A 28-year-old woman comes to the clinic due to generalized weakness and frequent, high-volume urination. She has had no dysuria, hematuria, or abdominal pain. The patient's symptoms have been ongoing for several months, but she cannot recall exactly when they began. She has no other medical conditions. The patient is a single mother of a 2-year-old child, has little social support, and occasionally uses alcohol and marijuana "to cope with the stress." Vital signs and physical examination are normal. Blood glucose is 95 mg/dL and serum sodium is 132 mEq/L. Urinalysis shows no white or red blood cells. During further evaluation, urine osmolality is serially measured while fluid intake is restricted; vasopressin is subsequently administered 7 hours into the test. The results are shown below. 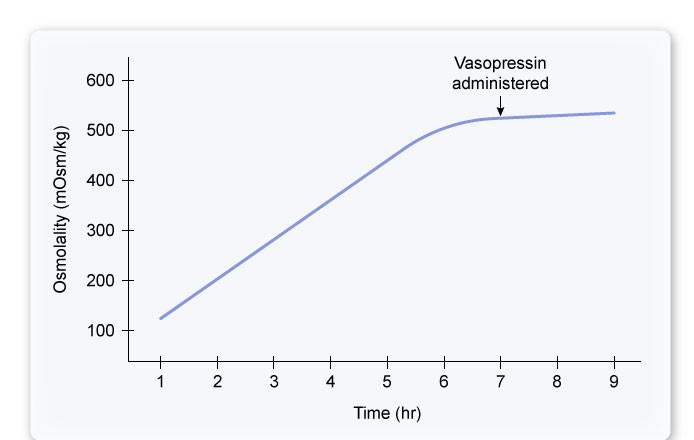 Which of the following is the most appropriate long-term treatment for this patient?
Which of the following is the most appropriate long-term treatment for this patient?
A) Desmopressin
B) Hydrochlorothiazide
C) Indomethacin
D) Insulin
E) Water restriction
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q424: A 65-year-old man is being evaluated in
Q425: A 32-year-old man comes to the emergency
Q426: A 76-year-old man comes to the hospital
Q427: A 46-year-old woman is hospitalized for recurrent
Q428: A 34-year-old woman comes to the hospital
Q430: A 2-year-old child is brought to his
Q431: A 35-year-old man who works as a
Q432: A 72-year-old woman is evaluated due to
Q433: A 60-year-old man comes to the office
Q434: A 45-year-old man comes to the emergency
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents