 100 milliliters. What happens to the pH?
A)It goes up.
B)It goes down.
C)It stays the same.
D)It depends on the temperature.
A)It goes up.
B)It goes down.
C)It stays the same.
D)It depends on the temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Describe three chemical properties of water that make it uniquely suited for its role as a central "molecule of life."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which statement BEST describes an effect of the low density of frozen water in a lake?
A)When water freezes, it contracts, decreasing the water level in the lake.
B)Water in a lake freezes from the bottom up, killing most aquatic organisms.
C)When water in a lake freezes, it floats, providing insulation for organisms below the ice.
D)Water removes thermal energy from the land around a lake, causing the lake to freeze.
A)When water freezes, it contracts, decreasing the water level in the lake.
B)Water in a lake freezes from the bottom up, killing most aquatic organisms.
C)When water in a lake freezes, it floats, providing insulation for organisms below the ice.
D)Water removes thermal energy from the land around a lake, causing the lake to freeze.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following is NOT a property of water?
A)contracts during freezing
B)floats when solid
C)is a good solvent
D)adheres to polar compounds
E)is a polar molecule
A)contracts during freezing
B)floats when solid
C)is a good solvent
D)adheres to polar compounds
E)is a polar molecule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which one of the following properties of water is primarily responsible for the ability of trees to draw water up from the roots to the leaves?
A)polarity
B)density
C)solvent capability
D)cohesion
E)pH neutrality
A)polarity
B)density
C)solvent capability
D)cohesion
E)pH neutrality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which one of the following represents the pH of a solution with the HIGHEST concentration of hydrogen ions?
A)1)0
B)4)5
C)7)0
D)9)1
E)11.5
A)1)0
B)4)5
C)7)0
D)9)1
E)11.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Part of the reason why salt dissolves in water is that hydrogen bonds form between water molecules and chlorine ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The association of individual water molecules with other water molecules is called _____ and occurs through _____ bonds between water molecules.
A)adhesion; polar covalent
B)cohesion; polar covalent
C)cohesion; hydrogen bonds
D)adhesion; hydrogen bonds
A)adhesion; polar covalent
B)cohesion; polar covalent
C)cohesion; hydrogen bonds
D)adhesion; hydrogen bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A water molecule contains what type of bond?
A)hydrogen
B)ionic
C)polar covalent
D)van der Waals interactions
A)hydrogen
B)ionic
C)polar covalent
D)van der Waals interactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What is the chemical basis for water's role as the universal solvent?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following statements about water is CORRECT?
A)Water is the most abundant molecule in living cells.
B)Water is a polar molecule.
C)Water has good solvent properties.
D)Water molecules form hydrogen bonds with other polar molecules.
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)Water is the most abundant molecule in living cells.
B)Water is a polar molecule.
C)Water has good solvent properties.
D)Water molecules form hydrogen bonds with other polar molecules.
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
You have an aqueous solution with a pH of 6.0. What would you add to make the solution more basic?
A)Hydrogen chloride (HCl)
B)Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
C)Sodium chloride (NaCl)
D)Deionized water (dH2O)
A)Hydrogen chloride (HCl)
B)Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
C)Sodium chloride (NaCl)
D)Deionized water (dH2O)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In a solution that has pH = 7.0, the ratio of protons (H+) to hydroxide ions (OH-) equals
A)70
B)7
C)1
D)1/7
E)1/70
A)70
B)7
C)1
D)1/7
E)1/70

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Several chemical properties make water uniquely suited for its role as a central "molecule of life." Which of the following is FALSE?
A)Hydrogen bonding leads to high cohesiveness between water molecules.
B)Water resists temperature changes.
C)Water molecules are always polar.
D)The structure of a water molecule is stabilized by hydrogen bonds.
E)Water is a good solvent of polar molecules and ions.
A)Hydrogen bonding leads to high cohesiveness between water molecules.
B)Water resists temperature changes.
C)Water molecules are always polar.
D)The structure of a water molecule is stabilized by hydrogen bonds.
E)Water is a good solvent of polar molecules and ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding a polar molecule?
A)A polar molecule is hydrophobic.
B)A polar molecule is hydrophilic.
C)A polar molecule will dissolve in water.
D)A polar molecule will not dissolve in water.
E)A polar molecule is hydrophilic and it will dissolve in water.
A)A polar molecule is hydrophobic.
B)A polar molecule is hydrophilic.
C)A polar molecule will dissolve in water.
D)A polar molecule will not dissolve in water.
E)A polar molecule is hydrophilic and it will dissolve in water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which one of the following statements about pH is INCORRECT?
A)An acidic solution has a higher concentration of protons than of hydroxide ions.
B)Physiological pH is defined as the pH of pure water, 7.0.
C)Some cellular compartments have different pH values than others.
D)The pH of a solution can range from 0 to 14.
E)A solution of pH 5 has a proton concentration 100 times greater than a solution of pH 7.
A)An acidic solution has a higher concentration of protons than of hydroxide ions.
B)Physiological pH is defined as the pH of pure water, 7.0.
C)Some cellular compartments have different pH values than others.
D)The pH of a solution can range from 0 to 14.
E)A solution of pH 5 has a proton concentration 100 times greater than a solution of pH 7.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 232 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



