Deck 25: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/92
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
1
A decline in money demand is
A)expansionary because it results in a decline in the real interest rate.
B)expansionary because it results in an increase in the nominal money supply.
C)contractionary because it results in a decline in the real interest rate.
D)contractionary because it results in a decline in the nominal money supply.
A)expansionary because it results in a decline in the real interest rate.
B)expansionary because it results in an increase in the nominal money supply.
C)contractionary because it results in a decline in the real interest rate.
D)contractionary because it results in a decline in the nominal money supply.
expansionary because it results in a decline in the real interest rate.
2
Expansionary shifts of the aggregate demand curve
A)can originate in either the assets market or the goods market.
B)can originate in the assets market, but not the goods market.
C)can originate in the goods market, but not the assets market.
D)cannot originate in either the assets market or the goods market.
A)can originate in either the assets market or the goods market.
B)can originate in the assets market, but not the goods market.
C)can originate in the goods market, but not the assets market.
D)cannot originate in either the assets market or the goods market.
can originate in either the assets market or the goods market.
3
The simultaneous equilibrium of the money, nonmoney asset, and goods markets is known as
A)nominal GDP.
B)potential GDP.
C)general equilibrium.
D)full equilibrium.
A)nominal GDP.
B)potential GDP.
C)general equilibrium.
D)full equilibrium.
general equilibrium.
4
Which of the following is NOT included in aggregate demand?
A)Demand for goods and services for consumption
B)Investment in business plant and equipment
C)Net exports
D)Investment in Treasury bonds
A)Demand for goods and services for consumption
B)Investment in business plant and equipment
C)Net exports
D)Investment in Treasury bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following would NOT shift the aggregate demand curve to the left?
A)An increase in money demand
B)A cut in federal government spending
C)An increase in the money supply
D)A decrease in consumption spending
A)An increase in money demand
B)A cut in federal government spending
C)An increase in the money supply
D)A decrease in consumption spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following will NOT shift the aggregate demand curve to the right?
A)A decline in the price level
B)An increase in government expenditures
C)A decline in money demand
D)An increase in the money supply
A)A decline in the price level
B)An increase in government expenditures
C)A decline in money demand
D)An increase in the money supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following expressions is correct?
A)Yd= C + I + G - NX.
B)Yd = C + I + G + NX.
C)Yd = C + I + (G - T) + NX.
D)Yd = C + I + (G - T) - NX.
A)Yd= C + I + G - NX.
B)Yd = C + I + G + NX.
C)Yd = C + I + (G - T) + NX.
D)Yd = C + I + (G - T) - NX.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A decrease in the price level will lead to
A)a decrease in the real interest rate and an increase in net exports.
B)an increase in the real interest rate and an increase in net exports.
C)a decrease in the real interest rate and a decrease in net exports.
D)an increase in the real interest rate and a decrease in net exports.
A)a decrease in the real interest rate and an increase in net exports.
B)an increase in the real interest rate and an increase in net exports.
C)a decrease in the real interest rate and a decrease in net exports.
D)an increase in the real interest rate and a decrease in net exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the aggregate demand-aggregate supply model, if the Federal Reserve decides to decrease the nominal money supply,
A)current output will fall, but the price level will rise.
B)current output will rise, but the price level will fall.
C)current output and the price level will both rise.
D)current output and the price level will both fall.
A)current output will fall, but the price level will rise.
B)current output will rise, but the price level will fall.
C)current output and the price level will both rise.
D)current output and the price level will both fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A rise in the real interest rate will cause which of the components of aggregate demand to decline?
A)Only C
B)Only C and I
C)Only C, I, and NX
D)C, I, G, and NX
A)Only C
B)Only C and I
C)Only C, I, and NX
D)C, I, G, and NX

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A shift of the AD curve
A)to the right is considered expansionary, and a shift to the left is considered contractionary.
B)to the left is considered expansionary, and a shift to the right is considered contractionary.
C)to the right or to the left is considered contractionary.
D)to the right or to the left is considered expansionary.
A)to the right is considered expansionary, and a shift to the left is considered contractionary.
B)to the left is considered expansionary, and a shift to the right is considered contractionary.
C)to the right or to the left is considered contractionary.
D)to the right or to the left is considered expansionary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following would shift the aggregate demand curve to the left?
A)An increase in the money supply
B)A cut in federal income taxes
C)An increase in money demand
D)An increase in the price level
A)An increase in the money supply
B)A cut in federal income taxes
C)An increase in money demand
D)An increase in the price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which events made the inflation that began in the late 1960s worse?
A)The large tax cuts of the early 1970s
B)The oil supply shocks of the mid-1970s
C)The large increases in the exchange value of the dollar in the early 1970s
D)The large reductions in the government spending in the late 1970s
A)The large tax cuts of the early 1970s
B)The oil supply shocks of the mid-1970s
C)The large increases in the exchange value of the dollar in the early 1970s
D)The large reductions in the government spending in the late 1970s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Points along the aggregate demand curve represent combinations of the price level and current output for which
A)the money market and the goods market are in equilibrium, but the market for nonmoney assets may not be.
B)the goods market and the market for nonmoney assets are in equilibrium, but the money market may not be.
C)the money market and the market for nonmoney assets are in equilibrium, but the goods market may not be.
D)the money market, the market for nonmoney assets, and the goods market must all be in equilibrium.
A)the money market and the goods market are in equilibrium, but the market for nonmoney assets may not be.
B)the goods market and the market for nonmoney assets are in equilibrium, but the money market may not be.
C)the money market and the market for nonmoney assets are in equilibrium, but the goods market may not be.
D)the money market, the market for nonmoney assets, and the goods market must all be in equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The aggregate demand curve illustrates the relationship between
A)the aggregate demand for goods and services, and the real interest rate.
B)the aggregate demand for goods and services, and the level of current output.
C)the level of current output and the real interest rate.
D)the aggregate demand for goods and services, and the aggregate price level.
A)the aggregate demand for goods and services, and the real interest rate.
B)the aggregate demand for goods and services, and the level of current output.
C)the level of current output and the real interest rate.
D)the aggregate demand for goods and services, and the aggregate price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
On what do economists place the blame for the persistent increases in the price level that began in the late 1960s?
A)The government's decision not to raise taxes to finance the Vietnam war
B)The deep recession that began in 1969
C)The Federal Reserve's failure to keep interest rates low
D)The slowdown in productivity growth
A)The government's decision not to raise taxes to finance the Vietnam war
B)The deep recession that began in 1969
C)The Federal Reserve's failure to keep interest rates low
D)The slowdown in productivity growth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The best explanation of why the aggregate demand curve has a negative slope is that
A)at a higher price level households cut back on their spending on goods and services.
B)at a higher price level business firms wish to produce more goods and services.
C)a higher price level results in lower real balances and a higher real interest rate.
D)a higher price level results in less government spending on transfers, such as unemployment insurance and social security payments.
A)at a higher price level households cut back on their spending on goods and services.
B)at a higher price level business firms wish to produce more goods and services.
C)a higher price level results in lower real balances and a higher real interest rate.
D)a higher price level results in less government spending on transfers, such as unemployment insurance and social security payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An increase in the price level reduces net exports because
A)it leads indirectly to a higher exchange rate.
B)it leads indirectly to a lower exchange rate.
C)it leads indirectly to a lower real interest rate.
D)it leads directly to higher real money balances.
A)it leads indirectly to a higher exchange rate.
B)it leads indirectly to a lower exchange rate.
C)it leads indirectly to a lower real interest rate.
D)it leads directly to higher real money balances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Everything else being constant, a lower real interest rate
A)increases desired saving and net exports.
B)decreases desired saving but increases net exports.
C)increases desired saving and investment.
D)increases desired investment but decreases net exports.
A)increases desired saving and net exports.
B)decreases desired saving but increases net exports.
C)increases desired saving and investment.
D)increases desired investment but decreases net exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What does stagflation mean?
A)Rising output and falling prices
B)Falling output and rising prices
C)Rising output and prices
D)Falling output and prices
A)Rising output and falling prices
B)Falling output and rising prices
C)Rising output and prices
D)Falling output and prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What does the coefficient a in the new classical expression for short-run aggregate supply represent?
A)The full employment level of output
B)The price level in the previous period
C)How much output responds when the actual price level differs from the expected price level
D)How much the price level responds when the actual level of output differs from the full employment level of output
A)The full employment level of output
B)The price level in the previous period
C)How much output responds when the actual price level differs from the expected price level
D)How much the price level responds when the actual level of output differs from the full employment level of output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The new classical explanation of aggregate supply is also known as
A)Monetarism.
B)Keynesianism.
C)the misperception theory.
D)the adaptive expectations theory.
A)Monetarism.
B)Keynesianism.
C)the misperception theory.
D)the adaptive expectations theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In the aggregate demand-aggregate supply model, if entrepreneurs become convinced that future profitability of capital has increased,
A)current output will fall, but the price level will rise.
B)current output will rise, but the price level will fall.
C)current output and the price level will both rise.
D)current output and the price level will both fall.
A)current output will fall, but the price level will rise.
B)current output will rise, but the price level will fall.
C)current output and the price level will both rise.
D)current output and the price level will both fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
An increase in all of the following will increase AD EXCEPT
A)investment.
B)savings.
C)exports.
D)government spending.
A)investment.
B)savings.
C)exports.
D)government spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If there is a recession in Europe
A)the aggregate demand curve in the United States will shift right.
B)the aggregate demand curve in the United States will shift left.
C)the aggregate demand curve in the United States will become steeper.
D)the aggregate demand curve in the United States will be unaffected.
A)the aggregate demand curve in the United States will shift right.
B)the aggregate demand curve in the United States will shift left.
C)the aggregate demand curve in the United States will become steeper.
D)the aggregate demand curve in the United States will be unaffected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If the coefficient a in the new classical expression for short-run aggregate supply were equal to zero,
A)aggregate output would always be at its full-employment level.
B)the short-run aggregate supply curve would slope down.
C)the short-run aggregate supply curve would be a horizontal line.
D)aggregate output would only differ from its full-employment level if the actual price level did not equal the expected price level.
A)aggregate output would always be at its full-employment level.
B)the short-run aggregate supply curve would slope down.
C)the short-run aggregate supply curve would be a horizontal line.
D)aggregate output would only differ from its full-employment level if the actual price level did not equal the expected price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
According to the new classical approach to the aggregate supply curve, the aggregate supply curve slopes upward because
A)increases in the price level result in lower real balances.
B)higher current output results in higher desired investment.
C)higher prices result in higher levels of spending as consumers attempt to stay ahead of inflation.
D)businesses have difficulty in distinguishing relative price increases from general price increases.
A)increases in the price level result in lower real balances.
B)higher current output results in higher desired investment.
C)higher prices result in higher levels of spending as consumers attempt to stay ahead of inflation.
D)businesses have difficulty in distinguishing relative price increases from general price increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Most economists believe that the aggregate supply curve is
A)upward-sloping in the short run, but vertical in the long run.
B)upward-sloping in the long run, but vertical in the short run.
C)upward-sloping in both the short run and in the long run.
D)vertical in both the short run and in the long run.
A)upward-sloping in the short run, but vertical in the long run.
B)upward-sloping in the long run, but vertical in the short run.
C)upward-sloping in both the short run and in the long run.
D)vertical in both the short run and in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The key concept in the new classical approach to the aggregate supply curve is
A)the impact of imperfect information on business decisions.
B)the impact of changes in the price level on real balances.
C)the inverse relationship between the real interest rate and desired investment spending.
D)the crowding out of investment spending by government spending.
A)the impact of imperfect information on business decisions.
B)the impact of changes in the price level on real balances.
C)the inverse relationship between the real interest rate and desired investment spending.
D)the crowding out of investment spending by government spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The new classical approach to the aggregate supply curve assumes that businesses are
A)better informed about the general price level than they are about prices in their own markets.
B)better informed about prices in their own markets than they are about the general price level.
C)equally well informed about prices in their own markets and the general price level.
D)reluctant to engage in investment spending because of a lack of information concerning future prices.
A)better informed about the general price level than they are about prices in their own markets.
B)better informed about prices in their own markets than they are about the general price level.
C)equally well informed about prices in their own markets and the general price level.
D)reluctant to engage in investment spending because of a lack of information concerning future prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Most economists believe that changes in the price level have
A)no effect on the quantity of output supplied in either the short run or the long run.
B)an effect on the quantity of output supplied in the short run, but not in the long run.
C)an effect on the quantity of output supplied in the long run, but not in the short run.
D)an effect on the quantity of output supplied in both the short run and the long run.
A)no effect on the quantity of output supplied in either the short run or the long run.
B)an effect on the quantity of output supplied in the short run, but not in the long run.
C)an effect on the quantity of output supplied in the long run, but not in the short run.
D)an effect on the quantity of output supplied in both the short run and the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
National savings is likely to decline for all of the following reasons EXCEPT
A)increase in expected future income.
B)increase in government purchases.
C)increased consumer pessimism.
D)tax cuts (assuming Ricardian equivalence does not hold).
A)increase in expected future income.
B)increase in government purchases.
C)increased consumer pessimism.
D)tax cuts (assuming Ricardian equivalence does not hold).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The Ricardian equivalence proposition will not hold if
A)the government finances its expenditures by borrowing rather than by taxing.
B)the government finances its expenditures by taxing rather than by borrowing.
C)consumers face restrictions on the amount they can borrow.
D)consumers finance their tax payments by borrowing.
A)the government finances its expenditures by borrowing rather than by taxing.
B)the government finances its expenditures by taxing rather than by borrowing.
C)consumers face restrictions on the amount they can borrow.
D)consumers finance their tax payments by borrowing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Most economists believe that the short-run aggregate supply curve
A)slopes down.
B)slopes up.
C)is a vertical line.
D)is a horizontal line.
A)slopes down.
B)slopes up.
C)is a vertical line.
D)is a horizontal line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In the aggregate demand-aggregate supply model, if firms expect businesses taxes to rise
A)current output will fall, but the price level will rise.
B)current output will rise, but the price level will fall.
C)current output and the price level will both rise.
D)current output and the price level will both fall.
A)current output will fall, but the price level will rise.
B)current output will rise, but the price level will fall.
C)current output and the price level will both rise.
D)current output and the price level will both fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The new classical explanation of aggregate supply in the short run builds on research by
A)Irving Fisher.
B)John Maynard Keynes.
C)Robert Lucas.
D)Robert Solow.
A)Irving Fisher.
B)John Maynard Keynes.
C)Robert Lucas.
D)Robert Solow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is the correct expression for short-run aggregate supply in the new classical view?
A)Y = Y + a(P - Pe)
B)Y = Y + a(P - Pe)
C)Y = Y + a(P + Pe)
D)Y = Y + a(P + Pe)
A)Y = Y + a(P - Pe)
B)Y = Y + a(P - Pe)
C)Y = Y + a(P + Pe)
D)Y = Y + a(P + Pe)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
According to AD-AS model, the primary long-run effect of increases in the money supply is
A)higher price level.
B)higher GDP.
C)lower price level.
D)lower GDP.
A)higher price level.
B)higher GDP.
C)lower price level.
D)lower GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The aggregate supply curve represents levels of output that producers are willing to sell at
A)each level of the real interest rate.
B)each level of real GDP.
C)each price level.
D)each inflation rate.
A)each level of the real interest rate.
B)each level of real GDP.
C)each price level.
D)each inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
According to the Ricardian equivalence proposition,
A)saving equals investment only at full employment.
B)a decline in the demand for money results in an equivalent increase in the demand for nonmoney assets.
C)the increase in current income from a tax cut is offset by higher taxes in the future to pay off the debt.
D)government spending is the equivalent of investment spending.
A)saving equals investment only at full employment.
B)a decline in the demand for money results in an equivalent increase in the demand for nonmoney assets.
C)the increase in current income from a tax cut is offset by higher taxes in the future to pay off the debt.
D)government spending is the equivalent of investment spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following best describes a price setter?
A)Firms in perfect competition
B)Pricing of products that are not standardized
C)Firms setting prices equal to the market price
D)Firms setting price equal to the aggregate price level
A)Firms in perfect competition
B)Pricing of products that are not standardized
C)Firms setting prices equal to the market price
D)Firms setting price equal to the aggregate price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In which of the following markets is a producer likely to be a price taker?
A)The apple market
B)The automobile market
C)The steel market
D)The college textbook market
A)The apple market
B)The automobile market
C)The steel market
D)The college textbook market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following best describes a price taker?
A)A firm taking the market price as given
B)Price strategies found in monopolistically competitive markets
C)Prices being set by long-term contracts
D)Firms taking the aggregate price level as given
A)A firm taking the market price as given
B)Price strategies found in monopolistically competitive markets
C)Prices being set by long-term contracts
D)Firms taking the aggregate price level as given

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following statements correctly describes the New Keynesian view of the response of the price level to changes in the money supply?
A)The price level is unrelated to the money supply.
B)The price level increases in proportion to increases in the money supply in the short run.
C)The price level adjusts slowly to changes in the money supply.
D)The price level is sticky in the long run, and thus doesn't fully respond to changes in the money supply.
A)The price level is unrelated to the money supply.
B)The price level increases in proportion to increases in the money supply in the short run.
C)The price level adjusts slowly to changes in the money supply.
D)The price level is sticky in the long run, and thus doesn't fully respond to changes in the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In the new Keynesian view, which of the following expressions correctly states the relationship between the price that an individual firm with flexible prices charges and the aggregate price level?
A)p = P + b(Y - Y)
B)P = p + b(Y - Y)
C)p = P + b(Y + Y)
D)p = P + b(Y - Y)
A)p = P + b(Y - Y)
B)P = p + b(Y - Y)
C)p = P + b(Y + Y)
D)p = P + b(Y - Y)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In the new Keynesian expression for the price level, c represents
A)the fraction of firms in the economy with sticky prices.
B)the marginal propensity to consume.
C)the responsiveness of the price level to differences between actual aggregate output and full-employment aggregate output.
D)the responsiveness of aggregate output to the difference between the actual price level and the expected price level.
A)the fraction of firms in the economy with sticky prices.
B)the marginal propensity to consume.
C)the responsiveness of the price level to differences between actual aggregate output and full-employment aggregate output.
D)the responsiveness of aggregate output to the difference between the actual price level and the expected price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
According to the new classical view, when the actual price level is greater than the expected price level
A)aggregate output is above the full employment level.
B)aggregate output is below the full employment level.
C)the aggregate supply curve will slope downward.
D)the coefficient a is equal to zero.
A)aggregate output is above the full employment level.
B)aggregate output is below the full employment level.
C)the aggregate supply curve will slope downward.
D)the coefficient a is equal to zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The existence of cost of living adjustments in many wage contracts
A)assures that these wages fully adjust to aggregate nominal disturbances.
B)results in these wages being completely rigid.
C)does not result in these wages fully adjusting to aggregate nominal disturbances.
D)is being phased out under recent federal legislation.
A)assures that these wages fully adjust to aggregate nominal disturbances.
B)results in these wages being completely rigid.
C)does not result in these wages fully adjusting to aggregate nominal disturbances.
D)is being phased out under recent federal legislation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following is the correct new Keynesian expression for the price level?
A)P = Pe + b[(1 - c)/c]ΔY
B)Pe = P + b[(1 - c)/c]ΔY
C)P = Pe + b[(1 + c)/c]ΔY
D)Pe = P + b[(1 + c)/c]ΔY
A)P = Pe + b[(1 - c)/c]ΔY
B)Pe = P + b[(1 - c)/c]ΔY
C)P = Pe + b[(1 + c)/c]ΔY
D)Pe = P + b[(1 + c)/c]ΔY

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In the new Keynesian view, the larger the proportion of firms in the economy with sticky prices,
A)the steeper the SRAS curve will be.
B)the flatter the SRAS curve will be.
C)the greater the increase in the price level for a given shift in the AD curve.
D)the less effective is fiscal policy in increasing output.
A)the steeper the SRAS curve will be.
B)the flatter the SRAS curve will be.
C)the greater the increase in the price level for a given shift in the AD curve.
D)the less effective is fiscal policy in increasing output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
New Keynesians believe that an increase in the nominal money supply will result in
A)no change in the price level.
B)a proportional increase in the price level.
C)a less than proportional increase in the price level.
D)a fall in the price level.
A)no change in the price level.
B)a proportional increase in the price level.
C)a less than proportional increase in the price level.
D)a fall in the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In the new Keynesian view, which of the following expressions correctly states the relationship between the price that an individual firm with sticky prices charges and the aggregate price level?
A)p = Pe + b(Ye- Ye)
B)Pe = p + b(Ye - Ye)
C)p = Pe + b(Ye + Y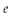 )
)
D)p = Pe + b(Y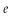 - Ye)
- Ye)
A)p = Pe + b(Ye- Ye)
B)Pe = p + b(Ye - Ye)
C)p = Pe + b(Ye + Y
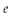 )
)D)p = Pe + b(Y
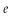 - Ye)
- Ye)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following statements is correct?
A)New classicals believe that the aggregate supply curve is vertical in the short run.
B)New Keynesians believe that the aggregate supply curve is vertical in the short run.
C)New Keynesians believe that the aggregate supply curve slopes upward in the long run.
D)New classicals believe that the aggregate supply curve slopes upward in the short run.
A)New classicals believe that the aggregate supply curve is vertical in the short run.
B)New Keynesians believe that the aggregate supply curve is vertical in the short run.
C)New Keynesians believe that the aggregate supply curve slopes upward in the long run.
D)New classicals believe that the aggregate supply curve slopes upward in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In the new Keynesian view a monopolistically competitive firm may fail to increase the price of its product as demand increases because
A)if it does so it will lose all of its customers.
B)the cost to it of changing prices may exceed the benefit of doing so.
C)prices of monopolistically competitive firms are regulated by the federal government and may only be changed with permission.
D)for a monopolistically competitive firm, price is below marginal cost.
A)if it does so it will lose all of its customers.
B)the cost to it of changing prices may exceed the benefit of doing so.
C)prices of monopolistically competitive firms are regulated by the federal government and may only be changed with permission.
D)for a monopolistically competitive firm, price is below marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If in the short run prices did not respond at all to changes in aggregate demand, the short-run aggregate supply curve would
A)be vertical.
B)be horizontal.
C)slope up.
D)slope down.
A)be vertical.
B)be horizontal.
C)slope up.
D)slope down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
According to the new classical view, aggregate output will differ from full-employment output
A)whenever saving does not equal investment.
B)only if the actual price level does not equal the expected price level.
C)only if the federal government's expenditures are greater than its tax receipts.
D)whenever imports exceed exports.
A)whenever saving does not equal investment.
B)only if the actual price level does not equal the expected price level.
C)only if the federal government's expenditures are greater than its tax receipts.
D)whenever imports exceed exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The difference between the Keynesian and new Keynesian approaches to the short-run aggregate supply curve is that
A)Keynesians assumed that the short-run aggregate supply curve was vertical or nearly vertical, while new Keynesians assume that it is nearly horizontal.
B)Keynesians focused on the difference between the actual and expected price levels, whereas new Keynesians believe this difference to be unimportant.
C)Keynesians believed that aggregate demand was more important than aggregate supply, whereas new Keynesians believe the reverse.
D)Keynesians assumed that the short-run aggregate supply curve was horizontal or nearly horizontal, whereas new Keynesians have provided economic explanations for price stickiness.
A)Keynesians assumed that the short-run aggregate supply curve was vertical or nearly vertical, while new Keynesians assume that it is nearly horizontal.
B)Keynesians focused on the difference between the actual and expected price levels, whereas new Keynesians believe this difference to be unimportant.
C)Keynesians believed that aggregate demand was more important than aggregate supply, whereas new Keynesians believe the reverse.
D)Keynesians assumed that the short-run aggregate supply curve was horizontal or nearly horizontal, whereas new Keynesians have provided economic explanations for price stickiness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A monopolistically competitive market differs from a perfectly competitive market in that a monopolistically competitive market has
A)more sellers.
B)products that are identical.
C)less sticky prices.
D)firms that are price setters.
A)more sellers.
B)products that are identical.
C)less sticky prices.
D)firms that are price setters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
An important difference between the new classical and new Keynesians views is that new classicals
A)assume that all firms are price takers, but new Keynesians assume that some firms are price setters.
B)take into account the existence of long-term nominal wage and price contracts, but new Keynesians do not believe they are important.
C)focus on the importance of investment spending, but new Keynesians believe that government spending is more important.
D)believe that the aggregate supply curve is horizontal, even in the short run, but new Keynesians believe that the aggregate supply curve slopes upward in the short run.
A)assume that all firms are price takers, but new Keynesians assume that some firms are price setters.
B)take into account the existence of long-term nominal wage and price contracts, but new Keynesians do not believe they are important.
C)focus on the importance of investment spending, but new Keynesians believe that government spending is more important.
D)believe that the aggregate supply curve is horizontal, even in the short run, but new Keynesians believe that the aggregate supply curve slopes upward in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If wages and prices in long-term contracts were fully indexed,
A)prices would be more sticky in the short run.
B)prices would be more sticky in the long run.
C)prices would be less sticky in the short run.
D)the stickiness of prices would not be affected.
A)prices would be more sticky in the short run.
B)prices would be more sticky in the long run.
C)prices would be less sticky in the short run.
D)the stickiness of prices would not be affected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The hypothesis that large negative shifts in aggregate demand reduce the full-employment level of output is known as
A)the real balance effect.
B)the perverse employment syndrome.
C)the real business cycle effect.
D)hysteresis.
A)the real balance effect.
B)the perverse employment syndrome.
C)the real business cycle effect.
D)hysteresis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following groups of economists think that aggregate supply is vertical in the long run?
A)Real business cycle
B)New Keynesian
C)New classical
D)All of the above
A)Real business cycle
B)New Keynesian
C)New classical
D)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following is most likely to have an impact on the growth of productivity?
A)A decrease in the price level
B)An increase in government regulation of workplace safety
C)An increase in the labor supply
D)A decrease in real money balances
A)A decrease in the price level
B)An increase in government regulation of workplace safety
C)An increase in the labor supply
D)A decrease in real money balances

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following is NOT an example of a supply shock?
A)A drought in the Midwest
B)A decline in natural gas prices following discovery of new fields
C)The introduction of a new line of computer-controlled machine tools in manufacturing
D)A substantial increase in federal government spending on medicare
A)A drought in the Midwest
B)A decline in natural gas prices following discovery of new fields
C)The introduction of a new line of computer-controlled machine tools in manufacturing
D)A substantial increase in federal government spending on medicare

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
When output exceeds its full-employment level,
A)the short-run aggregate supply function shifts up.
B)wages fall.
C)the short-run aggregate supply function shifts down.
D)aggregate supply exceeds aggregate demand.
A)the short-run aggregate supply function shifts up.
B)wages fall.
C)the short-run aggregate supply function shifts down.
D)aggregate supply exceeds aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Economists generally agree that in the long run changes in aggregate demand affect
A)aggregate output but not the price level.
B)the price level but not aggregate output.
C)both the price level and aggregate output.
D)neither the price level nor aggregate output.
A)aggregate output but not the price level.
B)the price level but not aggregate output.
C)both the price level and aggregate output.
D)neither the price level nor aggregate output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The Polish experience indicates that
A)the aggregate supply curve is vertical, even in the short run.
B)changes in the expected price level do not affect aggregate supply.
C)the transition from a centrally planned to a market economy can result in an upward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
D)increases in the factor productivity will shift the long-run aggregate supply curve to the left.
A)the aggregate supply curve is vertical, even in the short run.
B)changes in the expected price level do not affect aggregate supply.
C)the transition from a centrally planned to a market economy can result in an upward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
D)increases in the factor productivity will shift the long-run aggregate supply curve to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
When output is below its full-employment level, the short-run aggregate supply will shift down and to the right because
A)the expected price level will be below the actual price level.
B)workers' wages will decline.
C)prices of nonlabor inputs will rise.
D)workers' wages will rise.
A)the expected price level will be below the actual price level.
B)workers' wages will decline.
C)prices of nonlabor inputs will rise.
D)workers' wages will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If the economy is initially at equilibrium and an unexpected decline in aggregate demand takes place, in the short run aggregate output will
A)fall in the new classical view, but not in the new Keynesian view.
B)fall in the new Keynesian view, but not in the new classical view.
C)fall in both the new Keynesian and new classical views.
D)remain at full employment in both the new classical and new Keynesian views.
A)fall in the new classical view, but not in the new Keynesian view.
B)fall in the new Keynesian view, but not in the new classical view.
C)fall in both the new Keynesian and new classical views.
D)remain at full employment in both the new classical and new Keynesian views.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If the expected price level increases at the same time that the federal government cuts taxes, in the short run
A)aggregate output and the price level will both increase.
B)aggregate output will increase, but the price level will fall.
C)aggregate output and the price level will both fall.
D)the price level will increase, but aggregate output may either increase or decrease.
A)aggregate output and the price level will both increase.
B)aggregate output will increase, but the price level will fall.
C)aggregate output and the price level will both fall.
D)the price level will increase, but aggregate output may either increase or decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following would cause the long-run aggregate supply curve to shift?
A)An increase in the price level
B)A decrease in the expected price level
C)An increase in labor productivity
D)An autonomous increase in consumption spending
A)An increase in the price level
B)A decrease in the expected price level
C)An increase in labor productivity
D)An autonomous increase in consumption spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
An increase in the expected price level
A)shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve up and to the left.
B)shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve down and to the right.
C)has no effect on the short-run aggregate supply curve.
D)results in a movement along the short-run aggregate supply curve, rather than a shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
A)shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve up and to the left.
B)shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve down and to the right.
C)has no effect on the short-run aggregate supply curve.
D)results in a movement along the short-run aggregate supply curve, rather than a shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If oil prices fall at the same time that the federal government increases its spending, in the short run
A)aggregate output and the price level will both increase.
B)aggregate output will increase, but the price level will fall.
C)aggregate output and the price level will both fall.
D)aggregate output will increase, but the price level may either increase or decrease.
A)aggregate output and the price level will both increase.
B)aggregate output will increase, but the price level will fall.
C)aggregate output and the price level will both fall.
D)aggregate output will increase, but the price level may either increase or decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
An increase in oil prices will shift the short-run aggregate supply curve
A)up and to the left, causing the level of current output to fall.
B)up and to the left, causing the level of current output to rise.
C)down and to the right, causing the level of current output to rise.
D)down and to the right, causing the level of current output to fall.
A)up and to the left, causing the level of current output to fall.
B)up and to the left, causing the level of current output to rise.
C)down and to the right, causing the level of current output to rise.
D)down and to the right, causing the level of current output to fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If labor costs rise at the same time that the federal government decreases its spending, in the short run
A)aggregate output and the price level will both increase.
B)aggregate output will increase, but the price level will fall.
C)aggregate output and the price level will both fall.
D)aggregate output will fall, but the price level may either increase or decrease.
A)aggregate output and the price level will both increase.
B)aggregate output will increase, but the price level will fall.
C)aggregate output and the price level will both fall.
D)aggregate output will fall, but the price level may either increase or decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Monetary neutrality refers to the fact that changes in the money supply
A)affect output more in the long run than in the short run.
B)have no effect on output in the long run.
C)affect only output in the long run.
D)have a greater effect on prices in the short run than in the long run.
A)affect output more in the long run than in the short run.
B)have no effect on output in the long run.
C)affect only output in the long run.
D)have a greater effect on prices in the short run than in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
An increase in the price level
A)shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve up and to the left.
B)shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve down and to the right.
C)shifts the long-run aggregate supply curve to the left.
D)results in a movement along the short-run aggregate supply curve, rather than a shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
A)shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve up and to the left.
B)shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve down and to the right.
C)shifts the long-run aggregate supply curve to the left.
D)results in a movement along the short-run aggregate supply curve, rather than a shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following will NOT shift the short-run aggregate supply function?
A)Changes in labor costs
B)Changes in the costs of nonlabor inputs
C)Changes in the price level
D)Changes in the expected price level
A)Changes in labor costs
B)Changes in the costs of nonlabor inputs
C)Changes in the price level
D)Changes in the expected price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following statements is correct?
A)New classicals believe that the aggregate supply curve is a vertical line in both the short run and the long run.
B)Both new classicals and new Keynesians believe that the aggregate supply curve is vertical in the long run.
C)New Keynesians believe that the aggregate supply curve is vertical in the short run but not in the long run.
D)New Keynesians believe that the aggregate supply curve slopes upward in the long run.
A)New classicals believe that the aggregate supply curve is a vertical line in both the short run and the long run.
B)Both new classicals and new Keynesians believe that the aggregate supply curve is vertical in the long run.
C)New Keynesians believe that the aggregate supply curve is vertical in the short run but not in the long run.
D)New Keynesians believe that the aggregate supply curve slopes upward in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Between 1992 and the early 2000s, Poland experienced
A)strong economic growth, but increasing inflation.
B)weak economic growth, but falling inflation.
C)strong economic growth and falling inflation.
D)weak economic growth and increasing inflation.
A)strong economic growth, but increasing inflation.
B)weak economic growth, but falling inflation.
C)strong economic growth and falling inflation.
D)weak economic growth and increasing inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



