Deck 4: Interest Rates and Rates of Return
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/83
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Interest Rates and Rates of Return
1
Suppose First National Bank makes a one-year simple loan of $1,000 at 7% interest to Harry's Restaurant. At the end of one year Harry's Restaurant will pay First National
A)$934.58.
B)$1007.
C)$1700.
D)$1070.
A)$934.58.
B)$1007.
C)$1700.
D)$1070.
$1070.
2
A discount bond involves
A)interest payments from the borrower to the lender periodically during the life of the loan.
B)payment by the borrower to the lender of the face value of the loan at maturity.
C)no payment of principal by the borrower to the lender.
D)payment of interest by the borrower to the lender every six months during the life of the loan.
A)interest payments from the borrower to the lender periodically during the life of the loan.
B)payment by the borrower to the lender of the face value of the loan at maturity.
C)no payment of principal by the borrower to the lender.
D)payment of interest by the borrower to the lender every six months during the life of the loan.
payment by the borrower to the lender of the face value of the loan at maturity.
3
Suppose Matt's New Cars issues a discount bond with a face value of $10,000 payable in one year with an interest rate of 4%. How much will Acme receive for the bond?
A)$9600
B)$9615
C)$14,000
D)$10,400
A)$9600
B)$9615
C)$14,000
D)$10,400
$9615
4
The most common type of simple loan is a(an)
A)automobile loan from a bank.
B)mortgage loan from a bank.
C)commercial loan from a bank.
D)corporate bond.
A)automobile loan from a bank.
B)mortgage loan from a bank.
C)commercial loan from a bank.
D)corporate bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A simple loan involves
A)interest payments from the borrower to the lender periodically during the life of the loan.
B)no payment of interest by the borrower to the lender.
C)payment of interest by the borrower to the lender only at the time the loan matures.
D)no repayment of principal by the borrower to the lender.
A)interest payments from the borrower to the lender periodically during the life of the loan.
B)no payment of interest by the borrower to the lender.
C)payment of interest by the borrower to the lender only at the time the loan matures.
D)no repayment of principal by the borrower to the lender.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is NOT a discount bond?
A)A U.S. savings bond
B)A U.S. Treasury bill
C)A U.S. Treasury note
D)A zero-coupon bond
A)A U.S. savings bond
B)A U.S. Treasury bill
C)A U.S. Treasury note
D)A zero-coupon bond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A coupon bond involves
A)interest payments from the borrower to the lender periodically during the life of the loan and payment by the borrower to the lender of the face value of the loan at maturity.
B)interest payments from the borrower to the lender periodically during the life of the loan, but no payment by the borrower to the lender of the face value of the loan at maturity.
C)periodic payments by the borrower to the lender that include both principal and interest.
D)periodic payments by the borrower to the lender that include principal, but not interest.
A)interest payments from the borrower to the lender periodically during the life of the loan and payment by the borrower to the lender of the face value of the loan at maturity.
B)interest payments from the borrower to the lender periodically during the life of the loan, but no payment by the borrower to the lender of the face value of the loan at maturity.
C)periodic payments by the borrower to the lender that include both principal and interest.
D)periodic payments by the borrower to the lender that include principal, but not interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A debt instrument represents
A)an ownership claim by the purchaser on the issuer.
B)a promise by a borrower to repay principal plus interest to a lender.
C)an attempt by a borrower in default to restore his or her credit.
D)a nontaxable asset, owned primarily by large corporations.
A)an ownership claim by the purchaser on the issuer.
B)a promise by a borrower to repay principal plus interest to a lender.
C)an attempt by a borrower in default to restore his or her credit.
D)a nontaxable asset, owned primarily by large corporations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Issuers of coupon bonds
A)make a single payment of principal when the bonds matures, but multiple payments of interest over the life of the bond
B)make a single payment of interest and principal.
C)make multiple payments of principal, but a single payment of interest.
D)make a single payment of principal at the time the bond is issued and multiple payments of interest over the life of the bond.
A)make a single payment of principal when the bonds matures, but multiple payments of interest over the life of the bond
B)make a single payment of interest and principal.
C)make multiple payments of principal, but a single payment of interest.
D)make a single payment of principal at the time the bond is issued and multiple payments of interest over the life of the bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The coupon rate is the
A)yearly coupon payment divided by the face value of the bond.
B)yearly coupon payment divided by the market value of the bond.
C)difference between the face value of the bond and its par value.
D)difference between the face value of the bond and its market value.
A)yearly coupon payment divided by the face value of the bond.
B)yearly coupon payment divided by the market value of the bond.
C)difference between the face value of the bond and its par value.
D)difference between the face value of the bond and its market value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Suppose First National Bank makes a one-year simple loan of $1000 to Harry's Restaurant. If at the end of one year Harry's Restaurant pays First National $1400, then the interest rate on this loan must have been
A)0.04%.
B)0.4%.
C)1.04%.
D)4%.
A)0.04%.
B)0.4%.
C)1.04%.
D)4%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Debt instruments are also called
A)equities.
B)credit market instruments.
C)prospectuses.
D)units of account.
A)equities.
B)credit market instruments.
C)prospectuses.
D)units of account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is NOT true of a fixed payment loan?
A)The borrower is required to make regular periodic payments to the lender.
B)The payments made by the borrower include both interest and principal.
C)The borrower is left with a substantial unpaid principal at the maturity of the loan.
D)A home mortgage is an example of fixed payment loan.
A)The borrower is required to make regular periodic payments to the lender.
B)The payments made by the borrower include both interest and principal.
C)The borrower is left with a substantial unpaid principal at the maturity of the loan.
D)A home mortgage is an example of fixed payment loan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Suppose Matt's New Cars issues a one-year discount bond with a face value of $10,000, and received $9259, repaying $10,000 after one year. The interest rate on this bond would be
A)2.6%.
B)7.41%
C)8%.
D)10%.
A)2.6%.
B)7.41%
C)8%.
D)10%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A discount bond resembles a simple loan in that
A)the interest on neither is taxable.
B)the borrower repays in a single payment.
C)both represent assets to the borrowers who issue them.
D)both have par values greater than their face values.
A)the interest on neither is taxable.
B)the borrower repays in a single payment.
C)both represent assets to the borrowers who issue them.
D)both have par values greater than their face values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The amount of funds the borrower receives from the lender with a simple loan is called the
A)principal.
B)equity.
C)maturity.
D)collateral.
A)principal.
B)equity.
C)maturity.
D)collateral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Simple loans and discount bonds differ from coupon bonds and fixed-payment loans in that
A)interest on simple loans and discount bonds is taxable, while interest on coupon bonds and fixed-payment loans is not.
B)interest on coupon bonds and fixed-payment loans is taxable, while interest on simple loans and discount bonds is not.
C)interest rates on simple loans and discount bonds are generally higher than interest rates on comparable coupon bonds and fixed-payment loans.
D)interest on simple loans and discount bonds is paid in a single payment, while issuers of coupon bonds and fixed-payment loans make multiple payments of interest and principal.
A)interest on simple loans and discount bonds is taxable, while interest on coupon bonds and fixed-payment loans is not.
B)interest on coupon bonds and fixed-payment loans is taxable, while interest on simple loans and discount bonds is not.
C)interest rates on simple loans and discount bonds are generally higher than interest rates on comparable coupon bonds and fixed-payment loans.
D)interest on simple loans and discount bonds is paid in a single payment, while issuers of coupon bonds and fixed-payment loans make multiple payments of interest and principal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When you place your funds in a savings account at a bank, those funds are
A)an asset to you and a liability to the bank.
B)a liability to you and an asset to the bank.
C)an asset both to you and the bank.
D)a liability both to you and bank.
A)an asset to you and a liability to the bank.
B)a liability to you and an asset to the bank.
C)an asset both to you and the bank.
D)a liability both to you and bank.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The total payment to a lender for a simple loan is
A)P.
B)P + i.
C)i(1 + i).
D)P(1 + i).
A)P.
B)P + i.
C)i(1 + i).
D)P(1 + i).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is a coupon bond?
A)A U.S. savings bond
B)A U.S. Treasury bill
C)A U.S. Treasury note
D)A zero-coupon bond
A)A U.S. savings bond
B)A U.S. Treasury bill
C)A U.S. Treasury note
D)A zero-coupon bond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Compounding refers to
A)the calculation of interest rates after the compounding effect of taxes has been allowed for.
B)the paying back of both interest and principal during the life of a fixed payment loan.
C)the process of earning interest on both the interest and the principal of an investment.
D)the increased value of an investment that arises from the payment of periodic interest.
A)the calculation of interest rates after the compounding effect of taxes has been allowed for.
B)the paying back of both interest and principal during the life of a fixed payment loan.
C)the process of earning interest on both the interest and the principal of an investment.
D)the increased value of an investment that arises from the payment of periodic interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If you deposit $500 in a savings account at an annual interest rate of 5%, how much will you have in the account at the end of five years?
A)$625
B)$392
C)$638
D)$12,500
A)$625
B)$392
C)$638
D)$12,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The key to present value calculations is that they
A)allow easy comparison of taxable and non-taxable investments.
B)provide a common unit for measuring funds at different times.
C)provide accurate answers only in a low-inflation environment.
D)provide accurate answers only in a high-inflation environment.
A)allow easy comparison of taxable and non-taxable investments.
B)provide a common unit for measuring funds at different times.
C)provide accurate answers only in a low-inflation environment.
D)provide accurate answers only in a high-inflation environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
At an interest rate of 6%, what is the present value of $10,000 to be received five years from now?
A)$5000
B)$7473
C)$10,000
D)$13,382
A)$5000
B)$7473
C)$10,000
D)$13,382

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
At an interest rate of 3%, what is the present value of $1000 to be received five years from now?
A)$863
B)$1667
C)$1159
D)$850
A)$863
B)$1667
C)$1159
D)$850

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The key difficulty in answering the question: "Would you be better off financing your new home with a 15-year mortgage at 9% or by borrowing for five years at 8% and refinancing thereafter?" is that
A)housing prices are very erratic.
B)the tax deductibility of mortgage interest payments has changed over time.
C)dollars paid in different periods are not in the same units.
D)15-year mortgages are fixed-payment loans while 5-year mortgages are simple loans.
A)housing prices are very erratic.
B)the tax deductibility of mortgage interest payments has changed over time.
C)dollars paid in different periods are not in the same units.
D)15-year mortgages are fixed-payment loans while 5-year mortgages are simple loans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The yield to maturity is equal to
A)the interest rate at which the present value of an asset's returns is equal to its value today.
B)the face value or par value of a coupon bond.
C)any payments received from an asset at the date the asset matures.
D)interest rate on the asset minus any taxes owed on the interest received.
A)the interest rate at which the present value of an asset's returns is equal to its value today.
B)the face value or par value of a coupon bond.
C)any payments received from an asset at the date the asset matures.
D)interest rate on the asset minus any taxes owed on the interest received.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A one-year discount bond with a par value of $1000 sold today, at issuance, for $943 has a yield to maturity of
A)4.30%
B)5.70%
C)6.04%
D)9.43%
A)4.30%
B)5.70%
C)6.04%
D)9.43%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Treasury STRIPS are
A)coupon bonds.
B)simple loans.
C)discount bonds.
D)fixed payment loans.
A)coupon bonds.
B)simple loans.
C)discount bonds.
D)fixed payment loans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
For simple loans, the yield to maturity
A)is always less than the specified simple interest rate.
B)is always greater than the specified simple interest rate.
C)is always equal to the specified simple interest rate.
D)may be less than, greater than, or equal to the specified simple interest rate, depending on the maturity of the loan.
A)is always less than the specified simple interest rate.
B)is always greater than the specified simple interest rate.
C)is always equal to the specified simple interest rate.
D)may be less than, greater than, or equal to the specified simple interest rate, depending on the maturity of the loan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A one-year discount bond with a par value of $5000 sold today, at issuance, for $4750 has a yield to maturity of
A)5.00%.
B)5.26%.
C)2.50%.
D)9.75%.
A)5.00%.
B)5.26%.
C)2.50%.
D)9.75%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If you deposit $10,000 in a savings account at an annual interest rate of 6%, how much will you have in the account at the end of three years?
A)$8396
B)$11,800
C)$11,910
D)$31,800
A)$8396
B)$11,800
C)$11,910
D)$31,800

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is the yield to maturity on a simple loan that requires payment of $500 plus $30 in interest one year from now?
A)6%
B)6.38%
C)5.3%
D)Not enough information has been provided to determine the answer.
A)6%
B)6.38%
C)5.3%
D)Not enough information has been provided to determine the answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If the interest rate is 9%, what would you expect to pay for a discount bond paying $10,000 in two years?
A)$8417
B)$8200
C)$10,000
D)$11,881
A)$8417
B)$8200
C)$10,000
D)$11,881

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The concept of present value
A)reveals that discount bonds have higher interest rates than coupon bonds.
B)reveals that fixed payment loans have higher interest rates than discount bonds.
C)is useful in comparing interest rates for different financial instruments.
D)shows that it is unlikely that a simple loan will have a lower interest rate than a discount bond.
A)reveals that discount bonds have higher interest rates than coupon bonds.
B)reveals that fixed payment loans have higher interest rates than discount bonds.
C)is useful in comparing interest rates for different financial instruments.
D)shows that it is unlikely that a simple loan will have a lower interest rate than a discount bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is a fixed payment loan?
A)A home mortgage
B)A U.S. Treasury bill
C)A U.S. Treasury note
D)A zero-coupon bond
A)A home mortgage
B)A U.S. Treasury bill
C)A U.S. Treasury note
D)A zero-coupon bond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If the interest rate is 8%, what would you expect to pay for a discount bond paying $10,000 in ten years?
A)$4632
B)$9259
C)$10,000
D)$21,589
A)$4632
B)$9259
C)$10,000
D)$21,589

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Treasury STRIPS came into existence because
A)investors demanded a tax-free long-term bond.
B)the Treasury wished to shift from long-term borrowing to short-term borrowing.
C)high inflation rates led to an increased demand for high-yield bonds.
D)investors demanded long-term discount bonds.
A)investors demanded a tax-free long-term bond.
B)the Treasury wished to shift from long-term borrowing to short-term borrowing.
C)high inflation rates led to an increased demand for high-yield bonds.
D)investors demanded long-term discount bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
$1 received n years from now has a value today of
A)($1 + i)/i.
B)$1/(1 + i).
C)($1 + i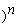 /i.
/i.
D)$1/(1 + i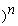
 .
.
A)($1 + i)/i.
B)$1/(1 + i).
C)($1 + i
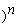 /i.
/i.D)$1/(1 + i
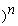
 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is NOT a fixed payment loan?
A)A home mortgage
B)A car loan
C)A U.S. Treasury note
D)A student loan
A)A home mortgage
B)A car loan
C)A U.S. Treasury note
D)A student loan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If, while you are holding a coupon bond, its market price falls, you can be sure that
A)the coupon payment you are receiving must have been reduced.
B)the interest rate on other similar bonds must have fallen.
C)the interest rate on other similar bonds must have risen.
D)the par value of the bond must have declined.
A)the coupon payment you are receiving must have been reduced.
B)the interest rate on other similar bonds must have fallen.
C)the interest rate on other similar bonds must have risen.
D)the par value of the bond must have declined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
For a specific change in the yield to maturity
A)the shorter the time until a bond matures, the greater will be the change in its price.
B)the longer the time until a bond matures, the greater will be the change in its price.
C)the longer the time until a bond matures, the greater will be the change in its par value.
D)the shorter the time until a bond matures, the greater will be the change in its coupon rate.
A)the shorter the time until a bond matures, the greater will be the change in its price.
B)the longer the time until a bond matures, the greater will be the change in its price.
C)the longer the time until a bond matures, the greater will be the change in its par value.
D)the shorter the time until a bond matures, the greater will be the change in its coupon rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If investors are willing to pay more than the par value for a bond, you can be sure that
A)the tax rate on the bond must be very low.
B)the coupon rate on the bond must be higher than on other similar bonds.
C)the coupon rate on the bond must be lower than on other similar bonds.
D)the par value for the bond must be very low.
A)the tax rate on the bond must be very low.
B)the coupon rate on the bond must be higher than on other similar bonds.
C)the coupon rate on the bond must be lower than on other similar bonds.
D)the par value for the bond must be very low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The current yield is equal to
A)the coupon divided by the market price of the bond.
B)the yield to maturity, if the bond is a coupon bond.
C)the coupon divided by the par value of the bond.
D)the market price of the bond divided by its par value.
A)the coupon divided by the market price of the bond.
B)the yield to maturity, if the bond is a coupon bond.
C)the coupon divided by the par value of the bond.
D)the market price of the bond divided by its par value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is fixed on a coupon bond?
A)Coupon rate
B)Current yield
C)Market price
D)Yield to maturity
A)Coupon rate
B)Current yield
C)Market price
D)Yield to maturity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If the current price of a bond is greater than its face value
A)an investor will receive a capital gain by holding the bond until maturity.
B)the yield to maturity must be less than the coupon rate.
C)the coupon rate must be less than the current yield.
D)the coupon rate must be equal to the current yield.
A)an investor will receive a capital gain by holding the bond until maturity.
B)the yield to maturity must be less than the coupon rate.
C)the coupon rate must be less than the current yield.
D)the coupon rate must be equal to the current yield.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
On a coupon bond, the yield to maturity
A)always equals the coupon rate.
B)equates the present value of all the bond's payments to its price today.
C)increases when the market price of the bond increases.
D)equals the coupon payment divided by the current price of the bond.
A)always equals the coupon rate.
B)equates the present value of all the bond's payments to its price today.
C)increases when the market price of the bond increases.
D)equals the coupon payment divided by the current price of the bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
An investor who buys a fifty-year corporate bond
A)must be expecting to still be alive in fifty years.
B)is subject to substantial reinvestment risk.
C)is probably expecting market interest rates to increase in the future.
D)is probably expecting market interest rates to decrease in the future.
A)must be expecting to still be alive in fifty years.
B)is subject to substantial reinvestment risk.
C)is probably expecting market interest rates to increase in the future.
D)is probably expecting market interest rates to decrease in the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A coupon bond has a coupon of $75, a par value of $1000, and a market price of $900. Its current yield equals
A)7.50%
B)8.33%
C)its yield to maturity.
D)Not enough information has been provided to calculate the current yield for this bond.
A)7.50%
B)8.33%
C)its yield to maturity.
D)Not enough information has been provided to calculate the current yield for this bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If an investor is certain that market interest rates will decline in the future, which of the following will she be most likely to purchase?
A)A six-month Treasury bill
B)A two-year Treasury note
C)A thirty-year Treasury bond
D)A fifty-year Tennessee Valley Authority bond
A)A six-month Treasury bill
B)A two-year Treasury note
C)A thirty-year Treasury bond
D)A fifty-year Tennessee Valley Authority bond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A bond's price and its yield to maturity are inversely related because
A)discounting future payments at a higher rate reduces the present value of the payments.
B)discounting future payments at a higher rate increases the present value of the payments.
C)an increase in the yield to maturity will lower a bond's coupon rate and hence its price.
D)a fall in a bond's price will lower its par value and hence its yield to maturity.
A)discounting future payments at a higher rate reduces the present value of the payments.
B)discounting future payments at a higher rate increases the present value of the payments.
C)an increase in the yield to maturity will lower a bond's coupon rate and hence its price.
D)a fall in a bond's price will lower its par value and hence its yield to maturity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If i is the yield to maturity of a fixed-payment loan,
A)the value of the loan today equals i times the sum of the values of all the loan payments.
B)i equals the present value of the loan payments.
C)the value of the loan today equals the sum of the values of the loan payments.
D)the value of the loan today equals the present value of the loan payments discounted at rate i.
A)the value of the loan today equals i times the sum of the values of all the loan payments.
B)i equals the present value of the loan payments.
C)the value of the loan today equals the sum of the values of the loan payments.
D)the value of the loan today equals the present value of the loan payments discounted at rate i.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If, while you are holding a coupon bond, the interest rates on other similar bonds fall, you can be sure that
A)the coupon payments on your bond will fall.
B)the market price of your bond will rise.
C)the market price of your bond will fall.
D)the par value of your bond will rise.
A)the coupon payments on your bond will fall.
B)the market price of your bond will rise.
C)the market price of your bond will fall.
D)the par value of your bond will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is the price of a coupon bond that has annual coupon payments of $75, a par value of $1000, a yield to maturity of 5%, and a maturity of two years?
A)$1043.08
B)$1046.49
C)$1000.00
D)$1150.00
A)$1043.08
B)$1046.49
C)$1000.00
D)$1150.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If the current price of a bond is equal to its face value,
A)there is no capital gain or loss from holding the bond until maturity.
B)the yield to maturity must be greater than the current yield.
C)the current yield must be greater than the coupon rate.
D)the coupon rate must be greater than the yield to maturity.
A)there is no capital gain or loss from holding the bond until maturity.
B)the yield to maturity must be greater than the current yield.
C)the current yield must be greater than the coupon rate.
D)the coupon rate must be greater than the yield to maturity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If the current price of a bond is less than its face value,
A)an investor will receive a capital gain by holding the bond until maturity.
B)the yield to maturity must be less than the current yield.
C)the coupon rate must be greater than the current yield.
D)the coupon rate must be equal to the current yield.
A)an investor will receive a capital gain by holding the bond until maturity.
B)the yield to maturity must be less than the current yield.
C)the coupon rate must be greater than the current yield.
D)the coupon rate must be equal to the current yield.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
U.S. Treasury bonds
A)carry no risk of default and are therefore not risky investments.
B)have constant yields to maturity and are therefore not risky investments.
C)have constant coupon rates and are therefore not risky investments.
D)are subject to fluctuations in their market prices and are therefore risky investments.
A)carry no risk of default and are therefore not risky investments.
B)have constant yields to maturity and are therefore not risky investments.
C)have constant coupon rates and are therefore not risky investments.
D)are subject to fluctuations in their market prices and are therefore risky investments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What is the price of a coupon bond that has annual coupon payments of $85, a par value of $1000, a yield to maturity of 10%, and a maturity of three years?
A)$211.38
B)$898.84
C)$962.70
D)$1255.0
A)$211.38
B)$898.84
C)$962.70
D)$1255.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following is NOT fixed on a coupon bond?
A)Coupon
B)Coupon rate
C)Market price
D)Par value
A)Coupon
B)Coupon rate
C)Market price
D)Par value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is the yield to maturity of a consol with a coupon of $85 and a price of $944.44?
A)5.56%
B)8.50%
C)9.00%
D)Not enough information has been provided to determine the answer.
A)5.56%
B)8.50%
C)9.00%
D)Not enough information has been provided to determine the answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The current yield is
A)always equal to the yield to maturity on a coupon bond.
B)always equal to the coupon rate on a coupon bond.
C)roughly equal to the yield to maturity on very long-term bonds.
D)roughly equal to the yield to maturity on a short-term bond.
A)always equal to the yield to maturity on a coupon bond.
B)always equal to the coupon rate on a coupon bond.
C)roughly equal to the yield to maturity on very long-term bonds.
D)roughly equal to the yield to maturity on a short-term bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
We would expect yields on long-term corporate bonds
A)to always be equal the coupon rate on those bonds.
B)to be far more stable than their market prices.
C)to vary inversely with their par values.
D)to always be higher than the yields on long-term U.S. Treasury bonds.
A)to always be equal the coupon rate on those bonds.
B)to be far more stable than their market prices.
C)to vary inversely with their par values.
D)to always be higher than the yields on long-term U.S. Treasury bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If the nominal interest rate is 5%, the tax rate is 25%, and the expected inflation rate is 3%, what is the real after-tax return?
A)-0.75%
B)0.75%
C)1.5%
D)6.75%
A)-0.75%
B)0.75%
C)1.5%
D)6.75%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The only case for which the bond price does not react to a change in the yield to maturity is when
A)the bond is a U.S. Treasury security.
B)the bond's coupon rate equals its current yield.
C)the bond's market price equals its par value.
D)the bond's holding period is the same as the number of years to maturity.
A)the bond is a U.S. Treasury security.
B)the bond's coupon rate equals its current yield.
C)the bond's market price equals its par value.
D)the bond's holding period is the same as the number of years to maturity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The bid price for a bond is
A)the minimum price that you are allowed to bid for a bond that is being auctioned by the government.
B)the maximum price that you are allowed to bid for a bond that is being auctioned by the government.
C)the price that you will receive from a securities dealer if you sell the bond.
D)the price that you must pay a securities dealer to purchase a bond.
A)the minimum price that you are allowed to bid for a bond that is being auctioned by the government.
B)the maximum price that you are allowed to bid for a bond that is being auctioned by the government.
C)the price that you will receive from a securities dealer if you sell the bond.
D)the price that you must pay a securities dealer to purchase a bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The total rate of return is equal to
A)the coupon rate plus the rate of capital gains.
B)the coupon rate plus the current yield.
C)the current yield plus the rate of capital gains.
D)the coupon rate multiplied by the rate of capital gains.
A)the coupon rate plus the rate of capital gains.
B)the coupon rate plus the current yield.
C)the current yield plus the rate of capital gains.
D)the coupon rate multiplied by the rate of capital gains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The expected real interest rate equals
A)the nominal interest rate minus the tax rate.
B)the nominal interest rate minus the expected rate of inflation.
C)the nominal interest rate plus the expected rate of inflation.
D)the yield to maturity on a coupon bond held to maturity.
A)the nominal interest rate minus the tax rate.
B)the nominal interest rate minus the expected rate of inflation.
C)the nominal interest rate plus the expected rate of inflation.
D)the yield to maturity on a coupon bond held to maturity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Suppose that a coupon bond is listed in The Wall Street Journal as having a coupon rate of 8.25% and a bid price of 120:19. Its current yield is
A)6.84%.
B)6.86%.
C)8.50%.
D)8.52%.
A)6.84%.
B)6.86%.
C)8.50%.
D)8.52%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The Fisher hypothesis holds that
A)in the long run the nominal interest rate equals the real interest rate.
B)the yield to maturity equals the real interest rate.
C)the nominal interest rate equals the coupon rate if the bond is held to maturity.
D)the nominal interest rate rises or falls point-for-point with expected inflation.
A)in the long run the nominal interest rate equals the real interest rate.
B)the yield to maturity equals the real interest rate.
C)the nominal interest rate equals the coupon rate if the bond is held to maturity.
D)the nominal interest rate rises or falls point-for-point with expected inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Suppose that the inflation rate is currently 8% and that most investors believe that inflation will remain at this level indefinitely. You are convinced, however, that the inflation will decline to 5% or less. Should you buy a 10-year Treasury bond or a 10-year TIPS?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The total rate of return is equal to the
A)sum of the coupon rate and the current yield.
B)yield to maturity.
C)sum of the current yield and the actual rate of capital gain.
D)sum of the current yield and the expected rate of capital gain.
A)sum of the coupon rate and the current yield.
B)yield to maturity.
C)sum of the current yield and the actual rate of capital gain.
D)sum of the current yield and the expected rate of capital gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When a bond is listed as having two maturity dates,
A)the bond is callable and may be redeemed by the issuer on the first maturity date.
B)half of the par value of the bond will be paid on the first date and the other half on the second date.
C)interest payments on the bond begin on the first date and end on the second date.
D)the purchaser may insist on being paid the par value of the bond on the first maturity date.
A)the bond is callable and may be redeemed by the issuer on the first maturity date.
B)half of the par value of the bond will be paid on the first date and the other half on the second date.
C)interest payments on the bond begin on the first date and end on the second date.
D)the purchaser may insist on being paid the par value of the bond on the first maturity date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following statements about the total rate of return is NOT correct?
A)The total rate of return may be greater or less than the current yield.
B)The total rate of return may be greater or less than the rate of capital gain.
C)The total rate of return may never be negative.
D)The total rate of return is greater than the coupon, holding everything else constant.
A)The total rate of return may be greater or less than the current yield.
B)The total rate of return may be greater or less than the rate of capital gain.
C)The total rate of return may never be negative.
D)The total rate of return is greater than the coupon, holding everything else constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In comparing the yield to maturity on a Treasury bill with the yield on a discount basis on the same bill, we can say that the yield to maturity
A)will always be greater than the yield on a discount basis.
B)will always be less than the yield on a discount basis.
C)will always be equal to the yield on a discount basis, provided the holding period is the same as the number of years to maturity.
D)rises whenever the yield on a discount basis falls.
A)will always be greater than the yield on a discount basis.
B)will always be less than the yield on a discount basis.
C)will always be equal to the yield on a discount basis, provided the holding period is the same as the number of years to maturity.
D)rises whenever the yield on a discount basis falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
With respect to U.S. Treasury bills,
A)the bid price is always greater than the asked price.
B)the asked price is always greater than the bid price.
C)the bid price is only greater than the asked price if investors expect interest rates to decline in the future.
D)the asked price is only greater than the bid price if investors expect interest rates to decline in the future.
A)the bid price is always greater than the asked price.
B)the asked price is always greater than the bid price.
C)the bid price is only greater than the asked price if investors expect interest rates to decline in the future.
D)the asked price is only greater than the bid price if investors expect interest rates to decline in the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Nominal interest rates are higher than real interest rates as long as
A)expected inflation is positive.
B)the government taxes interest income.
C)inflation is expected to decline in the future.
D)long-term interest rates are higher than short-term interest rates.
A)expected inflation is positive.
B)the government taxes interest income.
C)inflation is expected to decline in the future.
D)long-term interest rates are higher than short-term interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
What is the total rate of return on a bond with a coupon of $55 that was purchased for $900 and sold one year later for $950?
A)5.56%
B)6.11%
C)11.67%
D)12.43%
A)5.56%
B)6.11%
C)11.67%
D)12.43%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
What is the yield on a discount basis for a U.S. Treasury bill that has a face value of $10,000, has a price of $9500, and will mature in 180 days?
A)5.00%
B)5.25%
C)10.00%
D)10.67%
A)5.00%
B)5.25%
C)10.00%
D)10.67%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Investors who attempt to reduce their risk of fluctuating market interest rates by holding only short-term instruments
A)will succeed as long as the short-term instruments are Treasury bills.
B)will fail because short-term instruments are affected more by fluctuations in market interest rates than are long-term instruments.
C)will expose themselves to reinvestment risk.
D)will incur large capital gains.
A)will succeed as long as the short-term instruments are Treasury bills.
B)will fail because short-term instruments are affected more by fluctuations in market interest rates than are long-term instruments.
C)will expose themselves to reinvestment risk.
D)will incur large capital gains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following is the correct expression for the expected real interest rate?
A)r = i +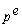
B)r = i -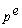
C)r = i/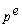
D)r =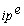
A)r = i +
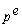
B)r = i -
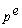
C)r = i/
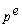
D)r =
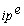

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



