Service Consumer A sends a message to Service A (1) , which then forwards the message to Service B (2) . Service B forwards the message to Service C (3) , which finally forwards the message to Service D (4) . Services A, B, and C each contain logic that reads the content of the message and, based on this content, determines which service to forward the message to. As a result, what is shown in the Figure is one of several possible runtime scenarios. 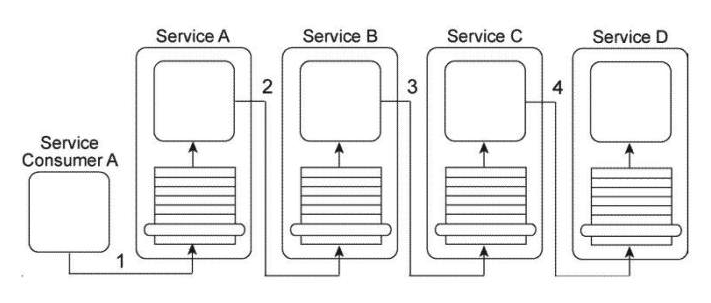 You are told that the current service composition architecture is having performance problems because of two specific reasons. First, too many services need to be explicitly invoked in order for the message to arrive at its destination. Secondly, because each of the intermediary services is required to read the entire message contents in order to determine where to forward the message to, it is taking too long for the overall task to complete. What steps can be taken to solve these problems without sacrificing any of the functionality that currently exists?
You are told that the current service composition architecture is having performance problems because of two specific reasons. First, too many services need to be explicitly invoked in order for the message to arrive at its destination. Secondly, because each of the intermediary services is required to read the entire message contents in order to determine where to forward the message to, it is taking too long for the overall task to complete. What steps can be taken to solve these problems without sacrificing any of the functionality that currently exists?
A) The Intermediate Routing pattern can be applied together with the Service Agent pattern in order to establish a set of service agents capable of intercepting and forwarding the message based on pre-defined routing logic. To avoid the need for service agents to read the entire message contents, the Messaging Metadata pattern can be applied so that content relevant to the routing logic is placed in the header of a message. This way, only the message header content needs to be read by the service agents.
B) The Intermediate Routing pattern can be applied together with the Service Agent pattern in order to establish a set of service agents capable of intercepting and forwarding the message based on pre-defined routing logic. To avoid the need for service agents to read the entire message contents, the Rules Centralization pattern can be applied so that content relevant to the routing logic is isolated into a separate Rules service. This way, service agents are only required to access the Rules service in order to determine where to forward messages to. The Standardized Service Contract principle will need to be applied to ensure that the new Rules service and the new service agents provide service contracts that are compliant to existing design standards.
C) The Intermediate Routing pattern can be applied together with the Service Agent pattern in order to establish a set of service agents capable of intercepting and forwarding the message based on pre-defined routing logic. The Service Discoverability principle can be applied to improve the communications quality of message contents, which will reduce the time required by service agents to read the message contents at runtime.
D) None of the above.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q14: Service A is a utility service that
Q15: Service A is a task service that
Q16: Service A is an entity service that
Q17: Services A, B, and C are non-agnostic
Q18: Service A is a task service that
Q20: Service Consumer A sends a message to
Q21: Service Consumer A sends a message with
Q22: Service Consumer A sends a message with
Q23: Service Consumer A invokes Service A (1).
Q24: Service Consumer A sends Service A a
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents