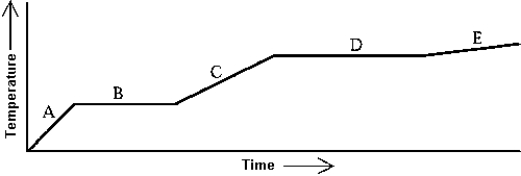
 Heat is added to a substance at a constant rate. The substance starts as a solid and is melted; the liquid is heated and vaporized; finally, the vapor is heated. This process is shown in the graph. The latent heat of vaporization can be found by
Heat is added to a substance at a constant rate. The substance starts as a solid and is melted; the liquid is heated and vaporized; finally, the vapor is heated. This process is shown in the graph. The latent heat of vaporization can be found by
A) multiplying the length of B in seconds) by the rate at which heat is added, and dividing by the mass of the substance.
B) multiplying the length of D in seconds) by the rate at which heat is added, and dividing by the mass of the substance.
C) multiplying the slope of A by the rate at which heat is added, and dividing by the mass of the substance.
D) multiplying the slope of C by the rate at which heat is added, and dividing by the mass of the substance.
E) multiplying the slope of E by the rate at which heat is added, and dividing by the mass of the substance.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q24: If the temperature on the warmer side
Q30: If the heat capacities of both ice
Q33: A certain blackbody radiates 100 W at
Q115: If 100 g of steam at 100°C
Q116: You add 50 g of ice cubes
Q117: When a substance changes phase, from solid
Q118: A 2.0-kg mass of iron specific heat
Q121: A small water reactor recently installed at
Q122: Two types of wall separate a refrigerated
Q125: ![]()
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents