You are studying a newly identified chromatin-remodeling complex, which you call NICRC.You decide to run an in vitro experiment to characterize the activity of the purified complex.Your molecular toolbox includes: (1) a 400-base-pair DNA molecule that has a single recognition site for the restriction endonuclease EcoRI, an enzyme that cleaves internal sites on double-stranded DNA (dsDNA); (2) purified EcoRI enzyme; (3) purified DNase I, a DNA endonuclease that will cleave dsDNA at nonspecific sites if they are exposed; and (4) core octamer histones.You are able to assemble core nucleosomes on this DNA template and test for NICRC activity.Figure 5-67A illustrates the DNA template used and indicates both the location of the EcoRI cleavage site and the size of the DNA fragments that are produced when it cuts.Figure 5-67B illustrates how the DNA molecules in your experiment looked after separation according to size by using gel electrophoresis.Your experiment had a total of six samples, each of which was treated according to the legend below the gel.The sizes of the DNA fragments observed are indicated on the left side of the gel. (A) 
(B)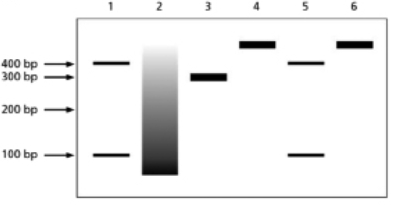
1. ECORI
2. DNase I
3. core octamer incubation, later treated with DNase I
4. core octamer incubation, later treated with EcoRI
5. core octamer incubation, addition of NICRC + ATP, later treated with EcoRI
6. core octamer incubation, addition of NICRC + ADP, later treated with EcoRI
Figure 5-67
A.Explain the results in lanes 1-4 and why it is important to have this information before you begin to test your remodeling complex.
B.What can you conclude about your purified remodeling complex from the results in lanes 5 and 6?
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q56: Given the sequence of one strand of
Q57: The human genome comprises 23 pairs of
Q58: Describe the mechanism by which heterochromatin can
Q59: Indicate whether the following statements are TRUE
Q60: For each of the following sentences,
Q62: When double-stranded DNA is heated, the two
Q63: For a better understanding of DNA structure,
Q64: Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty carried out experiments
Q65: A.Explain the reason why the cell requires
Q66: Consider the structure of the DNA double
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents