Deck 5: Genetics and the Development of the Human Brain
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/147
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Genetics and the Development of the Human Brain
1
About two-thirds of the cells traveling to the developing cortex follow radial glia, and the remaining one-third move in a horizontal direction instead, without using radial glia to guide them.
True
2
Critical periods occur in many animals, such as the imprinting observed in geese, but has not yet been observed in humans.
False
3
Which of the following is the best example of a phenotype?
A) Ryan has black hair.
B) Jessica has an allele for type O blood from her father and one for type A blood from her mother.
C) Andrew has two genes for freckles.
D) Elizabeth has two copies of the APOE3 allele.
A) Ryan has black hair.
B) Jessica has an allele for type O blood from her father and one for type A blood from her mother.
C) Andrew has two genes for freckles.
D) Elizabeth has two copies of the APOE3 allele.
Ryan has black hair.
4
Myelination of the human spinal cord and brain begins about 24 weeks following conception and is complete by the age of about 18 months.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Because the heritability of height is 81 percent, and the heritability of adult body mass index (BMI) is 59 percent, we can conclude that genetics play a stronger role in the development of height than BMI.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Joan has one APOE3 and one APOE4 allele. This means Joan is heterozygous for the APOE gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The human genome contains about ________ protein-building genes.
A) 9,500
B) 19,000
C) 100,000
D) 2.5 million
A) 9,500
B) 19,000
C) 100,000
D) 2.5 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Healthy brain activity as we age appears to be quite independent of lifestyle, so there is little any of us can do to prevent declines in this area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An individual organism's observable characteristics are known as the genotype.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is the best example of a genotype?
A) Nicole has green eyes.
B) Justin is taller than his parents.
C) Lauren has the same hair color as her fraternal twin sister.
D) Anthony has two copies of the APOE2 allele.
A) Nicole has green eyes.
B) Justin is taller than his parents.
C) Lauren has the same hair color as her fraternal twin sister.
D) Anthony has two copies of the APOE2 allele.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The generation and maintenance of good brain health is less well understood than the mechanisms responsible for disease, especially among older adults.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The physical characteristics of an organism is referred to as its
A) genome.
B) genotype.
C) phenotype.
D) chromosome.
A) genome.
B) genotype.
C) phenotype.
D) chromosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Females are much more likely than males to develop conditions influenced by genes that are located on the X chromosome, because they have two X chromosomes instead of one and therefore twice as much opportunity to experience problems with genes on those chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Without contact with any other embryonic cells, a mesodermal cell will differentiate into skin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
How many chromosomes are typically present in human cells?
A) 20 pairs for a total of 40 chromosomes
B) 21 pairs for a total of 42 chromosomes
C) 22 pairs for a total of 44 chromosomes
D) 23 pairs for a total of 46 chromosomes
A) 20 pairs for a total of 40 chromosomes
B) 21 pairs for a total of 42 chromosomes
C) 22 pairs for a total of 44 chromosomes
D) 23 pairs for a total of 46 chromosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
How many chromosomes do human beings receive from each parent?
A) 23
B) 46
C) 21
D) 42
A) 23
B) 46
C) 21
D) 42

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following species have the greatest number of genes in their genome?
A) plants
B) flies
C) yeast cells
D) human beings
A) plants
B) flies
C) yeast cells
D) human beings

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The genetic instructions of an organism is known as the
A) telomere.
B) genotype.
C) phenotype.
D) chromosome.
A) telomere.
B) genotype.
C) phenotype.
D) chromosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The human genome has the greatest number of genes of all species studied to date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Doctors recommend that those with phenylketonuria (PKU) adhere to the dietary restrictions associated with this condition throughout their lifetimes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Gene expression refers to the
A) division of the chromosomes in half during the formation of eggs and sperm.
B) passing along of genes that are located close to one another on a chromosome.
C) conversion of genetic instructions into a feature of a living cell.
D) imprinting of particular genes.
A) division of the chromosomes in half during the formation of eggs and sperm.
B) passing along of genes that are located close to one another on a chromosome.
C) conversion of genetic instructions into a feature of a living cell.
D) imprinting of particular genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Brandon and Jacob are identical twins. However, Brandon had a finger damaged in an accident, so even if you couldn't tell them apart from a distance, once you saw the finger you knew who was who. This difference is a characteristic of their
A) genotypes.
B) personalities.
C) heterozygous chromosomes.
D) phenotypes.
A) genotypes.
B) personalities.
C) heterozygous chromosomes.
D) phenotypes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
You were recently introduced to your roommate's sibling. To your surprise, even though the siblings are the same sex, they look nothing alike. Which of the following is the best explanation of this situation?
A) They must have different parents, as genetic inheritance ensures that they share a significant number of genes.
B) Although they started out very similar genetically, their genotypes have changed during development to make them look very different.
C) Given the number of different combinations of genes possible during reproduction, it may be that the two siblings don't really share many alleles.
D) One has expressed only recessive genes, while the other has not.
A) They must have different parents, as genetic inheritance ensures that they share a significant number of genes.
B) Although they started out very similar genetically, their genotypes have changed during development to make them look very different.
C) Given the number of different combinations of genes possible during reproduction, it may be that the two siblings don't really share many alleles.
D) One has expressed only recessive genes, while the other has not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The passing along of genes that are physically close to one another on the same chromosome is known as
A) linkage.
B) crossing over.
C) meiosis.
D) gene expression.
A) linkage.
B) crossing over.
C) meiosis.
D) gene expression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following accurately describes the attraction of bases between strands of DNA?
A) A pairs with T, and C pairs with G.
B) A pairs with C, and T pairs with G.
C) A pairs with G, and T pairs with C.
D) A pairs with U, and T pairs with G.
A) A pairs with T, and C pairs with G.
B) A pairs with C, and T pairs with G.
C) A pairs with G, and T pairs with C.
D) A pairs with U, and T pairs with G.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is the best definition of a gene?
A) an individual's set of observable characteristics
B) a hereditary unit made of DNA that occupies a fixed location on a chromosome
C) a molecule that encodes genetic information
D) a sequence of three bases on the DNA molecule that encodes one of twenty amino acids
A) an individual's set of observable characteristics
B) a hereditary unit made of DNA that occupies a fixed location on a chromosome
C) a molecule that encodes genetic information
D) a sequence of three bases on the DNA molecule that encodes one of twenty amino acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The _____ is a group of three consecutive bases in a gene that codes for one amino acid in a protein.
A) proteome
B) tripheme
C) ribosome
D) codon
A) proteome
B) tripheme
C) ribosome
D) codon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
During meiosis, the process where chromosomes exchange equivalent sections of genetic material is called
A) linkage.
B) crossing over.
C) meiosis.
D) gene expression.
A) linkage.
B) crossing over.
C) meiosis.
D) gene expression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Alternative versions of a particular gene are known as
A) single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).
B) imprinted genes.
C) alleles.
D) proteomes.
A) single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).
B) imprinted genes.
C) alleles.
D) proteomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Cystic fibrosis is a fatal lung condition that results from a recessive gene. If one parent is a healthy carrier for the condition while the other is not a carrier, what is the likely outcome for any children they might have?
A) The children will be heterozygous for cystic fibrosis, and all will develop the disease.
B) Fifty percent of their children will develop the disease, and the other fifty percent will be carriers.
C) None of the children will have the disease, and none will be carriers.
D) None of the children will have the disease, but each child has a fifty percent chance of being a carrier.
A) The children will be heterozygous for cystic fibrosis, and all will develop the disease.
B) Fifty percent of their children will develop the disease, and the other fifty percent will be carriers.
C) None of the children will have the disease, and none will be carriers.
D) None of the children will have the disease, but each child has a fifty percent chance of being a carrier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Huntington's disease, a fatal degenerative movement disorder, results from large numbers of codon repeats in the Huntingtin gene located on chromosome 4. This means that the
A) extra codon repeats will not impact the individual's phenotype.
B) affected Huntington gene will be silenced, producing no protein.
C) affected Huntington gene will produce a protein with abnormally large amounts of the amino acid encoded by the extra codons.
D) affected Huntington gene will produce a protein with abnormally small amounts of the amino acid encoded by the extra codons.
A) extra codon repeats will not impact the individual's phenotype.
B) affected Huntington gene will be silenced, producing no protein.
C) affected Huntington gene will produce a protein with abnormally large amounts of the amino acid encoded by the extra codons.
D) affected Huntington gene will produce a protein with abnormally small amounts of the amino acid encoded by the extra codons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Javier and Alyssa are brother and sister, and both have O type blood. They know that their mother has type A blood, but do not know their father's blood type. Given this information, what could their father's blood type be?
A) could be A, B, or O
B) must be O
C) must be A
D) could be AB or O
A) could be A, B, or O
B) must be O
C) must be A
D) could be AB or O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
An allele that produces a phenotypical trait regardless of whether or not its pair is homozygous or heterozygous is
A) imprinted.
B) dominant.
C) recessive.
D) an SNP.
A) imprinted.
B) dominant.
C) recessive.
D) an SNP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Sarah's mother has Huntington's disease, an illness that results from a dominant gene. Her father, on the other hand, does not have the illness. What is the likelihood that Sarah herself will develop the disease?
A) Sarah has no chance of developing the disease, as she would have inherited a healthy allele from her father.
B) Sarah has a 50 percent chance of developing the disease, as her mother could have given her either a healthy allele or an allele that produces the illness.
C) Sarah has a 50 percent chance of developing the disease, because her mother would not have the disease herself unless she was homozygous for Huntington's disease.
D) Sarah has a 25 percent chance of developing the disease, because her father could be a carrier.
A) Sarah has no chance of developing the disease, as she would have inherited a healthy allele from her father.
B) Sarah has a 50 percent chance of developing the disease, as her mother could have given her either a healthy allele or an allele that produces the illness.
C) Sarah has a 50 percent chance of developing the disease, because her mother would not have the disease herself unless she was homozygous for Huntington's disease.
D) Sarah has a 25 percent chance of developing the disease, because her father could be a carrier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In which of the following cells would you NOT find the same deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) as any of the other trillions of cells in your body?
A) red blood cells
B) leukocytes
C) white blood cells
D) basophils
A) red blood cells
B) leukocytes
C) white blood cells
D) basophils

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Nancy and Cliff had four children who did not have cystic fibrosis, but their fifth child was born with the disease. Cystic fibrosis is carried on a recessive gene. Given what you've learned in this chapter, how could this happen?
A) It wasn't until the fifth child that both parents passed on the allele for this illness.
B) Recessive genes normally skip a generation, but after the parents had five children, the gene was expressed.
C) Their fifth child must have been a boy, which makes it more probable that he would have the illness.
D) Their fifth child must have been a girl, which makes it more probable that she would have the illness.
A) It wasn't until the fifth child that both parents passed on the allele for this illness.
B) Recessive genes normally skip a generation, but after the parents had five children, the gene was expressed.
C) Their fifth child must have been a boy, which makes it more probable that he would have the illness.
D) Their fifth child must have been a girl, which makes it more probable that she would have the illness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In cases of partial dominance, a heterozygous offspring of two homozygous parents will
A) have a phenotype similar to the parent with dominant alleles.
B) have a phenotype similar to the parent with recessive alleles.
C) have phenotypes from both parents.
D) have a phenotype midway between the phenotypes of the homozygous parents.
A) have a phenotype similar to the parent with dominant alleles.
B) have a phenotype similar to the parent with recessive alleles.
C) have phenotypes from both parents.
D) have a phenotype midway between the phenotypes of the homozygous parents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A single human can produce eggs or sperm with more than _________ different combinations of his or her chromosomes.
A) 800
B) 8,000
C) 800,000
D) 8,000,000
A) 800
B) 8,000
C) 800,000
D) 8,000,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When either a mother's or father's version of a gene is expressed in a cell, but not both, we refer to the gene as
A) imprinted.
B) dominant.
C) recessive.
D) an SNP.
A) imprinted.
B) dominant.
C) recessive.
D) an SNP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The _____ is the set of all protein encoded and expressed by the genome of an organism.
A) proteome
B) tripheme
C) ribosome
D) codon
A) proteome
B) tripheme
C) ribosome
D) codon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A process that prevents the production of much higher amounts of protein in females than in males is known as
A) X inactivation.
B) imprinting.
C) crossing over.
D) linkage.
A) X inactivation.
B) imprinting.
C) crossing over.
D) linkage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A characteristic that results from genes on the X chromosome that are not duplicated on the Y chromosomes is referred to as being
A) recessive.
B) mutated.
C) an SNP.
D) sex-linked.
A) recessive.
B) mutated.
C) an SNP.
D) sex-linked.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The Minnesota Study of Twins Reared Apart found support for which of the following conclusions?
A) Identical twins are very similar to each other on a number of traits, regardless of whether the correlation for any particular trait was high or low.
B) Identical twins raised together are very similar to each other on a number of traits, but identical twins raised apart are not.
C) Identical twins are very similar on traits that are highly correlated, like fingerprint ridges, but not similar to each other on traits that are not highly correlated, like nonreligious social attitudes.
D) Identical twins are no more similar to each other on highly correlated traits than fraternal twins and non-twin siblings.
A) Identical twins are very similar to each other on a number of traits, regardless of whether the correlation for any particular trait was high or low.
B) Identical twins raised together are very similar to each other on a number of traits, but identical twins raised apart are not.
C) Identical twins are very similar on traits that are highly correlated, like fingerprint ridges, but not similar to each other on traits that are not highly correlated, like nonreligious social attitudes.
D) Identical twins are no more similar to each other on highly correlated traits than fraternal twins and non-twin siblings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Amber and Rachel are identical twins who were raised together, and Nicole and Kayla are identical twins who were adopted by different families at birth. Based on the findings of the Minnesota Study of Twins Reared Apart, what can we expect to see as these girls grow up?
A) Amber and Rachel will be have more similar nonreligious social attitudes than Nicole and Kayla.
B) Amber and Rachel will show about the same similarities in their nonreligious social attitudes as Nicole and Kayla.
C) Amber and Rachel will show less similarity in their nonreligious social attitudes than Nicole and Kayla.
D) None of the twins will share any substantial similarities in nonreligious social attitudes with her twin.
A) Amber and Rachel will be have more similar nonreligious social attitudes than Nicole and Kayla.
B) Amber and Rachel will show about the same similarities in their nonreligious social attitudes as Nicole and Kayla.
C) Amber and Rachel will show less similarity in their nonreligious social attitudes than Nicole and Kayla.
D) None of the twins will share any substantial similarities in nonreligious social attitudes with her twin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Calico cats have splotches of colors of fur arrayed on them, with the color being determined by different alleles of an X chromosome gene. Calico cats
A) can be male or female.
B) are almost always male, because the calico condition is sex-linked.
C) are always female, because the calico condition results from x-inactivation.
D) are the result of spontaneous mutations that do not affect the sex chromosomes.
A) can be male or female.
B) are almost always male, because the calico condition is sex-linked.
C) are always female, because the calico condition results from x-inactivation.
D) are the result of spontaneous mutations that do not affect the sex chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Two important processes that produce lasting but reversible changes in gene expression are histone modification and __________.
A) imprinting
B) crossing-over
C) x-linked gene mapping suppression
D) DNA methylation
A) imprinting
B) crossing-over
C) x-linked gene mapping suppression
D) DNA methylation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
_________ of the genes found on the X chromosome are duplicated on the Y chromosome.
A) All
B) None
C) Most
D) Some
A) All
B) None
C) Most
D) Some

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When variations in a single base are responsible for the difference between two alleles, the resulting condition is known as
A) X inactivation.
B) an imprinted gene.
C) a SNP.
D) a mutation.
A) X inactivation.
B) an imprinted gene.
C) a SNP.
D) a mutation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Red-green color deficiency is due to a recessive gene on the X chromosome. Women can be carriers or have color deficienty, and men are either color deficient or not. If an unaffected male and a female who is a carrier have children, what is your prediction as to the color deficiency status of their children?
A) Half of the couple's daughters, but none of their sons, are likely to have red-green color deficiency.
B) Half of the couple's sons, but none of their daughters, are likely to have red-green color deficiency.
C) None of the couple's children are likely to have red-green color deficiency.
D) All of the couple's children are likely to have red-green color deficiency.
A) Half of the couple's daughters, but none of their sons, are likely to have red-green color deficiency.
B) Half of the couple's sons, but none of their daughters, are likely to have red-green color deficiency.
C) None of the couple's children are likely to have red-green color deficiency.
D) All of the couple's children are likely to have red-green color deficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Extreme skewing in x-inactivation has been linked with which of the following characteristics in offspring?
A) hemophilia
B) colorblindness
C) Alzheimer's disease
D) autoimmune diseases
A) hemophilia
B) colorblindness
C) Alzheimer's disease
D) autoimmune diseases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A mutation of a person's DNA
A) always has negative outcomes.
B) always has positive outcomes.
C) can have positive, negative, or neutral outcomes.
D) has neither positive nor negative outcomes, because they are always recessive.
A) always has negative outcomes.
B) always has positive outcomes.
C) can have positive, negative, or neutral outcomes.
D) has neither positive nor negative outcomes, because they are always recessive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Research has shown that a person's height is about 81 percent heritable, whereas his or her BMI is about 59 percent heritable. Which of the following is the most accurate interpretation of these findings?
A) The variability we see in a population's height is more influenced by genetic factors than the variability we see in the population's weight.
B) Environmental factors account for only 19 percent of a person's height and 41 percent of a person's BMI.
C) We cannot make any conclusions about genetic contributions to either height or weight.
D) Knowing the relative genetic contributions to traits such as height or weight does not allow us to compare these two unrelated characteristics of people.
A) The variability we see in a population's height is more influenced by genetic factors than the variability we see in the population's weight.
B) Environmental factors account for only 19 percent of a person's height and 41 percent of a person's BMI.
C) We cannot make any conclusions about genetic contributions to either height or weight.
D) Knowing the relative genetic contributions to traits such as height or weight does not allow us to compare these two unrelated characteristics of people.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In their study of the heritability of autistic traits among Dutch teens, Rosa Hoekstra and her colleagues were careful to choose participants from a variety of backgrounds and circumstances. Why is careful sampling especially important to studies of heritability?
A) The effects of genetics are most obvious in populations that exclude extreme environmental conditions, such as affluent or very poor families.
B) Environmental influences are magnified in extreme environmental conditions, such as among affluent or very poor families.
C) Extremes of environmental conditions, such as affluent or very poor families, tend to magnify the influence of genetics.
D) These precautions are really not relevant, because heritability cannot be assessed experimentally.
A) The effects of genetics are most obvious in populations that exclude extreme environmental conditions, such as affluent or very poor families.
B) Environmental influences are magnified in extreme environmental conditions, such as among affluent or very poor families.
C) Extremes of environmental conditions, such as affluent or very poor families, tend to magnify the influence of genetics.
D) These precautions are really not relevant, because heritability cannot be assessed experimentally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Different versions of the APOE gene are correlated with the development of
A) hemophilia.
B) color deficiency.
C) breast cancer.
D) Alzheimer's disease.
A) hemophilia.
B) color deficiency.
C) breast cancer.
D) Alzheimer's disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Kyle plants a group of seeds in a pot of enriched soil and provides all the seeds with identical temperature, lighting, and water. When his plants are mature, he notices that they are quite different in height. Which of the following is the best conclusion Kyle could draw from his observations?
A) The differences in the height of his plants are due to equal contributions of environmental and genetic variables.
B) Holding the plants' environment constant has magnified the influence of genetic differences on the height of the plants.
C) Genetic variables are more influential than environmental variables in determining the height of Kyle's plants.
D) Kyle lacks sufficient information to draw any scientific conclusions from his observations.
A) The differences in the height of his plants are due to equal contributions of environmental and genetic variables.
B) Holding the plants' environment constant has magnified the influence of genetic differences on the height of the plants.
C) Genetic variables are more influential than environmental variables in determining the height of Kyle's plants.
D) Kyle lacks sufficient information to draw any scientific conclusions from his observations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Compared with non-twin siblings, fraternal twins
A) experience the same level of genetic and environmental influence.
B) have more genes in common.
C) have fewer environmental influences in common.
D) have more environmental influences in common.
A) experience the same level of genetic and environmental influence.
B) have more genes in common.
C) have fewer environmental influences in common.
D) have more environmental influences in common.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The presence of a recessive allele can
A) only be expressed when paired with a matching allele.
B) influence a genotype but not a phenotype.
C) influence the phenotype of female children but not male children.
D) influence a phenotype when it occurs in chromosome pairs or on the X chromosome of a male.
A) only be expressed when paired with a matching allele.
B) influence a genotype but not a phenotype.
C) influence the phenotype of female children but not male children.
D) influence a phenotype when it occurs in chromosome pairs or on the X chromosome of a male.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Tom's father has hemophilia, but Tom does not have the disease. What are the chances that Tom's children will have hemophilia?
A) Tom's sons will almost certainly have it because Tom will have inherited the recessive gene from this father.
B) Tom's daughters may be carriers, but his sons will not have the gene.
C) All of Tom's children will be carriers, but it will not be expressed until they have children.
D) None of Tom's children will be carriers or have the illness because his X gene came from his mother, who is not a carrier.
A) Tom's sons will almost certainly have it because Tom will have inherited the recessive gene from this father.
B) Tom's daughters may be carriers, but his sons will not have the gene.
C) All of Tom's children will be carriers, but it will not be expressed until they have children.
D) None of Tom's children will be carriers or have the illness because his X gene came from his mother, who is not a carrier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Queen Victoria of England had a son, Leopold, and a great-grandson, Tsarevich Alexei Nikolaevich Romanov of Russia, both of whom had hemophilia. We can conclude that
A) Queen Victoria must have had hemophilia, too.
B) Queen Victoria was a carrier for hemophilia.
C) Queen Victoria's husband, Prince Albert, must have been a carrier.
D) Leopold and Tsarevich Alexei probably developed hemophilia due to a spontaneous mutation, because their female relatives did not have the condition.
A) Queen Victoria must have had hemophilia, too.
B) Queen Victoria was a carrier for hemophilia.
C) Queen Victoria's husband, Prince Albert, must have been a carrier.
D) Leopold and Tsarevich Alexei probably developed hemophilia due to a spontaneous mutation, because their female relatives did not have the condition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In the Minnesota Study of Twins Reared Apart, identical twins were found to be
A) very similar in all characteristics studied, regardless of whether they were raised together or apart.
B) similar in some characteristics studied, but not all, regardless of whether they were raised together or apart.
C) similar in all characteristics studied only if they were raised together.
D) similar in some characteristics studied, but not all, only if they were raised together.
A) very similar in all characteristics studied, regardless of whether they were raised together or apart.
B) similar in some characteristics studied, but not all, regardless of whether they were raised together or apart.
C) similar in all characteristics studied only if they were raised together.
D) similar in some characteristics studied, but not all, only if they were raised together.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In human development, the nervous system develops from which germ layer?
A) the endoderm
B) the mesoderm
C) the ectoderm
D) the blastoderm
A) the endoderm
B) the mesoderm
C) the ectoderm
D) the blastoderm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Cells in the outer layers of the cerebral cortex are the ___________ to begin migrating, and they have the _____________ journey to their final destination.
A) first; shortest
B) first; longest
C) last; shortest
D) last; longest
A) first; shortest
B) first; longest
C) last; shortest
D) last; longest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In human development, which germ layer gives rise to the muscles, connective tissue, and bone and blood vessels?
A) the endoderm
B) the mesoderm
C) the ectoderm
D) the blastoderm
A) the endoderm
B) the mesoderm
C) the ectoderm
D) the blastoderm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
This figure illustrates which of the following processes? (Figure 5.14)
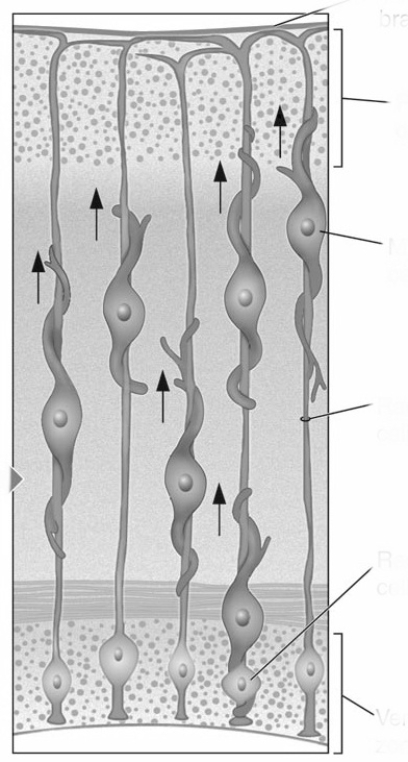
A) Migrating cells follow radial glia from the ventricular zone to the developing cortex.
B) Progenitor cells located in the ventricular zone produce daughter cells that remain in the ventricular zone or migrate.
C) Developing axons adhere to cell adhesion chemicals on the surface of other cells en route to forming synapses with target cells.
D) Guidepost cells release chemicals that either attract or repel growing axons.

A) Migrating cells follow radial glia from the ventricular zone to the developing cortex.
B) Progenitor cells located in the ventricular zone produce daughter cells that remain in the ventricular zone or migrate.
C) Developing axons adhere to cell adhesion chemicals on the surface of other cells en route to forming synapses with target cells.
D) Guidepost cells release chemicals that either attract or repel growing axons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
During which stage of development do new neurons form connections with other neurons?
A) Neurogenesis
B) Migration
C) Synaptogenesis
D) Differentiation
A) Neurogenesis
B) Migration
C) Synaptogenesis
D) Differentiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In human development, this layer develops into most of the internal organs.
A) the endoderm
B) the mesoderm
C) the ectoderm
D) the blastoderm
A) the endoderm
B) the mesoderm
C) the ectoderm
D) the blastoderm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Organization of the ventral neural tube into a motor system is primarily the result of
A) differentiation-inducing factors.
B) apoptosis.
C) Hox genes.
D) guidepost cells.
A) differentiation-inducing factors.
B) apoptosis.
C) Hox genes.
D) guidepost cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The neural plate develops along the _________ midline from cells in the _________.
A) dorsal; ectoderm
B) dorsal; mesoderm
C) ventral; ectoderm
D) ventral; endoderm
A) dorsal; ectoderm
B) dorsal; mesoderm
C) ventral; ectoderm
D) ventral; endoderm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Progenitor cells that divide to produce another progenitor cell and a migrating cell divide along a cleavage line that is _______ to the surface of the ________ zone.
A) perpendicular; dorsal
B) parallel; ventricular
C) perpendicular; dorsolateral
D) parallel; caudal
A) perpendicular; dorsal
B) parallel; ventricular
C) perpendicular; dorsolateral
D) parallel; caudal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Cells that develop into neurons and glia originate in the
A) ventricular zone.
B) radial glia.
C) forebrain.
D) spinal cord.
A) ventricular zone.
B) radial glia.
C) forebrain.
D) spinal cord.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Hox genes appear to be influential in developing the
A) entire brain.
B) spinal cord and hindbrain but not the midbrain or forebrain.
C) hindbrain and midbrain but not the forebrain.
D) spinal cord but not the brain.
A) entire brain.
B) spinal cord and hindbrain but not the midbrain or forebrain.
C) hindbrain and midbrain but not the forebrain.
D) spinal cord but not the brain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
At the peak of neurogenesis in humans, about how many new neural cells are produced per minute?
A) 10,000
B) 75,000
C) 250,000
D) 500,000
A) 10,000
B) 75,000
C) 250,000
D) 500,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
New cells formed at the ventricular zone begin to migrate after the _________ following conception.
A) seventh day
B) seventh week
C) fifth month
D) seventh month
A) seventh day
B) seventh week
C) fifth month
D) seventh month

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
During migration, most neurons are guided to their ultimate location by special progenitor cells known as
A) mitochondria.
B) radial glia.
C) oligodendrocytes.
D) synapses.
A) mitochondria.
B) radial glia.
C) oligodendrocytes.
D) synapses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Differentiation of the hindbrain occurs along the
A) rostral-caudal axis due to the activity of Hox genes.
B) ventral-dorsal dimension due to the activity of Hox genes.
C) rostral-caudal axis due to the activity of sonic hedgehog.
D) ventral-dorsal dimension due to the activity of BMP.
A) rostral-caudal axis due to the activity of Hox genes.
B) ventral-dorsal dimension due to the activity of Hox genes.
C) rostral-caudal axis due to the activity of sonic hedgehog.
D) ventral-dorsal dimension due to the activity of BMP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The interior of the neural tube will be retained in the adult brain as the
A) forebrain.
B) ventricles and central canal of the spinal cord.
C) hindbrain.
D) corpus callosum.
A) forebrain.
B) ventricles and central canal of the spinal cord.
C) hindbrain.
D) corpus callosum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following statements about radial glia is true?
A) They degenerate when migration is complete.
B) They differentiate into astrocytes.
C) They retain the ability to produce daughter cells.
D) They differentiate into neurons.
A) They degenerate when migration is complete.
B) They differentiate into astrocytes.
C) They retain the ability to produce daughter cells.
D) They differentiate into neurons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A(n) _____ is a fertilized egg during the first two weeks of a pregnancy.
A) zygote
B) embryo
C) blastocyst
D) fetus
A) zygote
B) embryo
C) blastocyst
D) fetus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
During weeks 3 to 8 of a pregnancy, the developing organism is called a(n)
A) zygote.
B) embryo.
C) blastocyst.
D) fetus.
A) zygote.
B) embryo.
C) blastocyst.
D) fetus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Cells from the ectoderm of the developing embryo that do not develop into nervous tissue, develop into
A) muscle and bone.
B) connective tissue.
C) skin.
D) internal organs.
A) muscle and bone.
B) connective tissue.
C) skin.
D) internal organs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 147 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



