Energy conservation with conservative forces: A box of mass m is pressed against (but is not attached to) an ideal spring of force constant k and negligible mass, compressing the spring a distance x. After it is released, the box slides up a frictionless incline as shown in the figure and eventually stops. If we repeat this experiment but instead compress the spring a distance of 2x 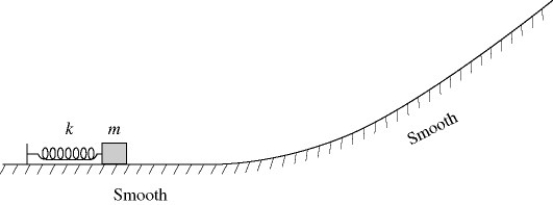
A) the box will go up the incline twice as high as before.
B) just as it moves free of the spring, the box will be traveling twice as fast as before.
C) just as it moves free of the spring, the box will be traveling four times as fast as before.
D) just as it moves free of the spring, the box will have twice as much kinetic energy as before.
E) just before it is released, the box has twice as much elastic potential energy as before.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q1: Energy conservation with nonconservative forces: A ball
Q2: Work-energy theorem: Two objects, one of mass
Q3: Hooke's law: Consider a plot of the
Q4: Hooke's law: Which of the graphs in
Q5: Energy conservation with nonconservative forces: Block 1
Q7: Energy conservation with conservative forces: Two stones,
Q8: Work-energy theorem: A 4.0-kg object is moving
Q9: Energy conservation with conservative forces: A box
Q10: Energy conservation with conservative forces: Two identical
Q11: Gravitational potential energy: Is it possible for
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents