Deck 31: Synthetic Polymers
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/33
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 31: Synthetic Polymers
1
____ a polyurethane
A)BF3 + H2O
B)elastomer
C)chain-growth polymer
D)AL(CH2CH3)3 + TiCl4
E)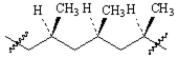
F)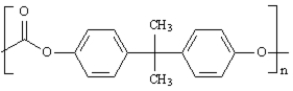
G)thermoplastic
H)homopolymer
I)plasticizers
J)thermosetting resins
K)copolymers
L)step-growth polymer
M)Grubb's catalyst
N)metallacycle
O)
P)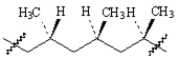
A)BF3 + H2O
B)elastomer
C)chain-growth polymer
D)AL(CH2CH3)3 + TiCl4
E)

F)

G)thermoplastic
H)homopolymer
I)plasticizers
J)thermosetting resins
K)copolymers
L)step-growth polymer
M)Grubb's catalyst
N)metallacycle
O)

P)


2
Rank the following monomers in order of increasing reactivity toward cationic polymerization (least reactive to most reactive). 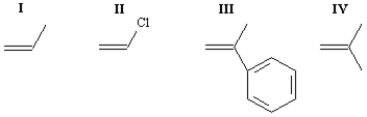
A)III,IV,I,II
B)II,I,IV,III
C)I,II,IV,III
D)IV,III,I,II

A)III,IV,I,II
B)II,I,IV,III
C)I,II,IV,III
D)IV,III,I,II
II,I,IV,III
3
_____ General structure: M=CHR
A)BF3 + H2O
B)elastomer
C)chain-growth polymer
D)AL(CH2CH3)3 + TiCl4
E)
F)
G)thermoplastic
H)homopolymer
I)plasticizers
J)thermosetting resins
K)copolymers
L)step-growth polymer
M)Grubb's catalyst
N)metallacycle
O)
P)
A)BF3 + H2O
B)elastomer
C)chain-growth polymer
D)AL(CH2CH3)3 + TiCl4
E)

F)

G)thermoplastic
H)homopolymer
I)plasticizers
J)thermosetting resins
K)copolymers
L)step-growth polymer
M)Grubb's catalyst
N)metallacycle
O)

P)

Grubb's catalyst
4
Exhibit 31-2
Draw the structure(s) of the monomer(s) used to make each of the following polymers.
Draw: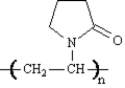
Draw the structure(s) of the monomer(s) used to make each of the following polymers.
Draw:


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
____ Isotactic propylene
A)BF3 + H2O
B)elastomer
C)chain-growth polymer
D)AL(CH2CH3)3 + TiCl4
E)
F)
G)thermoplastic
H)homopolymer
I)plasticizers
J)thermosetting resins
K)copolymers
L)step-growth polymer
M)Grubb's catalyst
N)metallacycle
O)
P)
A)BF3 + H2O
B)elastomer
C)chain-growth polymer
D)AL(CH2CH3)3 + TiCl4
E)

F)

G)thermoplastic
H)homopolymer
I)plasticizers
J)thermosetting resins
K)copolymers
L)step-growth polymer
M)Grubb's catalyst
N)metallacycle
O)

P)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
____ a Ziegler-Natta catalyst
A)BF3 + H2O
B)elastomer
C)chain-growth polymer
D)AL(CH2CH3)3 + TiCl4
E)
F)
G)thermoplastic
H)homopolymer
I)plasticizers
J)thermosetting resins
K)copolymers
L)step-growth polymer
M)Grubb's catalyst
N)metallacycle
O)
P)
A)BF3 + H2O
B)elastomer
C)chain-growth polymer
D)AL(CH2CH3)3 + TiCl4
E)

F)

G)thermoplastic
H)homopolymer
I)plasticizers
J)thermosetting resins
K)copolymers
L)step-growth polymer
M)Grubb's catalyst
N)metallacycle
O)

P)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Do you expect nitroethylene to be more or less reactive than ethylene toward cationic polymerization? Explain. 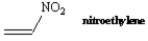
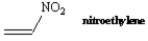

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
____ Small organic molecules that act as lubricants between polymer chains.
A)BF3 + H2O
B)elastomer
C)chain-growth polymer
D)AL(CH2CH3)3 + TiCl4
E)
F)
G)thermoplastic
H)homopolymer
I)plasticizers
J)thermosetting resins
K)copolymers
L)step-growth polymer
M)Grubb's catalyst
N)metallacycle
O)
P)
A)BF3 + H2O
B)elastomer
C)chain-growth polymer
D)AL(CH2CH3)3 + TiCl4
E)

F)

G)thermoplastic
H)homopolymer
I)plasticizers
J)thermosetting resins
K)copolymers
L)step-growth polymer
M)Grubb's catalyst
N)metallacycle
O)

P)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Exhibit 31-2
Draw the structure(s) of the monomer(s) used to make each of the following polymers.
Draw: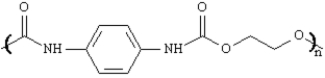
Draw the structure(s) of the monomer(s) used to make each of the following polymers.
Draw:


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Monomer A is copolymerized with Monomer B and is found to have the following structure: 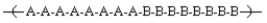 The type of copolymer formed is:
The type of copolymer formed is:
A)a random copolymer
B)an alternating copolymer
C)a block copolymer
D)a graft copolymer
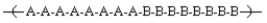 The type of copolymer formed is:
The type of copolymer formed is:A)a random copolymer
B)an alternating copolymer
C)a block copolymer
D)a graft copolymer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Rank the following monomers in order of increasing reactivity toward anionic polymerization (least reactive to most reactive). 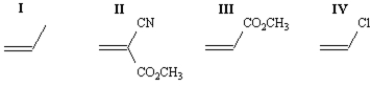
A)III,II,IV,I
B)II,III,I,II
C)I,IV,III,II
D)IV,III,II,I

A)III,II,IV,I
B)II,III,I,II
C)I,IV,III,II
D)IV,III,II,I

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Draw two repeating units of the polymer formed by the reaction of 1,3-butadiene with the following substance.Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled. 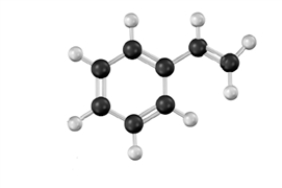


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
______ four-membered metal containing intermediate
A)BF3 + H2O
B)elastomer
C)chain-growth polymer
D)AL(CH2CH3)3 + TiCl4
E)
F)
G)thermoplastic
H)homopolymer
I)plasticizers
J)thermosetting resins
K)copolymers
L)step-growth polymer
M)Grubb's catalyst
N)metallacycle
O)
P)
A)BF3 + H2O
B)elastomer
C)chain-growth polymer
D)AL(CH2CH3)3 + TiCl4
E)

F)

G)thermoplastic
H)homopolymer
I)plasticizers
J)thermosetting resins
K)copolymers
L)step-growth polymer
M)Grubb's catalyst
N)metallacycle
O)

P)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
____ Bakelite is this type of polymer.
A)BF3 + H2O
B)elastomer
C)chain-growth polymer
D)AL(CH2CH3)3 + TiCl4
E)
F)
G)thermoplastic
H)homopolymer
I)plasticizers
J)thermosetting resins
K)copolymers
L)step-growth polymer
M)Grubb's catalyst
N)metallacycle
O)
P)
A)BF3 + H2O
B)elastomer
C)chain-growth polymer
D)AL(CH2CH3)3 + TiCl4
E)

F)

G)thermoplastic
H)homopolymer
I)plasticizers
J)thermosetting resins
K)copolymers
L)step-growth polymer
M)Grubb's catalyst
N)metallacycle
O)

P)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
____ Amorphous polymers that have the ability to stretch out and spring back to their original shape.
A)BF3 + H2O
B)elastomer
C)chain-growth polymer
D)AL(CH2CH3)3 + TiCl4
E)
F)
G)thermoplastic
H)homopolymer
I)plasticizers
J)thermosetting resins
K)copolymers
L)step-growth polymer
M)Grubb's catalyst
N)metallacycle
O)
P)
A)BF3 + H2O
B)elastomer
C)chain-growth polymer
D)AL(CH2CH3)3 + TiCl4
E)

F)

G)thermoplastic
H)homopolymer
I)plasticizers
J)thermosetting resins
K)copolymers
L)step-growth polymer
M)Grubb's catalyst
N)metallacycle
O)

P)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Exhibit 31-2
Draw the structure(s) of the monomer(s) used to make each of the following polymers.
Draw: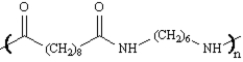
Draw the structure(s) of the monomer(s) used to make each of the following polymers.
Draw:


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
____ Produced by reactions in which each bond in the polymer is formed independently of the others.
A)BF3 + H2O
B)elastomer
C)chain-growth polymer
D)AL(CH2CH3)3 + TiCl4
E)
F)
G)thermoplastic
H)homopolymer
I)plasticizers
J)thermosetting resins
K)copolymers
L)step-growth polymer
M)Grubb's catalyst
N)metallacycle
O)
P)
A)BF3 + H2O
B)elastomer
C)chain-growth polymer
D)AL(CH2CH3)3 + TiCl4
E)

F)

G)thermoplastic
H)homopolymer
I)plasticizers
J)thermosetting resins
K)copolymers
L)step-growth polymer
M)Grubb's catalyst
N)metallacycle
O)

P)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
____ Polymers obtained when two or more different monomers are allowed to polymerize together.
A)BF3 + H2O
B)elastomer
C)chain-growth polymer
D)AL(CH2CH3)3 + TiCl4
E)
F)
G)thermoplastic
H)homopolymer
I)plasticizers
J)thermosetting resins
K)copolymers
L)step-growth polymer
M)Grubb's catalyst
N)metallacycle
O)
P)
A)BF3 + H2O
B)elastomer
C)chain-growth polymer
D)AL(CH2CH3)3 + TiCl4
E)

F)

G)thermoplastic
H)homopolymer
I)plasticizers
J)thermosetting resins
K)copolymers
L)step-growth polymer
M)Grubb's catalyst
N)metallacycle
O)

P)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Do you expect nitroethylene to be more or less reactive than ethylene toward anionic polymerization? Explain. 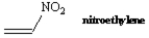
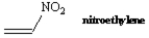

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Exhibit 31-2
Draw the structure(s) of the monomer(s) used to make each of the following polymers.
Draw: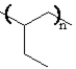
Draw the structure(s) of the monomer(s) used to make each of the following polymers.
Draw:


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Consider the following diagram representing crystallites.  Which type of polymer is represented?
Which type of polymer is represented?
A)thermoplastic
B)fiber
C)elastomer
D)thermosetting resins
 Which type of polymer is represented?
Which type of polymer is represented?A)thermoplastic
B)fiber
C)elastomer
D)thermosetting resins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In general,which of the following types of polymers would probably be the least crystalline?
A)isotactic
B)atactic
C)syndiotactic
A)isotactic
B)atactic
C)syndiotactic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is not a property of a crystalline polymer?
A)unaffected by steric properties of substituent groups
B)generally hard and durable
C)crystalline regions become amorphous on heating
D)contain highly organized regions
A)unaffected by steric properties of substituent groups
B)generally hard and durable
C)crystalline regions become amorphous on heating
D)contain highly organized regions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which type of polymer has a high glass transition temperature (Tg)?
A)thermoplastic
B)fiber
C)elastomer
D)thermosetting resins
A)thermoplastic
B)fiber
C)elastomer
D)thermosetting resins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Within a crystallite,the polymer chains are held together by:
A)disuflide bridges
B)hydrogen bonds
C)van der Walls forces
D)covalent bonds
A)disuflide bridges
B)hydrogen bonds
C)van der Walls forces
D)covalent bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Classify the following polymer. 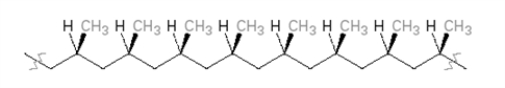
A)isotactic
B)syndiotactic
C)atactic

A)isotactic
B)syndiotactic
C)atactic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Draw the structure of the product produced by the acyclic diene metathesis (ADMET) of 1,6-heptadiene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is not an advantage of olefinic metathesis polymerization?
A)It can be used in the presence of many functional groups.
B)It results in an unsaturated polymer.
C)The resulting polymer is susceptible to further chemical changes.
D)ROMP reactions run with high efficiency but ADMET reactions do not.
E)All characterize olefinic metathesis polymerization procedures.
A)It can be used in the presence of many functional groups.
B)It results in an unsaturated polymer.
C)The resulting polymer is susceptible to further chemical changes.
D)ROMP reactions run with high efficiency but ADMET reactions do not.
E)All characterize olefinic metathesis polymerization procedures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Draw the structure of the monomer used to produce the following polymer segment using the ROMP method. 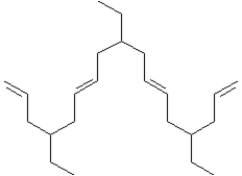


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which type of polymer is characterized by irregular chain length,low Tg,and only a small degree of cross-linking?
A)thermoplastic
B)fiber
C)elastomer
D)thermosetting resins
A)thermoplastic
B)fiber
C)elastomer
D)thermosetting resins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Classify the following polymer. 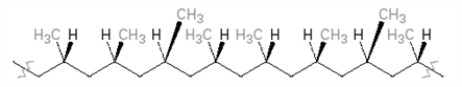
A)isotactic
B)syndiotactic
C)atactic

A)isotactic
B)syndiotactic
C)atactic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following monomers could produce atactic,isotactic,and syndiotactic polymers?
A)H2C=CH2
B)H2C=CClH
C)H2C=CCl2
D)Cl2C=CCl2
A)H2C=CH2
B)H2C=CClH
C)H2C=CCl2
D)Cl2C=CCl2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following represents the general structure of a urethane?
A)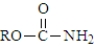
B)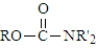
C)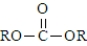
D)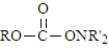
A)
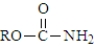
B)
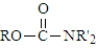
C)
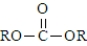
D)
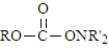

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



