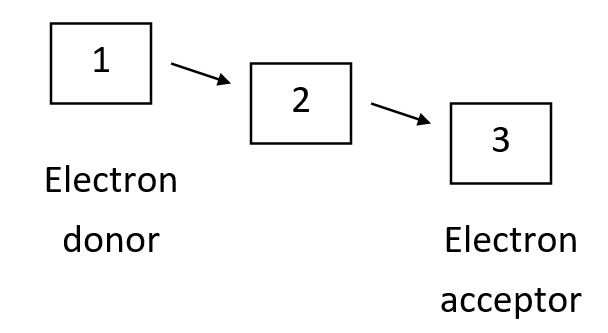
Proteins of the protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) family share common domains that harbor an active-site CXXC motif (C = cysteine; X = one of several residues). During the course of a redox reaction, one of the active-site cysteines in its reduced form can attack a disulfide bond in a substrate protein (that could itself be another PDI family member) to form a mixed disulfide between the enzyme and its substrate. This is then attacked by the other active-site cysteine, releasing the substrate in reduced form. The reverse of these reactions can occur instead in order to make disulfide bonds in target proteins. CXXA mutant PDI family proteins-in which one of the active-site cysteines is mutated to an alanine-can be trapped in the intermediate mixed disulfide state for an elongated time, facilitating the identification of their substrate proteins. Using these mutations in each of three interacting PDI family proteins-A, B, and C (one mutation at a time)-you have discovered that the mutant B interacts with A and C, while mutant A interacts with C but not with B. Finally, mutant C interacts with neither of the other two. The following diagram shows the thermodynamically favorable flow of electrons (plus protons) in the cascade involving these three proteins. Based on your results above, what proteins correspond to 1, 2, and 3 in the diagram, respectively? Your answer would be a three-letter string composed of letters A to C only, e.g. CBA.
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q36: Indicate whether each of the following descriptions
Q37: Which of the following is NOT a
Q38: Mitochondrial hsp70 is to matrix protein import
Q39: Indicate whether the C-terminus (C) or the
Q40: Compared to the cytosol, which of the
Q42: Indicate whether each of the following occurs
Q43: A protein is covalently attached to glycosylphosphatidylinositol.
Q44: Fill in the blank in the following
Q45: Indicate whether each of the following descriptions
Q46: Misfolded proteins in the ER may actively
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents