Passage
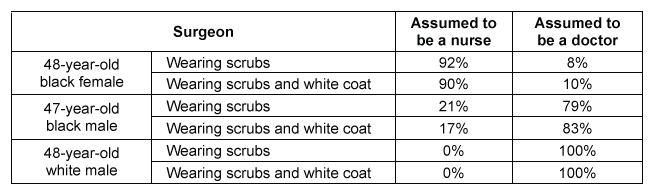
Numerous studies suggest that physicians make both conscious and unconscious assumptions about their patients, and these assumptions often impact patient care and outcomes. However, little research has focused on the assumptions patients make about their physicians.Researchers designed an observational study to investigate assumptions made by patients in health care settings. For this study, three different surgeons were asked to interact with pre-surgery patients whom they had never met using a standardized script. Each surgeon participated in 30 total interactions over the course of two weeks. The purpose of the study was to assess how the patient's assumptions regarding the surgeon's status were impacted by the surgeon's race, gender, and attire.According to the script, the surgeon did not introduce him- or herself upon entering the room. All three surgeons were in their late 40s; one surgeon was a black woman, one was a black man, and one was a white man. The surgeons wore either surgical scrubs alone or a white coat over their surgical scrubs. Researchers analyzed how patients addressed or referred to the surgeon to assess assumptions about the surgeon's role as a doctor or a nurse. The results are presented in Table 1.Table 1 Percentage of Patients Who Assumed the Surgeon Was a Doctor or a Nurse
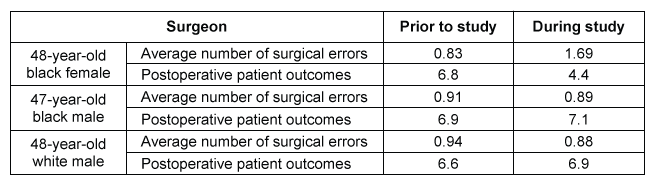
 The researchers also retrospectively analyzed minor (non-life-threatening) surgical errors and postoperative patient outcomes for one month prior to the study and during the study timeframe for each surgeon. The number of minor errors was averaged per surgery, and postoperative patient outcomes were quantified using a multifactor (eg, pain, infection, bleeding, other complications) assessment scale of 1 (worst outcome) to 12 (best outcome) .Table 2 Average Number of Minor Surgical Errors (Per Surgery) and Aggregated Postoperative Patient Outcome Scores
The researchers also retrospectively analyzed minor (non-life-threatening) surgical errors and postoperative patient outcomes for one month prior to the study and during the study timeframe for each surgeon. The number of minor errors was averaged per surgery, and postoperative patient outcomes were quantified using a multifactor (eg, pain, infection, bleeding, other complications) assessment scale of 1 (worst outcome) to 12 (best outcome) .Table 2 Average Number of Minor Surgical Errors (Per Surgery) and Aggregated Postoperative Patient Outcome Scores
-The assertion made in the first paragraph of the passage would be best supported by a study demonstrating that:
A) positive impression management strategies implemented by physicians correspond to increased patient trust.
B) front- and backstage behaviors of hospital patients do not correlate with length of hospital stay.
C) nonverbal communication between patient and physician is a better predictor of patient outcomes than verbal communication.
D) patients are more likely to make assumptions about their physicians based on salient social roles than on attire.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q144: Passage
Jake and his classmate Michael both grew
Q145: Passage
Bipolar disorder (BD), often characterized by periods
Q146: Passage
Physical modifications important for consolidating memory are
Q147: Passage
Bipolar disorder (BD), often characterized by periods
Q148: Passage
Bipolar disorder (BD), often characterized by periods
Q150: Passage
Numerous studies suggest that physicians make both
Q151: Passage
Jake and his classmate Michael both grew
Q152: Passage
Physical modifications important for consolidating memory are
Q153: Passage
Bipolar disorder (BD), often characterized by periods
Q154: Passage
Physical modifications important for consolidating memory are
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents