After release into the synaptic cleft, the neurotransmitter dopamine is actively taken up by the cells via specific dopamine transporters. The drug cocaine interferes with this process and is therefore called a reuptake inhibitor. The inhibition of the transporter at a certain cocaine concentration is qualitatively represented in the following graph. Based on this graph, which of the following describes the effect of cocaine on the kinetics of dopamine reuptake by the transporter? 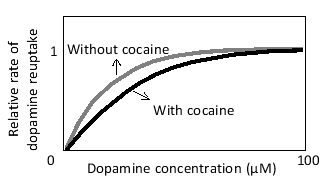
A) In the presence of cocaine, the maximal rate of transport (Vmₐₓ) is unaffected, but the apparent affinity of the transporter for dopamine is reduced.
B) In the presence of cocaine, the maximal rate of transport (Vmₐₓ) is reduced, but the apparent affinity of the transporter for dopamine is unaffected.
C) In the presence of cocaine, the maximal rate of transport (Vmₐₓ) is enhanced, but the apparent affinity of the transporter for dopamine is unaffected.
D) In the presence of cocaine, both the maximal rate of transport (Vmₐₓ) and the apparent affinity of the transporter for dopamine are enhanced.
E) In the presence of cocaine, both the maximal rate of transport (Vmₐₓ) and the apparent affinity of the transporter for dopamine are unaffected, but the transporter is nevertheless inhibited.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q13: Why do cells not have membrane transport
Q14: Most eukaryotic ABC transporters are involved in
Q15: The lactose permease in Escherichia coli is
Q16: Which of the following is a pump
Q17: An ion channel …
A) always mediates passive
Q19: Many amino acids in our diet are
Q20: Which of the following transporters mediates primary
Q21: A neuron's repetitive firing rate is limited
Q22: Aquaporin has a pair of key asparagine
Q23: Which of the following graphs better represents
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents