Deck 5: Uncertainty and Consumer Behavior
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/144
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Uncertainty and Consumer Behavior
1
Upon graduation,you are offered three jobs. 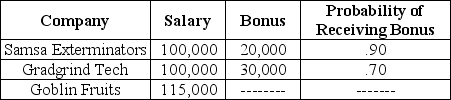 Rank the three job offers in terms of expected income,from the highest to the lowest.
Rank the three job offers in terms of expected income,from the highest to the lowest.
A)Samsa Exterminators,Gradgrind Tech,Goblin Fruits
B)Samsa Exterminators,Goblin Fruits,Gradgrind Tech
C)Gradgrind Tech,Samsa Exterminators,Goblin Fruits
D)Gradgrind Tech,Goblin Fruits,Samsa Exterminators
E)Goblin Fruits,Samsa Exterminators,Gradgrind Tech
 Rank the three job offers in terms of expected income,from the highest to the lowest.
Rank the three job offers in terms of expected income,from the highest to the lowest.A)Samsa Exterminators,Gradgrind Tech,Goblin Fruits
B)Samsa Exterminators,Goblin Fruits,Gradgrind Tech
C)Gradgrind Tech,Samsa Exterminators,Goblin Fruits
D)Gradgrind Tech,Goblin Fruits,Samsa Exterminators
E)Goblin Fruits,Samsa Exterminators,Gradgrind Tech
C
2
Consider the following information about job opportunities for new college graduates in Megalopolis:
Table 5.1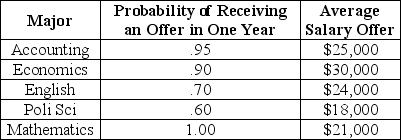
Refer to Table 5.1.Ranked highest to lowest in expected income,the majors are
A)economics,accounting,English,mathematics,political science.
B)mathematics,English,political science,accounting,economics.
C)economics,accounting,mathematics,English,political science.
D)English,economics,mathematics,accounting,political science.
E)accounting,English,mathematics,political science,economics.
Table 5.1

Refer to Table 5.1.Ranked highest to lowest in expected income,the majors are
A)economics,accounting,English,mathematics,political science.
B)mathematics,English,political science,accounting,economics.
C)economics,accounting,mathematics,English,political science.
D)English,economics,mathematics,accounting,political science.
E)accounting,English,mathematics,political science,economics.
C
3
Scenario 5.3:
Wanting to invest in the computer games industry,you select Whizbo,Yowzo and Zowiebo as the three best firms.Over the past 10 years,the three firms have had good years and bad years.The following table shows their performance: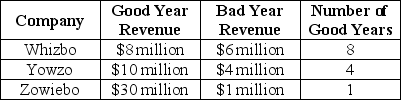
Refer to Scenario 5.3.Where is the highest expected revenue,based on the 10 years' past performance?
A)Whizbo
B)Yowzo
C)Zowiebo
D)Whizbo and Yowzo
E)Yowzo and Zowiebo
Wanting to invest in the computer games industry,you select Whizbo,Yowzo and Zowiebo as the three best firms.Over the past 10 years,the three firms have had good years and bad years.The following table shows their performance:

Refer to Scenario 5.3.Where is the highest expected revenue,based on the 10 years' past performance?
A)Whizbo
B)Yowzo
C)Zowiebo
D)Whizbo and Yowzo
E)Yowzo and Zowiebo
A
4
Scenario 5.3:
Wanting to invest in the computer games industry,you select Whizbo,Yowzo and Zowiebo as the three best firms.Over the past 10 years,the three firms have had good years and bad years.The following table shows their performance:
Refer to Scenario 5.3.Based on the 10 years' past performance,what is the probability of a good year for Zowiebo?
A)30/31
B)1/31
C)0)9
D)0)1
Wanting to invest in the computer games industry,you select Whizbo,Yowzo and Zowiebo as the three best firms.Over the past 10 years,the three firms have had good years and bad years.The following table shows their performance:

Refer to Scenario 5.3.Based on the 10 years' past performance,what is the probability of a good year for Zowiebo?
A)30/31
B)1/31
C)0)9
D)0)1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The information in the table below describes choices for a new doctor.The outcomes represent different macroeconomic environments,which the individual cannot predict.
Table 5.3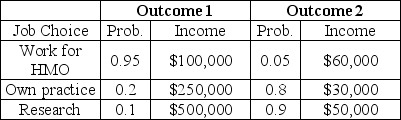
Refer to Table 5.3.Rank the doctor's job choices in order,least risky first.
A)Work for HMO,open own practice,do research
B)Work for HMO,do research,open own practice
C)Do research,open own practice,work for HMO
D)Do research,work for HMO,open own practice
E)Open own practice,work for HMO,do research
Table 5.3

Refer to Table 5.3.Rank the doctor's job choices in order,least risky first.
A)Work for HMO,open own practice,do research
B)Work for HMO,do research,open own practice
C)Do research,open own practice,work for HMO
D)Do research,work for HMO,open own practice
E)Open own practice,work for HMO,do research

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Scenario 5.2:
Randy and Samantha are shopping for new cars (one each).Randy expects to pay $15,000 with 1/5 probability and $20,000 with 4/5 probability.Samantha expects to pay $12,000 with 1/4 probability and $20,000 with 3/4 probability.
Refer to Scenario 5.2.Which of the following is true?
A)Randy has a higher expected expense than Samantha for the car.
B)Randy has a lower expected expense than Samantha for the car.
C)Randy and Samantha have the same expected expense for the car,and it is somewhat less than $20,000.
D)Randy and Samantha have the same expected expense for the car: $20,000.
E)It is not possible to calculate the expected expense for the car until the true probabilities are known.
Randy and Samantha are shopping for new cars (one each).Randy expects to pay $15,000 with 1/5 probability and $20,000 with 4/5 probability.Samantha expects to pay $12,000 with 1/4 probability and $20,000 with 3/4 probability.
Refer to Scenario 5.2.Which of the following is true?
A)Randy has a higher expected expense than Samantha for the car.
B)Randy has a lower expected expense than Samantha for the car.
C)Randy and Samantha have the same expected expense for the car,and it is somewhat less than $20,000.
D)Randy and Samantha have the same expected expense for the car: $20,000.
E)It is not possible to calculate the expected expense for the car until the true probabilities are known.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The information in the table below describes choices for a new doctor.The outcomes represent different macroeconomic environments,which the individual cannot predict.
Table 5.3
In Table 5.3,the standard deviation is
A)highest for the HMO choice,and it is $76,000.
B)lowest for the HMO choice.
C)higher for owning one's own practice than for going into research.
D)higher for the HMO choice than for going into research.
Table 5.3

In Table 5.3,the standard deviation is
A)highest for the HMO choice,and it is $76,000.
B)lowest for the HMO choice.
C)higher for owning one's own practice than for going into research.
D)higher for the HMO choice than for going into research.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The information in the table below describes choices for a new doctor.The outcomes represent different macroeconomic environments,which the individual cannot predict.
Table 5.3
Refer to Table 5.3.The expected returns are highest for the physician who
A)works for an HMO.
B)opens her own practice.
C)does research.
D)either opens her own practice or does research.
E)either works for an HMO or does research.
Table 5.3

Refer to Table 5.3.The expected returns are highest for the physician who
A)works for an HMO.
B)opens her own practice.
C)does research.
D)either opens her own practice or does research.
E)either works for an HMO or does research.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is the advantage of the standard deviation over the average deviation?
A)Because the standard deviation requires squaring of deviations before further computation,positive and negative deviations do not cancel out.
B)Because the standard deviation does not require squaring of deviations,it is easy to tell whether deviations are positive or negative.
C)The standard deviation removes the units from the calculation,and delivers a pure number.
D)The standard deviation expresses the average deviation in percentage terms,so that different choices can be more easily compared.
E)The standard deviation transforms subjective probabilities into objective ones so that calculations can be performed.
A)Because the standard deviation requires squaring of deviations before further computation,positive and negative deviations do not cancel out.
B)Because the standard deviation does not require squaring of deviations,it is easy to tell whether deviations are positive or negative.
C)The standard deviation removes the units from the calculation,and delivers a pure number.
D)The standard deviation expresses the average deviation in percentage terms,so that different choices can be more easily compared.
E)The standard deviation transforms subjective probabilities into objective ones so that calculations can be performed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Scenario 5.2:
Randy and Samantha are shopping for new cars (one each).Randy expects to pay $15,000 with 1/5 probability and $20,000 with 4/5 probability.Samantha expects to pay $12,000 with 1/4 probability and $20,000 with 3/4 probability.
Refer to Scenario 5.2.Randy's expected expense for his car is
A)$20,000.
B)$19,000.
C)$18,000.
D)$17,500.
E)$15,000.
Randy and Samantha are shopping for new cars (one each).Randy expects to pay $15,000 with 1/5 probability and $20,000 with 4/5 probability.Samantha expects to pay $12,000 with 1/4 probability and $20,000 with 3/4 probability.
Refer to Scenario 5.2.Randy's expected expense for his car is
A)$20,000.
B)$19,000.
C)$18,000.
D)$17,500.
E)$15,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The information in the table below describes choices for a new doctor.The outcomes represent different macroeconomic environments,which the individual cannot predict.
Table 5.3
Refer to Table 5.3.Rank the doctor's job options in expected income order,highest first.
A)Work for HMO,open own practice,do research.
B)Work for HMO,do research,open own practice.
C)Do research,open own practice,work for HMO.
D)Do research,work for HMO,open own practice.
E)Open own practice,work for HMO,do research.
Table 5.3

Refer to Table 5.3.Rank the doctor's job options in expected income order,highest first.
A)Work for HMO,open own practice,do research.
B)Work for HMO,do research,open own practice.
C)Do research,open own practice,work for HMO.
D)Do research,work for HMO,open own practice.
E)Open own practice,work for HMO,do research.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Scenario 5.3:
Wanting to invest in the computer games industry,you select Whizbo,Yowzo and Zowiebo as the three best firms.Over the past 10 years,the three firms have had good years and bad years.The following table shows their performance:
Refer to Scenario 5.3.The expected revenue from all three companies combined is
A)$11 million
B)$17.9 million.
C)$25.5 million.
D)$29.5 million.
E)$48 million.
Wanting to invest in the computer games industry,you select Whizbo,Yowzo and Zowiebo as the three best firms.Over the past 10 years,the three firms have had good years and bad years.The following table shows their performance:

Refer to Scenario 5.3.The expected revenue from all three companies combined is
A)$11 million
B)$17.9 million.
C)$25.5 million.
D)$29.5 million.
E)$48 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Consider the following information about job opportunities for new college graduates in Megalopolis:
Table 5.1
Refer to Table 5.1.Expected income for the first year is
A)highest in accounting.
B)highest in mathematics.
C)higher in English than in mathematics.
D)higher in political science than in economics.
E)highest in economics.
Table 5.1

Refer to Table 5.1.Expected income for the first year is
A)highest in accounting.
B)highest in mathematics.
C)higher in English than in mathematics.
D)higher in political science than in economics.
E)highest in economics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Scenario 5.3:
Wanting to invest in the computer games industry,you select Whizbo,Yowzo and Zowiebo as the three best firms.Over the past 10 years,the three firms have had good years and bad years.The following table shows their performance:
Refer to Scenario 5.3.Based on the 10 years' past performance,rank the companies' expected revenue,highest to lowest:
A)Whizbo,Yowzo,Zowiebo
B)Whizbo,Zowiebo,Yowzo
C)Zowiebo,Yowzo,Whizbo
D)Zowiebo,Whizbo,Yowzo
E)Zowiebo,with Whizbo and Yowzo tied for second
Wanting to invest in the computer games industry,you select Whizbo,Yowzo and Zowiebo as the three best firms.Over the past 10 years,the three firms have had good years and bad years.The following table shows their performance:

Refer to Scenario 5.3.Based on the 10 years' past performance,rank the companies' expected revenue,highest to lowest:
A)Whizbo,Yowzo,Zowiebo
B)Whizbo,Zowiebo,Yowzo
C)Zowiebo,Yowzo,Whizbo
D)Zowiebo,Whizbo,Yowzo
E)Zowiebo,with Whizbo and Yowzo tied for second

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Scenario 5.2:
Randy and Samantha are shopping for new cars (one each).Randy expects to pay $15,000 with 1/5 probability and $20,000 with 4/5 probability.Samantha expects to pay $12,000 with 1/4 probability and $20,000 with 3/4 probability.
Refer to Scenario 5.2.Samantha's expected expense for her car is
A)$20,000.
B)$19,000.
C)$18,000.
D)$17,500.
E)$15,000.
Randy and Samantha are shopping for new cars (one each).Randy expects to pay $15,000 with 1/5 probability and $20,000 with 4/5 probability.Samantha expects to pay $12,000 with 1/4 probability and $20,000 with 3/4 probability.
Refer to Scenario 5.2.Samantha's expected expense for her car is
A)$20,000.
B)$19,000.
C)$18,000.
D)$17,500.
E)$15,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The information in the table below describes choices for a new doctor.The outcomes represent different macroeconomic environments,which the individual cannot predict.
Table 5.3
Refer to Table 5.3.In order to weigh which of the job choices is riskiest,an individual should look at
A)the deviation,which is the difference between the probabilities of the two outcomes.
B)the deviation,which is the difference between the dollar amounts of the two outcomes.
C)the average deviation,which is found by averaging the dollar amounts of the two outcomes.
D)the standard deviation,which is the square root of the average squared deviation.
E)the standard deviation,which is the squared average square root of the deviation.
Table 5.3

Refer to Table 5.3.In order to weigh which of the job choices is riskiest,an individual should look at
A)the deviation,which is the difference between the probabilities of the two outcomes.
B)the deviation,which is the difference between the dollar amounts of the two outcomes.
C)the average deviation,which is found by averaging the dollar amounts of the two outcomes.
D)the standard deviation,which is the square root of the average squared deviation.
E)the standard deviation,which is the squared average square root of the deviation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
As president and CEO of MegaWorld industries,you must decide on some very risky alternative investments: 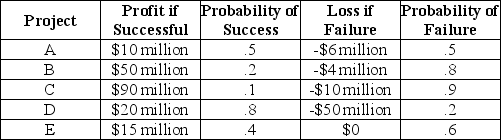 The highest expected return belongs to investment
The highest expected return belongs to investment
A)A)
B)B)
C)C)
D)D)
 The highest expected return belongs to investment
The highest expected return belongs to investmentA)A)
B)B)
C)C)
D)D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Table 5.4 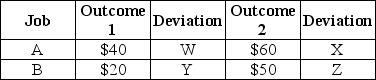
Refer to Table 5.4.If at Job B the $20 outcome occurs with probability .2,and the $50 outcome occurs with probability .8,then in absolute value
A)Y = Z = $6.
B)Y = Z = $24.
C)Y = Z = $35.
D)Y = $24; Z = $6.
E)Y = $6; Z = $24.

Refer to Table 5.4.If at Job B the $20 outcome occurs with probability .2,and the $50 outcome occurs with probability .8,then in absolute value
A)Y = Z = $6.
B)Y = Z = $24.
C)Y = Z = $35.
D)Y = $24; Z = $6.
E)Y = $6; Z = $24.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Table 5.4 
Refer to Table 5.4.If outcomes 1 and 2 are equally likely at Job A,then in absolute value
A)W = X = $10.
B)W = X = $20.
C)W = Y = $100.
D)W = Y = $200.
E)W = Y = $300.

Refer to Table 5.4.If outcomes 1 and 2 are equally likely at Job A,then in absolute value
A)W = X = $10.
B)W = X = $20.
C)W = Y = $100.
D)W = Y = $200.
E)W = Y = $300.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Table 5.4 
Refer to Table 5.4.If outcomes 1 and 2 are equally likely at Job A,then the standard deviation of payoffs at Job A is
A)$1.
B)$10.
C)$40.
D)$50.
E)$60.

Refer to Table 5.4.If outcomes 1 and 2 are equally likely at Job A,then the standard deviation of payoffs at Job A is
A)$1.
B)$10.
C)$40.
D)$50.
E)$60.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following is NOT a generally accepted measure of the riskiness of an investment?
A)Standard deviation
B)Expected value
C)Variance
D)none of the above
A)Standard deviation
B)Expected value
C)Variance
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The expected value is a measure of
A)risk.
B)variability.
C)uncertainty.
D)central tendency.
A)risk.
B)variability.
C)uncertainty.
D)central tendency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Use the following statements to answer this question: I.Subjective probabilities are based on individual perceptions about the relative likelihood of an event.
II)To be useful in microeconomic analysis,all interested parties should agree on the values of the relevant subjective probabilities for a particular problem.
A)I and II are true.
B)I is true and II is false.
C)II is true and I is false.
D)I and II are false.
II)To be useful in microeconomic analysis,all interested parties should agree on the values of the relevant subjective probabilities for a particular problem.
A)I and II are true.
B)I is true and II is false.
C)II is true and I is false.
D)I and II are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The expected value of a project is always the
A)median value of the project.
B)modal value of the project.
C)standard deviation of the project.
D)weighted average of the outcomes,with probabilities of the outcomes used as weights.
A)median value of the project.
B)modal value of the project.
C)standard deviation of the project.
D)weighted average of the outcomes,with probabilities of the outcomes used as weights.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Table 5.4 
Refer to Table 5.4.If at Job B the $20 outcome occurs with probability .2,and the $50 outcome occurs with probability .8,then the standard deviation of payoffs at Job B is nearest which value?
A)$10
B)$12
C)$20
D)$35
E)$44

Refer to Table 5.4.If at Job B the $20 outcome occurs with probability .2,and the $50 outcome occurs with probability .8,then the standard deviation of payoffs at Job B is nearest which value?
A)$10
B)$12
C)$20
D)$35
E)$44

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Assume that two investment opportunities have identical expected values of $100,000.Investment A has a variance of 25,000,while investment B's variance is 10,000.We would expect most investors (who dislike risk)to prefer investment opportunity
A)A because it has less risk.
B)A because it provides higher potential earnings.
C)B because it has less risk.
D)B because of its higher potential earnings.
A)A because it has less risk.
B)A because it provides higher potential earnings.
C)B because it has less risk.
D)B because of its higher potential earnings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Table 5.4 
Refer to Table 5.4.If outcomes 1 and 2 are equally likely at Job A,and if at Job B the $20 outcome occurs with probability .1,and the $50 outcome occurs with probability .9,then
A)Job A is safer because the difference in the probabilities is lower.
B)Job A is riskier only because the expected value is lower.
C)Job A is riskier because the standard deviation is higher.
D)Job B is riskier because the difference in the probabilities is higher.
E)There is no definite way given this information to tell how risky the two jobs are.

Refer to Table 5.4.If outcomes 1 and 2 are equally likely at Job A,and if at Job B the $20 outcome occurs with probability .1,and the $50 outcome occurs with probability .9,then
A)Job A is safer because the difference in the probabilities is lower.
B)Job A is riskier only because the expected value is lower.
C)Job A is riskier because the standard deviation is higher.
D)Job B is riskier because the difference in the probabilities is higher.
E)There is no definite way given this information to tell how risky the two jobs are.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
An investment opportunity has two possible outcomes,and the value of the investment opportunity is $250.One outcome yields a $100 payoff and has a probability of 0.25.What is the probability of the other outcome?
A)0
B)0)25
C)0)5
D)0)75
E)1)0
A)0
B)0)25
C)0)5
D)0)75
E)1)0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An investment opportunity is a sure thing; it will pay off $100 regardless of which of the three possible outcomes comes to pass.The variance of this investment opportunity:
A)is 0.
B)is 1.
C)is 2.
D)is -1.
E)cannot be determined without knowing the probabilities of each of the outcomes.
A)is 0.
B)is 1.
C)is 2.
D)is -1.
E)cannot be determined without knowing the probabilities of each of the outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Scenario 5.4:
Suppose an individual is considering an investment in which there are exactly three possible outcomes,whose probabilities and pay-offs are given below: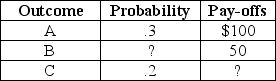 The expected value of the investment is $25.Although all the information is correct,information is missing.
The expected value of the investment is $25.Although all the information is correct,information is missing.
Refer to Scenario 5.4.What is the pay-off of outcome C?
A)-150
B)0
C)25
D)100
E)150
Suppose an individual is considering an investment in which there are exactly three possible outcomes,whose probabilities and pay-offs are given below:
 The expected value of the investment is $25.Although all the information is correct,information is missing.
The expected value of the investment is $25.Although all the information is correct,information is missing.Refer to Scenario 5.4.What is the pay-off of outcome C?
A)-150
B)0
C)25
D)100
E)150

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The variance of an investment opportunity:
A)cannot be negative.
B)has the same unit of measure as the variable from which it is derived.
C)is a measure of central tendency.
D)is unrelated to the standard deviation.
A)cannot be negative.
B)has the same unit of measure as the variable from which it is derived.
C)is a measure of central tendency.
D)is unrelated to the standard deviation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Scenario 5.4:
Suppose an individual is considering an investment in which there are exactly three possible outcomes,whose probabilities and pay-offs are given below: The expected value of the investment is $25.Although all the information is correct,information is missing.
The expected value of the investment is $25.Although all the information is correct,information is missing.
Refer to Scenario 5.4.What is the standard deviation of the investment?
A)0
B)16.58
C)56.12
D)90.14
E)none of the above
Suppose an individual is considering an investment in which there are exactly three possible outcomes,whose probabilities and pay-offs are given below:
 The expected value of the investment is $25.Although all the information is correct,information is missing.
The expected value of the investment is $25.Although all the information is correct,information is missing.Refer to Scenario 5.4.What is the standard deviation of the investment?
A)0
B)16.58
C)56.12
D)90.14
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
People often use probability statements to describe events that can only happen once.For example,a political consultant may offer their opinion about the probability that a particular candidate may win the next election.Probability statements like these are based on __________ probabilities.
A)frequency-based
B)objective
C)subjective
D)universally known
A)frequency-based
B)objective
C)subjective
D)universally known

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Scenario 5.4:
Suppose an individual is considering an investment in which there are exactly three possible outcomes,whose probabilities and pay-offs are given below: The expected value of the investment is $25.Although all the information is correct,information is missing.
The expected value of the investment is $25.Although all the information is correct,information is missing.
Refer to Scenario 5.4.What is the deviation of outcome A?
A)30
B)50
C)75
D)100
Suppose an individual is considering an investment in which there are exactly three possible outcomes,whose probabilities and pay-offs are given below:
 The expected value of the investment is $25.Although all the information is correct,information is missing.
The expected value of the investment is $25.Although all the information is correct,information is missing.Refer to Scenario 5.4.What is the deviation of outcome A?
A)30
B)50
C)75
D)100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
An investment opportunity has two possible outcomes.The expected value of the investment opportunity is $250.One outcome yields a $100 payoff and has a probability of 0.25.What is the payoff of the other outcome?
A)-$400
B)$0
C)$150
D)$300
E)none of the above
A)-$400
B)$0
C)$150
D)$300
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Scenario 5.4:
Suppose an individual is considering an investment in which there are exactly three possible outcomes,whose probabilities and pay-offs are given below: The expected value of the investment is $25.Although all the information is correct,information is missing.
The expected value of the investment is $25.Although all the information is correct,information is missing.
Refer to Scenario 5.4.What is the variance of the investment?
A)-75
B)275
C)3,150
D)4,637.50
E)8,125
Suppose an individual is considering an investment in which there are exactly three possible outcomes,whose probabilities and pay-offs are given below:
 The expected value of the investment is $25.Although all the information is correct,information is missing.
The expected value of the investment is $25.Although all the information is correct,information is missing.Refer to Scenario 5.4.What is the variance of the investment?
A)-75
B)275
C)3,150
D)4,637.50
E)8,125

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The weighted average of all possible outcomes of a project,with the probabilities of the outcomes used as weights,is known as the
A)variance.
B)standard deviation.
C)expected value.
D)coefficient of variation.
A)variance.
B)standard deviation.
C)expected value.
D)coefficient of variation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Scenario 5.4:
Suppose an individual is considering an investment in which there are exactly three possible outcomes,whose probabilities and pay-offs are given below: The expected value of the investment is $25.Although all the information is correct,information is missing.
The expected value of the investment is $25.Although all the information is correct,information is missing.
Refer to Scenario 5.4.What is the probability of outcome B?
A)0
B)-0.5
C)0)5
D)0)4
E)0)2
Suppose an individual is considering an investment in which there are exactly three possible outcomes,whose probabilities and pay-offs are given below:
 The expected value of the investment is $25.Although all the information is correct,information is missing.
The expected value of the investment is $25.Although all the information is correct,information is missing.Refer to Scenario 5.4.What is the probability of outcome B?
A)0
B)-0.5
C)0)5
D)0)4
E)0)2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Assume that one of two possible outcomes will follow a decision.One outcome yields a $75 payoff and has a probability of 0.3; the other outcome has a $125 payoff and has a probability of 0.7.In this case the expected value is
A)$85.
B)$60.
C)$110.
D)$35.
A)$85.
B)$60.
C)$110.
D)$35.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Blanca has her choice of either a certain income of $20,000 or a gamble with a 0.5 probability of $10,000 and a 0.5 probability of $30,000.The expected value of the gamble:
A)is less than $20,000.
B)is $20,000.
C)is greater than $20,000.
D)cannot be determined with the information provided.
A)is less than $20,000.
B)is $20,000.
C)is greater than $20,000.
D)cannot be determined with the information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The difference between the utility of expected income and expected utility from income is
A)zero because income generates utility.
B)positive because if utility from income is uncertain,it is worth less.
C)negative because if income is uncertain,it is worth less.
D)that expected utility from income is calculated by summing the utilities of possible incomes,weighted by their probability of occurring,and the utility of expected income is calculated by summing the possible incomes,weighted by their probability of occurring,and finding the utility of that figure.
E)that the utility of expected income is calculated by summing the utilities of possible incomes,weighted by their probability of occurring,and the expected utility of income is calculated by summing the possible incomes,weighted by their probability of occurring,and finding the utility of that figure.
A)zero because income generates utility.
B)positive because if utility from income is uncertain,it is worth less.
C)negative because if income is uncertain,it is worth less.
D)that expected utility from income is calculated by summing the utilities of possible incomes,weighted by their probability of occurring,and the utility of expected income is calculated by summing the possible incomes,weighted by their probability of occurring,and finding the utility of that figure.
E)that the utility of expected income is calculated by summing the utilities of possible incomes,weighted by their probability of occurring,and the expected utility of income is calculated by summing the possible incomes,weighted by their probability of occurring,and finding the utility of that figure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The concept of a risk premium applies to a person that is
A)risk averse.
B)risk neutral.
C)risk loving.
D)all of the above
A)risk averse.
B)risk neutral.
C)risk loving.
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Any risk-averse individual would always
A)take a 10% chance at $100 rather than a sure $10.
B)take a 50% chance at $4 and a 50% chance at $1 rather than a sure $1.
C)take a sure $10 rather than a 10% chance at $100.
D)take a sure $1 rather than a 50% chance at $4 and a 50% chance at losing $1.
E)do C or D above.
A)take a 10% chance at $100 rather than a sure $10.
B)take a 50% chance at $4 and a 50% chance at $1 rather than a sure $1.
C)take a sure $10 rather than a 10% chance at $100.
D)take a sure $1 rather than a 50% chance at $4 and a 50% chance at losing $1.
E)do C or D above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Scenario 5.6:
Consider the information in the table below,describing choices for a new doctor.The outcomes represent different macroeconomic environments,which the individual cannot predict.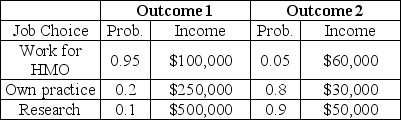
Refer to Scenario 5.6.If the doctor is risk-averse,she would accept
A)$50,000 for sure rather than take the risk of being a researcher.
B)$60,000 for sure (the minimum HMO outcome)rather than take the risk of being a researcher.
C)$95,000 for sure rather than face option 1 and option 2 in research.
D)$275,000 for sure (the average of option 1 and option 2 in research),but not less,rather than face the risk of those two options.
E)the research position because it has the highest possible income.
Consider the information in the table below,describing choices for a new doctor.The outcomes represent different macroeconomic environments,which the individual cannot predict.

Refer to Scenario 5.6.If the doctor is risk-averse,she would accept
A)$50,000 for sure rather than take the risk of being a researcher.
B)$60,000 for sure (the minimum HMO outcome)rather than take the risk of being a researcher.
C)$95,000 for sure rather than face option 1 and option 2 in research.
D)$275,000 for sure (the average of option 1 and option 2 in research),but not less,rather than face the risk of those two options.
E)the research position because it has the highest possible income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
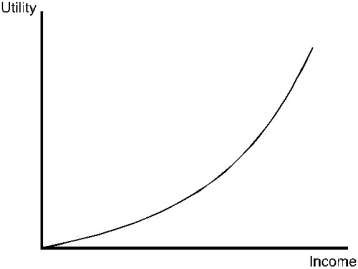 Figure 5.1
Figure 5.1In Figure 5.1,the marginal utility of income is
A)increasing as income increases.
B)constant for all levels of income.
C)diminishes as income increases.
D)None of the above is necessarily correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
 Figure 5.1
Figure 5.1An individual whose attitude toward risk is illustrated in Figure 5.1 is
A)risk averse.
B)risk loving.
C)risk neutral.
D)None of the above is necessarily correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
John Brown's utility of income function is U = log(I+1),where I represents income.From this information you can say that
A)John Brown is risk neutral.
B)John Brown is risk loving.
C)John Brown is risk averse.
D)We need more information before we can determine John Brown's preference for risk.
A)John Brown is risk neutral.
B)John Brown is risk loving.
C)John Brown is risk averse.
D)We need more information before we can determine John Brown's preference for risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A risk-averse individual prefers
A)the utility of expected income of a risky gamble to the expected utility of income of the same risky gamble.
B)the expected utility of income of a risky gamble to the utility of expected income of the same risky gamble.
C)outcomes with 50-50 odds to those with more divergent probabilities,no matter what the dollar outcomes.
D)outcomes with higher probabilities assigned to more favorable outcomes,no matter what the outcomes are.
E)outcomes with highly divergent probabilities so that one of the outcomes is almost certain.
A)the utility of expected income of a risky gamble to the expected utility of income of the same risky gamble.
B)the expected utility of income of a risky gamble to the utility of expected income of the same risky gamble.
C)outcomes with 50-50 odds to those with more divergent probabilities,no matter what the dollar outcomes.
D)outcomes with higher probabilities assigned to more favorable outcomes,no matter what the outcomes are.
E)outcomes with highly divergent probabilities so that one of the outcomes is almost certain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Amos Long's marginal utility of income function is given as: MU(I)= I1.5,where I represents income.From this you would say that he is
A)risk averse.
B)risk loving.
C)risk neutral.
D)none of the above
A)risk averse.
B)risk loving.
C)risk neutral.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Dante has two possible routes to travel on a business trip.One is more direct but more exhausting,taking one day but with a probability of business success of 1/4.The second takes three days,but has a probability of success of 2/3.If the value of Dante's time is $1000/day,the value of the business success is $12,000,and Dante is risk neutral,
A)it doesn't matter which path he takes,because he doesn't consider risk.
B)he should take the 1-day trip,because he doesn't consider risk.
C)he should take the 1-day trip,because $11,000 is greater than $9,000.
D)he should take the 3-day trip,because it will increase his expected net revenue by $3,000.
E)he should take the 3-day trip,because it will increase his expected net revenue by $5,000.
A)it doesn't matter which path he takes,because he doesn't consider risk.
B)he should take the 1-day trip,because he doesn't consider risk.
C)he should take the 1-day trip,because $11,000 is greater than $9,000.
D)he should take the 3-day trip,because it will increase his expected net revenue by $3,000.
E)he should take the 3-day trip,because it will increase his expected net revenue by $5,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Upon graduation,you are offered three jobs. 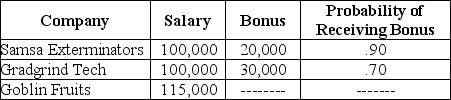 Which of the following is true?
Which of the following is true?
A)If you're risk-neutral,you go work for Goblin Fruits.
B)If you're risk-loving,you go work for Goblin Fruits.
C)If you're risk-neutral,you go work for Samsa Exterminators.
D)If you're risk-neutral,you go work for Gradgrind Tech.
 Which of the following is true?
Which of the following is true?A)If you're risk-neutral,you go work for Goblin Fruits.
B)If you're risk-loving,you go work for Goblin Fruits.
C)If you're risk-neutral,you go work for Samsa Exterminators.
D)If you're risk-neutral,you go work for Gradgrind Tech.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Scenario 5.6:
Consider the information in the table below,describing choices for a new doctor.The outcomes represent different macroeconomic environments,which the individual cannot predict.![<strong>Scenario 5.6: Consider the information in the table below,describing choices for a new doctor.The outcomes represent different macroeconomic environments,which the individual cannot predict. Refer to Scenario 5.6.The utility of expected income from research is</strong> A)U($275,000). B)U($95,000). C)[U($500,000)+ U($50,000)]/2. D))1U($500,000)+ .9U($50,000). E)dependent on which outcome actually occurs.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5357/11eab6bb_2876_df22_b96b_8b4cbbb7a905_TB5357_00_TB5357_00_TB5357_00.jpg)
Refer to Scenario 5.6.The utility of expected income from research is
A)U($275,000).
B)U($95,000).
C)[U($500,000)+ U($50,000)]/2.
D))1U($500,000)+ .9U($50,000).
E)dependent on which outcome actually occurs.
Consider the information in the table below,describing choices for a new doctor.The outcomes represent different macroeconomic environments,which the individual cannot predict.
![<strong>Scenario 5.6: Consider the information in the table below,describing choices for a new doctor.The outcomes represent different macroeconomic environments,which the individual cannot predict. Refer to Scenario 5.6.The utility of expected income from research is</strong> A)U($275,000). B)U($95,000). C)[U($500,000)+ U($50,000)]/2. D))1U($500,000)+ .9U($50,000). E)dependent on which outcome actually occurs.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5357/11eab6bb_2876_df22_b96b_8b4cbbb7a905_TB5357_00_TB5357_00_TB5357_00.jpg)
Refer to Scenario 5.6.The utility of expected income from research is
A)U($275,000).
B)U($95,000).
C)[U($500,000)+ U($50,000)]/2.
D))1U($500,000)+ .9U($50,000).
E)dependent on which outcome actually occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In the figure below,what is true about the two jobs? 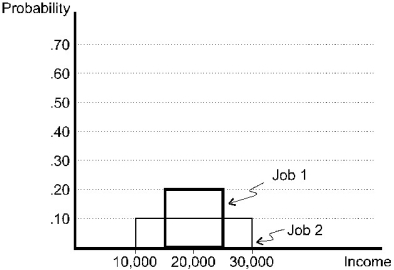
A)Job 1 has a lower standard deviation than Job 2.
B)All outcomes in both jobs have the same probability of occurrence.
C)A risk-averse person would prefer Job 2.
D)A risk-neutral person would prefer Job 1.
E)Job 1 has a higher expected income than Job 2.

A)Job 1 has a lower standard deviation than Job 2.
B)All outcomes in both jobs have the same probability of occurrence.
C)A risk-averse person would prefer Job 2.
D)A risk-neutral person would prefer Job 1.
E)Job 1 has a higher expected income than Job 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
An individual with a constant marginal utility of income will be
A)risk averse.
B)risk neutral.
C)risk loving.
D)insufficient information for a decision
A)risk averse.
B)risk neutral.
C)risk loving.
D)insufficient information for a decision

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Scenario 5.6:
Consider the information in the table below,describing choices for a new doctor.The outcomes represent different macroeconomic environments,which the individual cannot predict.![<strong>Scenario 5.6: Consider the information in the table below,describing choices for a new doctor.The outcomes represent different macroeconomic environments,which the individual cannot predict. Refer to Scenario 5.6.The expected utility of income from research is</strong> A)u($275,000). B)u($95,000). C)[u($500,000)+ u($50,000)]/2. D))1 u($500,000)+ .9 u($50,000). E)dependent on which outcome actually occurs.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5357/11eab6bb_2876_df22_b96b_8b4cbbb7a905_TB5357_00_TB5357_00_TB5357_00.jpg)
Refer to Scenario 5.6.The expected utility of income from research is
A)u($275,000).
B)u($95,000).
C)[u($500,000)+ u($50,000)]/2.
D))1 u($500,000)+ .9 u($50,000).
E)dependent on which outcome actually occurs.
Consider the information in the table below,describing choices for a new doctor.The outcomes represent different macroeconomic environments,which the individual cannot predict.
![<strong>Scenario 5.6: Consider the information in the table below,describing choices for a new doctor.The outcomes represent different macroeconomic environments,which the individual cannot predict. Refer to Scenario 5.6.The expected utility of income from research is</strong> A)u($275,000). B)u($95,000). C)[u($500,000)+ u($50,000)]/2. D))1 u($500,000)+ .9 u($50,000). E)dependent on which outcome actually occurs.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5357/11eab6bb_2876_df22_b96b_8b4cbbb7a905_TB5357_00_TB5357_00_TB5357_00.jpg)
Refer to Scenario 5.6.The expected utility of income from research is
A)u($275,000).
B)u($95,000).
C)[u($500,000)+ u($50,000)]/2.
D))1 u($500,000)+ .9 u($50,000).
E)dependent on which outcome actually occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A person with a diminishing marginal utility of income
A)will be risk averse.
B)will be risk neutral.
C)will be risk loving.
D)cannot decide without more information
A)will be risk averse.
B)will be risk neutral.
C)will be risk loving.
D)cannot decide without more information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Blanca would prefer a certain income of $20,000 to a gamble with a 0.5 probability of $10,000 and a 0.5 probability of $30,000.Based on this information:
A)we can infer that Blanca neutral.
B)we can infer that Blanca is risk averse.
C)we can infer that Blanca is risk loving.
D)we cannot infer Blanca's risk preferences.
A)we can infer that Blanca neutral.
B)we can infer that Blanca is risk averse.
C)we can infer that Blanca is risk loving.
D)we cannot infer Blanca's risk preferences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What would best explain why a generally risk-averse person would bet $100 during a night of blackjack in Las Vegas?
A)Risk aversion relates to income choices only,not expenditure choices.
B)Risk averse people may gamble under some circumstances.
C)The economics of gambling and the economics of income risk are two different things.
D)Risk-averse people attach high subjective probabilities to favorable outcomes,even when objective probabilities are known.
A)Risk aversion relates to income choices only,not expenditure choices.
B)Risk averse people may gamble under some circumstances.
C)The economics of gambling and the economics of income risk are two different things.
D)Risk-averse people attach high subjective probabilities to favorable outcomes,even when objective probabilities are known.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In figure below,what is true about the two jobs? 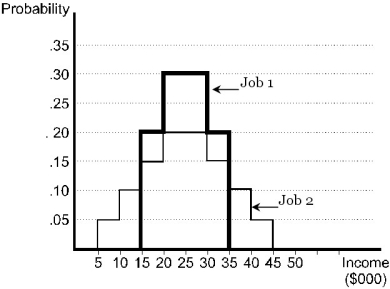
A)Job 1 has a larger standard deviation than Job 2.
B)All outcomes in both jobs have the same probability of occurrence.
C)A risk-averse person would prefer Job 2.
D)A risk-neutral person would prefer Job 1.
E)Job 1 has the same expected income as Job 2.

A)Job 1 has a larger standard deviation than Job 2.
B)All outcomes in both jobs have the same probability of occurrence.
C)A risk-averse person would prefer Job 2.
D)A risk-neutral person would prefer Job 1.
E)Job 1 has the same expected income as Job 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A risk-averse individual has
A)an increasing marginal utility of income.
B)an increasing marginal utility of risk.
C)a diminishing marginal utility of income.
D)a diminishing marginal utility of risk.
E)a constant marginal utility of income,but a diminishing marginal utility of risk.
A)an increasing marginal utility of income.
B)an increasing marginal utility of risk.
C)a diminishing marginal utility of income.
D)a diminishing marginal utility of risk.
E)a constant marginal utility of income,but a diminishing marginal utility of risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
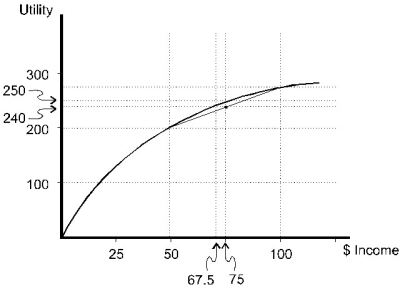 Figure 5.2
Figure 5.2The individual pictured in Figure 5.2
A)must be risk-averse.
B)must be risk-neutral.
C)must be risk-loving.
D)could be risk-averse,risk-neutral,or risk-loving.
E)could be risk-averse or risk-loving,but not risk-neutral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Scenario 5.7:
As president and CEO of MegaWorld industries,Natasha must decide on some very risky alternative investments.Consider the following: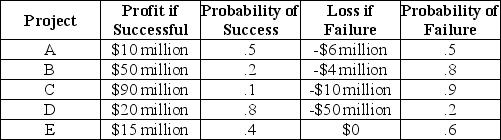
Refer to Scenario 5.7.Since Natasha is a risk-neutral executive,she would choose
A)A)
B)B)
C)C)
D)D)
E)E)
As president and CEO of MegaWorld industries,Natasha must decide on some very risky alternative investments.Consider the following:

Refer to Scenario 5.7.Since Natasha is a risk-neutral executive,she would choose
A)A)
B)B)
C)C)
D)D)
E)E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Smith just bought a house for $250,000.Earthquake insurance,which would pay $250,000 in the event of a major earthquake,is available for $25,000.Smith estimates that the probability of a major earthquake in the coming year is 10 percent,and that in the event of such a quake,the property would be worth nothing.The utility (U)that Smith gets from income (I)is given as follows: U(I)= I0.5.
Should Smith buy the insurance?
A)Yes.
B)No.
C)Smith is indifferent.
D)We need more information on Smith's attitude toward risk.
Should Smith buy the insurance?
A)Yes.
B)No.
C)Smith is indifferent.
D)We need more information on Smith's attitude toward risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
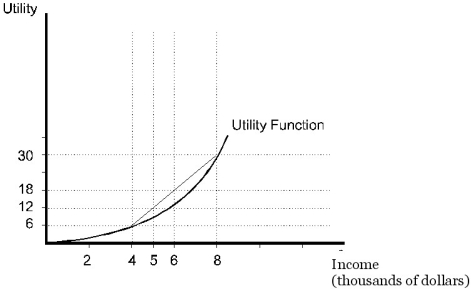 Figure 5.3
Figure 5.3The individual pictured in Figure 5.3
A)prefers a sure $6000 to a 50% chance of $4000 and a 50% chance of $8000.
B)has an expected utility of 12 from a 50% chance of $4000 and a 50% chance of $8000.
C)would receive a utility of 12 from a sure $6000.
D)would receive a utility of 18 from a sure $6000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Bill's utility function takes the form U(I)= exp(I)where I is Bill's income.Based on this utility function,we can see that Bill is:
A)risk averse
B)risk neutral
C)risk loving
D)He can exhibit two or more of these risk behaviors under this utility function.
A)risk averse
B)risk neutral
C)risk loving
D)He can exhibit two or more of these risk behaviors under this utility function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Individuals who fully insure their house and belongings against fire
A)have wasted their money if a fire does not occur.
B)generally do so in order that their after-fire wealth can be equal to their before-fire wealth.
C)generally do so in order that their after-fire wealth can be higher than their before-fire wealth.
D)generally do so in order to guarantee that the worst outcome,a fire with no insurance,does not occur.
E)can never come out as well financially after a fire as they were before it.
A)have wasted their money if a fire does not occur.
B)generally do so in order that their after-fire wealth can be equal to their before-fire wealth.
C)generally do so in order that their after-fire wealth can be higher than their before-fire wealth.
D)generally do so in order to guarantee that the worst outcome,a fire with no insurance,does not occur.
E)can never come out as well financially after a fire as they were before it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The object of diversification is
A)to reduce risk and fluctuations in income.
B)to reduce risk,but not to reduce fluctuations in income.
C)to reduce fluctuations in income,but not to reduce risk.
D)neither to reduce risk,nor to reduce fluctuations in income.
A)to reduce risk and fluctuations in income.
B)to reduce risk,but not to reduce fluctuations in income.
C)to reduce fluctuations in income,but not to reduce risk.
D)neither to reduce risk,nor to reduce fluctuations in income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
 Figure 5.3
Figure 5.3The individual pictured in Figure 5.3
A)must be risk-averse.
B)must be risk-neutral.
C)must be risk-loving.
D)could be risk-averse,risk-neutral,or risk-loving.
E)could be risk-averse or risk-loving,but not risk-neutral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
 Figure 5.3
Figure 5.3The individual pictured in Figure 5.3
A)would pay a risk premium of 2 utils to avoid facing the two outcomes.
B)would want to be paid a risk premium of 2 utils to give up the opportunity of facing the two outcomes.
C)would pay a risk premium of $1000 to avoid facing the two outcomes.
D)would want to be paid a risk premium of $1000 to give up the opportunity of facing the two outcomes.
E)has a risk premium of 2 utils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Consider the following information about job opportunities for new college graduates in Megalopolis:
Table 5.1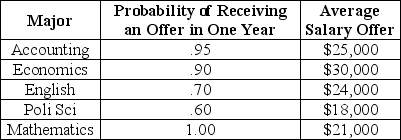
Refer to Table 5.1.A risk-averse student making a decision solely on the basis of the above information
A)would definitely become a math major.
B)would definitely not become an English major.
C)would definitely become a political science major.
D)might be either a mathematics major or English major,depending upon the utility of the average offer.
E)would definitely be indifferent between the accounting major and the English major if the probability of finding a job in accounting were any value higher than 0.95.
Table 5.1

Refer to Table 5.1.A risk-averse student making a decision solely on the basis of the above information
A)would definitely become a math major.
B)would definitely not become an English major.
C)would definitely become a political science major.
D)might be either a mathematics major or English major,depending upon the utility of the average offer.
E)would definitely be indifferent between the accounting major and the English major if the probability of finding a job in accounting were any value higher than 0.95.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Consider the following statements when answering this question; I.Without fire insurance,the expected value of homeownership for a risk averse homeowner is $W.Insurance companies are willing to sell this homeowner a policy that guarantees the homeowner a wealth of $W.
II)In a neighborhood where the price of houses are identical,the probability of a fire is identical,and the value of damage done by fires is identical,the risk premium for an insurance policy that repays all the cost of the fire damage does not vary across homeowners.
A)I and I are true.
B)I is true,and II is false.
C)I is false,and II is true.
D)I and II are false.
II)In a neighborhood where the price of houses are identical,the probability of a fire is identical,and the value of damage done by fires is identical,the risk premium for an insurance policy that repays all the cost of the fire damage does not vary across homeowners.
A)I and I are true.
B)I is true,and II is false.
C)I is false,and II is true.
D)I and II are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
 Figure 5.2
Figure 5.2The individual pictured in Figure 5.2
A)prefers a 50% chance of $100 and a 50% chance of $50 to a sure $75.
B)would receive a utility of 300 from a 50% chance of $100 and a 50% chance of $50.
C)would receive a utility of 300 from a sure $75.
D)would receive a utility of 250 from a sure $75.
E)is one for whom income is a measure of well-being.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
 Figure 5.2
Figure 5.2When facing a 50% chance of receiving $50 and a 50% chance of receiving $100,the individual pictured in Figure 5.2
A)would pay a risk premium of 10 utils to avoid facing the two outcomes.
B)would want to be paid a risk premium of 10 utils to give up the opportunity of facing the two outcomes.
C)would pay a risk premium of $7.50 to avoid facing the two outcomes.
D)would want to be paid a risk premium of $7.50 to avoid facing the two outcomes.
E)has a risk premium of 10 utils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A farmer lives on a flat plain next to a river.In addition to the farm,which is worth $F,the farmer owns financial assets worth $A.The river bursts its banks and floods the plain with probability P,destroying the farm.If the farmer is risk averse,then the willingness to pay for flood insurance unambiguously falls when
A)F is higher,and A is lower.
B)P is lower,and F is higher.
C)F & A are higher.
D)P is lower,and A is lower.
E)A is higher,and F is lower.
A)F is higher,and A is lower.
B)P is lower,and F is higher.
C)F & A are higher.
D)P is lower,and A is lower.
E)A is higher,and F is lower.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The law of large numbers:
A)can be used to explain why some people are risk averse and others are risk neutral or risk loving.
B)can be used to explain why some people choose to self-insure against random,single and largely unpredictable events.
C)states that large amounts of information are often preferred to small amounts of information.
D)states that the average outcome of a large number of similar events can often be predicted.
A)can be used to explain why some people are risk averse and others are risk neutral or risk loving.
B)can be used to explain why some people choose to self-insure against random,single and largely unpredictable events.
C)states that large amounts of information are often preferred to small amounts of information.
D)states that the average outcome of a large number of similar events can often be predicted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of these is NOT a generally accepted means of reducing risk?
A)Diversification
B)Insurance
C)Obtaining more information
D)none of the above
A)Diversification
B)Insurance
C)Obtaining more information
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Consider two upward sloping income-utility curves with income on the horizontal axis.The steeper curve represents risk preferences that are more:
A)risk averse.
B)risk loving.
C)loss averting.
D)We cannot answer this question without more information about the shapes of the curves.
A)risk averse.
B)risk loving.
C)loss averting.
D)We cannot answer this question without more information about the shapes of the curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A new toll road was built in Southern California between San Juan Capistrano and Costa Mesa.On average,drivers save 10 minutes taking this road as opposed to the old road.The toll is $2; the fine for not paying the toll is $76.The probability of catching and fining someone who does not pay the toll is 90%.Individuals who take the road and pay the toll must therefore value 10 minutes at a minimum
A)between $1.80 and $68.40.
B)between $2 and $68.40.
C)$1.80.
D)between $1.80 and $76.
E)more than $76.
A)between $1.80 and $68.40.
B)between $2 and $68.40.
C)$1.80.
D)between $1.80 and $76.
E)more than $76.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Consider the following information about job opportunities for new college graduates in Megalopolis:
Table 5.1
Refer to Table 5.1.A risk-neutral individual making a decision solely on the basis of the above information would choose to major in
A)accounting.
B)economics.
C)English.
D)political science.
E)mathematics.
Table 5.1

Refer to Table 5.1.A risk-neutral individual making a decision solely on the basis of the above information would choose to major in
A)accounting.
B)economics.
C)English.
D)political science.
E)mathematics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Scenario 5.7:
As president and CEO of MegaWorld industries,Natasha must decide on some very risky alternative investments.Consider the following:
Refer to Scenario 5.7.As a risk-neutral executive,Natasha
A)is indifferent between projects D and E.
B)prefers project E to project D,but do not necessarily consider E the best.
C)prefers project E to all other projects.
D)seeks the highest "profit if successful" of all the projects.
E)seeks the project with the most even odds.
As president and CEO of MegaWorld industries,Natasha must decide on some very risky alternative investments.Consider the following:

Refer to Scenario 5.7.As a risk-neutral executive,Natasha
A)is indifferent between projects D and E.
B)prefers project E to project D,but do not necessarily consider E the best.
C)prefers project E to all other projects.
D)seeks the highest "profit if successful" of all the projects.
E)seeks the project with the most even odds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



