A 4-month-old boy is brought to clinic by his mother for routine follow-up. He was last seen at his 2-month checkup. The mother reports that the patient continues to feed well but has noticed that his head is larger than other infants'. He can roll from front to back, sit straight when propped, and hold his head steady without support. The patient can bring objects to his mouth and make babbling sounds. The patient was born at 37 weeks gestation and adopted at birth. Temperature is 37.2 C (99 F) , pulse is 130/min, and respirations are 30/min. Examination shows a symmetrical head with an open and soft fontanelle. Pupils are equal and reactive, and extraocular movements are intact. Eyes and ears are in the normal positions. The neck is supple. Abdominal and skin examination is unremarkable. Extremities appear normal. Growth charts are shown in the exhibit.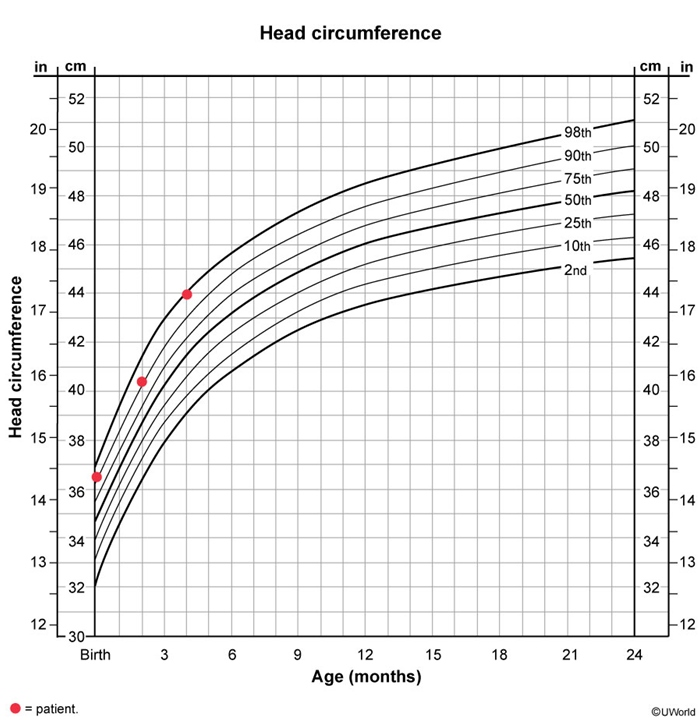
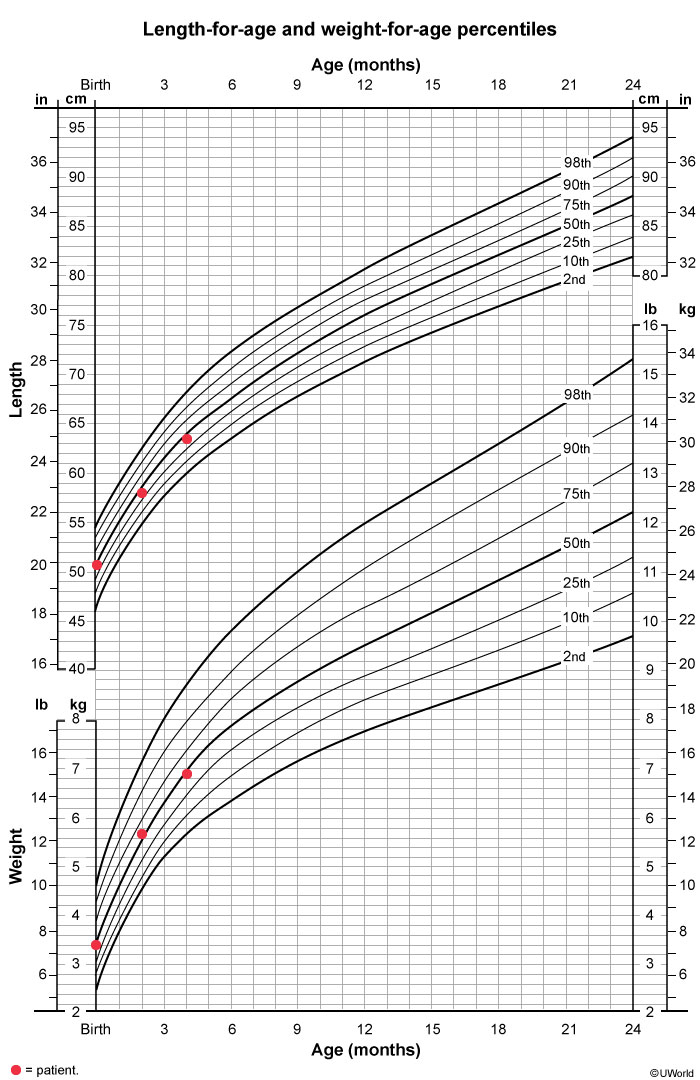 Head ultrasound shows normal ventricles and brain parenchyma. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
Head ultrasound shows normal ventricles and brain parenchyma. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A) Cranial molding helmet
B) Karyotype analysis
C) Lumbar puncture for opening pressure
D) MRI of the brain
E) Reassurance and continued observation
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q587: A 13-year-old girl comes to the office
Q588: A 3-week-old girl is evaluated in the
Q589: A 9-year-old boy is brought to the
Q590: A 16-month-old girl is brought to the
Q591: A 5-month-old boy is brought to the
Q593: A newborn boy is being evaluated in
Q594: A 1-day-old girl is being evaluated in
Q595: A 3-day-old boy is in the neonatal
Q596: A 6-year-old boy is brought to the
Q597: A 2-year-old boy is brought to the
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents