Deck 12: Learning and Memory
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/168
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Learning and Memory
1
Monkeys were most impaired in their performance on the delayed nonmatching to sample (DNMS) test following lesions in the interpositus nucleus of the cerebellum.
False
2
Habituation of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia californica is largely due to reduced responsiveness of the sensory neurons serving the siphon.
False
3
Behaviors that are species-specific, are activated by environmental stimuli and can be complex, are called
A) reflexes.
B) instincts.
C) habituation.
D) sensitization.
A) reflexes.
B) instincts.
C) habituation.
D) sensitization.
instincts.
4
Classical conditioning involves mostly involuntary behaviors, while operant conditioning involves mostly voluntary behaviors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Levels of protein kinase M zeta (PKM?) increase during the stage of LTP stabilization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The reduced response to a repeated harmless stimulus is an example of
A) instinctive behavior.
B) habituation.
C) sensitization.
D) classical conditioning.
A) instinctive behavior.
B) habituation.
C) sensitization.
D) classical conditioning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Changes in the magnitude of a response to environmental stimuli is typical in
A) instinctive behaviors.
B) reflexes.
C) associative learning.
D) non-associative learning.
A) instinctive behaviors.
B) reflexes.
C) associative learning.
D) non-associative learning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following processes represents the formation of a connection between two or more stimuli in one's environment?
A) instinctive behaviors
B) reflexes
C) associative learning
D) non-associative learning
A) instinctive behaviors
B) reflexes
C) associative learning
D) non-associative learning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The process that occurs following a strong stimulus, when the responses to subsequent stimuli are increased, is called
A) instinctive behavior.
B) habituation.
C) sensitization.
D) classical conditioning.
A) instinctive behavior.
B) habituation.
C) sensitization.
D) classical conditioning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Jamelis has figured out that his mother will be furious with him if he comes home after dinner time, so he has started making sure never to be that late. Jamelis is demonstrating
A) reflexes.
B) instincts.
C) fixed action patterns.
D) learned behaviors.
A) reflexes.
B) instincts.
C) fixed action patterns.
D) learned behaviors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Classical conditioning is an example of
A) a reflex.
B) a fixed action pattern.
C) associative learning.
D) non-associative learning.
A) a reflex.
B) a fixed action pattern.
C) associative learning.
D) non-associative learning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
"Fixed action patterns" are also known as
A) reflexes.
B) instincts.
C) associative learning stimuli.
D) non-associative learning stimuli.
A) reflexes.
B) instincts.
C) associative learning stimuli.
D) non-associative learning stimuli.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Although you may notice your air conditioner turning on, you no longer "hear" it running after a few minutes. Which of the following processes probably accounts for this change?
A) instinctive behavior
B) habituation
C) sensitization
D) classical conditioning
A) instinctive behavior
B) habituation
C) sensitization
D) classical conditioning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The retrieval of personal episodic memories coincided with increased activity in the prefrontal cortex and the posterior cingulate cortex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A quick, involuntary response that always occurs in the presence of specific stimuli is called a(n)
A) reflex.
B) instinct.
C) fixed action pattern.
D) learned behavior.
A) reflex.
B) instinct.
C) fixed action pattern.
D) learned behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Semantic and episodic memories are types of explicit memories.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Long-term potentiation (LTP) can be demonstrated outside the hippocampus at synapses involving neurotransmitters other than glutamate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Many mating and parenting behaviors, including the tail feather display of the male peacock, are examples of instinctive behaviors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience is called
A) learning.
B) instinct.
C) reflex.
D) fixed action pattern.
A) learning.
B) instinct.
C) reflex.
D) fixed action pattern.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Following a traumatic experience, the hippocampus experiences a refractory period but the amygdala does not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following memories are ones that are recalled explicitly
A) classical conditioning
B) sensitization
C) procedural memory
D) episodic memory
A) classical conditioning
B) sensitization
C) procedural memory
D) episodic memory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
It is _____ memory that contains our knowledge of how to do specific activities involving motor skills.
A) procedural
B) episodic
C) sensory
D) semantic
A) procedural
B) episodic
C) sensory
D) semantic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
When an animal learns that a particular stimulus occurs just prior to another event, what process has occurred?
A) sensitization
B) habituation
C) classical conditioning
D) extinction
A) sensitization
B) habituation
C) classical conditioning
D) extinction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When Thomas was a little boy, his mother often gave him a piece of candy whenever she had to bandage up a scraped elbow or knee. Now that Thomas is in college, he struggles with his weight because every time he feels sad or lonely, he craves something sweet to eat. It is likely that for Thomas, eating candy now serves as a(n)
A) conditioned stimulus.
B) conditioned response.
C) unconditioned stimulus.
D) unconditioned response.
A) conditioned stimulus.
B) conditioned response.
C) unconditioned stimulus.
D) unconditioned response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
______ memory can hold a limited amount of information (five to nine items) for 15 to 20 seconds.
A) Sensory
B) Short-term
C) Long-term
D) Episodic
A) Sensory
B) Short-term
C) Long-term
D) Episodic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The components of ______ memory include the central executive, phonological loop, visuospatial scratchpad, and episodic buffer.
A) sensory
B) working
C) long-term
D) episodic
A) sensory
B) working
C) long-term
D) episodic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In Pavlov's classic experiments with dogs and salivation, food serves as the
A) conditioned stimulus.
B) conditioned response.
C) unconditioned stimulus.
D) unconditioned response.
A) conditioned stimulus.
B) conditioned response.
C) unconditioned stimulus.
D) unconditioned response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
This type of memory is easier to demonstrate than to explain in words.
A) procedural
B) episodic
C) sensory
D) semantic
A) procedural
B) episodic
C) sensory
D) semantic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The best example of working memory from these examples is
A) what you had for breakfast this morning.
B) the question you just read and are trying to answer.
C) your best friend's name.
D) the instructions your professor gave you when you began taking this exam.
A) what you had for breakfast this morning.
B) the question you just read and are trying to answer.
C) your best friend's name.
D) the instructions your professor gave you when you began taking this exam.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Declarative memories include _________ memories.
A) procedural and sensory
B) episodic and semantic
C) procedural and episodic
D) semantic and sensory
A) procedural and sensory
B) episodic and semantic
C) procedural and episodic
D) semantic and sensory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The memories that are easiest to explain in words are
A) sensory
B) procedural
C) declarative
D) implicit
A) sensory
B) procedural
C) declarative
D) implicit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The type of memory that can hold unlimited amounts of information indefinitely is _____ memory.
A) sensory
B) working.
C) long-term
D) working
A) sensory
B) working.
C) long-term
D) working

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In Pavlov's classic experiments, salivation to a metronome is an example of a(n)
A) conditioned stimulus.
B) conditioned response.
C) unconditioned stimulus.
D) unconditioned response.
A) conditioned stimulus.
B) conditioned response.
C) unconditioned stimulus.
D) unconditioned response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which memories are easiest to demonstrate?
A) sensory
B) procedural
C) semantic and episodic
D) explicit
A) sensory
B) procedural
C) semantic and episodic
D) explicit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Memories of an individual's personal experience are stored in _________ memory.
A) procedural
B) episodic
C) working
D) semantic
A) procedural
B) episodic
C) working
D) semantic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The clearest example of episodic memory from these examples is
A) what you ate for dinner last night.
B) the meaning of the word exculpatory.
C) the name of the first president of the United States.
D) how to ride a bike.
A) what you ate for dinner last night.
B) the meaning of the word exculpatory.
C) the name of the first president of the United States.
D) how to ride a bike.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
As a young child, Eli was bitten by a dog, and he continues to be frightened anytime he sees a large dog. For Eli, dogs are a(n)
A) unconditioned response.
B) unconditioned stimulus.
C) conditioned response.
D) conditioned stimulus.
A) unconditioned response.
B) unconditioned stimulus.
C) conditioned response.
D) conditioned stimulus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
For days after a powerful earthquake, Lavonne jumped whenever an airplane flew over her house to land at the nearby airport. This response is likely a result of
A) instinct.
B) reflex.
C) habituation.
D) sensitization.
A) instinct.
B) reflex.
C) habituation.
D) sensitization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which type of memory can hold large amounts of information but only very briefly (a second or two)?
A) sensory
B) working
C) long-term
D) episodic
A) sensory
B) working
C) long-term
D) episodic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The type of memory that holds our knowledge of language and facts is ______ memory.
A) procedural
B) episodic
C) sensory
D) semantic
A) procedural
B) episodic
C) sensory
D) semantic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What type of channels is involved in the sensitization process of the siphon sensory neurons in Aplysia?
A) an ionotropic process, which results in the closing of calcium channels
B) a metabotropic process, which results in the closing of calcium channels
C) an ionotropic process, which results in the closing of potassium channels
D) a metabotropic process, which results in the closing of potassium channels
A) an ionotropic process, which results in the closing of calcium channels
B) a metabotropic process, which results in the closing of calcium channels
C) an ionotropic process, which results in the closing of potassium channels
D) a metabotropic process, which results in the closing of potassium channels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
After class, Mohammed regaled you with clever stories of his family cat when he was growing up. To tell you these stories, Mohammed was using his _____ memory.
A) sensory
B) working
C) episodic
D) semantic
A) sensory
B) working
C) episodic
D) semantic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Jonah required surgery on both of his temporal lobes. Following the surgery, Jonah suffered from severe anterograde amnesia and had great difficulty in
A) learning the name of the new occupational therapist assigned to his case.
B) learning to use his new cell phone.
C) remembering the details of his high school graduation.
D) remembering how to find the square root of a number.
A) learning the name of the new occupational therapist assigned to his case.
B) learning to use his new cell phone.
C) remembering the details of his high school graduation.
D) remembering how to find the square root of a number.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Depletion of available neurotransmitter in the presynaptic sensory neuron of Aplysia is the likely cause of
A) long-term habituation.
B) short-term habituation.
C) long-term sensitization.
D) short-term sensitization.
A) long-term habituation.
B) short-term habituation.
C) long-term sensitization.
D) short-term sensitization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Short-term habituation of the Aplysia gill-withdrawal reflex, lasting from minutes to several hours, probably results from
A) changes in the synapses between sensory and motor neurons.
B) decreased sensitivity of the sensory neurons.
C) fatigue in the muscles serving the gill.
D) stronger excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) in the interneurons.
A) changes in the synapses between sensory and motor neurons.
B) decreased sensitivity of the sensory neurons.
C) fatigue in the muscles serving the gill.
D) stronger excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) in the interneurons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The interneurons involved with sensitization in Aplysia form which of the following types of synapse?
A) axo-axonic synapses on sensory neurons serving the siphon
B) axo-dendritic synapses on sensory neurons serving the siphon
C) axo-axonic synapses on the motor neurons serving the gill
D) axo-dendritic synapses on the motor neurons serving the gill
A) axo-axonic synapses on sensory neurons serving the siphon
B) axo-dendritic synapses on sensory neurons serving the siphon
C) axo-axonic synapses on the motor neurons serving the gill
D) axo-dendritic synapses on the motor neurons serving the gill

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Repeated touching of the siphon in Aplysia will result in
A) habituation.
B) sensitization.
C) classical conditioning.
D) a fixed action pattern.
A) habituation.
B) sensitization.
C) classical conditioning.
D) a fixed action pattern.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Short-term habituation in Aplysia occurs when _________ neurotransmitter is released at synapses with _________ neurons.
A) less; gill motor
B) less; siphon sensory
C) more; gill motor
D) more; siphon sensory
A) less; gill motor
B) less; siphon sensory
C) more; gill motor
D) more; siphon sensory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The neurotransmitter _____ is released at axo-axonic synapses in Aplysia by neurons involved in sensitization.
A) dopamine
B) acetylcholine (ACh)
C) serotonin
D) norepinephrine
A) dopamine
B) acetylcholine (ACh)
C) serotonin
D) norepinephrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Changes in the NMDA receptor in Aplysia are believed to be the cause of
A) short-term sensitization.
B) long-term sensitization.
C) short-term habituation.
D) long-term habituation.
A) short-term sensitization.
B) long-term sensitization.
C) short-term habituation.
D) long-term habituation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The gill withdrawal reflex in Aplysia is controlled by neurons in the
A) brain.
B) buccal ganglia.
C) pedal ganglia.
D) abdominal ganglia.
A) brain.
B) buccal ganglia.
C) pedal ganglia.
D) abdominal ganglia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is an example of a procedural memory?
A) where you were when you heard about the Twin Towers being attacked
B) the name of your psychology professor
C) how to play your guitar
D) what you had for breakfast this morning
A) where you were when you heard about the Twin Towers being attacked
B) the name of your psychology professor
C) how to play your guitar
D) what you had for breakfast this morning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
You are on the phone with tech support after your software crashed. The technician is helping you go through the steps to reinstall the software, pausing from time to time to visualize the situation before telling you the next step. This technician is likely accessing ________ memory.
A) procedural
B) episodic
C) autobiographical
D) explicit
A) procedural
B) episodic
C) autobiographical
D) explicit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Just before class, Willis asked you the title and edition of the textbook being used as she ordered it online. Willis was using her ______ memory to hold this information while searching for the book.
A) sensory
B) working
C) procedural
D) semantic
A) sensory
B) working
C) procedural
D) semantic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In sensitization experiments, shocking the head or tail of Aplysia will result in a(n)
A) reduced gill-withdrawal reflex in response to siphon touch.
B) increased gill-withdrawal reflex in response to siphon touch.
C) absence of the gill-withdrawal reflex in response to siphon touch.
D) gill-withdrawal reflex in response to head touch but not siphon touch.
A) reduced gill-withdrawal reflex in response to siphon touch.
B) increased gill-withdrawal reflex in response to siphon touch.
C) absence of the gill-withdrawal reflex in response to siphon touch.
D) gill-withdrawal reflex in response to head touch but not siphon touch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Patients with anterograde amnesia show deficits in
A) declarative but not explicit memory.
B) explicit but not nondeclarative memory.
C) both explicit and declarative memory.
D) neither explicit nor declarative memory.
A) declarative but not explicit memory.
B) explicit but not nondeclarative memory.
C) both explicit and declarative memory.
D) neither explicit nor declarative memory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Before reading the chapter on neuropsychology in his behavioral neuroscience textbook, Christopher had never heard of brain worms. Once he had mastered this knowledge, information about brain worms became part of Christopher's _________ memory.
A) sensory
B) procedural
C) implicit
D) semantic
A) sensory
B) procedural
C) implicit
D) semantic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A good example of a semantic memory is which of these?
A) the name of the first president of the United States
B) what happened at your best childhood birthday party ever
C) how to ride a bike
D) where you were when you heard about the Twin Towers being attacked
A) the name of the first president of the United States
B) what happened at your best childhood birthday party ever
C) how to ride a bike
D) where you were when you heard about the Twin Towers being attacked

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In sensitization in Aplysia, what processes account for the stronger than normal responses of gill motor neurons?
A) extended action potentials in siphon sensory neurons, which result in the release of greater than normal amounts of neurotransmitter at synapses with gill motor neurons.
B) extended action potentials in siphon sensory neurons, which result in the release of less than normal amounts of neurotransmitter at synapses with gill motor neurons.
C) shortened action potentials in siphon sensory neurons, which result in the release of greater than normal amounts of neurotransmitter at synapses with gill motor neurons
D) shortened action potentials in siphon sensory neurons, which result in the release of less than normal amounts of neurotransmitter at synapses with gill motor neurons.
A) extended action potentials in siphon sensory neurons, which result in the release of greater than normal amounts of neurotransmitter at synapses with gill motor neurons.
B) extended action potentials in siphon sensory neurons, which result in the release of less than normal amounts of neurotransmitter at synapses with gill motor neurons.
C) shortened action potentials in siphon sensory neurons, which result in the release of greater than normal amounts of neurotransmitter at synapses with gill motor neurons
D) shortened action potentials in siphon sensory neurons, which result in the release of less than normal amounts of neurotransmitter at synapses with gill motor neurons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Habituation in Aplysia can last up to
A) three hours.
B) one day.
C) three days.
D) three weeks.
A) three hours.
B) one day.
C) three days.
D) three weeks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following proteins play a role in the structural changes associated with habituation or sensitization?
A) dystrophin
B) agrin
C) actin
D) myosin
A) dystrophin
B) agrin
C) actin
D) myosin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
"Associativity" in the Hebbian synapse refers to the
A) use of the same type of neurotransmitter in both the pre- and postsynaptic neurons.
B) simultaneous activity of several synapses on the same postsynaptic neuron.
C) nearly simultaneous activity of the pre- and postsynaptic neurons.
D) ability of the postsynaptic cell to use retrograde messengers such as nitric oxide (NO) to communicate with the presynaptic cell.
A) use of the same type of neurotransmitter in both the pre- and postsynaptic neurons.
B) simultaneous activity of several synapses on the same postsynaptic neuron.
C) nearly simultaneous activity of the pre- and postsynaptic neurons.
D) ability of the postsynaptic cell to use retrograde messengers such as nitric oxide (NO) to communicate with the presynaptic cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In studies of classical conditioning in Aplysia, which of the following usually serves as the unconditioned stimulus?
A) touching the mantle
B) touching the siphon
C) the gill-withdrawal reflex
D) electric shock to the tail
A) touching the mantle
B) touching the siphon
C) the gill-withdrawal reflex
D) electric shock to the tail

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Classical conditioning in Aplysia results primarily from
A) the release of larger amounts of neurotransmitter by the sensory neuron.
B) the release of smaller amounts of neurotransmitter by the sensory neuron.
C) increased sensitivity of the motor neuron.
D) larger numbers of active interneurons.
A) the release of larger amounts of neurotransmitter by the sensory neuron.
B) the release of smaller amounts of neurotransmitter by the sensory neuron.
C) increased sensitivity of the motor neuron.
D) larger numbers of active interneurons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The Schaffer collateral pathway connects
A) the dentate gyrus and Ammon's horn of the hippocampus.
B) association cortex and the hippocampus.
C) the CA3 and CA1 areas of Ammon's horn.
D) the hippocampus and the hypothalamus.
A) the dentate gyrus and Ammon's horn of the hippocampus.
B) association cortex and the hippocampus.
C) the CA3 and CA1 areas of Ammon's horn.
D) the hippocampus and the hypothalamus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The procedure illustrated in this figure will result in
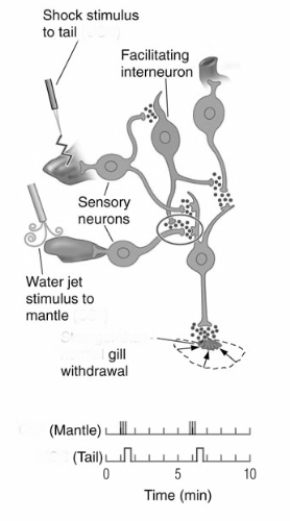
A) sensitization of the Aplysia gill-withdrawal reflex.
B) classical conditioning of the Aplysia gill-withdrawal reflex.
C) habituation of the Aplysia gill-withdrawal reflex.
D) extinction of the Aplysia gill-withdrawal reflex.

A) sensitization of the Aplysia gill-withdrawal reflex.
B) classical conditioning of the Aplysia gill-withdrawal reflex.
C) habituation of the Aplysia gill-withdrawal reflex.
D) extinction of the Aplysia gill-withdrawal reflex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Simultaneous activity of several synapses on the same postsynaptic neuron during LTP is referred to as
A) sensitization.
B) facilitation.
C) cooperativity.
D) potentiativity.
A) sensitization.
B) facilitation.
C) cooperativity.
D) potentiativity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The rapid series of shocks that is applied to demonstrate LTP is at a rate that is ______ that found in normal neuronal communication.
A) greater than
B) less than
C) about the same as
D) more irregular than
A) greater than
B) less than
C) about the same as
D) more irregular than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In studies of LTP in hippocampal tissue, a rapid series of shocks
A) increases postsynaptic potentials for hours.
B) increases postsynaptic potentials for up to 10 minutes after stimulation.
C) has progressively larger postsynaptic potentials during the series.
D) decreases the postsynaptic potentials.
A) increases postsynaptic potentials for hours.
B) increases postsynaptic potentials for up to 10 minutes after stimulation.
C) has progressively larger postsynaptic potentials during the series.
D) decreases the postsynaptic potentials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What fiber pathway is indicated in this illustration by the #8?
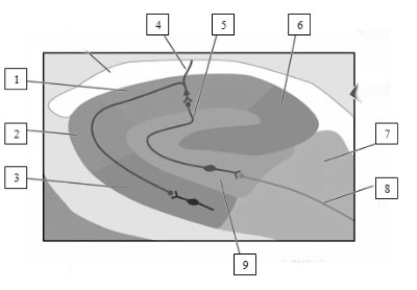
A) the perforant pathway
B) the fornix
C) the mossy fiber pathway
D) the climbing fiber pathway

A) the perforant pathway
B) the fornix
C) the mossy fiber pathway
D) the climbing fiber pathway

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Input from the rhinal cortex travels along
A) the perforant pathway to the dentate gyrus.
B) the fornix to the hypothalamus.
C) mossy fibers to CA3.
D) Schaffer collateral pathway to CA1.
A) the perforant pathway to the dentate gyrus.
B) the fornix to the hypothalamus.
C) mossy fibers to CA3.
D) Schaffer collateral pathway to CA1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Areas CA1 to CA4 are found in
A) the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus.
B) Ammon's horn in the hippocampus.
C) the parahippocampal cortex.
D) the rhinal cortex.
A) the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus.
B) Ammon's horn in the hippocampus.
C) the parahippocampal cortex.
D) the rhinal cortex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Output from the hippocampus travels via the
A) parahippocampal and rhinal cortices.
B) perforant pathway.
C) mossy fibers.
D) fornix.
A) parahippocampal and rhinal cortices.
B) perforant pathway.
C) mossy fibers.
D) fornix.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Operant conditioning in simple animals like Aplysia
A) cannot be demonstrated.
B) can result in increased biting behavior.
C) produces a stronger gill withdrawal response.
D) produces a weaker gill withdrawal response.
A) cannot be demonstrated.
B) can result in increased biting behavior.
C) produces a stronger gill withdrawal response.
D) produces a weaker gill withdrawal response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Mossy fibers in the hippocampus connect
A) input from the rhinal cortex to the dentate gyrus.
B) the dentate gyrus and CA3.
C) CA3 and CA1.
D) CA1 and the hypothalamus.
A) input from the rhinal cortex to the dentate gyrus.
B) the dentate gyrus and CA3.
C) CA3 and CA1.
D) CA1 and the hypothalamus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The classical conditioning studies in Aplysia found that gill withdrawal was the conditioned response to _____.
A) electrical shock to the tail
B) touching the CS+
C) touching the CS?
D) electrical shock to the siphon
A) electrical shock to the tail
B) touching the CS+
C) touching the CS?
D) electrical shock to the siphon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
LTP is similar to long-term memory in which of the following ways?
A) It requires input to be presented at rates of 2 per second or less.
B) It occurs only in the hippocampus.
C) It takes only seconds to develop and lasts indefinitely.
D) It requires the activity of neurons that release ACh.
A) It requires input to be presented at rates of 2 per second or less.
B) It occurs only in the hippocampus.
C) It takes only seconds to develop and lasts indefinitely.
D) It requires the activity of neurons that release ACh.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The dentate gyrus and Ammon's horn are both structures in the
A) hippocampus.
B) amygdala.
C) hypothalamus.
D) cerebellum.
A) hippocampus.
B) amygdala.
C) hypothalamus.
D) cerebellum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Studies have shown that the type of receptors responsible for LTP in the hippocampus is the ______ receptors.
A) gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
B) tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
C) nicotinic acetylcholine
D) N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate
A) gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
B) tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
C) nicotinic acetylcholine
D) N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
LTP may last
A) hours in living animals and indefinitely in a brain slice.
B) hours in a brain slice and indefinitely in living animals.
C) a few seconds in living animals and several hours in a brain slice.
D) a few seconds in a brain slice and several hours in living animals.
A) hours in living animals and indefinitely in a brain slice.
B) hours in a brain slice and indefinitely in living animals.
C) a few seconds in living animals and several hours in a brain slice.
D) a few seconds in a brain slice and several hours in living animals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



