Consumer surplus can be calculated as:
A) 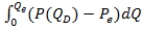 , where Qe and Pe are the equilibrium quantity and price, respectively, and P(QD) is the inverse demand curve.
, where Qe and Pe are the equilibrium quantity and price, respectively, and P(QD) is the inverse demand curve.
B) 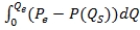 , where Qe and Pe are the equilibrium quantity and price, respectively, and P(QS) is the inverse supply curve.
, where Qe and Pe are the equilibrium quantity and price, respectively, and P(QS) is the inverse supply curve.
C) 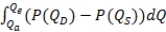 , where Qe is the quantity that would occur in free-market equilibrium and P(QD) and P(QS) are inverse demand and supply, respectively.
, where Qe is the quantity that would occur in free-market equilibrium and P(QD) and P(QS) are inverse demand and supply, respectively.
D) 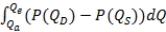 , where Qa denotes actual quantity, Qe is the quantity that would occur in free-market equilibrium, and P(QD) and P(QS) are inverse demand and supply, respectively.
, where Qa denotes actual quantity, Qe is the quantity that would occur in free-market equilibrium, and P(QD) and P(QS) are inverse demand and supply, respectively.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q3: (Figure: Market for Good X II) Before
Q4: (Figure: Price and Quantity IV) Suppose the
Q5: The demand and supply of pickles are
Q6: (Figure: Market for Tickets II) The size
Q7: (Figure: Market for Tickets II) The government
Q9: If the government subsidizes a product, what
Q10: (Figure: Price and Quantity V) For demand
Q11: To calculate producer surplus:
A) integrate the area
Q12: The demand for a good is given
Q13: The market for organic cabbage is represented
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents