Deck 21: Information for Capital Expenditure Decisions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/125
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: Information for Capital Expenditure Decisions
1
A machine costs $25 000. It is expected to generate annual revenue of $8000 and annual expenses of $2000 each year for five years. The required rate of return is 12 per cent. What is the net present value of the machine?
A) $21 630
B) $28 840
C) ($3370)
D) $3840
A) $21 630
B) $28 840
C) ($3370)
D) $3840
C
2
Capital budgeting is a tool required for:
A) long-term decisions.
B) higher sales and greater profits.
C) adequately financing various short- and long-term aspects of an organisation.
D) adequate capital investment in areas where it is least needed.
A) long-term decisions.
B) higher sales and greater profits.
C) adequately financing various short- and long-term aspects of an organisation.
D) adequate capital investment in areas where it is least needed.
A
3
The ___________ the discount rate used in a net present value analysis, the ___________ the present value of all future cash flows.
A) lower, higher
B) lower, lower
C) higher, lower
D) EITHER lower, higher OR higher, lower
A) lower, higher
B) lower, lower
C) higher, lower
D) EITHER lower, higher OR higher, lower
D
4
A project's time-adjusted rate of return is the actual economic return earned by the asset over its life. It is also known as the:
A) discounted cash flow.
B) net present value.
C) annuity discount factor.
D) internal rate of return.
A) discounted cash flow.
B) net present value.
C) annuity discount factor.
D) internal rate of return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The manager of George Pty Ltd is planning to purchase equipment costing $5000. The equipment will reduce operating costs by approximately $2000 per year over its three-year life. The manager has decided to purchase the equipment because over the three years the company will save $1000. The major problem with the manager's analysis is that:
A) the manager does not consider the time value of money.
B) the manager used the internal rate of return rather than the present value.
C) the manager did not use the annuity method.
D) the amount to be saved is only an approximation.
A) the manager does not consider the time value of money.
B) the manager used the internal rate of return rather than the present value.
C) the manager did not use the annuity method.
D) the amount to be saved is only an approximation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
How much money must be invested today to have $25 000 at the end of four years, if the rate of return is 20 per cent?
A) $17 075
B) $19 925
C) $22 325
D) None of the given answers
A) $17 075
B) $19 925
C) $22 325
D) None of the given answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Capital budgeting decisions involve decisions about:
A) emergency situations.
B) future cash inflows and cash outflows.
C) short-run planning situations.
D) cash inflows and outflows in current years.
A) emergency situations.
B) future cash inflows and cash outflows.
C) short-run planning situations.
D) cash inflows and outflows in current years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Investment project E has equal annual cash flows over its lifetime. The present value of the cash inflows from project E:
A) can be measured using the present value of an annuity.
B) must be measured year-by-year using a present value table.
C) can be measured using the future value of an annuity.
D) must be measured year-by-year using a future value table.
A) can be measured using the present value of an annuity.
B) must be measured year-by-year using a present value table.
C) can be measured using the future value of an annuity.
D) must be measured year-by-year using a future value table.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
You estimate that it will take five years to complete your university education. Your parents want to invest enough money today at 12 per cent to enable you to withdraw $5000 at the end of each year for the next five years with nothing left at the end of the five-year period. How much money do they need today?
A) $8810
B) $18 025
C) $25 000
D) $31 765
A) $8810
B) $18 025
C) $25 000
D) $31 765

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When undertaking a net present value analysis, the first step in the process would be to determine:
A) the interest rate at the end of the proposed investment period.
B) the internal rate of return on comparable projects in the past.
C) the return on assets for the organisation.
D) the cash flows during each year of the proposed investment.
A) the interest rate at the end of the proposed investment period.
B) the internal rate of return on comparable projects in the past.
C) the return on assets for the organisation.
D) the cash flows during each year of the proposed investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A series of equivalent cash flows is called an:
A) accretion.
B) annuity.
C) accrual.
D) accumulation.
A) accretion.
B) annuity.
C) accrual.
D) accumulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Magic Pty Ltd owes Jordan Pty Ltd money for the purchase of equipment. Jordan Pty Ltd has given Magic Pty Ltd three payment options:
Option 1: Immediate payment of $38 000 with no further payment.
Option 2: Three annual payments of $15 000 made at the end of each of the next three years.
Option 3: A single payment of $48 000 made at the end of the three years.
Magic Pty Ltd uses a hurdle rate of 10 per cent for investment decisions. Which option should Magic choose and what is the present value of that option?
A) Option 1 $38 000
B) Option 2 $37 305
C) Option 3 $34 164
D) Option 3 $36 048
Option 1: Immediate payment of $38 000 with no further payment.
Option 2: Three annual payments of $15 000 made at the end of each of the next three years.
Option 3: A single payment of $48 000 made at the end of the three years.
Magic Pty Ltd uses a hurdle rate of 10 per cent for investment decisions. Which option should Magic choose and what is the present value of that option?
A) Option 1 $38 000
B) Option 2 $37 305
C) Option 3 $34 164
D) Option 3 $36 048

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The use of future value to calculate the present value is called:
A) compounding.
B) the annuity method.
C) discounting.
D) present value approach.
A) compounding.
B) the annuity method.
C) discounting.
D) present value approach.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What will $5000 invested at 10 per cent today accumulate to at the end of five years?
A) $8810
B) $5500
C) $8055
D) $30 525
A) $8810
B) $5500
C) $8055
D) $30 525

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The internal rate of return for a proposed investment can be calculated:
A) if the cash flow table is identical to future values of a series of cash flows.
B) if the future value of a series of cash flows can be arrived at by the annuity accumulation factor.
C) by finding a discount rate that yields a zero net present value for a proposed investment.
D) by finding a discount rate that yields a positive net present value for a proposed investment.
A) if the cash flow table is identical to future values of a series of cash flows.
B) if the future value of a series of cash flows can be arrived at by the annuity accumulation factor.
C) by finding a discount rate that yields a zero net present value for a proposed investment.
D) by finding a discount rate that yields a positive net present value for a proposed investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The main concept of time value of money is:
A) that cash flows received in the distant future are not as valuable as cash flows received in the near future.
B) the recognition of all relevant costs in absolute dollars.
C) that cash flows received in different years should be treated as equal.
D) that cash payments made in the future have the same value today.
A) that cash flows received in the distant future are not as valuable as cash flows received in the near future.
B) the recognition of all relevant costs in absolute dollars.
C) that cash flows received in different years should be treated as equal.
D) that cash payments made in the future have the same value today.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Calculate the future value of money from the following: 
A) $150.00
B) $133.10
C) $161.05
D) $155.65

A) $150.00
B) $133.10
C) $161.05
D) $155.65

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
According to the net present value method, if the present value of cost savings exceeds the acquisition cost of a new machine:
A) the old machine should be retained.
B) the new machine should be purchased.
C) the old machine should be sold off without adding the new machine.
D) the old machine should be scrapped.
A) the old machine should be retained.
B) the new machine should be purchased.
C) the old machine should be sold off without adding the new machine.
D) the old machine should be scrapped.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements is/are true concerning the time value of money?
A) Money to be received seven years from now has a lower present value than money to be received in three years.
B) Money received seven years from now will have a lower present value if a higher discount rate is used.
C) Money received seven years from now will have a greater present value if a higher discount rate is used.
D) Money to be received seven years from now has a lower present value than money to be received in three years AND money received seven years from now will have a lower present value if a higher discount rate is used.
A) Money to be received seven years from now has a lower present value than money to be received in three years.
B) Money received seven years from now will have a lower present value if a higher discount rate is used.
C) Money received seven years from now will have a greater present value if a higher discount rate is used.
D) Money to be received seven years from now has a lower present value than money to be received in three years AND money received seven years from now will have a lower present value if a higher discount rate is used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If $2000 is invested at 10 per cent at the start of every year for three years, how much will you have accumulated at the end of the three years?
A) $6620
B) $6340
C) $6600
D) $6748
A) $6620
B) $6340
C) $6600
D) $6748

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The accounting rate of return equals:
A) (average incremental revenue - average incremental expenses including depreciation) / average investment.
B) (average incremental revenue - average investment) / average incremental expenses.
C) (average investment - average incremental income) / average investment.
D) (average investment - average incremental income) / average incremental income.
A) (average incremental revenue - average incremental expenses including depreciation) / average investment.
B) (average incremental revenue - average investment) / average incremental expenses.
C) (average investment - average incremental income) / average investment.
D) (average investment - average incremental income) / average incremental income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In which technique is it necessary to formulate scenarios?
A) Incremental analysis
B) Payback method
C) Real-options analysis
D) Accounting rate of return
A) Incremental analysis
B) Payback method
C) Real-options analysis
D) Accounting rate of return

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following statements about the accounting rate of return method is/are correct?
I) It is a simple way of screening investment proposals.
Ii) It is used by some managers because they believe this method parallels financial accounting statements.
Iii) It is more accurate than the payback method because it considers the time value of money.
A) ii and iii
B) iii
C) i and ii
D) All of the given answers
I) It is a simple way of screening investment proposals.
Ii) It is used by some managers because they believe this method parallels financial accounting statements.
Iii) It is more accurate than the payback method because it considers the time value of money.
A) ii and iii
B) iii
C) i and ii
D) All of the given answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The payback period is defined as:
A) initial investment / annual cash inflow.
B) annual cash inflow / initial investment.
C) initial investment / useful life of investment.
D) initial investment / present value of the cash flows, exclusive of initial investment.
A) initial investment / annual cash inflow.
B) annual cash inflow / initial investment.
C) initial investment / useful life of investment.
D) initial investment / present value of the cash flows, exclusive of initial investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The advantage(s) of the payback method of evaluating investment proposals is/are:
I) it recognises the time value of money.
Ii) it is easy to calculate and understand.
Iii) it recognises cash flows beyond the payback period.
Which of the above statements is/are true?
A) i and ii
B) ii and iii
C) ii
D) All of the given answers
I) it recognises the time value of money.
Ii) it is easy to calculate and understand.
Iii) it recognises cash flows beyond the payback period.
Which of the above statements is/are true?
A) i and ii
B) ii and iii
C) ii
D) All of the given answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The mayor of Smalltown, Western Australia, is considering the purchase of a computer system to automate the city's rate collections. The system costs $75 000 and has an estimated life of five years. The mayor estimates the following savings will result if the system is purchased. 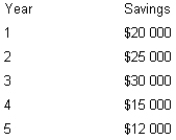
If Smalltown uses a 10 per cent discount rate for capital budgeting decisions, what is the net present value of the computer system?
A) $79 057
B) $11 658
C) $4057
D) $63 342
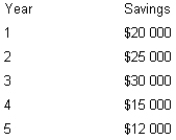
If Smalltown uses a 10 per cent discount rate for capital budgeting decisions, what is the net present value of the computer system?
A) $79 057
B) $11 658
C) $4057
D) $63 342

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The accounting rate of return method focuses on:
A) total accounting profit, which is based on accrual accounting procedures.
B) the incremental accounting profit that results from a project.
C) cash inflows from the project.
D) tax savings from a project.
A) total accounting profit, which is based on accrual accounting procedures.
B) the incremental accounting profit that results from a project.
C) cash inflows from the project.
D) tax savings from a project.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A hurdle rate is generally based on an estimate of the ___________________ of acquiring capital.
A) weighted average cost
B) average cost
C) total cost
D) investment opportunity rate
A) weighted average cost
B) average cost
C) total cost
D) investment opportunity rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A piece of equipment costs $24 000. It is expected to generate $7500 of annual cash revenues and $1500 of annual cash expenses. The disposal value at the end of the estimated 10-year life is $2000. What is the payback period?
A) 3.20 years
B) 6.67 years
C) 3.67 years
D) 4.00 years
A) 3.20 years
B) 6.67 years
C) 3.67 years
D) 4.00 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Cubbies Pty Ltd is considering the purchase of a new machine to replace an old machine. Selected cost data pertaining to the two machines is provided below. 
At the end of four years, the company plans to discontinue the product line for which the machines are used. Income taxes can be ignored. Calculate the net present value of the new machine, if Cubbies Pty Ltd's hurdle rate is 14 per cent.
A) ($903)
B) ($4097)
C) ($87)
D) ($2913)

At the end of four years, the company plans to discontinue the product line for which the machines are used. Income taxes can be ignored. Calculate the net present value of the new machine, if Cubbies Pty Ltd's hurdle rate is 14 per cent.
A) ($903)
B) ($4097)
C) ($87)
D) ($2913)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Both the net present value method and the internal rate of return method focus on:
A) periodic depreciation charges.
B) cash flows.
C) annuity discount factors.
D) total acquisition costs.
A) periodic depreciation charges.
B) cash flows.
C) annuity discount factors.
D) total acquisition costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The mayor of Smalltown, Western Australia, is considering the purchase of a computer system to automate the city's rate collections. The system costs $75 000 and has an estimated life of five years. The mayor estimates the following savings will result if the system is purchased. 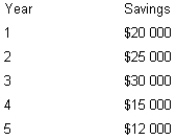
If Smalltown uses a 10 per cent discount rate for capital budgeting decisions, what can be said about the internal rate of return (IRR) if the net present value at 12 per cent is positive?
A) The IRR is greater than 12 per cent.
B) The IRR is between 10 per cent and 12 per cent.
C) The IRR is less than 10 per cent.
D) Insufficient information to determine.
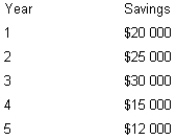
If Smalltown uses a 10 per cent discount rate for capital budgeting decisions, what can be said about the internal rate of return (IRR) if the net present value at 12 per cent is positive?
A) The IRR is greater than 12 per cent.
B) The IRR is between 10 per cent and 12 per cent.
C) The IRR is less than 10 per cent.
D) Insufficient information to determine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
LB Pty Ltd recently invested $25 000 in equipment with an estimated life of five years. The manager projects the following cash flows. 
What is the payback period?
A) 2.00 years
B) 2.50 years
C) 3.50 years
D) 4.00 years

What is the payback period?
A) 2.00 years
B) 2.50 years
C) 3.50 years
D) 4.00 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Bravo Pty Ltd is considering the addition of a new product line. The new product will require an initial capital outlay of $70 000 and is expected to have a five-year life cycle. The manager estimates that because of the new product, cash flow will increase over the next five years by the following amounts. 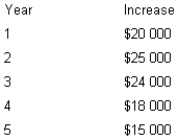
If Bravo's hurdle rate is 14 per cent, calculate the net present value of the new product line. (Income taxes can be ignored.)
A) $0
B) $71 406
C) $68 275
D) $1406
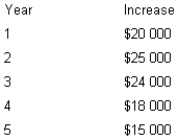
If Bravo's hurdle rate is 14 per cent, calculate the net present value of the new product line. (Income taxes can be ignored.)
A) $0
B) $71 406
C) $68 275
D) $1406

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following statements about capital budgeting post-audits is/are true?
I) The post-audit can be used to detect desirable projects that were rejected.
Ii) The post-audit can be used to detect undesirable projects that were accepted.
Iii) A post-audit may reveal shortcomings in the cash-flow projections process.
A) i and ii
B) ii and iii
C) i
D) All of the given answers
I) The post-audit can be used to detect desirable projects that were rejected.
Ii) The post-audit can be used to detect undesirable projects that were accepted.
Iii) A post-audit may reveal shortcomings in the cash-flow projections process.
A) i and ii
B) ii and iii
C) i
D) All of the given answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If the initial investment is $4000 and the annual cash inflow is $500, what is the payback period?
A) 20 years
B) 8 years
C) 4 years
D) 2 years
A) 20 years
B) 8 years
C) 4 years
D) 2 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A piece of equipment has an estimated five-year life, an internal rate of return of 12 per cent and estimated annual savings of $15 000. What was the cost of the equipment?
A) $75 000
B) $26 435
C) $54 075
D) $60 000
A) $75 000
B) $26 435
C) $54 075
D) $60 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Cubbies Pty Ltd is considering the purchase of a new machine to replace an old machine. Selected cost data pertaining to the two machines is provided below. 
At the end of four years, the company plans to discontinue the product line for which the machines are used. Income taxes can be ignored. Using the incremental cost approach, calculate the current period (i.e. year zero) cash flows relevant to acquiring the new machine.
A) $9000 outflow
B) $4000 inflow
C) $3000 outflow
D) $5000 outflow

At the end of four years, the company plans to discontinue the product line for which the machines are used. Income taxes can be ignored. Using the incremental cost approach, calculate the current period (i.e. year zero) cash flows relevant to acquiring the new machine.
A) $9000 outflow
B) $4000 inflow
C) $3000 outflow
D) $5000 outflow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The systematic follow up of each project to see how it turned out is called:
A) controlled capital expenditure.
B) post-audit.
C) cost performance.
D) cost evaluation phase.
A) controlled capital expenditure.
B) post-audit.
C) cost performance.
D) cost evaluation phase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The simple rate of return, rate of return on assets and the unadjusted rate of return are synonymous with:
A) the accounting rate of return.
B) the payback method.
C) the internal rate of return.
D) discounted cash flow.
A) the accounting rate of return.
B) the payback method.
C) the internal rate of return.
D) discounted cash flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Net present value is calculated using the:
A) required rate of return.
B) internal rate of return.
C) return on investment.
D) return on assets employed.
A) required rate of return.
B) internal rate of return.
C) return on investment.
D) return on assets employed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following reasons would explain the popularity of the payback technique?
A) It is simple to calculate.
B) Its results are easy to interpret and understand.
C) It provides a short-term filter to eliminate some projects.
D) All of the given answers
A) It is simple to calculate.
B) Its results are easy to interpret and understand.
C) It provides a short-term filter to eliminate some projects.
D) All of the given answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is the internal rate of return?
A) The discount rate at which the present value of expected cash inflows and outflows is equal.
B) The discount rate that makes the net present value of the cash flows equal zero.
C) The discount rate at which the present value of expected cash inflows and outflows is equal AND the discount rate that makes the net present value of the cash flows equal zero.
D) The present value factor used to discount cash flows.
A) The discount rate at which the present value of expected cash inflows and outflows is equal.
B) The discount rate that makes the net present value of the cash flows equal zero.
C) The discount rate at which the present value of expected cash inflows and outflows is equal AND the discount rate that makes the net present value of the cash flows equal zero.
D) The present value factor used to discount cash flows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Consider the following statements. Since money has a time value:
I) businesses will take tax deductions as early as possible.
Ii) businesses will take tax deductions as late as possible.
Iii) businesses will obtain a greater tax benefit by using the diminishing value method of depreciation.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A) i
B) ii
C) i and iii
D) ii and iii
I) businesses will take tax deductions as early as possible.
Ii) businesses will take tax deductions as late as possible.
Iii) businesses will obtain a greater tax benefit by using the diminishing value method of depreciation.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A) i
B) ii
C) i and iii
D) ii and iii

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If the incremental revenue increased by $1 million dollars, what would be the after-tax cash inflow (income tax rate of 28 per cent)?
A) $400 000
B) $1 008 000
C) $980 000
D) $720 000
A) $400 000
B) $1 008 000
C) $980 000
D) $720 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If the company's net profit is $1 000 000 and its income tax rate is 30 per cent, what is the income tax payment?
A) $700 000
B) $30 000
C) $300 000
D) $70 000
A) $700 000
B) $30 000
C) $300 000
D) $70 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What is the quantitative decision rule for the net present value method?
A) Accept investments whose return on investment exceeds the accounting rate of return.
B) Accept investments whose weighted average cost of capital exceeds the return on investment.
C) Accept investments whose required rate of return exceeds the internal rate of return.
D) Accept investments with a positive net present value.
A) Accept investments whose return on investment exceeds the accounting rate of return.
B) Accept investments whose weighted average cost of capital exceeds the return on investment.
C) Accept investments whose required rate of return exceeds the internal rate of return.
D) Accept investments with a positive net present value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following is not a technique applied to capital expenditure decisions?
A) Payback
B) Cash budgeting
C) Discounted cash flow analysis
D) Accounting rate of return
A) Payback
B) Cash budgeting
C) Discounted cash flow analysis
D) Accounting rate of return

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Determine the payback period from the following. Investment equipment with an eight-year useful life costs $1 000 000. Annual cash flows increase by $200 000 each year. The payback period is:
A) 5 years.
B) 6 years.
C) 7 years.
D) 8 years.
A) 5 years.
B) 6 years.
C) 7 years.
D) 8 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
For a capital investment of $800 000, what are the yearly cash inflows to the nearest thousand if the net present value is zero and a four-year annuity has a 12 per cent required rate of return?
A) $296 000
B) $189 000
C) $263 000
D) $275 000
A) $296 000
B) $189 000
C) $263 000
D) $275 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following statements about income taxes and capital budgeting decisions is/are correct?
I) Income taxes influence the amount of cash inflows and outflows in capital budgeting decisions.
Ii) Income taxes are not cash flows.
Iii) The effect of income taxes is not necessarily in the same year as the cash flow.
A) i
B) ii
C) ii and iii
D) i and iii
I) Income taxes influence the amount of cash inflows and outflows in capital budgeting decisions.
Ii) Income taxes are not cash flows.
Iii) The effect of income taxes is not necessarily in the same year as the cash flow.
A) i
B) ii
C) ii and iii
D) i and iii

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Suppose a firm has an asset that originally cost $5000 and currently has accumulated depreciation of $2000. The firm is subject to a 28 per cent income tax rate. Suppose the firm sells the asset for $2000. What was the book value before sale?
A) $5000
B) $2000
C) $3000
D) $1500
A) $5000
B) $2000
C) $3000
D) $1500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following statements regarding capital budgeting decision errors is/are true?
A) The consistent use of post-audits precludes an organisation from rejecting a desirable capital budgeting project.
B) The post-audit helps to detect errors that occur when an undesirable capital budgeting project is accepted.
C) The use of post-audits will not detect errors that occur when a desirable capital budgeting project is rejected.
D) The post-audit helps to detect errors that occur when an undesirable capital budgeting project is accepted AND the use of post-audits will not detect errors that occur when a desirable capital budgeting project is rejected.
A) The consistent use of post-audits precludes an organisation from rejecting a desirable capital budgeting project.
B) The post-audit helps to detect errors that occur when an undesirable capital budgeting project is accepted.
C) The use of post-audits will not detect errors that occur when a desirable capital budgeting project is rejected.
D) The post-audit helps to detect errors that occur when an undesirable capital budgeting project is accepted AND the use of post-audits will not detect errors that occur when a desirable capital budgeting project is rejected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is the quantitative decision rule for the internal rate of return method?
A) Accept investments whose return on investment exceeds the accounting rate of return.
B) Accept investments whose weighted average cost of capital exceeds the return on investment.
C) Accept investments whose required rate of return exceeds the internal rate of return.
D) Accept investments whose internal rate of return exceeds the required rate of return.
A) Accept investments whose return on investment exceeds the accounting rate of return.
B) Accept investments whose weighted average cost of capital exceeds the return on investment.
C) Accept investments whose required rate of return exceeds the internal rate of return.
D) Accept investments whose internal rate of return exceeds the required rate of return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A) Discounted cash flow techniques explicitly recognise the time value of money.
B) Payback recognises the time value of money.
C) Accounting rate of return recognises the time value of money.
D) Payback recognises the time value of money AND accounting rate of return recognises the time value of money.
A) Discounted cash flow techniques explicitly recognise the time value of money.
B) Payback recognises the time value of money.
C) Accounting rate of return recognises the time value of money.
D) Payback recognises the time value of money AND accounting rate of return recognises the time value of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following capital investment decision methods typically adjust for risk?
A) Net present value
B) Internal rate of return
C) Payback
D) Accounting rate of return
A) Net present value
B) Internal rate of return
C) Payback
D) Accounting rate of return

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Assuming interest rates average 6 per cent, how much would you need to save at the end of each year if you wished to accumulate one million dollars over 20 years?
A) $50 000
B) $43 800
C) $27 184
D) $14 565
A) $50 000
B) $43 800
C) $27 184
D) $14 565

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following statements is true?
A) For tax purposes, a business must use the straight-line method of depreciation.
B) For tax purposes, a business must use the diminishing value method of depreciation.
C) For tax purposes, a business may use either the straight line or diminishing value method of depreciation.
D) The depreciation method used for tax purposes must be the same as that used for external reporting.
A) For tax purposes, a business must use the straight-line method of depreciation.
B) For tax purposes, a business must use the diminishing value method of depreciation.
C) For tax purposes, a business may use either the straight line or diminishing value method of depreciation.
D) The depreciation method used for tax purposes must be the same as that used for external reporting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following relates to an advantage that the accounting rate of return method has over payback?
A) Time value of money
B) Proposal screening
C) The period of the analysis
D) Risk
A) Time value of money
B) Proposal screening
C) The period of the analysis
D) Risk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Projects with a zero or positive net present value (NPV) are accepted using the net present value method. Why is this so?
A) Because a non-negative NPV ensures the company will be profitable.
B) Because the company will have the relevant cash flow to pay its debts as, and when, they fall due.
C) Because the return is at least equal to the cost of capital.
D) Because a non-negative NPV ensures the company will be profitable AND because the company will have the relevant cash flow to pay its debts as, and when, they fall due.
A) Because a non-negative NPV ensures the company will be profitable.
B) Because the company will have the relevant cash flow to pay its debts as, and when, they fall due.
C) Because the return is at least equal to the cost of capital.
D) Because a non-negative NPV ensures the company will be profitable AND because the company will have the relevant cash flow to pay its debts as, and when, they fall due.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A machine will cost $28 000. It is estimated that it will generate $8000 in after-tax savings each year during its five-year life. What is the profitability index assuming a hurdle rate of 10 per cent?
A) 1.08
B) 0.92
C) 1.24
D) 1.43
A) 1.08
B) 0.92
C) 1.24
D) 1.43

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The manager of Malan Pty Ltd wants to buy a new machine to replace the one currently being used. The new machine will cost $100 000 with no disposal value at the end of a five-year useful life. The manager estimates that the machine will reduce annual operating costs by $30 000. Depreciation will be $20 000 per year for five years. The tax rate for each year is expected to be 20 per cent and the company has an after-tax hurdle rate of 12 per cent. What is the after-tax accounting rate of return computed based on the initial investment?
A) 8%
B) 20%
C) 4%
D) 10%
A) 8%
B) 20%
C) 4%
D) 10%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Wakefield Company management evaluates future projects based on their profitability index. The company is currently reviewing five similar projects and must choose one project. Pertinent information regarding the projects is as follows. 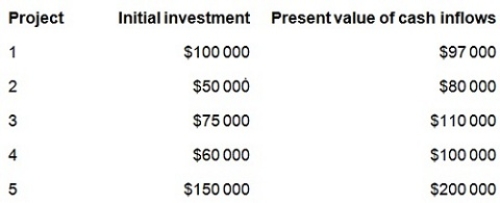
Which project should Wakefield Company select if the decision is based entirely on profitability index?
A) Project 1
B) Project 2
C) Project 3
D) Project 4

Which project should Wakefield Company select if the decision is based entirely on profitability index?
A) Project 1
B) Project 2
C) Project 3
D) Project 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Charlotte Computer Services is considering purchasing equipment at $100 000. It is anticipated the equipment will have a useful life of five years. It will be depreciated on a straight-line basis. Operating revenue is expected to be $74 000 per annum and operating expenses $25 000 per annum. The equipment is subject to an investment allowance of 10 per cent and the tax rate is 30 per cent. The after-tax hurdle rate is 12 per cent. What is the net present value of the investment?
A) $45 282
B) $7545
C) $70 825
D) $48 282
A) $45 282
B) $7545
C) $70 825
D) $48 282

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Abco Pty Ltd is considering the purchase of $60 000 in tools. The manager estimates that the tools will generate $25 000 in savings during each year of a four-year life. The tools will be depreciated based on the following schedule. 
The expected tax rate is 30 per cent. What is the tax effect of the depreciation in year 3? (Ignore time value of money)
A) $9000
B) $6300
C) $2700
D) $1823

The expected tax rate is 30 per cent. What is the tax effect of the depreciation in year 3? (Ignore time value of money)
A) $9000
B) $6300
C) $2700
D) $1823

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If a proposal's profitability index is greater than one, the:
A) net present value is negative.
B) net present value is positive.
C) net present value cannot be determined by the profitability index.
D) proposal should be rejected.
A) net present value is negative.
B) net present value is positive.
C) net present value cannot be determined by the profitability index.
D) proposal should be rejected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Suppose a firm has an asset that originally cost $5000 and currently has accumulated depreciation of $2000. The firm is subject to a 28 per cent income tax rate. Suppose the firm sells the asset for $2000. What will be the loss without regard to taxes?
A) ($1000)
B) ($3000)
C) ($1120)
D) ($2000)
A) ($1000)
B) ($3000)
C) ($1120)
D) ($2000)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The profitability index is calculated by:
A) multiplying the present value of inflows by the initial investment.
B) multiplying the initial investment by the discount rate.
C) dividing the present value of net inflows by the initial investment.
D) dividing the initial investment by the present value of net inflows.
A) multiplying the present value of inflows by the initial investment.
B) multiplying the initial investment by the discount rate.
C) dividing the present value of net inflows by the initial investment.
D) dividing the initial investment by the present value of net inflows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Rogers Company purchased equipment for $30 000 in December of 2014. It is expected to generate $10 000 per year in additional revenue and $2000 per year in additional cash expenses beginning in 2015. Depreciation in 2015 will be $3000. The firm's tax rate is 40 per cent. What is the annual after-tax cash flow in 2015?
A) $8000
B) $4800
C) $6000
D) $3600
A) $8000
B) $4800
C) $6000
D) $3600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Abco Pty Ltd is considering the purchase of $60 000 in tools. The manager estimates that the tools will generate $25 000 in savings during each year of a four-year life. The tools will be depreciated based on the following schedule. 
The expected tax rate is 30 per cent. What is the net present value of the investment, assuming an after-tax hurdle rate of 14 per cent?
A) $5001
B) ($9005)
C) $23 700
D) ($1720)

The expected tax rate is 30 per cent. What is the net present value of the investment, assuming an after-tax hurdle rate of 14 per cent?
A) $5001
B) ($9005)
C) $23 700
D) ($1720)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Among the benefits of advanced technologies that are difficult to quantify is/are:
A) greater flexibility.
B) reduction of non-value-added activities.
C) increased inventory levels.
D) greater flexibility AND reduction of non-value-added activities.
A) greater flexibility.
B) reduction of non-value-added activities.
C) increased inventory levels.
D) greater flexibility AND reduction of non-value-added activities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following is not a difficulty in applying the net present value investment decision model to investments in advanced technologies?
A) Management bias toward incremental projects
B) Use of short time horizons
C) Difficulty in quantifying the synergistic benefits of adopting multiple capital expenditure proposals
D) Use of hurdle rates that are too low
A) Management bias toward incremental projects
B) Use of short time horizons
C) Difficulty in quantifying the synergistic benefits of adopting multiple capital expenditure proposals
D) Use of hurdle rates that are too low

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The manager of Malan Pty Ltd wants to buy a new machine to replace the one currently being used. The new machine will cost $100 000 with no disposal value at the end of a five-year useful life. The manager estimates that the machine will reduce annual operating costs by $30 000. Depreciation will be $20 000 per year for five years. The tax rate for each year is expected to be 20 per cent and the company has an after-tax hurdle rate of 12 per cent. What is the after-tax net present value of the machine?
A) $100 940
B) $8150
C) $940
D) ($13 480)
A) $100 940
B) $8150
C) $940
D) ($13 480)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
One criterion that managers sometimes apply in ranking investment proposals is called the:
A) profitability index.
B) annuity index.
C) investment opportunity index.
D) capital ranking approach.
A) profitability index.
B) annuity index.
C) investment opportunity index.
D) capital ranking approach.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Net present value analysis often indicates that investment proposals in advanced technologies should be rejected when in reality the investment is justified. This can occur because:
A) hurdle rates are too low.
B) some benefits are difficult to quantify.
C) the time horizons used are too long.
D) the cash flows are certain.
A) hurdle rates are too low.
B) some benefits are difficult to quantify.
C) the time horizons used are too long.
D) the cash flows are certain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The manager of Malan Pty Ltd wants to buy a new machine to replace the one currently being used. The new machine will cost $100 000 with no disposal value at the end of a five-year useful life. The manager estimates that the machine will reduce annual operating costs by $30 000. Depreciation will be $20 000 per year for five years. The tax rate for each year is expected to be 20 per cent and the company has an after-tax hurdle rate of 12 per cent. What is the annual after-tax cash flow for years 1 to 5 associated with the purchase of the new machine?
A) $30 000
B) $28 000
C) $24 000
D) $22 000
A) $30 000
B) $28 000
C) $24 000
D) $22 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The following data applies: 
What would be the present value of the after-tax cash flow for year 0?
A) ($10 000)
B) $0
C) $4726
D) $4000

What would be the present value of the after-tax cash flow for year 0?
A) ($10 000)
B) $0
C) $4726
D) $4000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The manager of Malan Pty Ltd wants to buy a new machine to replace the one currently being used. The new machine will cost $100 000 with no disposal value at the end of a five-year useful life. The manager estimates that the machine will reduce annual operating costs by $30 000. Depreciation will be $20 000 per year for five years. The tax rate for each year is expected to be 20 per cent and the company has an after-tax hurdle rate of 12 per cent. What is the after-tax payback period of the machine?
A) 3.33 years
B) 3.57 years
C) 4.17 years
D) 4.55 years
A) 3.33 years
B) 3.57 years
C) 4.17 years
D) 4.55 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Charlotte Computer Services is considering purchasing equipment at $100 000. It is anticipated the equipment will have a useful life of five years. It will be depreciated on a straight-line basis. Operating revenue is expected to be $74 000 per annum and operating expenses $25 000 per annum. The equipment is subject to an investment allowance of 10 per cent and the tax rate is 30 per cent. The after-tax hurdle rate is 12 per cent. What is the tax effect of the depreciation?
A) $3000
B) $21 630
C) $24 630
D) $6000
A) $3000
B) $21 630
C) $24 630
D) $6000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Charlotte Computer Services is considering purchasing equipment at $100 000. It is anticipated the equipment will have a useful life of five years. It will be depreciated on a straight-line basis. Operating revenue is expected to be $74 000 per annum and operating expenses $25 000 per annum. The equipment is subject to an investment allowance of 10 per cent and the tax rate is 30 per cent. The after-tax hurdle rate is 12 per cent. The reduction in tax due to the investment allowance is:
A) $10 000.
B) $3000.
C) $7000.
D) $8700.
A) $10 000.
B) $3000.
C) $7000.
D) $8700.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



