Deck 28: Biomolecules: Nucleic Acids
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/44
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 28: Biomolecules: Nucleic Acids
1
Draw and label the four DNA nucleosides.
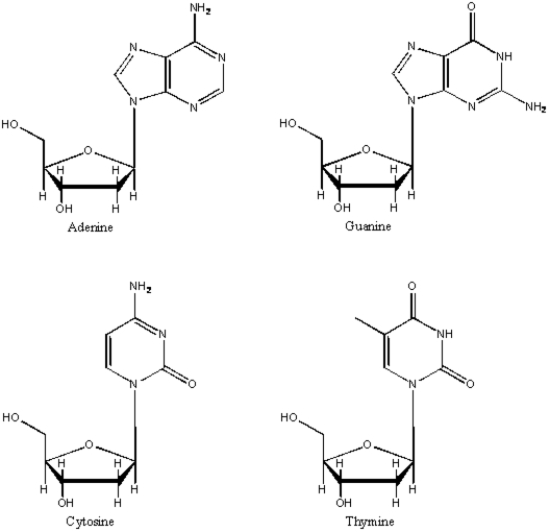
2
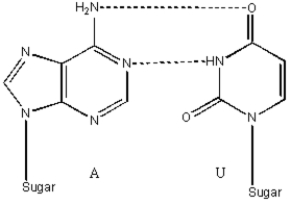
Draw and label an A-U base pair.Indicate all hydrogen bonds with a dashed line.
3
Of the two sets of DNA base pairs,which would you expect to be stronger and why?
The G-C base pair is the stronger of the two as it has three hydrogen bonds whereas the A-T base pair has only two.
4
_____ uridine
A)Sanger dideoxy method
B)GAUCGUAAA
C)Watson-Crick
D)translation
E)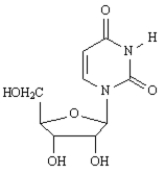
F)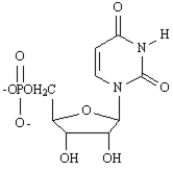
G)transcription
H)Maxam-Gilbert method
I)AUGGCUGAG
J)replication
K)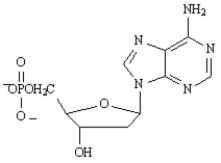
L)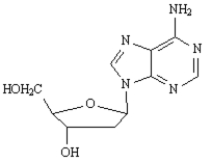 M)AGATCGCTC
M)AGATCGCTC
A)Sanger dideoxy method
B)GAUCGUAAA
C)Watson-Crick
D)translation
E)

F)

G)transcription
H)Maxam-Gilbert method
I)AUGGCUGAG
J)replication
K)

L)
 M)AGATCGCTC
M)AGATCGCTC
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
_____ 2'-deoxyadenosine 5'-phosphate
A)Sanger dideoxy method
B)GAUCGUAAA
C)Watson-Crick
D)translation
E)
F)
G)transcription
H)Maxam-Gilbert method
I)AUGGCUGAG
J)replication
K)
L) M)AGATCGCTC
M)AGATCGCTC
A)Sanger dideoxy method
B)GAUCGUAAA
C)Watson-Crick
D)translation
E)

F)

G)transcription
H)Maxam-Gilbert method
I)AUGGCUGAG
J)replication
K)

L)
 M)AGATCGCTC
M)AGATCGCTC
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Describe,in general terms,the steps involved in the automated synthesis of the DNA sequence GCT.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Draw and label an A-T base pair.Indicate all hydrogen bonds with a dashed line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
_____ a pyrimidine nucleoside
A)Sanger dideoxy method
B)GAUCGUAAA
C)Watson-Crick
D)translation
E)
F)
G)transcription
H)Maxam-Gilbert method
I)AUGGCUGAG
J)replication
K)
L) M) AGATCGCTC
M) AGATCGCTC
A)Sanger dideoxy method
B)GAUCGUAAA
C)Watson-Crick
D)translation
E)

F)

G)transcription
H)Maxam-Gilbert method
I)AUGGCUGAG
J)replication
K)

L)
 M) AGATCGCTC
M) AGATCGCTC
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Draw and label the four RNA nucleosides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
_____ DNA sequencing method for the human genome
A)Sanger dideoxy method
B)GAUCGUAAA
C)Watson-Crick
D)translation
E)
F)
G)transcription
H)Maxam-Gilbert method
I)AUGGCUGAG
J)replication
K)
L) M)AGATCGCTC
M)AGATCGCTC
A)Sanger dideoxy method
B)GAUCGUAAA
C)Watson-Crick
D)translation
E)

F)

G)transcription
H)Maxam-Gilbert method
I)AUGGCUGAG
J)replication
K)

L)
 M)AGATCGCTC
M)AGATCGCTC
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
_____ RNA base sequence complementary to the DNA base sequence which codes for Leu−Ala−Phe:
CTAGCATTT
A)Sanger dideoxy method
B)GAUCGUAAA
C)Watson-Crick
D)translation
E)
F)
G)transcription
H)Maxam-Gilbert method
I)AUGGCUGAG
J)replication
K)
L) M)AGATCGCTC
M)AGATCGCTC
CTAGCATTT
A)Sanger dideoxy method
B)GAUCGUAAA
C)Watson-Crick
D)translation
E)

F)

G)transcription
H)Maxam-Gilbert method
I)AUGGCUGAG
J)replication
K)

L)
 M)AGATCGCTC
M)AGATCGCTC
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
_____ process by which mRNA directs protein synthesis
A)Sanger dideoxy method
B)GAUCGUAAA
C)Watson-Crick
D)translation
E)
F)
G)transcription
H)Maxam-Gilbert method
I)AUGGCUGAG
J)replication
K)
L) M)AGATCGCTC
M)AGATCGCTC
A)Sanger dideoxy method
B)GAUCGUAAA
C)Watson-Crick
D)translation
E)

F)

G)transcription
H)Maxam-Gilbert method
I)AUGGCUGAG
J)replication
K)

L)
 M)AGATCGCTC
M)AGATCGCTC
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
While the Watson-Crick G-C and A-T base pairs are the most common,other non-standard base pairs are encountered.Draw and label a G-U base pair.Indicate all hydrogen bonds with a dashed line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
_____ a purine nucleoside
A)Sanger dideoxy method
B)GAUCGUAAA
C)Watson-Crick
D)translation
E)
F)
G)transcription
H)Maxam-Gilbert method
I)AUGGCUGAG
J)replication
K)
L)
M) AGATCGCTC
A)Sanger dideoxy method
B)GAUCGUAAA
C)Watson-Crick
D)translation
E)

F)

G)transcription
H)Maxam-Gilbert method
I)AUGGCUGAG
J)replication
K)

L)

M) AGATCGCTC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is the primary structural difference between RNA nucleotides and DNA nucleotides?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
_____ RNA base sequence with guanine at the 3' end.
A)Sanger dideoxy method
B)GAUCGUAAA
C)Watson-Crick
D)translation
E)
F)
G)transcription
H)Maxam-Gilbert method
I)AUGGCUGAG
J)replication
K)
L) M) AGATCGCTC
M) AGATCGCTC
A)Sanger dideoxy method
B)GAUCGUAAA
C)Watson-Crick
D)translation
E)

F)

G)transcription
H)Maxam-Gilbert method
I)AUGGCUGAG
J)replication
K)

L)
 M) AGATCGCTC
M) AGATCGCTC
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The process invented in 1986 which allows multiple copies of a given DNA sequence to be produced is:
A)the polymerase chain reaction.
B)the Sanger dideoxy method.
C)the Maxam-Gilbert method.
D)the restriction endonuclease reaction.
A)the polymerase chain reaction.
B)the Sanger dideoxy method.
C)the Maxam-Gilbert method.
D)the restriction endonuclease reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
_____ DNA base sequence with cytosine at the 3' end.
A)Sanger dideoxy method
B)GAUCGUAAA
C)Watson-Crick
D)translation
E)
F)
G)transcription
H)Maxam-Gilbert method
I)AUGGCUGAG
J)replication
K)
L)
M) AGATCGCTC
A)Sanger dideoxy method
B)GAUCGUAAA
C)Watson-Crick
D)translation
E)

F)

G)transcription
H)Maxam-Gilbert method
I)AUGGCUGAG
J)replication
K)

L)

M) AGATCGCTC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Because of the structure of the RNA sugar-phosphate backbone,RNA is subject to base-promoted hydrolysis,as shown below.Suggest a mechanism for base-promoted RNA hydrolysis. 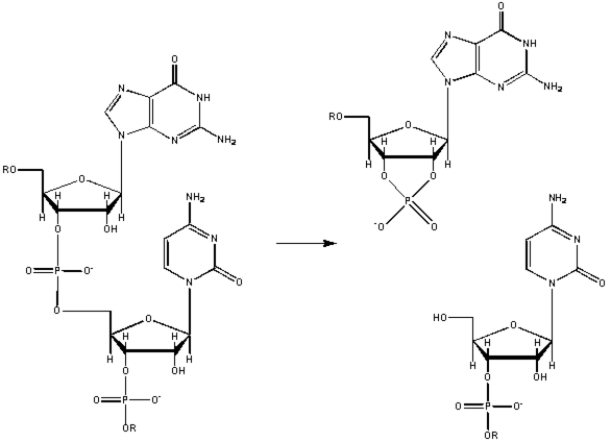


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Draw and label a G-C base pair.Indicate all hydrogen bonds with a dashed line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
1) Label the anticodon
2) Label the position of attachment of the amino acid
3) Draw the structure of the amino acid that would be attached
4) Indicate the corresponding mRNA codon
2) Label the position of attachment of the amino acid
3) Draw the structure of the amino acid that would be attached
4) Indicate the corresponding mRNA codon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When DNA is replicated,the new chain is synthesized in what direction?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
During DNA synthesis,the free amino group does not need to be protected for which base?
A)Adenine
B)Guanine
C)Thymine
D)Cytosine
A)Adenine
B)Guanine
C)Thymine
D)Cytosine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Give a one sentence definition of translation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the purpose of the addition of aqueous ammonia during the synthesis of DNA?
A)Cleavage of the ester bond to the silica support
B)Removal of the groups protecting the free amino group of the bases
C)Removal of the protecting group of the 5' -OH of the sugar
D)Ammonia accomplishes all of the above.
A)Cleavage of the ester bond to the silica support
B)Removal of the groups protecting the free amino group of the bases
C)Removal of the protecting group of the 5' -OH of the sugar
D)Ammonia accomplishes all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In the diagram below,fill in the terms in the appropriate places indicated by a letter. 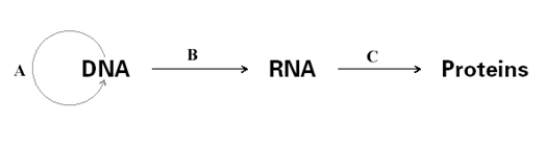
A)A - replication,B - transcription,C - translation
B)A - replication,B - translation,C - transcription
C)A - transcription,B - replication,C - translation
D)A - translation,B - transcription,C - replication

A)A - replication,B - transcription,C - translation
B)A - replication,B - translation,C - transcription
C)A - transcription,B - replication,C - translation
D)A - translation,B - transcription,C - replication

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
During DNA synthesis,how is the 5' -OH of deoxyribose protected?
A)With a p-dimethoxytrityl group
B)With a benzoyl group
C)With an isobutryl group
D)With a β-cyanoethyl group
E)This group does not need to be protected.
A)With a p-dimethoxytrityl group
B)With a benzoyl group
C)With an isobutryl group
D)With a β-cyanoethyl group
E)This group does not need to be protected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Consider the following diagram. 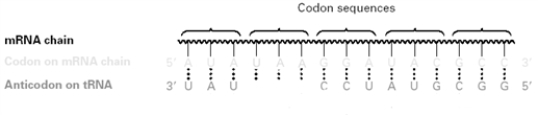 What amino acid corresponds to the second codon from the left?
What amino acid corresponds to the second codon from the left?
A)Tyrosine
B)Asparagine
C)Isoleucine
D)None,the mRNA codon is a stop signal
 What amino acid corresponds to the second codon from the left?
What amino acid corresponds to the second codon from the left?A)Tyrosine
B)Asparagine
C)Isoleucine
D)None,the mRNA codon is a stop signal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Consider the following diagram. 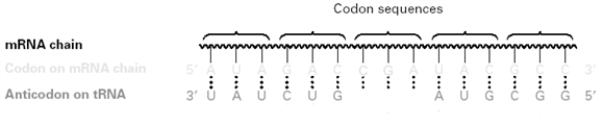 Which letter should be filled in on the bottom line?
Which letter should be filled in on the bottom line?
A)GCU
B)UCG
C)GCT
D)TGC
 Which letter should be filled in on the bottom line?
Which letter should be filled in on the bottom line?A)GCU
B)UCG
C)GCT
D)TGC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Give a one sentence definition of replication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Give a one sentence definition of transcription.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Consider the following diagram. 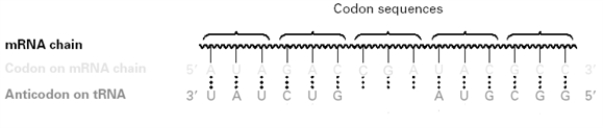
What DNA sequence (5' to 3') would correspond to the third codon?
A)GCU
B)TCG
C)UGC
D)GCT

What DNA sequence (5' to 3') would correspond to the third codon?
A)GCU
B)TCG
C)UGC
D)GCT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Consider DNA sequencing experiments using 2',3'-dideoxyribonucleoside triphosphates.Which of the following is not correct?
A)2',3'-dideoxyribonucleoside triphosphates are added to the replicating strand by DNA polymerase.
B)There are four types of 2',3'-dideoxyribonucleoside triphosphates used.
C)The sequence of 2',3'-dideoxyribonucleoside triphosphates in the replicated DNA yields the DNA structure.
D)DNA replication ceases when a 2',3'-dideoxyribonucleoside triphosphates is added to the replicating strand.
A)2',3'-dideoxyribonucleoside triphosphates are added to the replicating strand by DNA polymerase.
B)There are four types of 2',3'-dideoxyribonucleoside triphosphates used.
C)The sequence of 2',3'-dideoxyribonucleoside triphosphates in the replicated DNA yields the DNA structure.
D)DNA replication ceases when a 2',3'-dideoxyribonucleoside triphosphates is added to the replicating strand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Give the single letter amino acid sequence that is coded for by the following segment of DNA coding strand (sense strand)?
(5') GCA-TTT-CTA-ACT-TGA-GGG (3')
(5') GCA-TTT-CTA-ACT-TGA-GGG (3')

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Consider the following molecular model.Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled. 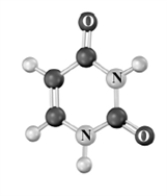 Which of the following is a characteristic of this compound?
Which of the following is a characteristic of this compound?
A)Found in DNA
B)Found in both DNA and RNA
C)Pyrimidine base
D)Pairs with thymine
 Which of the following is a characteristic of this compound?
Which of the following is a characteristic of this compound?A)Found in DNA
B)Found in both DNA and RNA
C)Pyrimidine base
D)Pairs with thymine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Identify any errors in the figure shown below. 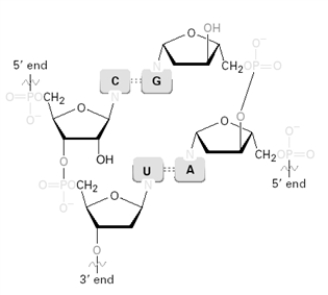


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Consider the DNA polymerase chain reaction.After 5 cycles have been completed,how many copies of the original DNA are present?
A)10
B)32
C)64
D)128
A)10
B)32
C)64
D)128

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In determining DNA sequencing using the Sanger dideoxy method,how many colors will appear in the resulting data display?
A)2
B)4
C)6
D)8
A)2
B)4
C)6
D)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
On the diagram of DNA, identify:
1) major groove
2) minor groove
3) position of the sugar-phosphate backbone
4) site of possible intercalation
1) major groove
2) minor groove
3) position of the sugar-phosphate backbone
4) site of possible intercalation


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Consider the following molecular model.Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled. 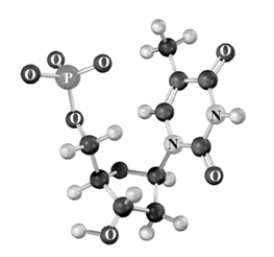 Which of the following is a characteristic of this structure?
Which of the following is a characteristic of this structure?
A)Nucleoside
B)Contains ribose
C)Contains a purine base
D)Found only in DNA
 Which of the following is a characteristic of this structure?
Which of the following is a characteristic of this structure?A)Nucleoside
B)Contains ribose
C)Contains a purine base
D)Found only in DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Using the PCR method for synthesizing DNA,why don't the two DNA strands recombine during the cooling phase?
A)The temperature used
B)The concentration of the primers
C)Presence of Mg2+
D)Presence of Taq polymerase
A)The temperature used
B)The concentration of the primers
C)Presence of Mg2+
D)Presence of Taq polymerase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following statement correctly describes DNA replication?
A)Replication occurs in the direction.
direction.
B)Ligases link the Okazaki fragments to form the lagging strand.
C)The leading strand is replicated discontinuously.
D)One strand is replicated while the other strand is replicated
while the other strand is replicated
 .
.
A)Replication occurs in the
 direction.
direction.B)Ligases link the Okazaki fragments to form the lagging strand.
C)The leading strand is replicated discontinuously.
D)One strand is replicated
 while the other strand is replicated
while the other strand is replicated .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When the β-cyanoethyl group is removed during DNA synthesis,H2CCHCN is produced as a product.This reaction is likely to be:
A)E1
B)E2
C)E1cB
D)SN1
E)SN2
A)E1
B)E2
C)E1cB
D)SN1
E)SN2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following summarizes the steps in DNA synthesis using the PCR method?
A)Anneal-denature-synthesize
B)Synthesize-denature-anneal
C)Denature-anneal-synthesize
D)Denature-synthesize-anneal
A)Anneal-denature-synthesize
B)Synthesize-denature-anneal
C)Denature-anneal-synthesize
D)Denature-synthesize-anneal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



