Deck 11: Cell Division: Variations, Regulation, and Cancer
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/169
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Cell Division: Variations, Regulation, and Cancer
1
Reproduction by mitotic cell division:
A)results in two daughter cells that are genetically identical.
B)is asexual reproduction.
C)persists in mature plant cells for continued growth.
D)continues in mature adult humans to replace damaged and worn-out cells.
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)results in two daughter cells that are genetically identical.
B)is asexual reproduction.
C)persists in mature plant cells for continued growth.
D)continues in mature adult humans to replace damaged and worn-out cells.
E)All of these choices are correct.
E
2
The process of cell division in a prokaryotic cell is called:
A)binary fusion.
B)mitosis.
C)binary fission.
D)cytokinesis.
A)binary fusion.
B)mitosis.
C)binary fission.
D)cytokinesis.
C
3
Given that the correct number of chromosomes is vital to the proper functioning of a cell, which of the statements below is CORRECT if a cell passes from G1 to S phase in the cell cycle?
A)The cell copies its chromosomes and enters G2 or it returns to G1.
B)The cell completes the process of cell division or it dies.
C)The cell divides or it returns to G1 and enters G0.
A)The cell copies its chromosomes and enters G2 or it returns to G1.
B)The cell completes the process of cell division or it dies.
C)The cell divides or it returns to G1 and enters G0.
B
4
Mitosis MOST likely evolved from what process?
A)meiosis
B)the cell cycle
C)cytokinesis
D)binary fission
A)meiosis
B)the cell cycle
C)cytokinesis
D)binary fission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A skin cell in G2 of interphase has _____ as much DNA as it had in G1.
A)half
B)twice
C)exactly
D)one-fourth
E)four times
A)half
B)twice
C)exactly
D)one-fourth
E)four times

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Replication of DNA in a eukaryote occurs during which phase of the cell cycle?
A)M phase
B)G1 phase
C)G2 phase
D)S phase
A)M phase
B)G1 phase
C)G2 phase
D)S phase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A mutation acquired by a bacterium will very likely be inherited by all daughter cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
It is estimated that there are a total of 50-100 trillion cells in the human body. Starting from a fertilized egg, how many cell divisions would be required to produce 50 trillion cells, assuming that every cell divides in every cycle?
A)455 divisions
B)45.5 divisions
C)100 divisions
D)one division per day for nine months
A)455 divisions
B)45.5 divisions
C)100 divisions
D)one division per day for nine months

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is NOT true of mitotic cell division?
A)It occurs in eukaryotes, but not in prokaryotes.
B)It is a highly regulated process.
C)It is a form of asexual reproduction.
D)It is a process that is very important in the life cycle of sexually reproducing organisms.
E)It does not require DNA replication.
A)It occurs in eukaryotes, but not in prokaryotes.
B)It is a highly regulated process.
C)It is a form of asexual reproduction.
D)It is a process that is very important in the life cycle of sexually reproducing organisms.
E)It does not require DNA replication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The CORRECT sequence of steps in the eukaryotic cell cycle is:
A)G1 S phase G2 mitosis cytokinesis.
B)G0 S phase G1 S phase G2 mitosis cytokinesis.
C)G0 S phase G1 G2 cytokinesis mitosis.
D)G0 S phase G1 S phase G2 cytokinesis mitosis.
E)G1 S phase G2 cytokinesis mitosis.
A)G1 S phase G2 mitosis cytokinesis.
B)G0 S phase G1 S phase G2 mitosis cytokinesis.
C)G0 S phase G1 G2 cytokinesis mitosis.
D)G0 S phase G1 S phase G2 cytokinesis mitosis.
E)G1 S phase G2 cytokinesis mitosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following reproduce by binary fission?
A)bacteria
B)archaea
C)chloroplasts
D)mitochondria
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)bacteria
B)archaea
C)chloroplasts
D)mitochondria
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
All of the following happen during mitosis EXCEPT:
A)condensing of chromosomes.
B)synthesis of DNA.
C)formation of the spindle.
D)separation of sister chromatids at the centromeres.
A)condensing of chromosomes.
B)synthesis of DNA.
C)formation of the spindle.
D)separation of sister chromatids at the centromeres.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The division of genetic material in a eukaryotic cell is called:
A)genetic fission.
B)mitosis.
C)cytokinesis.
D)replication.
A)genetic fission.
B)mitosis.
C)cytokinesis.
D)replication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Paramecium is a single-cell eukaryotic organism that can reproduce by mitotic cell division. Prior to the M phase of the cell cycle, which of the following must occur?
A)The cell must replicate its chromosomes.
B)The cell must first be fertilized.
C)The nucleus must divide.
D)Sister chromatids must be separated.
E)The nuclear envelope must disintegrate.
A)The cell must replicate its chromosomes.
B)The cell must first be fertilized.
C)The nucleus must divide.
D)Sister chromatids must be separated.
E)The nuclear envelope must disintegrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The division of the cell's cytoplasm in a eukaryotic cell is known as:
A)cytokinesis.
B)cell fission.
C)mitosis.
D)both cytokinesis and mitosis..
A)cytokinesis.
B)cell fission.
C)mitosis.
D)both cytokinesis and mitosis..

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells reproduce by mitotic cell division. Regardless of the type of cell, all cells must _____ before they divide.
A)make a copy of their genetic information
B)separate sister chromatids from one another
C)complete mitosis
D)reconstruct their nucleus
A)make a copy of their genetic information
B)separate sister chromatids from one another
C)complete mitosis
D)reconstruct their nucleus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is circled in this electron micrograph? 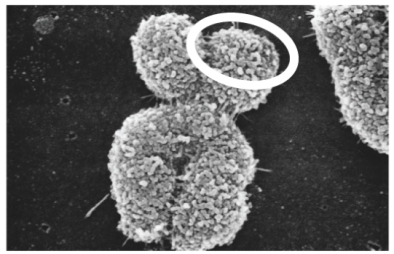 Photo credit: Biophoto Associates/Science Source
Photo credit: Biophoto Associates/Science Source
A)one double-stranded DNA molecule
B)one single strand of a DNA molecule
C)two double-stranded DNA molecules
 Photo credit: Biophoto Associates/Science Source
Photo credit: Biophoto Associates/Science SourceA)one double-stranded DNA molecule
B)one single strand of a DNA molecule
C)two double-stranded DNA molecules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The genetic information of daughter cells is always exactly the same as the genetic information of the parent in binary fission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following steps in prokaryotic binary fission is CORRECT?
A)DNA is replicated bidirectionally from a single point on the circular chromosome.
B)The two replicated chromosomes remain attached to the plasma membrane.
C)The cell continues to grow outward symmetrically, separating the two chromosomes.
D)Cell wall material is laid down at the midpoint to separate the two daughter cells.
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)DNA is replicated bidirectionally from a single point on the circular chromosome.
B)The two replicated chromosomes remain attached to the plasma membrane.
C)The cell continues to grow outward symmetrically, separating the two chromosomes.
D)Cell wall material is laid down at the midpoint to separate the two daughter cells.
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is NOT true about the eukaryotic cell cycle?
A)There are two stages to the cell cycle: M phase and interphase.
B)The M phase consists of two events: mitosis and cytokinesis.
C)Interphase is typically the shortest of the two stages of the cell cycle.
D)There are three phases of interphase: the S phase and two gap phases.
E)Some cells pause between M phase and S phase for more than a year.
A)There are two stages to the cell cycle: M phase and interphase.
B)The M phase consists of two events: mitosis and cytokinesis.
C)Interphase is typically the shortest of the two stages of the cell cycle.
D)There are three phases of interphase: the S phase and two gap phases.
E)Some cells pause between M phase and S phase for more than a year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A cell that is not actively dividing is in what phase of the cell cycle?
A)G1
B)G0
C)G1'
D)G2
A)G1
B)G0
C)G1'
D)G2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In a dividing plant cell, a phragmoplast structure forms during telophase that directs vesicles carrying cell wall components to the middle of the cell, assembling a new cell wall called the cell plate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is circled in this electron micrograph? 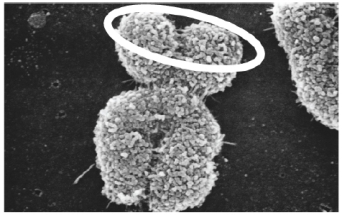 Photo credit: Biophoto Associates/Science Source
Photo credit: Biophoto Associates/Science Source
A)one double-stranded DNA molecule
B)one single strand of a DNA molecule
C)two double-stranded DNA molecules
 Photo credit: Biophoto Associates/Science Source
Photo credit: Biophoto Associates/Science SourceA)one double-stranded DNA molecule
B)one single strand of a DNA molecule
C)two double-stranded DNA molecules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What would happen to the daughter cells if the G2 phase of the parent cell is shortened?
A)The cells would be smaller than normal.
B)The cells would be missing chromosomes.
C)The cells would not undergo cytokinesis.
D)The cells would be larger than normal.
A)The cells would be smaller than normal.
B)The cells would be missing chromosomes.
C)The cells would not undergo cytokinesis.
D)The cells would be larger than normal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Why would a compound that interferes with bacterial cell wall synthesis be useful for treating a bacterial infection?
A)It would prevent the cells from becoming larger.
B)It would prevent replication of DNA.
C)It would limit the spread of the infection through cell division.
D)It would prevent replication of DNA, and it would limit the spread of the infection.
A)It would prevent the cells from becoming larger.
B)It would prevent replication of DNA.
C)It would limit the spread of the infection through cell division.
D)It would prevent replication of DNA, and it would limit the spread of the infection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
How many copies of each gene are present in human skin cells at G2 of interphase?
A)2
B)4
C)6
D)8
A)2
B)4
C)6
D)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding binary fission?
A)Proteins only anchor the original circular genome to the plasma membrane; the copy produced by DNA replication is free floating.
B)In binary fission, cell division is typically asymmetrical, with one daughter cell appearing much smaller than the other.
C)Tubulin, rather than FtsZ, is responsible for cell division during binary fission.
D)DNA replication during binary fission is a bidirectional process, occurring in opposite directions.
E)None of the other answer options is correct.
A)Proteins only anchor the original circular genome to the plasma membrane; the copy produced by DNA replication is free floating.
B)In binary fission, cell division is typically asymmetrical, with one daughter cell appearing much smaller than the other.
C)Tubulin, rather than FtsZ, is responsible for cell division during binary fission.
D)DNA replication during binary fission is a bidirectional process, occurring in opposite directions.
E)None of the other answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A researcher is studying a population of cells with two major phases. The first phase is relatively short (it lasts approximately 1 hour), whereas the second stage is much longer (it lasts approximately 12 hours) and is characterized by an increase in the DNA content of cells. This second stage is MOST likely:
A)mitosis.
B)cytokinesis.
C)interphase.
D)G0.
A)mitosis.
B)cytokinesis.
C)interphase.
D)G0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What would happen during cell division if the cell is deficient in actin?
A)The sister chromatids would not separate.
B)The mitotic spindle would not form.
C)The cell would not divide.
D)The centromeres would not split.
A)The sister chromatids would not separate.
B)The mitotic spindle would not form.
C)The cell would not divide.
D)The centromeres would not split.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The CORRECT sequence of steps in the M phase of the cell cycle is:
A)prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, nuclear division.
B)prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis.
C)prophase, metaphase, prometaphase, anaphase, nuclear division, telophase.
D)prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis, nuclear division.
A)prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, nuclear division.
B)prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis.
C)prophase, metaphase, prometaphase, anaphase, nuclear division, telophase.
D)prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis, nuclear division.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What cellular process(es) is/are responsible for the increase in protein content associated with the gap phases of the cell cycle?
A)gene expression
B)glycolysis
C)protein synthesis
D)both gene expression and protein synthesis
A)gene expression
B)glycolysis
C)protein synthesis
D)both gene expression and protein synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the role of the protein FtsZ?
A)It forms a ring at the site of constriction.
B)It is involved in the attachment of DNA to the plasma membrane.
C)It is responsible for the replication of DNA.
D)It forms the new cell wall between daughter cells.
A)It forms a ring at the site of constriction.
B)It is involved in the attachment of DNA to the plasma membrane.
C)It is responsible for the replication of DNA.
D)It forms the new cell wall between daughter cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The prokaryotic protein FtsZ is evolutionarily related to eukaryotic tubulin. What does this mean?
A)The gene sequence for FtsZ is similar to tubulin.
B)The amino acid sequence for FtsZ is similar to tubulin.
C)The overall protein structure of FtsZ is similar to tubulin.
D)The two proteins evolved from a common ancestral protein.
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)The gene sequence for FtsZ is similar to tubulin.
B)The amino acid sequence for FtsZ is similar to tubulin.
C)The overall protein structure of FtsZ is similar to tubulin.
D)The two proteins evolved from a common ancestral protein.
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Evidence exists (especially in dinoflagellates) that mitosis evolved from binary fission. For example, in certain eukaryotic cells during mitosis, DNA is attached to the membrane of the nucleus (much like a circular chromosome of a bacterium is attached to the plasma membrane).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
How many copies of each gene are present in human skin cells at G1 of interphase?
A)2
B)4
C)6
D)8
A)2
B)4
C)6
D)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In what way is cytokinesis in plant cells similar to binary fission in a bacterium?
A)Cell wall material is deposited to separate the daughter cells.
B)A ring of actin filaments constricts the plasma membrane between the two nuclei to separate the daughter cells.
C)A microtubulin-like structure constricts the plasma membrane between the two nuclei to separate the daughter cells.
D)A motor protein slides microtubules in a contractile ring at the plasma membrane between the two nuclei to separate the daughter cells.
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)Cell wall material is deposited to separate the daughter cells.
B)A ring of actin filaments constricts the plasma membrane between the two nuclei to separate the daughter cells.
C)A microtubulin-like structure constricts the plasma membrane between the two nuclei to separate the daughter cells.
D)A motor protein slides microtubules in a contractile ring at the plasma membrane between the two nuclei to separate the daughter cells.
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What would happen if a defect in S phase occurred during cell division?
A)There could be too few chromosomes.
B)There could be too many chromosomes.
C)There could be a lack of cytoplasm.
D)All organelles may not be duplicated.
A)There could be too few chromosomes.
B)There could be too many chromosomes.
C)There could be a lack of cytoplasm.
D)All organelles may not be duplicated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Taxol is an anti-cancer drug that prevents uncontrolled cell proliferation by stabilizing microtubules, which causes arrest of the cell cycle. If dividing cells are treated with Taxol, at what stage of the cell cycle would you predict the arrest would occur?
A)prophase
B)metaphase
C)anaphase
D)telophase
E)G1 of interphase
A)prophase
B)metaphase
C)anaphase
D)telophase
E)G1 of interphase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is NOT a step in the process of binary fission?
A)replication of DNA
B)formation of a new cell wall
C)rearrangement of the microtubule cytoskeleton
D)elongation of the cell
A)replication of DNA
B)formation of a new cell wall
C)rearrangement of the microtubule cytoskeleton
D)elongation of the cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Muscle cells in the mammalian heart are multinucleate, meaning that multiple nuclei are present in the cytoplasm of a large cell. Predict what is different about the cell cycle in a muscle cell.
A)The G1 and G2 phases are extended.
B)Cytokinesis does not occur.
C)S phase happens twice.
D)M phase is inhibited.
A)The G1 and G2 phases are extended.
B)Cytokinesis does not occur.
C)S phase happens twice.
D)M phase is inhibited.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The centrosome is:
A)a region of the chromosome where sister chromatids are attached to each other.
B)a region of the chromosome where kinetochores attach.
C)a region of the chromosome where microtubules attach to chromosomes during mitosis.
D)the microtubule organizing center for the mitotic spindle.
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)a region of the chromosome where sister chromatids are attached to each other.
B)a region of the chromosome where kinetochores attach.
C)a region of the chromosome where microtubules attach to chromosomes during mitosis.
D)the microtubule organizing center for the mitotic spindle.
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Sister chromatids are BEST described as two DNA molecules that have:
A)the same genes in the same order but having different alleles.
B)the same alleles of the same genes in a different order.
C)different genes in the same order and possibly having different alleles of some genes.
D)different alleles of the same genes arranged in a different order.
E)virtually identical sequences of nucleotides.
A)the same genes in the same order but having different alleles.
B)the same alleles of the same genes in a different order.
C)different genes in the same order and possibly having different alleles of some genes.
D)different alleles of the same genes arranged in a different order.
E)virtually identical sequences of nucleotides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In which phase of mitosis does the mitotic spindle form?
A)prophase
B)metaphase
C)anaphase
D)telophase
A)prophase
B)metaphase
C)anaphase
D)telophase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In which phase of mitosis do sister chromatids separate?
A)prophase
B)metaphase
C)anaphase
D)telophase
A)prophase
B)metaphase
C)anaphase
D)telophase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
When homologous chromosomes are aligned with each other and arranged as pairs in order of decreasing size, the resulting portrait is referred to as a _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
How many chromosome pairs are there in a normal human genome?
A)22
B)23
C)46
D)64
A)22
B)23
C)46
D)64

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What is the function of histone proteins?
A)to package DNA in eukaryotic chromosomes
B)to connect chromosomes to the mitotic spindle
C)to organize the microtubules that make up the spindle
D)to attach sister chromatids together
A)to package DNA in eukaryotic chromosomes
B)to connect chromosomes to the mitotic spindle
C)to organize the microtubules that make up the spindle
D)to attach sister chromatids together

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Asexual reproduction occurs in:
A)unicellular eukaryotes.
B)animal cells.
C)plant cells.
D)bacterial cells.
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)unicellular eukaryotes.
B)animal cells.
C)plant cells.
D)bacterial cells.
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
When in the cell cycle would you find sister chromatids?
A)G1
B)S
C)G2
D)S and G2
A)G1
B)S
C)G2
D)S and G2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In which phase of mitosis do chromosomes line up at the middle of the cell?
A)prophase
B)metaphase
C)anaphase
D)telophase
A)prophase
B)metaphase
C)anaphase
D)telophase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In which phase of mitosis do chromosomes condense?
A)prophase
B)metaphase
C)anaphase
D)telophase
A)prophase
B)metaphase
C)anaphase
D)telophase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A human cell with a total of 23 chromosomes is:
A)haploid.
B)diploid.
C)polyploid.
D)aneuploid.
A)haploid.
B)diploid.
C)polyploid.
D)aneuploid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Is there a difference in genetic material between sister chromatids? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following statements is NOT true about sister chromatids?
A)They are identical or nearly identical DNA sequences.
B)They are attached to each other at the centromere.
C)They are formed in the S phase of the cell cycle when the chromosome undergoes replication.
D)They are formed when the prokaryotic circular chromosome attaches at the plasma membrane.
E)They are the same as homologous chromosomes.
A)They are identical or nearly identical DNA sequences.
B)They are attached to each other at the centromere.
C)They are formed in the S phase of the cell cycle when the chromosome undergoes replication.
D)They are formed when the prokaryotic circular chromosome attaches at the plasma membrane.
E)They are the same as homologous chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Mitotic cell division is considered asexual because:
A)the daughter cells receive DNA from one parent cell.
B)this form of cell division is most similar to binary fission.
C)the daughter cells are genetically identical.
D)the daughter cells receive DNA from one parent cell, and the daughter cells are genetically identical.
A)the daughter cells receive DNA from one parent cell.
B)this form of cell division is most similar to binary fission.
C)the daughter cells are genetically identical.
D)the daughter cells receive DNA from one parent cell, and the daughter cells are genetically identical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What is the function of the centromere?
A)to attach the DNA to the plasma membrane
B)to attach the chromosome to the spindle
C)to attach the sister chromatids to each other
D)to organize the microtubules to form a spindle
A)to attach the DNA to the plasma membrane
B)to attach the chromosome to the spindle
C)to attach the sister chromatids to each other
D)to organize the microtubules to form a spindle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Colchicine is a drug that is used in plant breeding to create polyploids. It blocks the assembly of microtubules. If dividing cells are treated with colchicine, at what stage of mitosis would you predict the arrest would occur?
A)prophase
B)metaphase
C)late anaphase
D)telophase
E)G1 of interphase
A)prophase
B)metaphase
C)late anaphase
D)telophase
E)G1 of interphase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In which phase of mitosis does the nuclear envelope reform?
A)prophase
B)metaphase
C)anaphase
D)telophase
A)prophase
B)metaphase
C)anaphase
D)telophase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In which phase of mitosis do spindle microtubules shorten?
A)prophase
B)metaphase
C)anaphase
D)telophase
A)prophase
B)metaphase
C)anaphase
D)telophase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A phragmoplast functions to:
A)stimulate the growth of the microtubule spindle.
B)anchor microtubules to sister chromatids.
C)break down the nuclear envelope.
D)form a new cell wall.
A)stimulate the growth of the microtubule spindle.
B)anchor microtubules to sister chromatids.
C)break down the nuclear envelope.
D)form a new cell wall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In a diploid individual, one chromosome carries A and B genes, and the homologous chromosome carries different forms (alleles) of these same genes, a and b. If there is a single crossover between these two genes involving non-sister chromatids during metaphase I of meiosis, the resulting four gametes are:
A)AB, AB, ab, ab.
B)AB, ab, AB, ab.
C)AaBb, AaBb, AaBb, AaBb.
D)AB, Ab, aB, ab.
E)Ab, Ab, aB, aB.
A)AB, AB, ab, ab.
B)AB, ab, AB, ab.
C)AaBb, AaBb, AaBb, AaBb.
D)AB, Ab, aB, ab.
E)Ab, Ab, aB, aB.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Sister chromatids are separated during:
A)mitosis.
B)meiosis I and mitosis.
C)meiosis II and mitosis.
D)meiosis I.
E)meiosis II.
A)mitosis.
B)meiosis I and mitosis.
C)meiosis II and mitosis.
D)meiosis I.
E)meiosis II.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The FoxP2 gene is thought to be involved in language in humans. At prophase I, how many copies of the FoxP2 gene are present in a cell? Keep in mind that humans are diploid.
A)two copies, one on each homologous chromosome
B)four copies, one on each sister chromatid in a pair of homologous chromosomes
C)eight copies, one on each sister chromatid in a pair of homologous chromosomes
D)eight copies, one on each strand of each chromatid per homologous pair
A)two copies, one on each homologous chromosome
B)four copies, one on each sister chromatid in a pair of homologous chromosomes
C)eight copies, one on each sister chromatid in a pair of homologous chromosomes
D)eight copies, one on each strand of each chromatid per homologous pair

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Consider a diploid organism with a haploid complement of four chromosomes. At prophase I, how many total chromosomes will be present in a cell?
A)4, one complete set of chromosomes
B)8, four pairs of homologous chromosomes
C)12, four pairs of homologous chromosomes and their haploid complement
D)16, four pairs of homologous chromosomes and two sister chromatids per chromosome
A)4, one complete set of chromosomes
B)8, four pairs of homologous chromosomes
C)12, four pairs of homologous chromosomes and their haploid complement
D)16, four pairs of homologous chromosomes and two sister chromatids per chromosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
During meiosis, genetic variability is introduced during which of the following phases?
A)anaphase II
B)metaphase I
C)prophase I
D)prophase II
E)prometaphase I
A)anaphase II
B)metaphase I
C)prophase I
D)prophase II
E)prometaphase I

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
At the start of mitosis, how many centromeres are present in a human cell?
A)12
B)23
C)46
D)92
A)12
B)23
C)46
D)92

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What protein forms the contractile ring during cytokinesis in animal cells?
A)kinesin
B)actin
C)dynein
D)DNA polymerase
A)kinesin
B)actin
C)dynein
D)DNA polymerase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In meiosis, recombination occurs:
A)during prophase I and II and involves exchange of chromosome fragments between all four chromatids.
B)only during prophase I and involves exchange between chromatids of homologous chromosomes.
C)only during prophase I and involves exchange of chromosome fragments between sister chromatids.
D)during prophase I and II and involves exchange of chromosome fragments between sister chromatids.
A)during prophase I and II and involves exchange of chromosome fragments between all four chromatids.
B)only during prophase I and involves exchange between chromatids of homologous chromosomes.
C)only during prophase I and involves exchange of chromosome fragments between sister chromatids.
D)during prophase I and II and involves exchange of chromosome fragments between sister chromatids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
At the start of mitosis, how many sister chromatids are present in a human cell?
A)23
B)92
C)46
D)12
A)23
B)92
C)46
D)12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A homologous chromosome pair is best described as two chromosomes that have:
A)the same genes in the same order but possibly with different alleles of some of the genes.
B)the same alleles of the same genes in the same order.
C)the same genes possibly arranged in a different order with potentially different alleles of some of the genes.
D)different alleles of the same genes arranged in a different order.
E)identical sequences of nucleotides.
A)the same genes in the same order but possibly with different alleles of some of the genes.
B)the same alleles of the same genes in the same order.
C)the same genes possibly arranged in a different order with potentially different alleles of some of the genes.
D)different alleles of the same genes arranged in a different order.
E)identical sequences of nucleotides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The epithelial cells in the skin of an animal have 24 chromosomes. How many chromosomes are present in the gametes of this animal?
