Passage
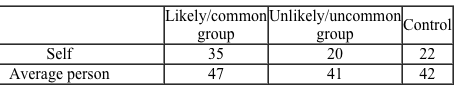
People tend to believe that they are less vulnerable to negative outcomes or events than others. This is known as the self-positivity bias, a specific type of attributional bias in social psychology. Health psychologists suggest that the self-positivity bias may prevent people from being persuaded to take precautionary measures against certain health risks because behavior change is predicated on the perceived risk of contracting the disease in question. If a persuasive message cannot overcome the self-positivity bias, then behavior change is unlikely.In Study 1, researchers hypothesized that when told that an infectious disease can be contracted by engaging in likely or common behavior, people will experience less self-positivity bias than when told the disease can be contracted through unlikely or uncommon behavior. Ninety participants were randomly assigned to a likely/common group, an unlikely/uncommon group, and a control group. All participants read the same paragraph about the health consequences of viral meningitis and how it is contracted. For the likely/common group, the paragraph included, "Viral meningitis is caused by enteroviruses (common virus causing 'stomach flulike' symptoms) and can be contracted through close contact (touching, kissing) with an infected person." For the unlikely/uncommon group, the paragraph included, "Viral meningitis is caused by lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus and can be contracted through coming into contact with the blood, feces, urine, or saliva of an infected mouse." All participants were asked to estimate the likelihood of contracting the disease themselves and the likelihood for the average person (Table 1) .Table 1 Mean Estimated Probability of Contracting Viral Meningitis, by Group
 In Study 2, 120 participants read a newspaper article about hepatitis C and were then randomly assigned to one of four experimental conditions, each receiving additional information about either two or eight relatively uncommon behaviors (eg, getting a tattoo, sharing a needle) or relatively common behaviors (eg, sharing a toothbrush, not bandaging a cut) that could spread the disease. Participants rated their concern for contracting hepatitis C on a scale of 1 (not at all concerned) to 7 (most concerned) (Table 2) .Table 2 Mean Concern of Contracting Hepatitis C Score, by Group and Condition
In Study 2, 120 participants read a newspaper article about hepatitis C and were then randomly assigned to one of four experimental conditions, each receiving additional information about either two or eight relatively uncommon behaviors (eg, getting a tattoo, sharing a needle) or relatively common behaviors (eg, sharing a toothbrush, not bandaging a cut) that could spread the disease. Participants rated their concern for contracting hepatitis C on a scale of 1 (not at all concerned) to 7 (most concerned) (Table 2) .Table 2 Mean Concern of Contracting Hepatitis C Score, by Group and Condition

-The results in Table 1 can also be explained by which of the following?
A) Evolutionary game theory
B) Cognitive dissonance theory
C) Drive reduction theory
D) Labeling theory
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q112: Passage
Health psychologists interested in studying the influence
Q113: Passage
Trait theorists believe that all people have
Q114: Passage
People tend to believe that they are
Q115: Passage
Health psychologists interested in studying the influence
Q116: Passage
Health psychologists interested in studying the influence
Q118: Passage
Health psychologists interested in studying the influence
Q119: Passage
The last several decades have seen a
Q120: Passage
Trait theorists believe that all people have
Q121: Passage
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and generalized anxiety
Q122: Passage
Numerous studies suggest that physicians make both
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents