Passage
Korsakoff syndrome (KS) is caused by a thiamin (vitamin B1) deficiency that often results from chronic alcohol consumption. If KS is diagnosed during its earliest stages, its course may be reversed with thiamin supplements; otherwise, it progresses into a permanent type of dementia that includes severe cognitive dysfunction and memory loss. Alzheimer disease (AD) is associated with a different type of dementia that worsens over time, eventually causing memory loss, cognitive dysfunction, and severe brain atrophy.In one study, KS and AD subjects were assessed using the Corsi block-tapping task, which measures nonverbal memory. The experiment consisted of 10 KS subjects, 10 AD subjects, and 10 healthy control subjects. The control group was matched by age, gender, and premorbid IQ (intelligence quotient preceding the occurrence of symptoms) to the KS and AD groups.
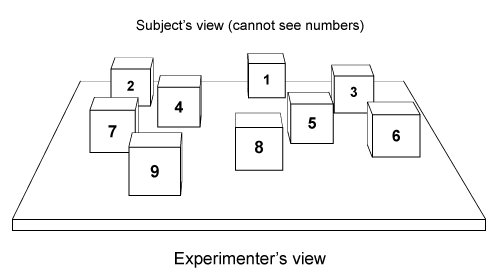 Figure 1 Corsi block-tapping taskThe Corsi block-tapping task consists of nine wooden blocks placed randomly on a board (Figure 1) . To assess subjects' nonverbal memory, the experimenter touched four numbered blocks (numbers were visible only to the experimenter) in a specific pattern. Each subject was then asked to touch the same four blocks in the same sequence, either immediately or after a delay of 5-25 seconds. Subjects were required to perform a distractor task during the delay period. For the distractor task, subjects were asked to watch and reproduce a finger-tapping sequence first demonstrated by the experimenter. Experimenters would touch a finger on their right hand to a finger on their left hand according to a specific sequence (eg, index finger to ring finger, then pinky finger to middle finger) and the subjects would try to do the same.Results indicated that compared to controls, subjects with AD and KS were significantly impaired on the delayed memory task, although all subjects showed a significantly greater number of errors with increases in the delay interval.
Figure 1 Corsi block-tapping taskThe Corsi block-tapping task consists of nine wooden blocks placed randomly on a board (Figure 1) . To assess subjects' nonverbal memory, the experimenter touched four numbered blocks (numbers were visible only to the experimenter) in a specific pattern. Each subject was then asked to touch the same four blocks in the same sequence, either immediately or after a delay of 5-25 seconds. Subjects were required to perform a distractor task during the delay period. For the distractor task, subjects were asked to watch and reproduce a finger-tapping sequence first demonstrated by the experimenter. Experimenters would touch a finger on their right hand to a finger on their left hand according to a specific sequence (eg, index finger to ring finger, then pinky finger to middle finger) and the subjects would try to do the same.Results indicated that compared to controls, subjects with AD and KS were significantly impaired on the delayed memory task, although all subjects showed a significantly greater number of errors with increases in the delay interval.
-Based on study results and the legend below, which of the following graphs best displays the mean and 95% confidence intervals for accuracy scores for each group? 
A) 
B) 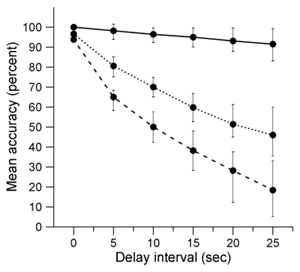
C) 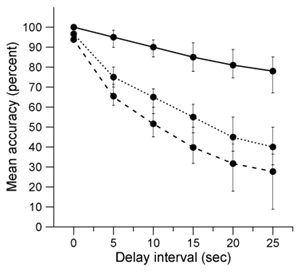
D) 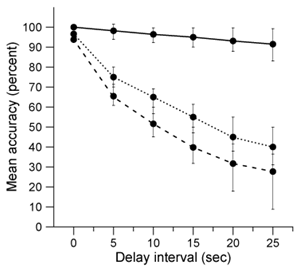
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q215: Passage
Human emotions play an important role in
Q216: Passage
The term "health disparities" describes a systematic
Q217: Passage
Until the middle of the twentieth century,
Q218: Passage
Until the middle of the twentieth century,
Q219: Passage
Human emotions play an important role in
Q221: Passage
The term "health disparities" describes a systematic
Q222: Passage
Until recently, deviance has generally been conceptualized
Q223: Passage
In 2010, the United States (U.S.) had
Q224: A woman who wants a baby but
Q225: Passage
Until recently, deviance has generally been conceptualized
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents