Deck 16: Mendelian Inheritance
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/191
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Mendelian Inheritance
1
Mothers who consume excessive alcohol during pregnancy may have babies who are affected with a pattern of physical and mental disabilities known as fetal alcohol syndrome. Similarly, mothers who become addicted to drugs during pregnancy may have babies who show signs of addiction. Do these examples contradict the statement that traits acquired by the parents are not transmitted to the offspring?
Fetal alcohol syndrome and newborn addiction are developmental disorders that take place in the womb. Neither the mother's genes nor those of the offspring are changed by alcoholism or drug addiction, so the examples do not contradict the statement that traits acquired by the parents are not transmitted to the offspring. Properly understood, the principle is that traits acquired by the parents do not alter the parents' genes, and therefore do not affect the hereditary traits of the offspring.
2
_____ suggests that traits in offspring resemble the average of the parents.
A)Mendelian inheritance
B)Natural selection
C)Blending inheritance
D)Eugenic inheritance
A)Mendelian inheritance
B)Natural selection
C)Blending inheritance
D)Eugenic inheritance
C
3
For a trait such as flower color in snapdragons that is determined by two alleles with incomplete dominance, the offspring of true-breeding parents show an intermediate phenotype. This is also what would be expected of blending inheritance. The difference is that the trait with:
A)Mendelian inheritance will lose the variation over time.
B)blending inheritance will lose the variation over time.
C)Mendelian inheritance shows no segregation in the F2 generation.
D)blending inheritance shows segregation in the F2 generation.
A)Mendelian inheritance will lose the variation over time.
B)blending inheritance will lose the variation over time.
C)Mendelian inheritance shows no segregation in the F2 generation.
D)blending inheritance shows segregation in the F2 generation.
B
4
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding Hippocrates' theory of trait inheritance?
A)This theory influenced later evolutionary biologists, such as Charles Darwin and Jean-Baptiste Lamarck.
B)This theory stated that each body part could produce heritable substances that could be passed onto progeny.
C)This theory was likely the first to postulate how specific traits are inherited.
D)This theory supported the idea that characteristics, such as muscle strength, can be passed from parents to offspring.
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)This theory influenced later evolutionary biologists, such as Charles Darwin and Jean-Baptiste Lamarck.
B)This theory stated that each body part could produce heritable substances that could be passed onto progeny.
C)This theory was likely the first to postulate how specific traits are inherited.
D)This theory supported the idea that characteristics, such as muscle strength, can be passed from parents to offspring.
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is considered a trait?
A)fur length in cats
B)height in humans
C)leaf shape in trees
D)beak size in owls
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)fur length in cats
B)height in humans
C)leaf shape in trees
D)beak size in owls
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If the concept of blending inheritance were true, would variation increase or decrease over time?
A)It would increase.
B)It would decrease.
C)It would stay the same.
A)It would increase.
B)It would decrease.
C)It would stay the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If blending inheritance was an accurate model of transmission genetics, which of the following would be TRUE?
A)Variation in natural populations would remain the same over time.
B)Variation in natural populations would increase over time.
C)Variation in natural populations would decrease over time.
D)Variation would increase in some populations, decrease in some populations, and remain the same in some populations.
E)Mutation would not contribute to variation in natural populations.
A)Variation in natural populations would remain the same over time.
B)Variation in natural populations would increase over time.
C)Variation in natural populations would decrease over time.
D)Variation would increase in some populations, decrease in some populations, and remain the same in some populations.
E)Mutation would not contribute to variation in natural populations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Darwin believed in blending inheritance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Imagine two different pea plant strains: one of which has a trait that is produced by the interaction of many genes, and the other of which has a trait that is produced by a single gene with two alleles and incomplete dominance. If each of these pea plant strains self-fertilizes, how would the progeny of each cross differ?
A)They would not differ, and progeny of both crosses would have an array of phenotypes that vary continuously across a range.
B)The progeny from the cross of the plant with the single-gene trait would all be identical, whereas the progeny from the cross of the plant with the multiple-gene trait would vary continuously across a spectrum.
C)The progeny from the cross of the plant with the single gene trait would have three phenotypes, whereas the progeny of the cross of the plant with the trait caused by many genes would have a more complex array of phenotypes.
A)They would not differ, and progeny of both crosses would have an array of phenotypes that vary continuously across a range.
B)The progeny from the cross of the plant with the single-gene trait would all be identical, whereas the progeny from the cross of the plant with the multiple-gene trait would vary continuously across a spectrum.
C)The progeny from the cross of the plant with the single gene trait would have three phenotypes, whereas the progeny of the cross of the plant with the trait caused by many genes would have a more complex array of phenotypes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Imagine that blending inheritance was true, and black and white rabbits mated as in the example in the textbook. If the offspring show only half the intensity of black pigment after one generation, how many generations would be required for them to show 1/64th the intensity of black pigment?
A)3
B)4
C)5
D)6
E)7
A)3
B)4
C)5
D)6
E)7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A true-breeding black rabbit is crossed with a true-breeding white rabbit to produce an F1 generation with 8 individuals. If blending inheritance were true, which of the following would represent the expected phenotype of the F1 generation?
A)8 black rabbits, 0 white rabbits, 0 grey rabbits
B)2 black rabbits, 2 white rabbits, 4 grey rabbits
C)0 black rabbits, 0 white rabbits, 8 grey rabbits
D)4 black rabbits, 2 white rabbits, 2 grey rabbits
E)6 black rabbits, 2 white rabbits, 0 grey rabbits
A)8 black rabbits, 0 white rabbits, 0 grey rabbits
B)2 black rabbits, 2 white rabbits, 4 grey rabbits
C)0 black rabbits, 0 white rabbits, 8 grey rabbits
D)4 black rabbits, 2 white rabbits, 2 grey rabbits
E)6 black rabbits, 2 white rabbits, 0 grey rabbits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is TRUE of blending inheritance?
A)Blending inheritance explains the disappearance of a trait several generations after it appeared.
B)Blending inheritance leads to an increase in variation over time.
C)Blending inheritance allows for rare variants of traits to increase in frequency.
D)None of the answer options is correct.
A)Blending inheritance explains the disappearance of a trait several generations after it appeared.
B)Blending inheritance leads to an increase in variation over time.
C)Blending inheritance allows for rare variants of traits to increase in frequency.
D)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
As a result of the principle of blending inheritance, no grey rabbits actually exist. Over time, grey fur in rabbits has been diluted to white fur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In 1871, Francis Galton reported experiments in which, in each of multiple generations, he transfused blood from a true-breeding strain of black rabbits into individuals of a true-breeding strain of white rabbits. Nevertheless, he reported, in each generation the kits (babies) of the white rabbits were as white as their parents. In regard to heredity, this experiment demonstrates that:
A)characteristics of blood are not hereditary.
B)red blood cells (erythrocytes)have no nucleus.
C)blood transfusions do not affect hereditary characteristics.
D)the recipient's coat color is not affected by blood transfusions.
E)None of the other answer options is correct.
A)characteristics of blood are not hereditary.
B)red blood cells (erythrocytes)have no nucleus.
C)blood transfusions do not affect hereditary characteristics.
D)the recipient's coat color is not affected by blood transfusions.
E)None of the other answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
An offspring affected with fetal alcohol syndrome caused by excessive consumption of alcohol by the mother is not an example of the inheritance of an acquired trait because the:
A)mother can be treated for alcoholism.
B)child can be treated for fetal alcohol syndrome.
C)genes for excessive alcohol consumption are already mutated in the mother.
D)the mother's alcoholism affects the development of the fetus, not its genes.
A)mother can be treated for alcoholism.
B)child can be treated for fetal alcohol syndrome.
C)genes for excessive alcohol consumption are already mutated in the mother.
D)the mother's alcoholism affects the development of the fetus, not its genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Imagine that blending inheritance was true, and black and white rabbits mated as in the example in the book. If the offspring show only half the intensity of black pigment after one generation, how many generations would be required for them to show 1/16th the intensity of black pigment?
A)3
B)4
C)5
D)6
E)7
A)3
B)4
C)5
D)6
E)7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is NOT be considered an acquired trait?
A)dyed hair color
B)eye color
C)muscle strength
D)leg amputation
E)scars
A)dyed hair color
B)eye color
C)muscle strength
D)leg amputation
E)scars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Aristotle (384-322 BCE) seems to have been the first person to point out that men who have become bald have male offspring who are born with hair, which implies that acquired characteristics are not transmitted to offspring. Now we know that hereditary pattern baldness has a characteristic age of onset, a time at which the hair falls out and baldness gradually spreads. This new knowledge means that:
A)acquired characteristics are transmitted to the offspring.
B)pattern baldness is not an acquired trait.
C)Aristotle was wrong: Bald males do have bald sons.
D)None of the answer options is correct.
A)acquired characteristics are transmitted to the offspring.
B)pattern baldness is not an acquired trait.
C)Aristotle was wrong: Bald males do have bald sons.
D)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Imagine that you are standing next to Aristotle in early Greece. You both see an older, balding man with visible age spots on his skin. This man also appears to be a wounded soldier, whose left leg has been amputated. What might Aristotle say to you?
A)"Because that man is balding, his sons may also be born bald."
B)"Because that man has age spots on his skin, his children were likely also born with spots."
C)"Because that man is missing a leg, his children are likely also missing legs."
D)"Because that man is balding and has age spots, his children will likely go bald and will develop age spots."
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)"Because that man is balding, his sons may also be born bald."
B)"Because that man has age spots on his skin, his children were likely also born with spots."
C)"Because that man is missing a leg, his children are likely also missing legs."
D)"Because that man is balding and has age spots, his children will likely go bald and will develop age spots."
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In 1891, August Weismann reported an experiment in which he cut the tails off 10 mice in each of 19 consecutive generations. The expected result is:
A)after the first generation of amputation, the progeny are born with no tails.
B)offspring are born with progressively shorter tails in each generation.
C)offspring are born with tails that are the same length as their parents for a few generations, but subsequent generations of offspring have shorter tails.
D)all generations of offspring have tails of approximately the same length.
A)after the first generation of amputation, the progeny are born with no tails.
B)offspring are born with progressively shorter tails in each generation.
C)offspring are born with tails that are the same length as their parents for a few generations, but subsequent generations of offspring have shorter tails.
D)all generations of offspring have tails of approximately the same length.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Mendel's experiments with garden peas differed from those of other plant hybridizers of the time in that Mendel:
A)studied true-breeding strains instead of poorly defined material.
B)focused on a small number of easily contrasted traits instead of a large number of more complex traits.
C)quantified his results and looked for statistical patterns instead of simply noting the presence or absence of a trait among a group of offspring.
D)performed no crosses between strains, whereas other hybridizers did.
E)studied true-breeding strains, focused on a small number of easily contrasted traits, and quantified results.
A)studied true-breeding strains instead of poorly defined material.
B)focused on a small number of easily contrasted traits instead of a large number of more complex traits.
C)quantified his results and looked for statistical patterns instead of simply noting the presence or absence of a trait among a group of offspring.
D)performed no crosses between strains, whereas other hybridizers did.
E)studied true-breeding strains, focused on a small number of easily contrasted traits, and quantified results.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In a reciprocal cross:
A)both parents are male.
B)both parents are female.
C)heterozygous genotypes are crossed with homozygous genotypes.
D)the sexes are interchanged relative to the trait.
A)both parents are male.
B)both parents are female.
C)heterozygous genotypes are crossed with homozygous genotypes.
D)the sexes are interchanged relative to the trait.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following situations would have caused Mendel to observe patterns of inheritance that supported the model of blending inheritance instead of transmission of alleles causing discrete differences?
A)if Mendel chose traits controlled by more than a single gene
B)if Mendel chose traits controlled by a single gene, but that gene had more than two alleles affecting the phenotype
C)if Mendel chose traits affected by both the genotype and the environment
D)All of these choices are correct.
A)if Mendel chose traits controlled by more than a single gene
B)if Mendel chose traits controlled by a single gene, but that gene had more than two alleles affecting the phenotype
C)if Mendel chose traits affected by both the genotype and the environment
D)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Mendel used true-breeding strains of peas. Which true-breeding strain of peas would have been easier to produce: true-breeding peas with the trait caused by a dominant allele or a recessive allele?
A)dominant allele
B)recessive allele
C)Both strains would be equally easy to produce.
A)dominant allele
B)recessive allele
C)Both strains would be equally easy to produce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The term "dominant allele" is shorthand for an allele:
A)that always produces a functional product.
B)that produces a functional product under certain conditions.
C)whose presence results in a dominant trait.
D)with epistasis that alters the expected F2 ratio of 9:3:3:1.
A)that always produces a functional product.
B)that produces a functional product under certain conditions.
C)whose presence results in a dominant trait.
D)with epistasis that alters the expected F2 ratio of 9:3:3:1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In genetic crosses, the symbol Aa refers to a:
A)genotype.
B)phenotype.
C)morphotype.
D)holotype.
E)archetype.
A)genotype.
B)phenotype.
C)morphotype.
D)holotype.
E)archetype.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In a homozygous genotype:
A)both alleles for a given trait are the same.
B)the two alleles for a given trait are different.
C)the individual will be phenotypically dominant.
D)the individual will be phenotypically recessive.
E)both alleles for a given trait are the same, and the individual will be phenotypically dominant.
A)both alleles for a given trait are the same.
B)the two alleles for a given trait are different.
C)the individual will be phenotypically dominant.
D)the individual will be phenotypically recessive.
E)both alleles for a given trait are the same, and the individual will be phenotypically dominant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In Mendel's peas, an individual that is heterozygous for seed color:
A)has only one kind of allele for seed color.
B)has two different alleles for seed color.
C)will express the dominant allele.
D)will express the recessive allele.
E)has two different alleles for seed color and will express the dominant allele.
A)has only one kind of allele for seed color.
B)has two different alleles for seed color.
C)will express the dominant allele.
D)will express the recessive allele.
E)has two different alleles for seed color and will express the dominant allele.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A genotype is:
A)one of several forms of a gene.
B)the particular combination of alleles present in a given organism.
C)the expression of a trait in an individual.
D)the location of a gene on a chromosome.
E)None of the other answer options is correct.
A)one of several forms of a gene.
B)the particular combination of alleles present in a given organism.
C)the expression of a trait in an individual.
D)the location of a gene on a chromosome.
E)None of the other answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The statement that, in garden peas, yellow seed is dominant to green seed means that:
A)when a true-breeding yellow seed parent is crossed with a true-breeding green seed parent, all offspring will have green seeds.
B)when a true-breeding yellow seed parent is crossed with a true-breeding green seed parent, all offspring will have yellow seeds.
C)when a true-breeding yellow seed parent is crossed with a true-breeding green seed parent, 1/2 of the offspring will have yellow seeds and 1/2 will have green seeds.
D)when a true-breeding yellow seed parent is crossed with a true-breeding green seed parent, 3/4 of the offspring will have yellow seeds and 1/4 will have green seeds.
E)we can't predict seed color in the offspring of a true-breeding yellow seed parent and a true-breeding green seed parent.
A)when a true-breeding yellow seed parent is crossed with a true-breeding green seed parent, all offspring will have green seeds.
B)when a true-breeding yellow seed parent is crossed with a true-breeding green seed parent, all offspring will have yellow seeds.
C)when a true-breeding yellow seed parent is crossed with a true-breeding green seed parent, 1/2 of the offspring will have yellow seeds and 1/2 will have green seeds.
D)when a true-breeding yellow seed parent is crossed with a true-breeding green seed parent, 3/4 of the offspring will have yellow seeds and 1/4 will have green seeds.
E)we can't predict seed color in the offspring of a true-breeding yellow seed parent and a true-breeding green seed parent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In Mendel's garden peas, each cell in a pea plant has a total of:
A)one allele for each gene.
B)two alleles for each gene.
C)one allele for each gene, if it is a true-breeding parent and two if it is an F1 offspring.
D)one allele for each gene, if it has green seeds and two if it has yellow seeds.
E)between one and four alleles for each gene.
A)one allele for each gene.
B)two alleles for each gene.
C)one allele for each gene, if it is a true-breeding parent and two if it is an F1 offspring.
D)one allele for each gene, if it has green seeds and two if it has yellow seeds.
E)between one and four alleles for each gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A reproductive cell, or gamete, has:
A)one allele of each gene.
B)two alleles of each gene.
C)one allele of each gene if it is homozygous and two if it is heterozygous.
D)one allele of each gene if it is true-breeding and two if it is an F1 offspring.
E)between one and four alleles of each gene.
A)one allele of each gene.
B)two alleles of each gene.
C)one allele of each gene if it is homozygous and two if it is heterozygous.
D)one allele of each gene if it is true-breeding and two if it is an F1 offspring.
E)between one and four alleles of each gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In modern terminology, a true-breeding strain is:
A)hybrid.
B)dominant.
C)heterozygous.
D)homozygous.
A)hybrid.
B)dominant.
C)heterozygous.
D)homozygous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The Augustinian monk Gregor Mendel believed that organisms only passed on traits to their progeny-he had no concept of what genes were.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Mendel's experiments with garden peas differed from those of other plant hybridizers of the time in that:
A)Mendel studied true-breeding strains instead of poorly defined material.
B)Mendel focused on a small number of easily contrasted traits instead of a large number of more complex traits.
C)Mendel quantified his results and looked for statistical patterns instead of simply noting the presence or absence of a trait among a group of offspring.
D)Mendel performed no crosses between strains, whereas other hybridizers did.
E)Mendel studied true-breeding strains, focused on a small number of easily contrasted traits, and quantified results.
A)Mendel studied true-breeding strains instead of poorly defined material.
B)Mendel focused on a small number of easily contrasted traits instead of a large number of more complex traits.
C)Mendel quantified his results and looked for statistical patterns instead of simply noting the presence or absence of a trait among a group of offspring.
D)Mendel performed no crosses between strains, whereas other hybridizers did.
E)Mendel studied true-breeding strains, focused on a small number of easily contrasted traits, and quantified results.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
When Mendel crossed true-breeding yellow-seed plants with true-breeding green-seed plants, the offspring were genotypically:
A)yellow seed.
B)green seed.
C)a mixture of yellow and green seed.
D)made up of a combination of yellow and green alleles.
A)yellow seed.
B)green seed.
C)a mixture of yellow and green seed.
D)made up of a combination of yellow and green alleles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When Mendel crossed true-breeding yellow-seed plants with true-breeding green-seed plants, the offspring were phenotypically:
A)yellow-seed plants.
B)green-seed plants.
C)a mixture of yellow and green seeds.
D)made up of a combination of yellow and green alleles.
A)yellow-seed plants.
B)green-seed plants.
C)a mixture of yellow and green seeds.
D)made up of a combination of yellow and green alleles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
An allele is:
A)one of several forms of a gene.
B)the particular combination of genes for a given trait in a given organism.
C)the expression of a trait in an individual.
D)the location of a gene on a chromosome.
E)None of the answer options is correct.
A)one of several forms of a gene.
B)the particular combination of genes for a given trait in a given organism.
C)the expression of a trait in an individual.
D)the location of a gene on a chromosome.
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A phenotype is:
A)one of several forms of a gene.
B)the particular combination of alleles present in a given organism.
C)the expression of a trait in an individual.
D)the location of a gene on a chromosome.
E)None of the other answer options is correct.
A)one of several forms of a gene.
B)the particular combination of alleles present in a given organism.
C)the expression of a trait in an individual.
D)the location of a gene on a chromosome.
E)None of the other answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Why was the theory of blending inheritance eventually disproven?
A)Although the theory of blending inheritance accounted for a great deal of variation in a population, the theory of natural selection yielded explanations for every phenotype observed in a population.
B)The theory of blending inheritance suggested that inheritance is a diversifying force, but it is actually a homogenizing force.
C)It suggested that traits such as blue eyes were recessive, but such traits are in fact actually the result of rare dominant mutations arising in populations.
D)It was based on the fact that the phenotypes of progeny of a given cross typically resemble either parent-and never present "intermediate" phenotypes (i.e., such as grey fur).
E)It was eventually disproven by demonstrating segregation of alleles for the inheritance of many traits in diverse types of organisms.
A)Although the theory of blending inheritance accounted for a great deal of variation in a population, the theory of natural selection yielded explanations for every phenotype observed in a population.
B)The theory of blending inheritance suggested that inheritance is a diversifying force, but it is actually a homogenizing force.
C)It suggested that traits such as blue eyes were recessive, but such traits are in fact actually the result of rare dominant mutations arising in populations.
D)It was based on the fact that the phenotypes of progeny of a given cross typically resemble either parent-and never present "intermediate" phenotypes (i.e., such as grey fur).
E)It was eventually disproven by demonstrating segregation of alleles for the inheritance of many traits in diverse types of organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
You are given two populations of true-breeding tomato plants with two simple dominant/recessive traits that sort independently. Using the multiplication rule, how many different phenotypic combinations would you expect to see in the F2 generation? In what phenotypic ratio?
A)two, 3:1
B)three, 9:6:1
C)four, 9:3:3:1
A)two, 3:1
B)three, 9:6:1
C)four, 9:3:3:1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Why was it important for Mendel to remove the anthers from pea plants in his experiments when crossing two different true-breeding pea plants?
A)to prevent self-fertilization
B)to make sure self-fertilization would occur
C)to protect the pea plants from environmental pollen
D)to stimulate the pea plants to ovulate
A)to prevent self-fertilization
B)to make sure self-fertilization would occur
C)to protect the pea plants from environmental pollen
D)to stimulate the pea plants to ovulate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
One of Mendel's most important discoveries was:
A)dominance.
B)segregation.
C)mutation.
D)equivalence of reciprocal crosses.
A)dominance.
B)segregation.
C)mutation.
D)equivalence of reciprocal crosses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding Charles Darwin?
A)Darwin subscribed to the idea of blending inheritance, which posed problems to certain aspects of his work.
B)He believed that inheritance could be considered a homogenizing force.
C)He established the theory of natural selection.
D)He could not successfully synthesize the theory of blending inheritance with his theory of natural selection.
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)Darwin subscribed to the idea of blending inheritance, which posed problems to certain aspects of his work.
B)He believed that inheritance could be considered a homogenizing force.
C)He established the theory of natural selection.
D)He could not successfully synthesize the theory of blending inheritance with his theory of natural selection.
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is an allele?
A)one of several different forms of a gene
B)the external appearance of an organism
C)a spontaneous mutation
D)a group of unrelated genes seen in true-breeding stock
E)a circular strand of DNA capable of self-replication
A)one of several different forms of a gene
B)the external appearance of an organism
C)a spontaneous mutation
D)a group of unrelated genes seen in true-breeding stock
E)a circular strand of DNA capable of self-replication

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding Mendel's work?
A)He did not use true-breeding pea strains.
B)He provided no numerical or statistical data for any of his experiments.
C)He focused on a subset of easily discernible traits in pea plants.
D)His work utilized several different traits and several different strains of pea plants, some of which were not considered true-breeding.
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)He did not use true-breeding pea strains.
B)He provided no numerical or statistical data for any of his experiments.
C)He focused on a subset of easily discernible traits in pea plants.
D)His work utilized several different traits and several different strains of pea plants, some of which were not considered true-breeding.
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
According to the principle of segregation, a heterozygous plant with alleles Aa will produce:
A)gametes with only the A allele.
B)gametes with only the a allele.
C)gametes in the ratio of 1 A allele:1 a allele.
D)gametes in the ratio of 3 A alleles:1 a allele.
E)some gametes with the A allele and some with the a allele, but in no predictable ratio.
A)gametes with only the A allele.
B)gametes with only the a allele.
C)gametes in the ratio of 1 A allele:1 a allele.
D)gametes in the ratio of 3 A alleles:1 a allele.
E)some gametes with the A allele and some with the a allele, but in no predictable ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If one of the traits Mendel studied was encoded by a single gene with three alleles that produced different phenotypes, what would he have observed if he crossed all possible pairs of the three true-breeding lines in the F1 and F2 generations?
A)In each of the crosses, he would have observed two phenotypes in the F1 generation.
B)Only a single phenotype would have been observed in the F1 generation because only one allele can be dominant.
C)No evidence would exist for the law of segregation.
D)No true-breeding plants would have been produced in the F2.
E)None of the answer options is correct.
A)In each of the crosses, he would have observed two phenotypes in the F1 generation.
B)Only a single phenotype would have been observed in the F1 generation because only one allele can be dominant.
C)No evidence would exist for the law of segregation.
D)No true-breeding plants would have been produced in the F2.
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A high school student wants to repeat Mendel's classic experiments for her science fair. To stay true to Mendel's work, what must the student do?
A)She must allow true-breeding pea plants to self-fertilize.
B)She must remove the male organs (anthers)from plants she has designated as females.
C)She must hand-pollinate the pea plants and keep careful track of the traits demonstrated by male and female parents.
D)She must leave the pollinated plants uncovered, so that they can receive adequate amounts of light, carbon dioxide, and water.
E)She must remove the male organs (anthers)from plants she has designated as females, and she must hand-pollinate plants and keep track of the traits seen in male and female parents.
A)She must allow true-breeding pea plants to self-fertilize.
B)She must remove the male organs (anthers)from plants she has designated as females.
C)She must hand-pollinate the pea plants and keep careful track of the traits demonstrated by male and female parents.
D)She must leave the pollinated plants uncovered, so that they can receive adequate amounts of light, carbon dioxide, and water.
E)She must remove the male organs (anthers)from plants she has designated as females, and she must hand-pollinate plants and keep track of the traits seen in male and female parents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
True-breeding plants are typically heterozygous for most genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Imagine that a rancher has a herd of cattle with brown hides and short horns. All of his cattle are also relatively short in stature. If all of these traits were true-breeding, what could you say about the progeny of these cattle?
A)It is impossible to determine the traits of such progeny-they will likely demonstrate different hide colors, horn lengths, and heights.
B)The progeny of these cattle will have short horns, but a variety of hide colors and heights.
C)The progeny of these cattle will have brown, black, white, and spotted hides.
D)Because the cattle are true-breeding, the progeny of this herd will all be sterile.
E)The progeny of these cattle will be short in stature and have brown hides and short horns.
A)It is impossible to determine the traits of such progeny-they will likely demonstrate different hide colors, horn lengths, and heights.
B)The progeny of these cattle will have short horns, but a variety of hide colors and heights.
C)The progeny of these cattle will have brown, black, white, and spotted hides.
D)Because the cattle are true-breeding, the progeny of this herd will all be sterile.
E)The progeny of these cattle will be short in stature and have brown hides and short horns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following genotypes would result in a true-breeding stock?
A)AA or Aa or aa
B)Aa, but not AA or aa
C)AA, but not Aa or aa
D)aa, but not Aa or AA
E)AA or aa, but not Aa
A)AA or Aa or aa
B)Aa, but not AA or aa
C)AA, but not Aa or aa
D)aa, but not Aa or AA
E)AA or aa, but not Aa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In Mendel's experiments, his parental pea plants are referred to as the F1 generation, and their progeny are referred to as the P1 generation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What made the plant hybridization studies performed by Mendel more successful than plant hybridization studies performed by others?
A)Mendel did not use true-breeding organisms because he wanted to assess the inheritance of more than one trait per breeding.
B)Mendel was the first to identify characteristics of pea plants that could be observed as phenotypes.
C)Mendel's understanding of natural selection inspired his methodology to examine the effect of environmental stressors on genetic diversity.
D)Mendel used statistical analysis to analyze the phenotypes he observed.
E)Mendel used qualitative analysis to evaluate the genotypes he observed.
A)Mendel did not use true-breeding organisms because he wanted to assess the inheritance of more than one trait per breeding.
B)Mendel was the first to identify characteristics of pea plants that could be observed as phenotypes.
C)Mendel's understanding of natural selection inspired his methodology to examine the effect of environmental stressors on genetic diversity.
D)Mendel used statistical analysis to analyze the phenotypes he observed.
E)Mendel used qualitative analysis to evaluate the genotypes he observed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following was NOT a trait that Mendel studied in pea plants?
A)leaf size
B)seed color
C)flower color
D)plant height
E)seed shape or texture
A)leaf size
B)seed color
C)flower color
D)plant height
E)seed shape or texture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following represents the expected genotypes of an F1 generation consisting of 16 individuals from a cross of a true-breeding black (BB) rabbit and a true-breeding white (bb) rabbit?
A)16 BB, 0 bb, 0 Bb
B)8 BB, 8 bb, 0 Bb
C)4 BB, 4 bb, 8 Bb
D)0 BB, 0 bb, 16 Bb
A)16 BB, 0 bb, 0 Bb
B)8 BB, 8 bb, 0 Bb
C)4 BB, 4 bb, 8 Bb
D)0 BB, 0 bb, 16 Bb

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A true-breeding black rabbit is crossed with a true-breeding white rabbit to produce an F1 generation of 15 individuals. If the black color trait is dominant, which of the following represents the expected phenotype of an F1 generation cross?
A)15 black rabbits, 0 white rabbits, 0 grey rabbits
B)5 black rabbits, 5 white rabbits, 6 grey rabbits
C)0 black rabbits, 0 white rabbits, 15 grey rabbits
D)5 black rabbits, 3 white rabbits, 7 grey rabbits
E)0 black rabbits, 15 white rabbits, 0 grey rabbits
A)15 black rabbits, 0 white rabbits, 0 grey rabbits
B)5 black rabbits, 5 white rabbits, 6 grey rabbits
C)0 black rabbits, 0 white rabbits, 15 grey rabbits
D)5 black rabbits, 3 white rabbits, 7 grey rabbits
E)0 black rabbits, 15 white rabbits, 0 grey rabbits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding the yellow-seed pea plants of Mendel's work?
A)Yellow-seed plants produce copious amounts of chlorophyll.
B)Yellow-seed plants have an enzyme that breaks down chlorophyll.
C)The yellow seed color of these plants is a recessive trait (compared to green seed color).
D)Yellow seeds in these plants only appear in the P1 generation and never in the F1 generation.
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)Yellow-seed plants produce copious amounts of chlorophyll.
B)Yellow-seed plants have an enzyme that breaks down chlorophyll.
C)The yellow seed color of these plants is a recessive trait (compared to green seed color).
D)Yellow seeds in these plants only appear in the P1 generation and never in the F1 generation.
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Huntington's disease is a devastating neurological disorder. If a child of an affected parent receives one copy of the Huntington allele, he or she will develop Huntington's disease. Thus, Huntington's disease is considered _____ trait.
A)a recessive
B)a dominant
C)a neutral
D)a reciprocal
E)either a neutral or recessive
A)a recessive
B)a dominant
C)a neutral
D)a reciprocal
E)either a neutral or recessive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Consider Mendel's experiments involving the trait of round versus wrinkled peas. In some experiments, Mendel removed the anthers of the flowers from a plant that was true-breeding for round peas and applied pollen from the anthers of a plant that was true-breeding for wrinkled peas. What would have happened if Mendel missed some anthers that he was trying to remove from the true-breeding round pea plants, and then counted the peas produced by a plant that bore a mix of round and wrinkled pollen? Indicate which of the following must be TRUE.
A)The F1 peas produced would have mixed phenotypes.
B)The F1 peas produced would have a single phenotype.
C)The F2 peas would have phenotypes in a 9:3:3:1 ratio.
D)The F2 peas would all have the phenotype of the parental plant with the anthers not properly removed.
E)The F1 peas would have phenotypes in a 1:1 ratio.
A)The F1 peas produced would have mixed phenotypes.
B)The F1 peas produced would have a single phenotype.
C)The F2 peas would have phenotypes in a 9:3:3:1 ratio.
D)The F2 peas would all have the phenotype of the parental plant with the anthers not properly removed.
E)The F1 peas would have phenotypes in a 1:1 ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In the F2 generation of Mendel's monohybrid crosses, the 1:2:1 ratio refers to:
A)single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).
B)copy-number variations (CNVs).
C)variable number of tandem repeats (VNTRs).
D)genotypes.
E)phenotypes.
A)single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).
B)copy-number variations (CNVs).
C)variable number of tandem repeats (VNTRs).
D)genotypes.
E)phenotypes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Among the progeny of a heterozygous round (Aa) × homozygous wrinkled (aa) testcross, three seeds are chosen at random. What is the probability that two seeds are round and the other is wrinkled?
A)(1/2)3
B)2(1/2)3
C)3(1/2)3
D)4(1/2)3
A)(1/2)3
B)2(1/2)3
C)3(1/2)3
D)4(1/2)3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In the F2 generation of Mendel's monohybrid crosses, the 3:1 ratio refers to:
A)single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).
B)copy-number variations (CNVs).
C)variable number of tandem repeats (VNTRs).
D)genotypes.
E)phenotypes.
A)single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).
B)copy-number variations (CNVs).
C)variable number of tandem repeats (VNTRs).
D)genotypes.
E)phenotypes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In the F2 generation of a homozygous round (AA) × homozygous wrinkled (aa) cross in peas, three seeds are chosen at random. What is the probability that two seeds are round and the other is wrinkled?
A)(1/4)3
B)3(1/4)(3/4)2
C)3(1/4)2(3/4)
D)(3/4)3
A)(1/4)3
B)3(1/4)(3/4)2
C)3(1/4)2(3/4)
D)(3/4)3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following ratios is associated with Mendel's discoveries?
A)3:1
B)1:2
C)1:2:1
D)9:3:3:1
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)3:1
B)1:2
C)1:2:1
D)9:3:3:1
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The expression (1/2 A + 1/2 a)2 is the mathematical equivalent of a:
A)hybridization.
B)testcross.
C)Punnett square.
D)nondisjunction.
A)hybridization.
B)testcross.
C)Punnett square.
D)nondisjunction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Among the progeny of a heterozygous round (Aa) × homozygous wrinkled (aa) testcross, three seeds are chosen at random. What is the probability that all three seeds are round?
A)(1/2)3
B)2(1/2)3
C)3(1/2)3
D)4(1/2)3
A)(1/2)3
B)2(1/2)3
C)3(1/2)3
D)4(1/2)3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Flower color in snapdragons is due to a gene with incomplete dominance: CRCR plants have red flowers, CRCW have pink flowers, and CWCW plants have white flowers. Which cross is expected to yield progeny with flower colors in a ratio of 1 red:1 pink?
A)CRCR × CRCW
B)CRCR × CWCW
C)CRCW × CRCW
D)CRCW ×CWCW
E)CWCW × CWCW
A)CRCR × CRCW
B)CRCR × CWCW
C)CRCW × CRCW
D)CRCW ×CWCW
E)CWCW × CWCW

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A pea plant is heterozygous (Aa) for seed color and heterozygous (Bb) for seed shape. According to Mendel's principle of independent assortment:
A)each gamete will contain either a seed-color allele or a seed-shape allele, but not both.
B)a gamete that contains dominant allele for seed color must also contain the dominant allele for seed shape.
C)a gamete that contains dominant allele for seed color must also contain the recessive allele for seed shape.
D)a gamete that contains the dominant allele for seed color is equally likely to contain the dominant or the recessive allele for seed shape.
E)possible gamete genotypes are AB or ab; each is equally likely to occur.
A)each gamete will contain either a seed-color allele or a seed-shape allele, but not both.
B)a gamete that contains dominant allele for seed color must also contain the dominant allele for seed shape.
C)a gamete that contains dominant allele for seed color must also contain the recessive allele for seed shape.
D)a gamete that contains the dominant allele for seed color is equally likely to contain the dominant or the recessive allele for seed shape.
E)possible gamete genotypes are AB or ab; each is equally likely to occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Flower color in snapdragons is due to a gene with incomplete dominance: CRCR plants have red flowers, CRCW have pink flowers, and CWCW plants have white flowers. Which cross is expected to yield progeny that all have pink flowers?
A)CRCR × CRCW
B)CRCR × CWCW
C)CRCW × CRCW
D)CRCW ×CWCW
E)CWCW × CWCW
A)CRCR × CRCW
B)CRCR × CWCW
C)CRCW × CRCW
D)CRCW ×CWCW
E)CWCW × CWCW

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Based on the bands observed for the VNTR (variable number of tandem repeats) polymorphism in the accompanying gel diagram, which of the individuals M, H, K, or L could be siblings of individual X? 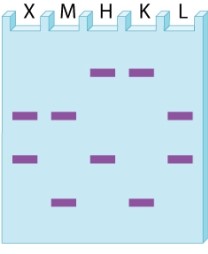
A)individual M
B)individual H
C)individual K
D)individual L
E)All of these choices are correct.

A)individual M
B)individual H
C)individual K
D)individual L
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In the F2 generation of a homozygous round (AA) × homozygous wrinkled (aa) cross in peas, two round seeds are chosen at random. What is the probability that one is AA and the other Aa?
A)(1/3)2
B)(2/3)(1/3)
C)2(2/3)(1/3)
D)(2/3)2
A)(1/3)2
B)(2/3)(1/3)
C)2(2/3)(1/3)
D)(2/3)2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The bands observed in a gel for a VNTR (variable number of tandem repeats) polymorphism in a father (F) and mother (M) are shown in the accompanying diagram. What possible patterns of bands are expected among their offspring? 
A)(1, 2), (1, 3), (2, 3), (3, 4)
B)(1, 2), (1, 4), (2, 3), (3, 4)
C)(1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 3), (2, 4)
D)(1, 3), (2, 3), (1, 4), (3, 4)

A)(1, 2), (1, 3), (2, 3), (3, 4)
B)(1, 2), (1, 4), (2, 3), (3, 4)
C)(1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 3), (2, 4)
D)(1, 3), (2, 3), (1, 4), (3, 4)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
If you crossed a true-breeding yellow-seed plant (AA) with a heterozygous yellow-seed plant (Aa), offspring:
A)genotypes would be 1 AA:2 Aa.
B)genotypes would be 1 Aa:1 aa.
C)genotypes would be 1 AA:1 Aa.
D)phenotypes would be 1/2 yellow-seed plants and 1/2 green-seed plants.
E)genotypes would be 1 Aa:1 aa and would be 1/2 yellow-seed plants and 1/2 green-seed plants.
A)genotypes would be 1 AA:2 Aa.
B)genotypes would be 1 Aa:1 aa.
C)genotypes would be 1 AA:1 Aa.
D)phenotypes would be 1/2 yellow-seed plants and 1/2 green-seed plants.
E)genotypes would be 1 Aa:1 aa and would be 1/2 yellow-seed plants and 1/2 green-seed plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If you crossed two heterozygous yellow-seed pea plants (genotypes Aa), the relative frequency of:
A)the a allele in each parent's gametes would be 1/2.
B)the A allele in each parent's gametes would be 1/2.
C)green-seed plants (genotype aa)would be 1/4.
D)homozygous yellow-seed plants (genotype AA)would be 1/4.
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)the a allele in each parent's gametes would be 1/2.
B)the A allele in each parent's gametes would be 1/2.
C)green-seed plants (genotype aa)would be 1/4.
D)homozygous yellow-seed plants (genotype AA)would be 1/4.
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In the F2 generation of a homozygous round (AA) × homozygous wrinkled (aa) cross in peas, three seeds are chosen at random. What is the probability that all three seeds are round?
A)(1/4)3
B)3(1/4)(3/4)2
C)3(1/4)2(3/4)
D)(3/4)3
A)(1/4)3
B)3(1/4)(3/4)2
C)3(1/4)2(3/4)
D)(3/4)3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A Punnett square is merely a graphical way to depict the expression:
A)(1/2 A + 1/2 a).
B)(1/2 A + 1/2 a)2.
C)(1/2 A + 1/2 a)3.
D)(3/4 A + 1/4 a).
A)(1/2 A + 1/2 a).
B)(1/2 A + 1/2 a)2.
C)(1/2 A + 1/2 a)3.
D)(3/4 A + 1/4 a).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Flower color in snapdragons is due to a gene with incomplete dominance: CRCR plants have red flowers, CRCW have pink flowers, and CWCW plants have white flowers. What types and ratios of flower color are expected among the progeny of a cross of pink × white?
A)1 red:2 pink:1 white
B)1 red:1 pink
C)1 pink:1 white
D)all pink
E)all white
A)1 red:2 pink:1 white
B)1 red:1 pink
C)1 pink:1 white
D)all pink
E)all white

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
In meiosis, allele separation at _____ is the chromosomal basis of segregation.
A)prophase
B)metaphase
C)anaphase
D)telophase
A)prophase
B)metaphase
C)anaphase
D)telophase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following processes would result in gametes that violate Mendel's principle of segregation?
A)dominance
B)independent assortment
C)epistasis
D)nondisjunction
A)dominance
B)independent assortment
C)epistasis
D)nondisjunction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



