Deck 5: Atmospheric and Oceanic Circulations
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/116
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Atmospheric and Oceanic Circulations
1
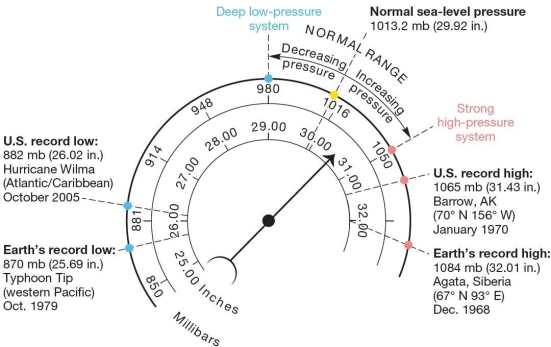 Atmospheric pressure readings and conversions.Scales express barometric air pressure in millibars and inches of mercury (Hg),with average air pressure values and recorded pressure extremes. Normal sea level pressure has a value of
Atmospheric pressure readings and conversions.Scales express barometric air pressure in millibars and inches of mercury (Hg),with average air pressure values and recorded pressure extremes. Normal sea level pressure has a value ofA)1013.2 millibars.
B)28.50 inches of lead.
C)32.01 inches of mercury.
D)500 millibars.
E)32.01 inches of mercury
A
2
An aneroid barometer
A)uses a meter long tube for measuring air pressure.
B)uses a chamber that expands or contracts with changes in air pressure.
C)requires the use of mercury.
D)is a hypothetical instrument for measuring air pressure.
E)is placed in a white louvered box.
A)uses a meter long tube for measuring air pressure.
B)uses a chamber that expands or contracts with changes in air pressure.
C)requires the use of mercury.
D)is a hypothetical instrument for measuring air pressure.
E)is placed in a white louvered box.
B
3
A(n)is an instrument used to measure wind speed.
A)anemometer
B)wind vane
C)barometer
D)sling psychrometer
E)thermometer
A)anemometer
B)wind vane
C)barometer
D)sling psychrometer
E)thermometer
A
4
A(n)is an instrument used to measure wind direction.
A)anemometer
B)wind vane
C)barometer
D)sling psychrometer
E)thermometer
A)anemometer
B)wind vane
C)barometer
D)sling psychrometer
E)thermometer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
An increase in air pressure will cause the mercury in a barometer to
A)rise.
B)fall.
C)freeze.
D)boil.
E)condense.
A)rise.
B)fall.
C)freeze.
D)boil.
E)condense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The average height of a column of mercury (Hg)in a barometer at sea level is
A)1013 inches.
A)760 mm (76 cm).
B)dependent on the temperature.
C)29.00 millibars.
D)32.01 inches.
A)1013 inches.
A)760 mm (76 cm).
B)dependent on the temperature.
C)29.00 millibars.
D)32.01 inches.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
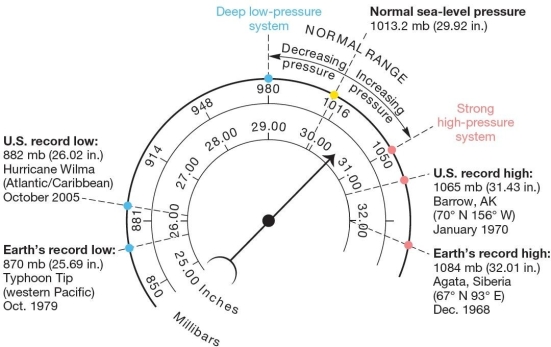 Atmospheric pressure readings and conversions.Scales express barometric air pressure in millibars and inches of mercury (Hg),with average air pressure values and recorded pressure extremes. The Earth's lowest barometric pressures are associated with
Atmospheric pressure readings and conversions.Scales express barometric air pressure in millibars and inches of mercury (Hg),with average air pressure values and recorded pressure extremes. The Earth's lowest barometric pressures are associated withA)hurricanes (typhoons).
B)frontal systems (cold and warm fronts).
C)cold and dry climates.
D)sea level.
E)very cold temperatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
is used in a barometer because .
A)Water;it is liquid at normal air temperature
B)Water;it is denser than mercury
C)Mercury;it will rise more than water will under the same air pressure
D)Mercury;it is denser than water
E)Alcohol;it will not freeze in extreme cold weather
A)Water;it is liquid at normal air temperature
B)Water;it is denser than mercury
C)Mercury;it will rise more than water will under the same air pressure
D)Mercury;it is denser than water
E)Alcohol;it will not freeze in extreme cold weather

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Air flow is initiated by the
A)Coriolis force.
B)pressure gradient force.
C)friction force.
D)centrifugal force.
E)gravitational force.
A)Coriolis force.
B)pressure gradient force.
C)friction force.
D)centrifugal force.
E)gravitational force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is not true of the wind?
A)It is initiated by the pressure gradient force.
B)It blows from regions of high pressure to regions of low pressure.
C)The direction of flow can be affected by the rotation of Earth.
D)Air blows from regions of hotter air to regions of colder air.
E)Winds are named based on the direction from which they blow.
A)It is initiated by the pressure gradient force.
B)It blows from regions of high pressure to regions of low pressure.
C)The direction of flow can be affected by the rotation of Earth.
D)Air blows from regions of hotter air to regions of colder air.
E)Winds are named based on the direction from which they blow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The Beaufort wind scale measures wind speed
A)with an anemometer.
B)by observed effects.
C)using satellites.
D)with a wind vane.
E)utilizing a barometer.
A)with an anemometer.
B)by observed effects.
C)using satellites.
D)with a wind vane.
E)utilizing a barometer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
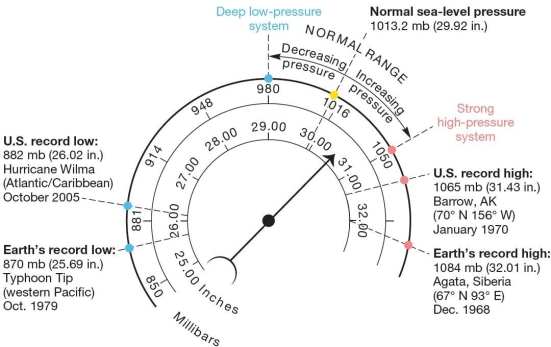 Atmospheric pressure readings and conversions.Scales express barometric air pressure in millibars and inches of mercury (Hg),with average air pressure values and recorded pressure extremes. The highest surface air pressure ever recorded occurred when the air was
Atmospheric pressure readings and conversions.Scales express barometric air pressure in millibars and inches of mercury (Hg),with average air pressure values and recorded pressure extremes. The highest surface air pressure ever recorded occurred when the air wasA)very cold.
B)very hot.
C)very wet.
D)very high above the surface of Earth.
E)moderately warm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is not a determinant of wind speed and direction?
A)electromagnetic force
B)pressure gradient force
C)Coriolis force
D)friction force
E)gravitational force
A)electromagnetic force
B)pressure gradient force
C)Coriolis force
D)friction force
E)gravitational force

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Winds are named based on
A)the direction from which they originate.
B)the direction in which they are blowing.
C)the scientist who first described them.
D)the altitude at which they occur.
E)consensus by the World Meteorological Organization.
A)the direction from which they originate.
B)the direction in which they are blowing.
C)the scientist who first described them.
D)the altitude at which they occur.
E)consensus by the World Meteorological Organization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Evangelista Torricelli developed the first
A)aneroid barometer.
B)mercury barometer.
C)anemometer.
D)water-based barometer.
E)vacuum pump barometer.
A)aneroid barometer.
B)mercury barometer.
C)anemometer.
D)water-based barometer.
E)vacuum pump barometer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Airplanes measure their altitude using
A)a mercury barometer.
B)an anemometer.
C)a hygrometer.
D)an aneroid barometer.
E)sextants.
A)a mercury barometer.
B)an anemometer.
C)a hygrometer.
D)an aneroid barometer.
E)sextants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The horizontal motion of air relative to Earth's surface is
A)barometric pressure.
B)wind.
C)convection flow.
D)a result of equalized pressure across the surface.
E)conduction.
A)barometric pressure.
B)wind.
C)convection flow.
D)a result of equalized pressure across the surface.
E)conduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Evangelista Torricelli,a pupil of Galileo,determined
A)atmospheric pressure is uniform in the troposphere.
B)winds flow from airs of high to low pressure.
C)large-scale circulations of winds.
D)air pressure varied with weather conditions.
E)wind speed is a function of pressure gradients.
A)atmospheric pressure is uniform in the troposphere.
B)winds flow from airs of high to low pressure.
C)large-scale circulations of winds.
D)air pressure varied with weather conditions.
E)wind speed is a function of pressure gradients.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An instrument used to measure air pressure is
A)a wind vane.
B)an aneroid barometer.
C)a mercury thermometer.
D)an anemometer.
E)thermometer.
A)a wind vane.
B)an aneroid barometer.
C)a mercury thermometer.
D)an anemometer.
E)thermometer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
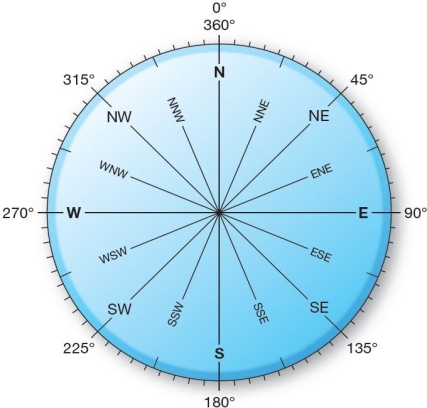 Sixteen wind directions identified on a wind compass.Winds are named for the direction from which they originate. If a wind is blowing from a compass direction of 202.5°,the wind is from the
Sixteen wind directions identified on a wind compass.Winds are named for the direction from which they originate. If a wind is blowing from a compass direction of 202.5°,the wind is from theA)north (N).
B)south (S).
C)northwest (NW).
D)south-southwest (SSW).
E)north-northeast (NNE).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If there is a steeper pressure gradient,wind will be than areas with a gradual pressure gradient.
A)lighter
B)warmer
C)stronger
D)cooler
E)weaker
A)lighter
B)warmer
C)stronger
D)cooler
E)weaker

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
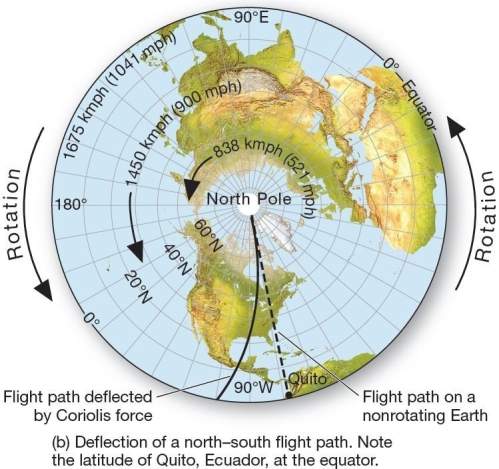 The Coriolis force-an apparent deflection If an airplane flew from the North Pole due south along the 90° meridian and did not correct course,it would land
The Coriolis force-an apparent deflection If an airplane flew from the North Pole due south along the 90° meridian and did not correct course,it would landA)on the 90° meridian.
B)east of the 90° meridian.
C)west of the 90° meridian.
D)north of the 90° meridian.
E)south of the 90° meridian.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A isoline of equal pressure plotted on a weather map is known as an
A)isotherm.
B)isoplat.
C)isobar.
D)isohyet.
E)isobath.
A)isotherm.
B)isoplat.
C)isobar.
D)isohyet.
E)isobath.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is true regarding the effects of the Coriolis force?
A)The amount of Coriolis deflection is uniform from equator to poles.
B)Coriolis deflection occurs only along parallels,not meridians.
C)The Coriolis force is zero at the poles,increasing to maximum along the equator.
D)The strength of the apparent deflection varies with speed of Earth's rotation.
E)Slowly moving objects are deflected more than rapidly moving objects.
A)The amount of Coriolis deflection is uniform from equator to poles.
B)Coriolis deflection occurs only along parallels,not meridians.
C)The Coriolis force is zero at the poles,increasing to maximum along the equator.
D)The strength of the apparent deflection varies with speed of Earth's rotation.
E)Slowly moving objects are deflected more than rapidly moving objects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
On a weather map of air pressure,what can you infer from a closer spacing of isobars?
A)little without knowing temperature patterns
B)a steep pressure gradient creating a slower flow of air
C)a steep pressure gradient creating a faster flow of air
D)higher pressures
E)a weak pressure gradient creating a slower flow of air
A)little without knowing temperature patterns
B)a steep pressure gradient creating a slower flow of air
C)a steep pressure gradient creating a faster flow of air
D)higher pressures
E)a weak pressure gradient creating a slower flow of air

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following describes the pressure gradient force?
A)It drives air from areas of higher to lower barometric pressure.
B)It decreases with height above the surface.
C)It causes apparent deflection of winds from a straight path.
D)It is the only force acting on atmospheric flows in the upper troposphere.
E)It exerts a virtually uniform force on the atmosphere.
A)It drives air from areas of higher to lower barometric pressure.
B)It decreases with height above the surface.
C)It causes apparent deflection of winds from a straight path.
D)It is the only force acting on atmospheric flows in the upper troposphere.
E)It exerts a virtually uniform force on the atmosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The deflection produced by the Coriolis force is caused by
A)Earth's rotation on its axis.
B)differing pressure gradients.
C)friction caused by gravitational force.
D)air temperature differences.
E)the uneven heating of Earth's surface.
A)Earth's rotation on its axis.
B)differing pressure gradients.
C)friction caused by gravitational force.
D)air temperature differences.
E)the uneven heating of Earth's surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The frictional force effect on winds
A)is lessened in areas with rougher surfaces.
B)is negligible at altitudes above 500 m (~1,600 ft).
C)increases with increasing altitude.
D)is constant,regardless of time of day or year.
E)increases with altitude.
A)is lessened in areas with rougher surfaces.
B)is negligible at altitudes above 500 m (~1,600 ft).
C)increases with increasing altitude.
D)is constant,regardless of time of day or year.
E)increases with altitude.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which is true of air flowing into low pressure center?
A)Air converges and ascends.
B)Air diverges and ascends.
C)Air converges and descends.
D)Air diverges and descends.
E)The air movement is called anticyclonic.
A)Air converges and ascends.
B)Air diverges and ascends.
C)Air converges and descends.
D)Air diverges and descends.
E)The air movement is called anticyclonic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Upper tropospheric winds that flow parallel to isobars are called
A)geostrophic winds.
B)NE trades winds.
C)easterlies.
D)westerlies.
E)Hadley cells.
A)geostrophic winds.
B)NE trades winds.
C)easterlies.
D)westerlies.
E)Hadley cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
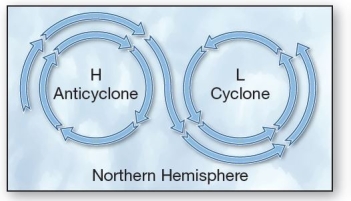 Three physical forces that produce winds: pressure gradient,Coriolis,and friction. The figure shows examples of
Three physical forces that produce winds: pressure gradient,Coriolis,and friction. The figure shows examples ofA)a high pressure center (anticyclone).
B)winds influenced by the pressure gradient force only.
C)wind movement based on the frictional force only.
D)geostrophic winds.
E)winds influenced by the Coriolis force only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The Coriolis force
A)drives air from areas of higher to lower barometric pressure.
B)decreases with height above the surface.
C)causes the apparent deflection of winds from a straight path.
D)is the only force acting on flows of air in the upper troposphere.
E)exerts a virtually uniform force on the atmosphere.
A)drives air from areas of higher to lower barometric pressure.
B)decreases with height above the surface.
C)causes the apparent deflection of winds from a straight path.
D)is the only force acting on flows of air in the upper troposphere.
E)exerts a virtually uniform force on the atmosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In the absence of friction,the combined effect of the Coriolis force and the pressure gradient force produces
A)geostrophic winds at altitude above the ground.
B)surface winds.
C)air flow from low to high pressure centers.
D)air flow in a north-south direction.
E)air flow perpendicular to the isobars.
A)geostrophic winds at altitude above the ground.
B)surface winds.
C)air flow from low to high pressure centers.
D)air flow in a north-south direction.
E)air flow perpendicular to the isobars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If surface winds were influenced only by the pressure gradient force and Coriolis force (i.e. ,without the frictional force),
A)winds would flow in a straight line from areas of higher to lower pressure.
B)winds would flow parallel to isobars and at high rates of speed.
C)there would be no winds at all.
D)the effects would vary depending on surface texture.
E)wind speed and direction would be reduced.
A)winds would flow in a straight line from areas of higher to lower pressure.
B)winds would flow parallel to isobars and at high rates of speed.
C)there would be no winds at all.
D)the effects would vary depending on surface texture.
E)wind speed and direction would be reduced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
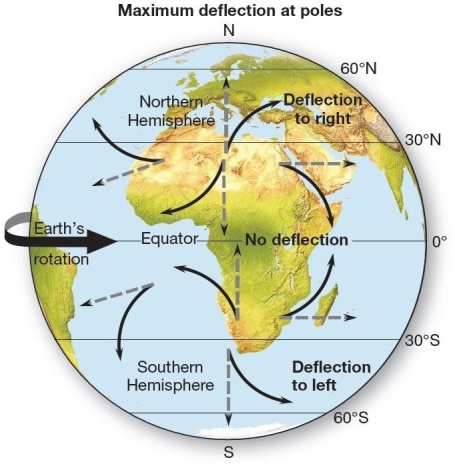 The Coriolis force-an apparent deflection Objects and wind moving over distance and time on Earth's surface are
The Coriolis force-an apparent deflection Objects and wind moving over distance and time on Earth's surface areA)always deflected from a straight path to the west in the Southern Hemisphere.
B)affected only by the pressure gradient and friction force.
C)always deflected to the right by the friction force.
D)apparently deflected from a straight path to the right in the Northern Hemisphere.
E)uniformly affected regardless of the latitude at which the objects and winds are found.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following would cause the Coriolis force to increase?
A)increase in wind speed
B)occurrence closer to the equator
C)increase in friction
D)movement over very small areas
E)Nothing;the Coriolis force is a constant.
A)increase in wind speed
B)occurrence closer to the equator
C)increase in friction
D)movement over very small areas
E)Nothing;the Coriolis force is a constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is true of high pressure areas?
A)Air ascends and converges.
B)Air descends and diverges.
C)Air ascends and diverges.
D)Air descends and converges.
E)They are called cyclones.
A)Air ascends and converges.
B)Air descends and diverges.
C)Air ascends and diverges.
D)Air descends and converges.
E)They are called cyclones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If Earth did not rotate,air would flow
A)perpendicular to the isobars,i.e. ,straight across the isobars.
B)to the right of its direction of motion in the Northern Hemisphere.
C)to the left of its direction of motion in the Northern Hemisphere.
D)parallel to the isobars.
E)in a circular pattern.
A)perpendicular to the isobars,i.e. ,straight across the isobars.
B)to the right of its direction of motion in the Northern Hemisphere.
C)to the left of its direction of motion in the Northern Hemisphere.
D)parallel to the isobars.
E)in a circular pattern.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In the Northern Hemispheres,winds spiraling counterclockwise into a low pressure area are
A)cyclonic.
B)anticyclonic.
C)geostrophic..
D)meridional.
E)Coriolis.
A)cyclonic.
B)anticyclonic.
C)geostrophic..
D)meridional.
E)Coriolis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Air flow in a Northern Hemisphere high pressure zone is
A)downward,outward and clockwise.
B)downward,outward and counterclockwise.
C)inward,upward and clockwise.
D)inward,upward and counterclockwise.
E)downward,inward and clockwise.
A)downward,outward and clockwise.
B)downward,outward and counterclockwise.
C)inward,upward and clockwise.
D)inward,upward and counterclockwise.
E)downward,inward and clockwise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The Aleutian low and Icelandic low are
A)dominant in the winter and weaken or disappear in the summer.
B)dominant in the summer and weaken or disappear in the winter.
C)dominant in the spring and fall and weaken or disappear in the summer and winter.
D)dominant year-round,but tend to be strongest in the summer.
E)dominant in the summer and winter and weaken or disappear in the spring and fall.
A)dominant in the winter and weaken or disappear in the summer.
B)dominant in the summer and weaken or disappear in the winter.
C)dominant in the spring and fall and weaken or disappear in the summer and winter.
D)dominant year-round,but tend to be strongest in the summer.
E)dominant in the summer and winter and weaken or disappear in the spring and fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is associated with the Sahara and the Arabian Deserts?
A)subpolar lows
B)world's equatorial rain forests
C)subtropical high pressure
D)major agricultural regions
E)intertropical convergence zone
A)subpolar lows
B)world's equatorial rain forests
C)subtropical high pressure
D)major agricultural regions
E)intertropical convergence zone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
On Earth between 30° north and the equator,winds flow from the as they flow out of the pressure zone toward the ITCZ.
A)NE;subtropical high
B)NW;subtropical high
C)SE;subtropical high
D)SW;subtropical high
E)NE;polar high
A)NE;subtropical high
B)NW;subtropical high
C)SE;subtropical high
D)SW;subtropical high
E)NE;polar high

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Between 20° to 35° north and 20° to 35° south are
A)the largest zone of water surpluses in the world.
B)warm and wet conditions,and the world's great tropical forests.
C)the world's arid and semi-arid desert regions.
D)cyclonic systems of low pressure.
E)converging winds resulting in moist,warm rising air.
A)the largest zone of water surpluses in the world.
B)warm and wet conditions,and the world's great tropical forests.
C)the world's arid and semi-arid desert regions.
D)cyclonic systems of low pressure.
E)converging winds resulting in moist,warm rising air.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
During the winter,the Bermuda High migrates to the and becomes the .
A)east;Aleutian Low
B)west;Pacific High
C)west;Aleutian Low
D)west;Azores High
E)east;Azores High
A)east;Aleutian Low
B)west;Pacific High
C)west;Aleutian Low
D)west;Azores High
E)east;Azores High

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Winds that blow predominantly from the northeast and the southeast and converging at the ITCZ are the
A)westerlies.
B)polar easterlies.
C)horse latitudes.
D)trade winds.
E)jet streams.
A)westerlies.
B)polar easterlies.
C)horse latitudes.
D)trade winds.
E)jet streams.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following is an example of primary circulation?
A)migratory high and low pressure systems
B)the monsoons
C)general circulation of the atmosphere
D)land and sea breezes
E)Santa Ana winds
A)migratory high and low pressure systems
B)the monsoons
C)general circulation of the atmosphere
D)land and sea breezes
E)Santa Ana winds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following primary pressure areas are produced by thermal factors,rather than dynamic factors?
A)subtropical high and subpolar low
B)equatorial low and polar high
C)equatorial low and Bermuda High
D)Aleutian Low and Icelandic Low
E)Azores High and Icelandic Low
A)subtropical high and subpolar low
B)equatorial low and polar high
C)equatorial low and Bermuda High
D)Aleutian Low and Icelandic Low
E)Azores High and Icelandic Low

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Calm winds associated weak pressure gradient and the vertical ascent of air in the ITCZ are known as
A)Hadley cells.
B)the horse latitudes.
C)the doldrums.
D)westerlies.
E)Azores High.
A)Hadley cells.
B)the horse latitudes.
C)the doldrums.
D)westerlies.
E)Azores High.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ)is associated with
A)the horse latitudes.
B)the principal midlatitude circulations.
C)the equatorial low-pressure trough.
D)subtropical high-pressure development.
E)year-round exceptionally dry conditions.
A)the horse latitudes.
B)the principal midlatitude circulations.
C)the equatorial low-pressure trough.
D)subtropical high-pressure development.
E)year-round exceptionally dry conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is an example of tertiary circulation?
A)migratory high and low pressure systems
B)subtropical high pressure systems
C)general circulation of the atmosphere
D)weather patterns
E)land-sea breezes
A)migratory high and low pressure systems
B)subtropical high pressure systems
C)general circulation of the atmosphere
D)weather patterns
E)land-sea breezes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following primary pressure areas are produced by dynamic factors,rather than thermal factors?
A)subtropical high and subpolar low
B)equatorial low and polar high
C)equatorial low and Bermuda high
D)polar high and Icelandic Low
E)Azores High and equatorial low
A)subtropical high and subpolar low
B)equatorial low and polar high
C)equatorial low and Bermuda high
D)polar high and Icelandic Low
E)Azores High and equatorial low

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is true of Hadley cells?
A)They dominate the polar circulation.
B)Upper-air flow moves northward and southward into the subtropics.
C)They are associated with the subpolar low pressure systems.
D)They occur at great depth in the oceans.
E)The westerlies emerge as a result of these cells.
A)They dominate the polar circulation.
B)Upper-air flow moves northward and southward into the subtropics.
C)They are associated with the subpolar low pressure systems.
D)They occur at great depth in the oceans.
E)The westerlies emerge as a result of these cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The winds converging at the equatorial low are known as
A)polar easterlies.
B)westerlies.
C)doldrums.
D)jet streams.
E)trade winds.
A)polar easterlies.
B)westerlies.
C)doldrums.
D)jet streams.
E)trade winds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is an example of secondary circulation?
A)migratory high and low pressure systems
B)weather patterns
C)general circulation of the atmosphere
D)mountain and valley breezes
E)Santa Ana winds
A)migratory high and low pressure systems
B)weather patterns
C)general circulation of the atmosphere
D)mountain and valley breezes
E)Santa Ana winds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following is not true of the intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ)?
A)Constant high Sun altitude and daylength create energy surpluses.
B)Warm,moisture-laden airs converge along the ITCZ.
C)A band of precipitation is associated with the ITCZ.
D)Lighter,less dense air,rising air characterize the ITCZ.
E)The ITCZ is stationary throughout the year.
A)Constant high Sun altitude and daylength create energy surpluses.
B)Warm,moisture-laden airs converge along the ITCZ.
C)A band of precipitation is associated with the ITCZ.
D)Lighter,less dense air,rising air characterize the ITCZ.
E)The ITCZ is stationary throughout the year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Regions of windless,hot,dry air in the subtropical highs are colloquially known as
A)Hadley cells.
B)the doldrums.
C)the horse latitudes.
D)westerlies.
E)ITCZ.
A)Hadley cells.
B)the doldrums.
C)the horse latitudes.
D)westerlies.
E)ITCZ.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The tropical atmospheric circulation associated with rising winds along the intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ)and descending air in the subtropics are called
A)polar cells.
B)Ferrel cells.
C)Rosby waves.
D)Hadley cells.
E)jet streams.
A)polar cells.
B)Ferrel cells.
C)Rosby waves.
D)Hadley cells.
E)jet streams.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following matches is incorrect relative to air circulation?
A)anticyclone - high pressure center
B)cyclone - low pressure center
C)anticyclone - clockwise circulation in the Southern Hemisphere
D)cyclone - counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere
E)cyclone - clockwise circulation in the Southern Hemisphere
A)anticyclone - high pressure center
B)cyclone - low pressure center
C)anticyclone - clockwise circulation in the Southern Hemisphere
D)cyclone - counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere
E)cyclone - clockwise circulation in the Southern Hemisphere

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The intertropical convergence zone is characterized by
A)convergence and uplift of warm surface air.
B)convergence and subsidence of cold surface air.
C)divergence and uplift of warm surface air.
D)divergence and subsidence of cold surface air.
E)low rainfall and cool conditions.
A)convergence and uplift of warm surface air.
B)convergence and subsidence of cold surface air.
C)divergence and uplift of warm surface air.
D)divergence and subsidence of cold surface air.
E)low rainfall and cool conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Light and variable winds-which caused difficulties for mariners in the days of sailing ships- occur under the
A)subpolar low and equatorial low.
B)subpolar low and subtropical high.
C)equatorial low and subtropical high.
D)equatorial low and subpolar low.
E)westerlies and trade winds.
A)subpolar low and equatorial low.
B)subpolar low and subtropical high.
C)equatorial low and subtropical high.
D)equatorial low and subpolar low.
E)westerlies and trade winds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Sea-breezes
A)result from water heating and cooling faster than land surfaces.
B)form because of higher pressure over the land than the sea.
C)involve onshore (toward the land)air flows that develop in the afternoon.
D)occur because warmer air is denser and settles to the surface of the land.
E)tend to cause higher temperatures on land as winds blow towards the sea.
A)result from water heating and cooling faster than land surfaces.
B)form because of higher pressure over the land than the sea.
C)involve onshore (toward the land)air flows that develop in the afternoon.
D)occur because warmer air is denser and settles to the surface of the land.
E)tend to cause higher temperatures on land as winds blow towards the sea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
During the day along the coast,the wind tends to blow toward the because .
A)land;land heats more rapidly than water
B)land;land heats more slowly than water
C)water;water heats more slowly than land
D)water;water heats more rapidly than land
E)areas of highest pressure;land and water have similar specific heat
A)land;land heats more rapidly than water
B)land;land heats more slowly than water
C)water;water heats more slowly than land
D)water;water heats more rapidly than land
E)areas of highest pressure;land and water have similar specific heat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
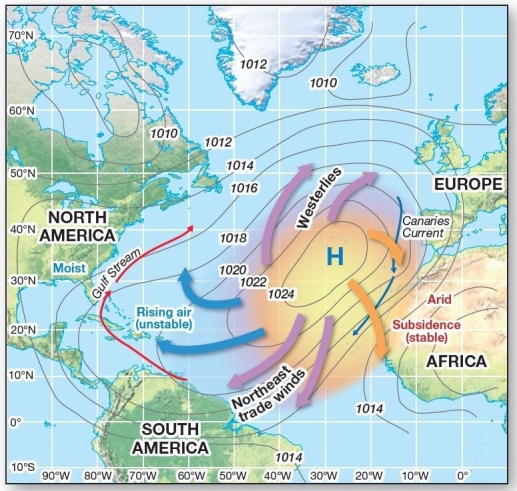 Subtropical high-pressure system in the Atlantic The western side of subtropical high pressure cells
Subtropical high-pressure system in the Atlantic The western side of subtropical high pressure cellsA)tends to be cool and moist.
B)produces surface winds that pass over warm ocean currents.
C)has strong subsidence resulting in dry,semi-arid and arid surface conditions.
D)remains in the same position all year;i.e. ,they do not migrate with the high Sun.
E)corresponds with Earth's major desert regions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
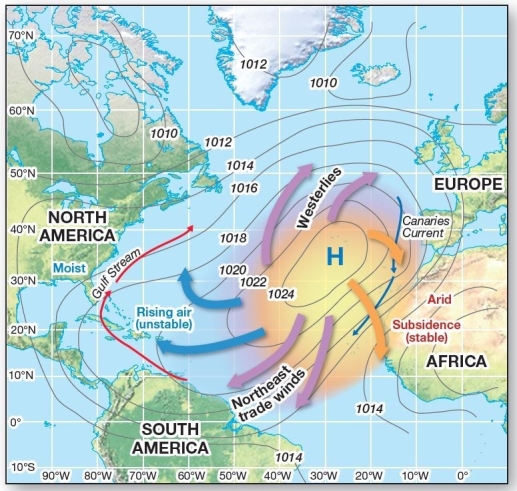 Subtropical high-pressure system in the Atlantic The subtropical high pressure system in the Atlantic and associated cool and warm currents
Subtropical high-pressure system in the Atlantic The subtropical high pressure system in the Atlantic and associated cool and warm currentsA)bring cool waters to the eastern shores of the United States.
B)influence the warm and dry conditions in the Bahamas.
C)circulate warm ocean currents along the western African coast.
D)contribute west African deserts (dry,stable climate).
E)result in heavy rainfall on the western side of continents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following is false regarding the jet streams?
A)Core speeds can exceed 300 kmph (190 mph).
B)They weaken during each of the hemisphere's summer and strengthen during its winter.
C)They occur above the subtropics and the polar front.
D)They have no known effect on surface weather systems.
E)They can be several hundred kilometers wide and over 2 km thick.
A)Core speeds can exceed 300 kmph (190 mph).
B)They weaken during each of the hemisphere's summer and strengthen during its winter.
C)They occur above the subtropics and the polar front.
D)They have no known effect on surface weather systems.
E)They can be several hundred kilometers wide and over 2 km thick.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The polar high pressure cells
A)are the strongest of the four primary pressure areas.
B)are cyclonic in nature.
C)produce the weak,variable polar easterlies.
D)are more pronounced at the North Pole than at the South Pole.
E)are associated with the polar front.
A)are the strongest of the four primary pressure areas.
B)are cyclonic in nature.
C)produce the weak,variable polar easterlies.
D)are more pronounced at the North Pole than at the South Pole.
E)are associated with the polar front.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The most prominent movement in the upper-level westerly geostrophic wind flows are the
A)Rossby waves.
B)jet streams.
C)cyclones.
D)anticyclones.
E)Ferrel cells
A)Rossby waves.
B)jet streams.
C)cyclones.
D)anticyclones.
E)Ferrel cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The area of conflict between colder and warmer air masses in the subpolar region
A)is most distinctive during summer months in each respective hemisphere.
B)is unrelated to the formation of cyclonic storms.
C)is termed the polar front.
D)is referred to as the subtropical contact zone.
E)encircles Earth at about the latitude of the polar high.
A)is most distinctive during summer months in each respective hemisphere.
B)is unrelated to the formation of cyclonic storms.
C)is termed the polar front.
D)is referred to as the subtropical contact zone.
E)encircles Earth at about the latitude of the polar high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which association is incorrect?
A)Equatorial low - Hot/Dry
B)Polar High - Cold/Dry
C)Subpolar low - 60° N/S
D)Subtropical High - 20-35° N/S
E)ITCZ - 20-35° N/S
A)Equatorial low - Hot/Dry
B)Polar High - Cold/Dry
C)Subpolar low - 60° N/S
D)Subtropical High - 20-35° N/S
E)ITCZ - 20-35° N/S

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Mountain and valley breezes
A)are characterized by warmer air descending mountain slopes during the day and valley air ascending the mountain slopes at night.
B)are caused by valley floors heating more quickly than valley slopes during the day and cooling more rapidly at night.
C)involve warm air rising upslope during the day,creating an area of low pressure;at night it is reversed with a low pressure area forming on the valley floor.
D)are secondary wind systems.
E)result from daytime high pressure systems developing upslope.
A)are characterized by warmer air descending mountain slopes during the day and valley air ascending the mountain slopes at night.
B)are caused by valley floors heating more quickly than valley slopes during the day and cooling more rapidly at night.
C)involve warm air rising upslope during the day,creating an area of low pressure;at night it is reversed with a low pressure area forming on the valley floor.
D)are secondary wind systems.
E)result from daytime high pressure systems developing upslope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The 2014 winter storm dubbed the "polar vortex" was associated with moving further south than usual.
A)Hadley cells
B)Rossby waves
C)the jet stream
D)monsoons
E)Ferrel cells
A)Hadley cells
B)Rossby waves
C)the jet stream
D)monsoons
E)Ferrel cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
are waving undulations within the upper-air westerly wind flow.
A)Hadley cells
B)Rossby waves
C)The jet stream
D)Monsoons
E)Ferrel cells
A)Hadley cells
B)Rossby waves
C)The jet stream
D)Monsoons
E)Ferrel cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The polar high pressure system is best characterized as
A)converging and ascending cool air.
B)cold and dry with weak anticyclonic high pressure.
C)strong cyclonic activity during the long summer months.
D)cool and moist year-round.
E)an area of contrast between cold and warm air.
A)converging and ascending cool air.
B)cold and dry with weak anticyclonic high pressure.
C)strong cyclonic activity during the long summer months.
D)cool and moist year-round.
E)an area of contrast between cold and warm air.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Santa Ana winds
A)bring cool,moisture-laden air from the east to the southern California coast.
B)are not associated with pressure gradients in the way other winds are.
C)flow from lower to higher elevation,expanding and cooling in the process.
D)blow eastward,bringing moisture laden air from the Pacific Ocean to the Great Basin.
E)create wildfire conditions by bringing heat and dryness as they flow southwest.
A)bring cool,moisture-laden air from the east to the southern California coast.
B)are not associated with pressure gradients in the way other winds are.
C)flow from lower to higher elevation,expanding and cooling in the process.
D)blow eastward,bringing moisture laden air from the Pacific Ocean to the Great Basin.
E)create wildfire conditions by bringing heat and dryness as they flow southwest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which is true of upper atmospheric circulation?
A)It refers to the winds in the thermosphere.
B)These winds are unrelated to surface weather patterns and of no consequence to the atmosphere's general circulation.
C)Middle and upper tropospheric circulation is an important component of the atmosphere's general circulation.
D)These winds flow principally from the east in the mesosphere.
E)These stratospheric winds are responsible for the movement of CFCs to the poles,contributing to ozone depletion.
A)It refers to the winds in the thermosphere.
B)These winds are unrelated to surface weather patterns and of no consequence to the atmosphere's general circulation.
C)Middle and upper tropospheric circulation is an important component of the atmosphere's general circulation.
D)These winds flow principally from the east in the mesosphere.
E)These stratospheric winds are responsible for the movement of CFCs to the poles,contributing to ozone depletion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Dry,warm downslope winds occurring on the leeward side of Cascades and Rockies are called
A)bora.
B)mistral.
C)chinooks.
D)taku.
E)monsoons.
A)bora.
B)mistral.
C)chinooks.
D)taku.
E)monsoons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
On Earth between 30° and 60° north,winds flow from the as they flow out of the pressure zone toward the pressure zone.
A)northeast;subtropical high;subpolar low
B)west-southwest;subtropical high;subpolar low
C)northeast;subpolar low;subtropical high
D)west-southwest;subpolar low;subtropical high
E)southeast;ITCZ;subtropical high
A)northeast;subtropical high;subpolar low
B)west-southwest;subtropical high;subpolar low
C)northeast;subpolar low;subtropical high
D)west-southwest;subpolar low;subtropical high
E)southeast;ITCZ;subtropical high

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Katabatic winds are
A)localized winds associated with sea-breezes.
B)another name for mountain-valley breezes.
C)unrelated to pressure differences.
D)regional-scale,gravity-driven winds that bring high density air downslope.
E)usually weaker than local winds,but significant due to the area they cover.
A)localized winds associated with sea-breezes.
B)another name for mountain-valley breezes.
C)unrelated to pressure differences.
D)regional-scale,gravity-driven winds that bring high density air downslope.
E)usually weaker than local winds,but significant due to the area they cover.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The dominant surface winds from the subtropics to high latitudes are the
A)westerlies.
B)trade winds.
C)polar easterlies.
D)geostrophic winds.
E)jet streams.
A)westerlies.
B)trade winds.
C)polar easterlies.
D)geostrophic winds.
E)jet streams.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



