Deck 28: Inflation: Causes and Consequences
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/92
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 28: Inflation: Causes and Consequences
1
If during a particular year, the money supply grows 7%, output grows 2%, and velocity falls 2%, the inflation rate will be
A)3%.
B)7%.
C)9%.
D)11%.
A)3%.
B)7%.
C)9%.
D)11%.
3%.
2
About how much would you have needed in 2006 to buy something that cost $0.10 in 1939?
A)$0.25
B)$0.50
C)$1.00
D)$10.00
A)$0.25
B)$0.50
C)$1.00
D)$10.00
$1.00
3
According to the equation of exchange, the percentage change in the nominal money supply ( 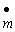 ) is equal to
) is equal to
A)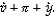
B)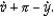
C)
D)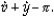
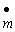 ) is equal to
) is equal toA)
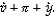
B)
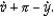
C)

D)
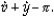

4
If during a particular year, output grows 5%, velocity declines 2%, and the inflation rate is 1%, then the money supply must have grown
A)-6%.
B)2%.
C)4%.
D)8%.
A)-6%.
B)2%.
C)4%.
D)8%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is the correct expression of the equation of exchange?
A)MY = PV
B)MP = VY
C)M/P = VY
D)MV = PY
A)MY = PV
B)MP = VY
C)M/P = VY
D)MV = PY

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If during a particular year, the money supply grows 6%, output grows 4%, and velocity grows 2%, the inflation rate will be
A)0%.
B)4%.
C)8%.
D)12%.
A)0%.
B)4%.
C)8%.
D)12%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
All else being equal, a one-time increase in the money supply leads to
A)inflation.
B)a one-time increase in the price level.
C)a one-time shift to the left in the AD curve.
D)a permanent shift to the right in the SRAS curve.
A)inflation.
B)a one-time increase in the price level.
C)a one-time shift to the left in the AD curve.
D)a permanent shift to the right in the SRAS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is NOT a widely used measure of the price level?
A)The Price Level Indicator
B)The Producer Price Index
C)The Consumer Price Index
D)The GDP Implicit Price Deflator
A)The Price Level Indicator
B)The Producer Price Index
C)The Consumer Price Index
D)The GDP Implicit Price Deflator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A 10% inflation rate means that
A)prices of some important goods and services have increased by 10%.
B)every price in the economy has increased by 10%.
C)the money supply has increased by 10%.
D)the price level has increased by 10%.
A)prices of some important goods and services have increased by 10%.
B)every price in the economy has increased by 10%.
C)the money supply has increased by 10%.
D)the price level has increased by 10%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Between 1939 and 2006 consumer prices rose about
A)10%.
B)50%.
C)100%.
D)1000%.
A)10%.
B)50%.
C)100%.
D)1000%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Holding everything else constant, which of the following would cause an increase in short-term inflation?
A)A decrease in the nominal money supply
B)A decrease in net exports
C)A decrease in consumer spending
D)A decrease in the growth rate of aggregate supply
A)A decrease in the nominal money supply
B)A decrease in net exports
C)A decrease in consumer spending
D)A decrease in the growth rate of aggregate supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Nobel laureate Milton Friedman is known for his assertion that,
A)"Inflation is caused solely by government budget deficits."
B)"Inflation is always and everywhere a monetary phenomenon."
C)"The evils of inflation are greatly overrated."
D)"Inflation is the opium of the masses."
A)"Inflation is caused solely by government budget deficits."
B)"Inflation is always and everywhere a monetary phenomenon."
C)"The evils of inflation are greatly overrated."
D)"Inflation is the opium of the masses."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In which of the following decades was the rate of inflation the highest?
A)1930s
B)1970s
C)1980s
D)1990s
A)1930s
B)1970s
C)1980s
D)1990s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
According to the equation of exchange, the velocity of money is equal to
A)M/PY.
B)PY/M.
C)PM/Y.
D)MY/P.
A)M/PY.
B)PY/M.
C)PM/Y.
D)MY/P.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements is correct?
A)Throughout U.S. history prices have fallen in more years than they have risen.
B)Prices have risen every year in the United States since 1800.
C)Prices have fallen in the majority of years since 1939.
D)Prices fell every year in the 1980s.
A)Throughout U.S. history prices have fallen in more years than they have risen.
B)Prices have risen every year in the United States since 1800.
C)Prices have fallen in the majority of years since 1939.
D)Prices fell every year in the 1980s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
At the beginning of the twenty-first century most economists
A)urged the Fed to focus on its goal of high employment.
B)urged central banks to focus their energy on low inflation.
C)believed the underlying inflation rate in the United States was higher than it had been in the late 1970s.
D)were critical of the performance of Alan Greenspan has Chairman of the Fed.
A)urged the Fed to focus on its goal of high employment.
B)urged central banks to focus their energy on low inflation.
C)believed the underlying inflation rate in the United States was higher than it had been in the late 1970s.
D)were critical of the performance of Alan Greenspan has Chairman of the Fed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Suppose the Fed sets an inflation target of 2% a year. If economic growth averages 3% per year and velocity grows by 1% per year, by how much should it increase the money supply each year?
A)2%
B)4%
C)5%
D)6%
A)2%
B)4%
C)5%
D)6%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If everything else is held constant, which of the following would NOT lead to short-term inflation?
A)An increase in the growth rate of aggregate supply
B)An increase in the nominal money supply
C)An increase in consumer spending
D)An increase in government spending
A)An increase in the growth rate of aggregate supply
B)An increase in the nominal money supply
C)An increase in consumer spending
D)An increase in government spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
According to the equation of exchange, the percentage change in the price level (π) is equal to
A)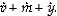
B)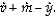
C)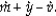
D)
A)
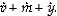
B)
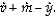
C)
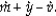
D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following statements is correct concerning the views of new Keynesians and new classicals concerning aggregate supply?
A)New classical economists believe the short-run and long-run aggregate supply curves are both vertical.
B)New Keynesian economists believe the short-run and long-run aggregate supply curves slope upward.
C)Both new Keynesian and new classical economists believe the aggregate supply curve is vertical in the long run.
D)Both new Keynesian and new classical economists believe the aggregate supply curve slopes upward in the long run.
A)New classical economists believe the short-run and long-run aggregate supply curves are both vertical.
B)New Keynesian economists believe the short-run and long-run aggregate supply curves slope upward.
C)Both new Keynesian and new classical economists believe the aggregate supply curve is vertical in the long run.
D)Both new Keynesian and new classical economists believe the aggregate supply curve slopes upward in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following statements is correct according to both new classical and new Keynesian economists?
A)An unexpected increase in the money supply will increase only prices in the short run, whereas an unexpected increase in government spending will increase both prices and output.
B)An unexpected increase in government spending will increase both prices and output in the short run.
C)An unexpected increase in government spending will increase only output in the short run.
D)Unexpected increases in the money supply or in government spending will increase only prices in the short run.
A)An unexpected increase in the money supply will increase only prices in the short run, whereas an unexpected increase in government spending will increase both prices and output.
B)An unexpected increase in government spending will increase both prices and output in the short run.
C)An unexpected increase in government spending will increase only output in the short run.
D)Unexpected increases in the money supply or in government spending will increase only prices in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Sustained inflation will be caused by a sustained growth in the nominal money supply at a rate faster than the growth rate of velocity and the growth rate of output according to
A)new Keynesian economists but not according to new classical economists.
B)new classical economists but not according to new Keynesian economists.
C)both new classical and new Keynesian economists.
D)neither new classical nor new Keynesian economists.
A)new Keynesian economists but not according to new classical economists.
B)new classical economists but not according to new Keynesian economists.
C)both new classical and new Keynesian economists.
D)neither new classical nor new Keynesian economists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
During the 1980s countries like Argentina and Israel experienced
A)high average rates of inflation and rapid average rates of growth of the nominal money supply.
B)low average rates of inflation and rapid average rates of growth of the nominal money supply.
C)high average rates of inflation and slow average rates of growth of the nominal money supply.
D)low average rates of inflation and slow average rates of growth of the nominal money supply.
A)high average rates of inflation and rapid average rates of growth of the nominal money supply.
B)low average rates of inflation and rapid average rates of growth of the nominal money supply.
C)high average rates of inflation and slow average rates of growth of the nominal money supply.
D)low average rates of inflation and slow average rates of growth of the nominal money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Expansionary fiscal policy will produce inflation only if
A)it takes the form of a cut in personal income taxes.
B)it takes the form of a cut in corporate profit taxes.
C)it takes the form of an increase in government spending.
D)it is accompanied by a sustained increase in the money supply.
A)it takes the form of a cut in personal income taxes.
B)it takes the form of a cut in corporate profit taxes.
C)it takes the form of an increase in government spending.
D)it is accompanied by a sustained increase in the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
According to new classical economists, sustained expected increases in the nominal money supply will lead to
A)increases in output in the short run and sustained increases in prices in the long run.
B)sustained increases in prices, with no short-run increases in output.
C)short-run increases in prices and output, with a stable price level and no increases in output in the long run.
D)sustained increases in both prices and output in the long run.
A)increases in output in the short run and sustained increases in prices in the long run.
B)sustained increases in prices, with no short-run increases in output.
C)short-run increases in prices and output, with a stable price level and no increases in output in the long run.
D)sustained increases in both prices and output in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A one-time increase in oil prices will cause a short-run
A)increase in the price level and in the level of current output.
B)increase in the price level and a short-run decrease in the level of current output.
C)decrease in the price level and in the level of current output.
D)decrease in the price level and a short-run increase in the level of current output.
A)increase in the price level and in the level of current output.
B)increase in the price level and a short-run decrease in the level of current output.
C)decrease in the price level and in the level of current output.
D)decrease in the price level and a short-run increase in the level of current output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following statements is correct?
A)Both new Keynesian and new classical economists believe money is neutral in the short run.
B)New Keynesian economists believe money is neutral in the short run, but new classical economists do not.
C)Both new Keynesian and new classical economists believe money is neutral in the long run.
D)New classical economists believe money is neutral in the long run, but new Keynesian economists do not.
A)Both new Keynesian and new classical economists believe money is neutral in the short run.
B)New Keynesian economists believe money is neutral in the short run, but new classical economists do not.
C)Both new Keynesian and new classical economists believe money is neutral in the long run.
D)New classical economists believe money is neutral in the long run, but new Keynesian economists do not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Government budget deficits can be inflationary in the long run only if they
A)occur as a result of large cuts in the personal income tax rate.
B)occur as a result of large increases in defense spending.
C)cause a leftward shift in the SRAS curve.
D)are accompanied by rapid growth in the monetary base.
A)occur as a result of large cuts in the personal income tax rate.
B)occur as a result of large increases in defense spending.
C)cause a leftward shift in the SRAS curve.
D)are accompanied by rapid growth in the monetary base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following statements is correct concerning the views of new Keynesians and new classicals concerning aggregate supply?
A)New classical economists believe the short-run and long-run aggregate supply curves are both vertical.
B)New Keynesian economists believe the short-run and long-run aggregate supply curves slope upward.
C)Both new Keynesian and new classical economists believe the aggregate supply curve slopes upward in the long run.
D)Both new Keynesian and new classical economists believe the aggregate supply curve slopes upward in the short run.
A)New classical economists believe the short-run and long-run aggregate supply curves are both vertical.
B)New Keynesian economists believe the short-run and long-run aggregate supply curves slope upward.
C)Both new Keynesian and new classical economists believe the aggregate supply curve slopes upward in the long run.
D)Both new Keynesian and new classical economists believe the aggregate supply curve slopes upward in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Why has the Fed made low inflation a major goal in recent decades?
A)Because high inflation rates reduce the tax revenues collected by the federal government
B)Because they wish to avoid the rapid and sustained price increases that occurred during the 1970s
C)Because Congress passed a law in 1981 mandating the Fed to reduce the inflation rate to 2%
D)Because high inflation rates increase the value of the dollar and make U.S. goods less competitive in foreign markets
A)Because high inflation rates reduce the tax revenues collected by the federal government
B)Because they wish to avoid the rapid and sustained price increases that occurred during the 1970s
C)Because Congress passed a law in 1981 mandating the Fed to reduce the inflation rate to 2%
D)Because high inflation rates increase the value of the dollar and make U.S. goods less competitive in foreign markets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Long-term inflation is principally
A)the result of chronic federal budget deficits.
B)the result of the slowdown in the growth rate of aggregate supply since 1973.
C)caused by excess wage demands by unionized workers.
D)a monetary phenomenon.
A)the result of chronic federal budget deficits.
B)the result of the slowdown in the growth rate of aggregate supply since 1973.
C)caused by excess wage demands by unionized workers.
D)a monetary phenomenon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A one-time cut in taxes
A)can result in inflation.
B)can result in a one-time increase in the price level, but cannot result in inflation.
C)can result in a one-time decrease in the price level, but cannot result in inflation.
D)will cause a dollar-for-dollar increase in the money supply.
A)can result in inflation.
B)can result in a one-time increase in the price level, but cannot result in inflation.
C)can result in a one-time decrease in the price level, but cannot result in inflation.
D)will cause a dollar-for-dollar increase in the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Inflation occurs whenever
A)there is a one-time increase in the money supply.
B)there is a one-time increase in government spending.
C)the growth rate of nominal aggregate demand exceeds the growth rate of aggregate supply over sustained periods of time.
D)the growth rate of nominal aggregate supply exceeds the growth rate of aggregate demand over sustained periods of time.
A)there is a one-time increase in the money supply.
B)there is a one-time increase in government spending.
C)the growth rate of nominal aggregate demand exceeds the growth rate of aggregate supply over sustained periods of time.
D)the growth rate of nominal aggregate supply exceeds the growth rate of aggregate demand over sustained periods of time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following statements is correct concerning the views of new Keynesians and new classicals concerning the short-run effects of an unexpected increase in aggregate demand?
A)New classical economists believe that unexpected increases in aggregate demand affect only prices.
B)New Keynesian economists believe that unexpected increases in aggregate demand affect only output.
C)Both new Keynesian and new classical economists believe that unexpected increases in aggregate demand affect only output.
D)Both new Keynesian and new classical economists believe that unexpected increases in aggregate demand affect both output and prices.
A)New classical economists believe that unexpected increases in aggregate demand affect only prices.
B)New Keynesian economists believe that unexpected increases in aggregate demand affect only output.
C)Both new Keynesian and new classical economists believe that unexpected increases in aggregate demand affect only output.
D)Both new Keynesian and new classical economists believe that unexpected increases in aggregate demand affect both output and prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The reason that the U.S. economy has experienced long-term inflation since World War II is
A)the high tax rates imposed by the federal government.
B)the large budget deficits run by the federal government.
C)the rate of growth of the money supply has been too fast relative to the rates of growth of velocity and output.
D)the long-run increases in the prices of oil and other basic commodities.
A)the high tax rates imposed by the federal government.
B)the large budget deficits run by the federal government.
C)the rate of growth of the money supply has been too fast relative to the rates of growth of velocity and output.
D)the long-run increases in the prices of oil and other basic commodities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Inflation places a tax on real money balances
A)by increasing the public's demand for real money balances.
B)when those balances pay less than the market rate of interest.
C)because nominal interest payments are deductible on the personal tax, whereas real interest payments are not.
D)whenever the actual inflation rate is less than the expected inflation rate.
A)by increasing the public's demand for real money balances.
B)when those balances pay less than the market rate of interest.
C)because nominal interest payments are deductible on the personal tax, whereas real interest payments are not.
D)whenever the actual inflation rate is less than the expected inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
According to new Keynesian economists, sustained expected increases in the nominal money supply will lead to
A)increases in output in the short run and sustained increases in prices in the long run.
B)sustained increases in prices, with no short-run increases in output.
C)short-run increases in prices and output, with a stable price level and no increases in output in the long run.
D)sustained increases in both prices and output in the long run.
A)increases in output in the short run and sustained increases in prices in the long run.
B)sustained increases in prices, with no short-run increases in output.
C)short-run increases in prices and output, with a stable price level and no increases in output in the long run.
D)sustained increases in both prices and output in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Sustained growth in the money supply doesn't affect real output in the long run but does lead to inflation according to
A)new classical economists, but not new Keynesian economists.
B)both new classical and new Keynesian economists.
C)new Keynesian economists, but not new classical economists.
D)neither new classical nor new Keynesian economists.
A)new classical economists, but not new Keynesian economists.
B)both new classical and new Keynesian economists.
C)new Keynesian economists, but not new classical economists.
D)neither new classical nor new Keynesian economists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the money supply is unchanged, expansionary fiscal policy
A)cannot result in an increase in the price level.
B)cannot result in an increase in output.
C)cannot result in prolonged inflation.
D)results in prolonged inflation provided it was unexpected.
A)cannot result in an increase in the price level.
B)cannot result in an increase in output.
C)cannot result in prolonged inflation.
D)results in prolonged inflation provided it was unexpected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A supply shock that is not responded to with an expansionary policy will result in
A)a one-time increase in the price level, but not inflation.
B)neither a one-time increase in the price level nor inflation.
C)both a one-time increase in the price level and inflation.
D)inflation, but not a one-time increase in the price level.
A)a one-time increase in the price level, but not inflation.
B)neither a one-time increase in the price level nor inflation.
C)both a one-time increase in the price level and inflation.
D)inflation, but not a one-time increase in the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Cost-push inflation results from
A)workers' pressure for higher wages.
B)policymakers' attempts to increase aggregate demand for current output above the full-employment level.
C)attempts by financial markets to deal with bracket creep.
D)attempts by the public to receive higher after-tax returns on their savings.
A)workers' pressure for higher wages.
B)policymakers' attempts to increase aggregate demand for current output above the full-employment level.
C)attempts by financial markets to deal with bracket creep.
D)attempts by the public to receive higher after-tax returns on their savings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The tax code
A)adjusts values of inventories for inflation, but does not adjust the value of depreciation allowances.
B)adjusts the value of depreciation allowances for inflation, but does not adjust values of inventories.
C)adjusts both values of inventories and the value of depreciation allowances for inflation.
D)adjusts neither the values of inventories nor the value of depreciation allowances for inflation.
A)adjusts values of inventories for inflation, but does not adjust the value of depreciation allowances.
B)adjusts the value of depreciation allowances for inflation, but does not adjust values of inventories.
C)adjusts both values of inventories and the value of depreciation allowances for inflation.
D)adjusts neither the values of inventories nor the value of depreciation allowances for inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The Humphrey-Hawkins Act of 1978
A)committed the federal government to promoting full employment, even if it comes at the expense of a stable price level.
B)committed the federal government to promoting a stable price level, even if it comes at the expense of full employment.
C)committed the federal government to promoting full employment and a stable price level.
D)removed the Secretary of the Treasury from the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve.
A)committed the federal government to promoting full employment, even if it comes at the expense of a stable price level.
B)committed the federal government to promoting a stable price level, even if it comes at the expense of full employment.
C)committed the federal government to promoting full employment and a stable price level.
D)removed the Secretary of the Treasury from the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A hyperinflation is particularly costly to an economy because
A)the real tax burden imposed on the public increases dramatically.
B)there is a large redistribution of wealth from borrowers to lenders.
C)prices no longer indicate value or direct resource allocation.
D)the demand for real money balances increases significantly.
A)the real tax burden imposed on the public increases dramatically.
B)there is a large redistribution of wealth from borrowers to lenders.
C)prices no longer indicate value or direct resource allocation.
D)the demand for real money balances increases significantly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A classic example of hyperinflation occurred
A)in Japan in the 1970s.
B)in the United Kingdom in the 1960s.
C)in the United States in the 1930s.
D)in Germany in the 1920s.
A)in Japan in the 1970s.
B)in the United Kingdom in the 1960s.
C)in the United States in the 1930s.
D)in Germany in the 1920s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Inflation generates an excess burden whenever
A)it is greater than zero.
B)income tax brackets are not indexed.
C)the public's shoe leather costs exceed the government's revenue gain from the inflation tax.
D)bracket creep exceeds the public's shoe leather costs.
A)it is greater than zero.
B)income tax brackets are not indexed.
C)the public's shoe leather costs exceed the government's revenue gain from the inflation tax.
D)bracket creep exceeds the public's shoe leather costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the face of workers pushing for higher wages, an accommodating monetary policy will result in
A)a higher price level and a lower level of current output.
B)a lower price level and a higher level of current output.
C)a higher price level and a higher level of current output.
D)a lower price level and a lower level of current output.
A)a higher price level and a lower level of current output.
B)a lower price level and a higher level of current output.
C)a higher price level and a higher level of current output.
D)a lower price level and a lower level of current output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Inflation that is higher than expected redistributes wealth from
A)employers to employees under nominal wage contracts.
B)borrowers to lenders.
C)lenders to borrowers.
D)the federal government to taxpayers.
A)employers to employees under nominal wage contracts.
B)borrowers to lenders.
C)lenders to borrowers.
D)the federal government to taxpayers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The key reason that expected inflation can distort financial decisions is that
A)lenders pay taxes on nominal rather than real returns.
B)lenders have an easier time calculating expected inflation than do borrowers.
C)expected inflation reduces the real value of the national debt.
D)expected inflation results in substantial menu costs.
A)lenders pay taxes on nominal rather than real returns.
B)lenders have an easier time calculating expected inflation than do borrowers.
C)expected inflation reduces the real value of the national debt.
D)expected inflation results in substantial menu costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Shoe leather costs of inflation
A)increase as the inflation rate rises.
B)decline as the inflation rate rises.
C)would be eliminated by the indexing of income tax brackets.
D)are the same as menu costs.
A)increase as the inflation rate rises.
B)decline as the inflation rate rises.
C)would be eliminated by the indexing of income tax brackets.
D)are the same as menu costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Economists believe that the most serious costs of inflation arise from
A)bracket creep.
B)menu costs.
C)redistributions of wealth owing to unexpected inflation.
D)uncertainty about the rate of inflation.
A)bracket creep.
B)menu costs.
C)redistributions of wealth owing to unexpected inflation.
D)uncertainty about the rate of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
When inflation fluctuates significantly,
A)the signals provided by relative prices improve.
B)the signals provided by relative prices are distorted.
C)the cost of inflation is minimized.
D)nominal interest rates will be low.
A)the signals provided by relative prices improve.
B)the signals provided by relative prices are distorted.
C)the cost of inflation is minimized.
D)nominal interest rates will be low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If the nominal interest rate on saving is 5% and the expected inflation rate is 2%, what is the after-tax return on saving if the tax rate is 25%?
A)1.75%
B)2.25%
C)3%
D)5.75%
A)1.75%
B)2.25%
C)3%
D)5.75%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Inflation that is lower than expected redistributes wealth from
A)employers to employees under nominal wage contracts.
B)borrowers to lenders.
C)lenders to borrowers.
D)the federal government to taxpayers.
A)employers to employees under nominal wage contracts.
B)borrowers to lenders.
C)lenders to borrowers.
D)the federal government to taxpayers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If the nominal interest rate on saving is 12% and the expected inflation rate is 6%, what is the percentage reduction in real interest income resulting from a tax of 25%?
A)25%
B)50%
C)60%
D)100%
A)25%
B)50%
C)60%
D)100%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Menu costs of inflation are costs arising from
A)the failure to fully index the tax system for inflation.
B)attempts by households and firms to avoid paying an inflation tax on money balances.
C)the need for firms to change prices during times of inflation.
D)high nominal interest rates.
A)the failure to fully index the tax system for inflation.
B)attempts by households and firms to avoid paying an inflation tax on money balances.
C)the need for firms to change prices during times of inflation.
D)high nominal interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Bracket creep
A)results in a tax on money balances.
B)would be zero if the same tax rate were applied to all income.
C)is greater in 2001 than it was in 1971.
D)invariably leads to an excess burden.
A)results in a tax on money balances.
B)would be zero if the same tax rate were applied to all income.
C)is greater in 2001 than it was in 1971.
D)invariably leads to an excess burden.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Cost-push inflation
A)originates in the desire of policymakers to expand employment.
B)will result in increases in output, unless policymakers adjust aggregate demand in response.
C)cannot persist in the long run unless ratified by policymakers.
D)was outlawed by the Humphrey-Hawkins Act of 1978.
A)originates in the desire of policymakers to expand employment.
B)will result in increases in output, unless policymakers adjust aggregate demand in response.
C)cannot persist in the long run unless ratified by policymakers.
D)was outlawed by the Humphrey-Hawkins Act of 1978.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Stanley Fischer has estimated that the annual excess burden in the United States of an inflation rate of 5% is approximately
A)$30 million.
B)$30 billion.
C)$300 billion.
D)$3 trillion.
A)$30 million.
B)$30 billion.
C)$300 billion.
D)$3 trillion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Despite its costs, governments typically resist eliminating inflation because
A)doing so would result in lost output and jobs when the economy is near full employment.
B)the increase in menu costs because of inflation increases the governments' tax revenues.
C)as net lenders, governments benefit from inflation.
D)governments lack the knowledge of how to eliminate inflation.
A)doing so would result in lost output and jobs when the economy is near full employment.
B)the increase in menu costs because of inflation increases the governments' tax revenues.
C)as net lenders, governments benefit from inflation.
D)governments lack the knowledge of how to eliminate inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Economists who back the use of rules by the Fed believe that they would result in
A)a lower government budget deficit.
B)increased credibility for Fed actions.
C)the eventual adoption of price controls.
D)lower growth rates of aggregate supply.
A)a lower government budget deficit.
B)increased credibility for Fed actions.
C)the eventual adoption of price controls.
D)lower growth rates of aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
During the 1970s
A)Japanese disinflation policy was not credible, but that of the United States was credible.
B)neither Japanese nor U.S. disinflation policies were credible.
C)both Japanese and U.S. disinflation policies were credible.
D)U.S. disinflation policy was not credible, but Japanese disinflation policy was credible.
A)Japanese disinflation policy was not credible, but that of the United States was credible.
B)neither Japanese nor U.S. disinflation policies were credible.
C)both Japanese and U.S. disinflation policies were credible.
D)U.S. disinflation policy was not credible, but Japanese disinflation policy was credible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
New Keynesian economists question the credibility of cold turkey disinflation in the real world because
A)the independence of central banks allows them to disregard public opinion.
B)households and businesses do not form their expectations rationally.
C)a reduction in money growth may reduce output and employment substantially in the short run.
D)central banks lack the tools to bring the inflation rate down even in the long run.
A)the independence of central banks allows them to disregard public opinion.
B)households and businesses do not form their expectations rationally.
C)a reduction in money growth may reduce output and employment substantially in the short run.
D)central banks lack the tools to bring the inflation rate down even in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A rule specifying a constant rate of growth of M1 during the early 1980s
A)was adopted in the United States, but not in Japan.
B)would have resulted in greater inflation than actually occurred.
C)would have resulted in a more contractionary policy than the one the Fed actually pursued.
D)was dropped following an acceleration in the inflation rate.
A)was adopted in the United States, but not in Japan.
B)would have resulted in greater inflation than actually occurred.
C)would have resulted in a more contractionary policy than the one the Fed actually pursued.
D)was dropped following an acceleration in the inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The typical firm will find that its payoff to reducing price increases after the announcement of a disinflation policy
A)increases if it believes that the policy will actually be carried out.
B)decreases if it believes that the policy will actually be carried out.
C)is independent of whether the policy is actually carried out.
D)depends on movements in the LRAS curve.
A)increases if it believes that the policy will actually be carried out.
B)decreases if it believes that the policy will actually be carried out.
C)is independent of whether the policy is actually carried out.
D)depends on movements in the LRAS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Cold turkey disinflation
A)is very costly in terms of lost output in both the new classical and new Keynesian views.
B)is virtually costless in terms of lost output in both the new classical and new Keynesian views.
C)is very costly in terms of lost output in the new classical view, but virtually costless in the new Keynesian view.
D)is very costly in terms of lost output in the new Keynesian view, but virtually costless in the new classical view.
A)is very costly in terms of lost output in both the new classical and new Keynesian views.
B)is virtually costless in terms of lost output in both the new classical and new Keynesian views.
C)is very costly in terms of lost output in the new classical view, but virtually costless in the new Keynesian view.
D)is very costly in terms of lost output in the new Keynesian view, but virtually costless in the new classical view.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In the new Keynesian view, disinflation is costly primarily because
A)workers and firms lack rational expectations.
B)policy announcements are rarely credible.
C)nominal wages and prices are sticky.
D)disinflation policy shifts the LRAS curve.
A)workers and firms lack rational expectations.
B)policy announcements are rarely credible.
C)nominal wages and prices are sticky.
D)disinflation policy shifts the LRAS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
During the late 1970s, households, businesses, and policymakers shifted to the opinion that
A)higher inflation was acceptable provided it resulted in higher employment.
B)higher inflation was acceptable provided it resulted in higher output.
C)reducing inflation was necessary even if it resulted in lower levels of employment and output.
D)a reduction in inflation should take place provided it did not result in disinflation.
A)higher inflation was acceptable provided it resulted in higher employment.
B)higher inflation was acceptable provided it resulted in higher output.
C)reducing inflation was necessary even if it resulted in lower levels of employment and output.
D)a reduction in inflation should take place provided it did not result in disinflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A disinflation policy that lacks credibility
A)results in a leftward shift of the AD curve.
B)will increase the lost output and jobs that result from the policy.
C)will work only if the economy is experiencing a hyperinflation.
D)will have no effect on inflation.
A)results in a leftward shift of the AD curve.
B)will increase the lost output and jobs that result from the policy.
C)will work only if the economy is experiencing a hyperinflation.
D)will have no effect on inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Under a rules strategy for monetary policy, the Fed would
A)follow specific and publicly announced guidelines for policy.
B)adjust monetary policy as it sees fit.
C)target the growth rate of M1, but not the growth rate of M2.
D)target the growth rate of M2, but not the growth rate of M1.
A)follow specific and publicly announced guidelines for policy.
B)adjust monetary policy as it sees fit.
C)target the growth rate of M1, but not the growth rate of M2.
D)target the growth rate of M2, but not the growth rate of M1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
New Keynesian and new classical economists agree that
A)policymakers cannot permanently maintain the unemployment rate below the natural rate.
B)production beyond the full-employment level of output is impossible, even in the short run.
C)in the long run the inflation rate must be zero.
D)the LRAS curve slopes up.
A)policymakers cannot permanently maintain the unemployment rate below the natural rate.
B)production beyond the full-employment level of output is impossible, even in the short run.
C)in the long run the inflation rate must be zero.
D)the LRAS curve slopes up.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Whom did President Jimmy Carter appoint chair of the Board of Governors of the Fed in order to convince the public about his anti-inflation resolve?
A)Alan Greenspan
B)Milton Friedman
C)Paul Volcker
D)Arthur Burns
A)Alan Greenspan
B)Milton Friedman
C)Paul Volcker
D)Arthur Burns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In the new Keynesian view, a disinflation policy
A)will almost always result in a recession.
B)will rarely be credible.
C)should use the cold turkey, rather than the gradual, approach.
D)shifts the LRAS curve.
A)will almost always result in a recession.
B)will rarely be credible.
C)should use the cold turkey, rather than the gradual, approach.
D)shifts the LRAS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Unless ratified by policymakers, cost-push inflation will result in
A)persistent long-run inflation.
B)hyperinflation.
C)output beyond the full-employment level.
D)a recession.
A)persistent long-run inflation.
B)hyperinflation.
C)output beyond the full-employment level.
D)a recession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
New classical economists believe that the best way to reduce inflation is to
A)do so gradually.
B)do so all at once.
C)use wage and price guidelines.
D)bring on a recession, which gradually reduces cost-push inflation.
A)do so gradually.
B)do so all at once.
C)use wage and price guidelines.
D)bring on a recession, which gradually reduces cost-push inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If during a three-year period policymakers attempt to keep unemployment below the natural rate of unemployment, in the new Keynesian view
A)the LRAS curve will shift to the right.
B)the LRAS curve will shift to the left.
C)the total amount of output produced during the period will be smaller than in the new classical view.
D)the total amount of output produced during the period will be greater than in the new classical view.
A)the LRAS curve will shift to the right.
B)the LRAS curve will shift to the left.
C)the total amount of output produced during the period will be smaller than in the new classical view.
D)the total amount of output produced during the period will be greater than in the new classical view.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
At the natural rate of unemployment,
A)the unemployment rate is zero.
B)only the structurally and the frictionally unemployed are without jobs.
C)only the frictionally unemployed are without jobs.
D)the economy is producing at its maximum level of output.
A)the unemployment rate is zero.
B)only the structurally and the frictionally unemployed are without jobs.
C)only the frictionally unemployed are without jobs.
D)the economy is producing at its maximum level of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Demand-pull inflation results from
A)workers' pressure for higher wages.
B)policymakers' attempts to increase aggregate demand for current output above the full-employment level.
C)attempts by financial markets to deal with bracket creep.
D)attempts by the public to receive higher after-tax returns on their savings.
A)workers' pressure for higher wages.
B)policymakers' attempts to increase aggregate demand for current output above the full-employment level.
C)attempts by financial markets to deal with bracket creep.
D)attempts by the public to receive higher after-tax returns on their savings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Disinflation is
A)a decline in the price level.
B)an inflation rate lower than the natural rate of inflation.
C)a decline in the long-run rate of inflation.
D)an inflation rate higher than the natural rate of inflation.
A)a decline in the price level.
B)an inflation rate lower than the natural rate of inflation.
C)a decline in the long-run rate of inflation.
D)an inflation rate higher than the natural rate of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Attempts by policymakers to keep the rate of unemployment below the natural rate of unemployment for a sustained period of time will result in
A)demand-pull inflation.
B)permanently higher levels of output.
C)a recession.
D)a shift of the LRAS curve to the left.
A)demand-pull inflation.
B)permanently higher levels of output.
C)a recession.
D)a shift of the LRAS curve to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



