Deck 3: Reactions of Alkanes: Bond-Dissociation Energies,radical Halogenation,and Relative Reactivity
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/34
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Reactions of Alkanes: Bond-Dissociation Energies,radical Halogenation,and Relative Reactivity
1
What is the major product of the following reaction? 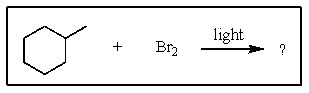
A)
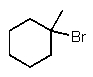
B)
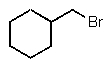
C)
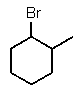
D)
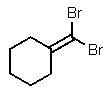
E) no reaction occurs

A)

B)

C)

D)

E) no reaction occurs

2
Hyperconjugation is most useful for stabilizing which of the following?
A) neopentyl radical
B) tert-butyl radical
C) isopropyl radical
D) ethyl radical
E) methyl radical
A) neopentyl radical
B) tert-butyl radical
C) isopropyl radical
D) ethyl radical
E) methyl radical
tert-butyl radical
3
The order of radical stability is:
A) 3° > 2° > 1° > Me
B) 3° < 2° < 1° < Me
C) all are about equal in stability
D) Me > primary
E) tertiary and methyl are equal in stability
A) 3° > 2° > 1° > Me
B) 3° < 2° < 1° < Me
C) all are about equal in stability
D) Me > primary
E) tertiary and methyl are equal in stability
3° > 2° > 1° > Me
4
Which of the following reaction types are typical of alkanes?
A) addition
B) elimination
C) radical substitution
D) reduction
E) more than one of these is correct
A) addition
B) elimination
C) radical substitution
D) reduction
E) more than one of these is correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is a propagation step in the free-radical bromination of methane?
A)
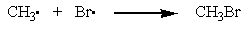
B)
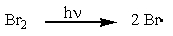
C)

D)
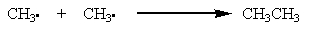
E)

A)
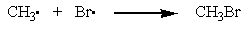
B)
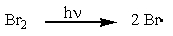
C)

D)
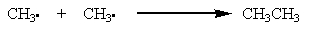
E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the reactions below would you expect to have the largest positive ?
A)
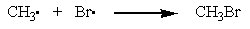
B)
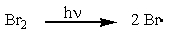
C)

D)
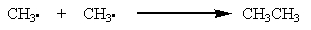
E)

A)
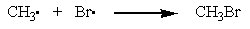
B)
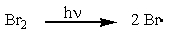
C)

D)
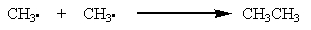
E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Predict the major product of the following reaction: 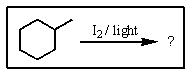
A)
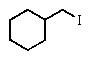
B)
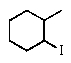
C)
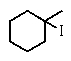
D)
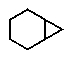
E) no reaction

A)

B)

C)

D)

E) no reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Free-radical fluorination demonstrates little regio-selectivity because
A) fluorine is too small to have steric hinderance.
B) free-radical reactions are never regio-selective.
C) a late transition state is involved.
D) an early transition state is involved.
E) fluorine is too unreactive.
A) fluorine is too small to have steric hinderance.
B) free-radical reactions are never regio-selective.
C) a late transition state is involved.
D) an early transition state is involved.
E) fluorine is too unreactive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Alkanes are noted for their (choose one)
A) high reactivity with acids.
B) toxicity.
C) intense odor.
D) lack of reactivity.
E) water-solubility.
A) high reactivity with acids.
B) toxicity.
C) intense odor.
D) lack of reactivity.
E) water-solubility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is true for an early transition state?
A) The starting materials resemble the products.
B) The reaction proceeds very slowly.
C) The transition state resembles the reactants.
D) The transition state resembles the products.
E) both B and C
A) The starting materials resemble the products.
B) The reaction proceeds very slowly.
C) The transition state resembles the reactants.
D) The transition state resembles the products.
E) both B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Predict the major monofluorination product from the following reaction: 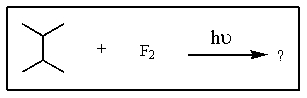
A)
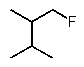
B)
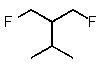
C)
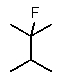
D)
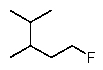
E)
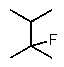

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which,if any,of the following would you choose to accomplish the reaction shown below in the best yield? 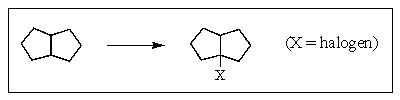
A) F2,light
B) Cl2,light
C) Br2,light
D) I2,light
E) None of the above.

A) F2,light
B) Cl2,light
C) Br2,light
D) I2,light
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In a carbon radical,the carbon possesses how many valence electrons?
A) 4
B) 5
C) 6
D) 7
E) 8
A) 4
B) 5
C) 6
D) 7
E) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the carbon-carbon bonds indicated would be the weakest? 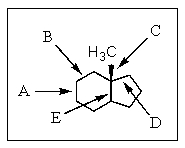
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Predict the major product of the following reaction: 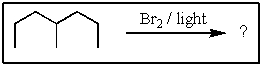
A)
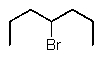
B)
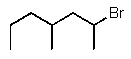
C)
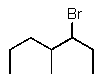
D)
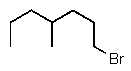
E)
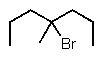

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Given the relative reactivities of various kinds of hydrogens,the major product expected from mono-bromination of 2-methylbutane would be what? 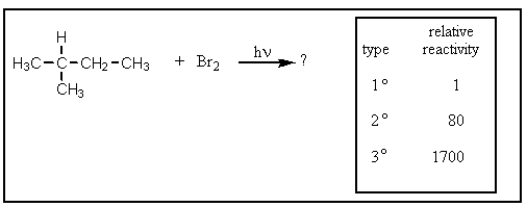
A)
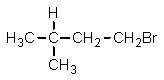
B)
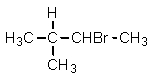
C)
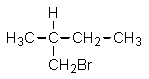
D)
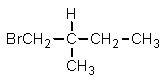
E)
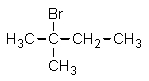

A)
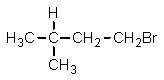
B)
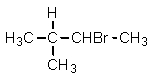
C)
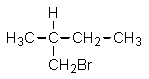
D)
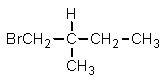
E)
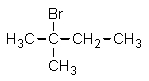

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What reactant is needed to complete and balance the following reaction? 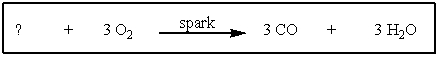
A) C3H8
B) C2H6
C) C3H4
D) C3H6
E) C6H12

A) C3H8
B) C2H6
C) C3H4
D) C3H6
E) C6H12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In a carbon radical,the single unpaired electron resides in:
A) sp2 orbital
B) sp3 orbital
C) s orbital
D) p orbital
E) None of the above.
A) sp2 orbital
B) sp3 orbital
C) s orbital
D) p orbital
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which one of the reactions below will not proceed and accounts for why iodine added to a free-radical chlorination or bromination will greatly slow or even stop the reaction?
A)
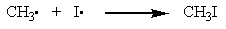
B)
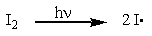
C)

D)

E)

A)
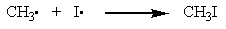
B)
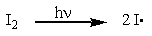
C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is not true of free-radical halogenation reactions?
A) Fluorine is more reactive than chlorine in these reactions.
B) Bromine is more selective than chlorine.
C) The reactions require either light or high temperatures to proceed.
D) Brominations are faster than chlorinations.
E) These reactions are irreversible.
A) Fluorine is more reactive than chlorine in these reactions.
B) Bromine is more selective than chlorine.
C) The reactions require either light or high temperatures to proceed.
D) Brominations are faster than chlorinations.
E) These reactions are irreversible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Carbon dioxide is an essential greenhouse gas that insulates the planet and maintains a surface temperature that allows life to flourish.Human activities have resulted in a dramatic increase in the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.Which of the following reactions produce the most carbon dioxide per mole of carbon-containing starting material? (Note that these equations are not balanced.)
A)
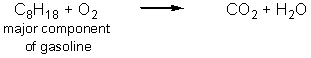
B)
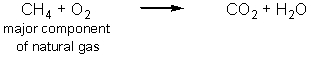
C)

D) All produce the same amount of carbon dioxide.
E) None of these reactions produce carbon dioxide.
A)

B)

C)

D) All produce the same amount of carbon dioxide.
E) None of these reactions produce carbon dioxide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following would you not expect to be formed in even small amounts during the free-radical chlorination of methane?
A) CH2Cl2
B) CH3CH3
C) CHCl3
D) CCl4
E) Some of all of these would be formed.
A) CH2Cl2
B) CH3CH3
C) CHCl3
D) CCl4
E) Some of all of these would be formed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Rank the following radicals in decreasing order of stability. 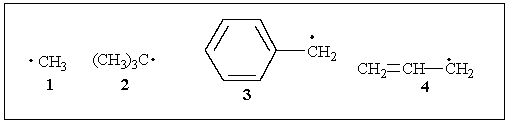
A) 3 > 4 > 2 > 1
B) 3 > 2 > 4 > 1
C) 2 > 3 > 4 > 1
D) 2 > 4 > 3 > 1
E) 1 > 2 > 3 > 4

A) 3 > 4 > 2 > 1
B) 3 > 2 > 4 > 1
C) 2 > 3 > 4 > 1
D) 2 > 4 > 3 > 1
E) 1 > 2 > 3 > 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
How many constitutional isomers can be formed from the monochlorination of the hydrocarbon shown below? 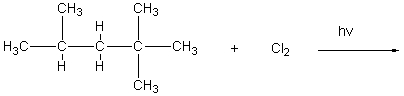
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
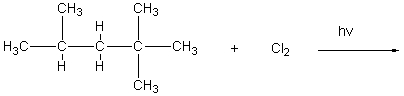
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following hydrocarbons would yield only a single mono-chloro derivative under free radical chlorination conditions? (Cl2/h )
A)
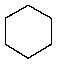
B)
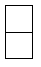
C)
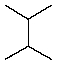
D)
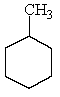
E)
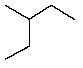
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What reactant is needed to complete and balance the following reaction? 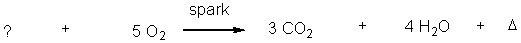
A) C3H8
B) C2H6
C) C3H4
D) C3H6
E) C6H12
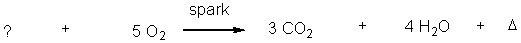
A) C3H8
B) C2H6
C) C3H4
D) C3H6
E) C6H12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Chemists have determined that chlorofluorocarbons are contributing to destruction of the protective ozone layer.Upon irradiation of chlorofluorcarbons,chlorine radicals are produced and react with the ozone via the chemical process shown below.Which of the following statement(s)are true based upon these equations? 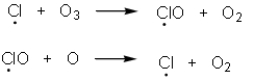
A) Termination steps in the equations above are contributing to ozone depletion.
B) A single chlorine radical is capable of destroying many molecules of ozone since it is regenerated.
C) Chlorine radicals are the result of a heterolytic cleavage of the C-Cl bond of the chlorofluorocarbon.
D) A,B and C are correct.
E) B and C are correct.

A) Termination steps in the equations above are contributing to ozone depletion.
B) A single chlorine radical is capable of destroying many molecules of ozone since it is regenerated.
C) Chlorine radicals are the result of a heterolytic cleavage of the C-Cl bond of the chlorofluorocarbon.
D) A,B and C are correct.
E) B and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which is most true about the function of a catalyst?
A) Catalysts speed up the reaction by lowering the transition state of a reaction.
B) Catalysts usually need higher temperatures to promote reactions.
C) Catalysts lower the energies of the reactants.
D) Catalysts lower the energies of the products.
E) Catalysts increase the yield of the reaction.
A) Catalysts speed up the reaction by lowering the transition state of a reaction.
B) Catalysts usually need higher temperatures to promote reactions.
C) Catalysts lower the energies of the reactants.
D) Catalysts lower the energies of the products.
E) Catalysts increase the yield of the reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which alkane below would you expect to have the lowest heat of combustion?
A)

B)
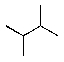
C)
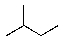
D)
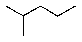
E) All would be the same.
A)

B)

C)

D)

E) All would be the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Given the relative reactivities of various kinds of hydrogens,the major product expected from mono-chlorination of 2-methylbutane would be what? 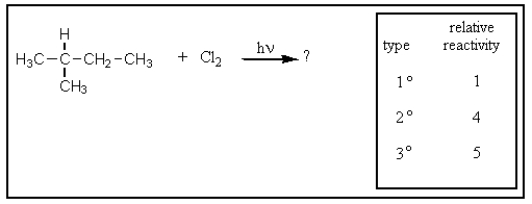
A)
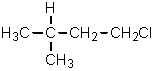
B)
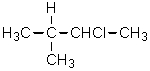
C)
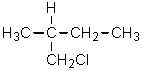
D)
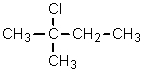
E) There is no way to predict this.

A)
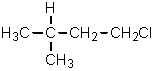
B)
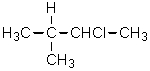
C)
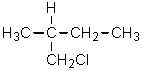
D)

E) There is no way to predict this.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
How many different products will result if radical monobromination of the following compound only occurs at 3° carbons. 
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4

A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Give the relative reactivity in decreasing order for free radical halogenation of (CH3)3CH.
A) F > Cl >Br
B) Cl > Br > F
C) Br > F > Cl
D) Br > Cl > F
E) I > F > Cl
A) F > Cl >Br
B) Cl > Br > F
C) Br > F > Cl
D) Br > Cl > F
E) I > F > Cl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The following reaction represents what type of process? 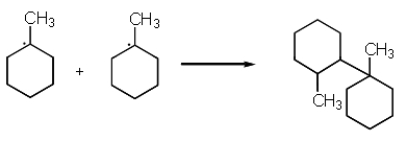
A) Propagation
B) Termination
C) Initiation
D) Nucleophilic addition
E) None of the above.

A) Propagation
B) Termination
C) Initiation
D) Nucleophilic addition
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In a free radical termination step:
A) an initiator starts a chain reaction.
B) free radicals recombine with one another.
C) a radical reacts to form another radical.
D) the activation energy is high.
E) a reactive intermediate is formed.
A) an initiator starts a chain reaction.
B) free radicals recombine with one another.
C) a radical reacts to form another radical.
D) the activation energy is high.
E) a reactive intermediate is formed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