A)6
B)12
C)24
D)48
A)6
B)12
C)24
D)48

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What would happen if a chromosome only connected to the mitotic spindle at one of its kinetochores?
A)One of the daughter cells would have an extra copy of that chromosome.
B)The sister chromatids would not separate.
C)The chromosome would not line up properly at metaphase.
D)All of these choices are correct.
A)One of the daughter cells would have an extra copy of that chromosome.
B)The sister chromatids would not separate.
C)The chromosome would not line up properly at metaphase.
D)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Why don't plant cells use a contractile ring to divide their daughter cells?
A)Plant cells don't have an actin cytoskeleton.
B)Plant cells don't form daughter cells.
C)A contractile ring can't "pinch" a cell wall.
D)Plant cells don't have plasma membranes.
A)Plant cells don't have an actin cytoskeleton.
B)Plant cells don't form daughter cells.
C)A contractile ring can't "pinch" a cell wall.
D)Plant cells don't have plasma membranes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Why are the X and Y chromosomes NOT considered homologous?
A)they come from different parents
B)they do not carry the same set of genes
C)mammalian males carry two very different chromosomes
D)they do not carry the same set of genes, and mammalian males carry two very different sex chromosomes
A)they come from different parents
B)they do not carry the same set of genes
C)mammalian males carry two very different chromosomes
D)they do not carry the same set of genes, and mammalian males carry two very different sex chromosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A female Komodo dragon is diploid. She produces diploid offspring that are genetically identical to each other and to her. In this case, reproduction requires:
A)mitosis.
B)meiosis.
C)mitosis followed by meiosis.
D)meiosis followed by mitosis.
E)None of the other answer options is correct.
A)mitosis.
B)meiosis.
C)mitosis followed by meiosis.
D)meiosis followed by mitosis.
E)None of the other answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following has the MOST similarity in nucleotide sequence?
A)homologous chromosomes
B)nonhomologous chromosomes
C)sister chromatids
D)complementary strands of DNA
E)maternal and paternal copies of the same chromosome
A)homologous chromosomes
B)nonhomologous chromosomes
C)sister chromatids
D)complementary strands of DNA
E)maternal and paternal copies of the same chromosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The two strands in a molecule of DNA are:
A)exact copies of each other.
B)homologous.
C)complementary.
D)sister chromatids.
E)diploid.
A)exact copies of each other.
B)homologous.
C)complementary.
D)sister chromatids.
E)diploid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The microtubules that form the mitotic spindle extend out from the centrosome. Where would you expect to find the plus (fast assembling) end of a spindle microtubule?
A)at the centrosome
B)away from the centrosome
C)at the kinetochore
D)away from the centrosome, at the kinetochore
A)at the centrosome
B)away from the centrosome
C)at the kinetochore
D)away from the centrosome, at the kinetochore

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Look carefully at the image of the human karyotype shown in Figure 11.3. What is the significance of the small differences between homologous chromosomes? 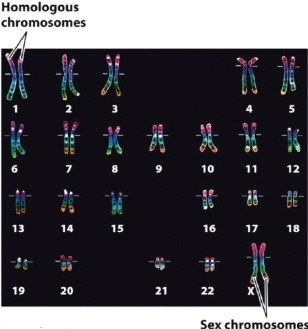 Photo credit: ISM/Phototake.
Photo credit: ISM/Phototake.
A)Each homologous chromosome in a pair is from a different parent.
B)Some of this person's DNA is mutated, possibly causing disease.
C)Chromosomes may not be completely replicated during S phase.
D)The differences are a result of the way the material was prepared.
 Photo credit: ISM/Phototake.
Photo credit: ISM/Phototake.A)Each homologous chromosome in a pair is from a different parent.
B)Some of this person's DNA is mutated, possibly causing disease.
C)Chromosomes may not be completely replicated during S phase.
D)The differences are a result of the way the material was prepared.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The random alignment of maternal and paternal homologous chromosomes during metaphase I is one of the ways genetic variability among gametes comes about. For example, it is possible for an organism with 4 pairs of homologous chromosomes to produce gametes with up to 16 different combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes (24 = 16). In the case of humans with 23 pairs of chromosomes, there are over 8 million possible combinations. How many possible combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes are possible in the gametes of an organism with 8 chromosomes?
A)16
B)64
C)256
D)512
E)1024
A)16
B)64
C)256
D)512
E)1024

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



