The following information relates to Questions
daniela ibarra is a senior analyst in the fixed-income department of a large wealth manage-ment firm. Marten Koning is a junior analyst in the same department, and david lok is a member of the credit research team.
The firm invests in a variety of bonds. ibarra is presently analyzing a set of bonds with some similar characteristics, such as four years until maturity and a par value of €1,000. exhibit 1 includes details of these bonds.
exhibit 1 a brief description of the bonds being analyzed bond descriptionb1 a zero-coupon, four-year corporate bond with a par value of €1,000. The wealth management firm's research team has estimated that the risk-neutral probability of default (the hazard rate) for each date for the bond is 1.50%, and the recovery rate is 30%.b2 a bond similar to b1, except that it has a fixed annual coupon rate of 6% paid annually.
b3 a bond similar to b2 but rated aa.
b4 a bond similar to b2 but the coupon rate is the one-year benchmark rate plus 4%.ibarra asks Koning to assist her with analyzing the bonds. She wants him to perform the analysis with the assumptions that there is no interest rate volatility and that the government bond yield curve is flat at 3%.ibarra performs the analysis assuming an upward-sloping yield curve and volatile interest rates. exhibit 2 provides the data on annual payment benchmark government bonds.1 She uses these data to construct a binomial interest rate tree (shown in exhibit 3) based on an assump-tion of future interest rate volatility of 20%.
1 For simplicity, this exhibit uses
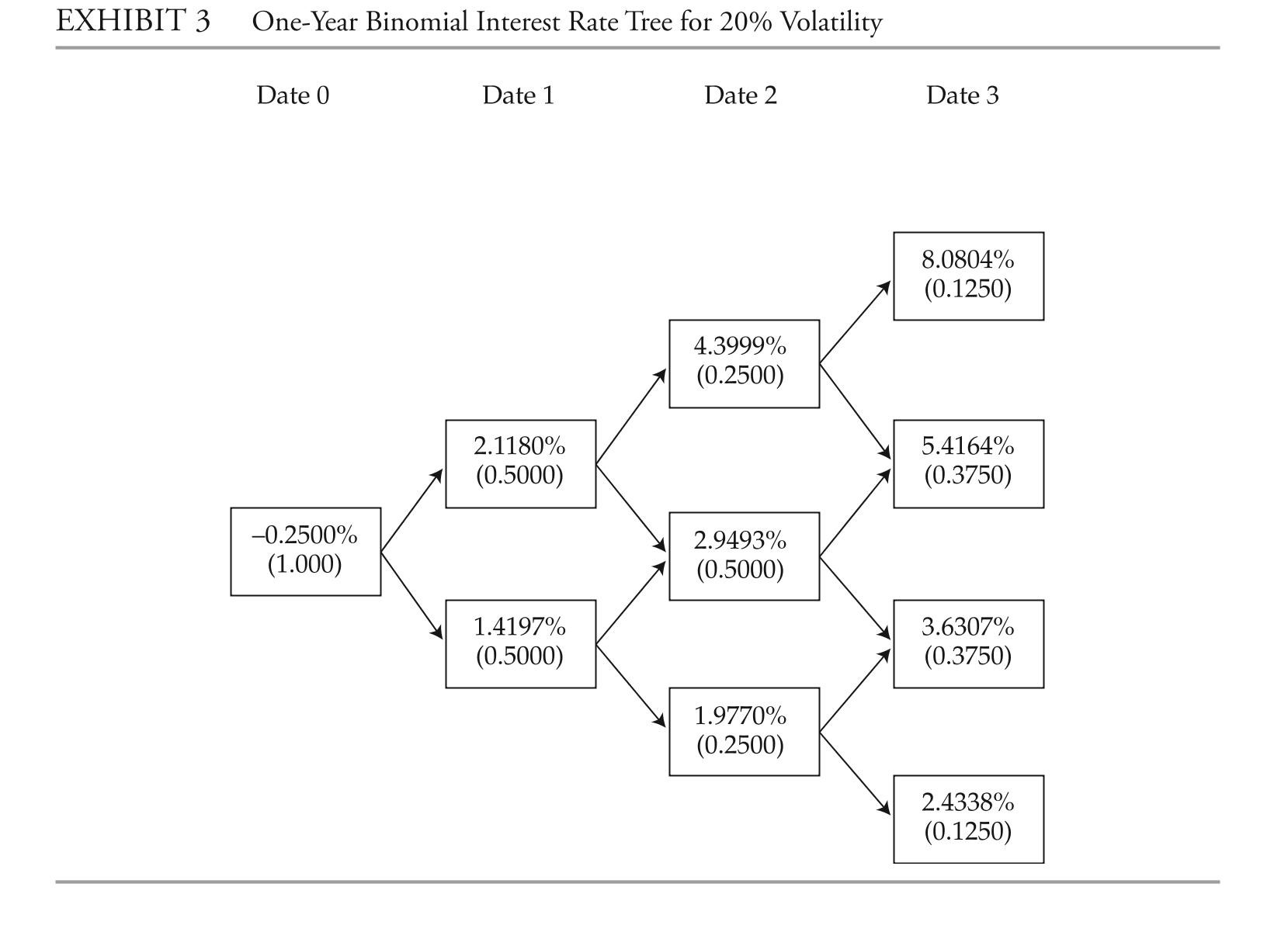 answer the first five questions (1-4) based on the assumptions made by Marten Koning,the junior analyst. answer questions (8-12) based on the assumptions made by daniela ibarra, the senior analyst.
answer the first five questions (1-4) based on the assumptions made by Marten Koning,the junior analyst. answer questions (8-12) based on the assumptions made by daniela ibarra, the senior analyst.
Note: all calculations in this problem set are carried out on spreadsheets to preserve reci-sion. The rounded results are reported in the solutions.
-during the presentation about how the research team estimates the probability of default for a particular bond issuer, lok is asked for his thoughts on the shape of the
Term structure of credit spreads. Which statement is he most likely to include in his
Response?
A) The term structure of credit spreads typically is flat or slightly upward sloping for high-quality investment-grade bonds. high-yield bonds are more sensitive to the
Credit cycle, however, and can have a more upwardly sloped term structure of credit
Spreads than investment-grade bonds or even an inverted curve.
B) The term structure of credit spreads for corporate bonds is always upward sloping, the more so the weaker the credit quality because probabilities of default are positively
Correlated with the time to maturity.
C) There is no consistent pattern to the term structure of credit spreads. The shape of the credit term structure depends entirely on industry factors.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q9: The following information relates to Questions
Q10: The following information relates to Questions
Q11: The following information relates to Questions
Q12: The following information relates to Questions
Q13: The following information relates to Questions
Q15: The following information relates to Questions
Q16: The following information relates to Questions
Q17: The following information relates to Questions
Q18: The following information relates to Questions
Q19: The following information relates to Questions
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents