One of the buffers that contribute to pH stability in human blood is carbonic acid (H₂CO₃) . Carbonic acid is a weak acid that, when placed in an aqueous solution, dissociates into a bicarbonate ion (HCO₃⁻) and a hydrogen ion (H⁺) . (See figure.) 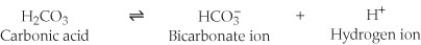
If the pH of blood drops, one would expect ________.
A) a decrease in the concentration of H₂CO₃ and an increase in the concentration of HCO₃⁻
B) the concentration of bicarbonate ions (HCO₃⁻) to increase
C) the HCO₃⁻ to act as a base and remove excess H⁺ by the formation of H₂CO₃
D) the HCO₃⁻ to act as an acid and remove excess H⁺ by the formation of H₂CO₃
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q32: A 0.01 M solution of a substance
Q33: How much of 0.5 M glucose (molecular
Q35: A solution with a pH of 2
Q36: Use the following figure to answer the
Q38: Rank, from low to high, the pH
Q38: What is the hydroxyl ion (OH⁻) concentration
Q39: How does 0.5 M sucrose (molecular mass
Q40: Use the following figure to answer the
Q42: Measurements show that the pH of a
Q52: Which of the following is a hydrophobic
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents