Passage
Psychotic disorders are characterized by a loss of contact with reality. The most common psychotic disorder is schizophrenia, which has a typical onset of psychotic symptoms in early adulthood. Schizophrenia displays considerable inter-individual variation throughout the course of the disorder; many factors appear to influence its progression. Comorbid (co-occurring) conditions, common in schizophrenia, may lead to poorer prognoses. For example, research suggests that fewer depressive symptoms are moderately associated with higher rates of medication compliance, whereas more depressive symptoms are associated with increased future relapses. The early detection of psychosis also appears to have a significant impact on long-term outcomes in schizophrenia. A first psychotic episode that goes untreated for a longer period is associated with more future hospitalizations and a diminished response to future therapeutic interventions.Researchers conducted a study to determine which was better at predicting the development of psychosis, a major component of schizophrenia, in high-risk young adults: the presence of certain speech pattern features or a standard clinical symptom inventory. The participant sample was restricted to 50 younger adults (age 18-30) who either met criteria for prodromal syndrome (preclinical signs of psychosis) or had a first-degree relative with schizophrenia.Every three months for three years, participants were interviewed and given the Symptoms of Psychosis Inventory (SPI) , a standardized clinical assessment designed to measure psychosis and related symptoms. The SPI contains two subscales based on the major symptoms of schizophrenia: the Positive Symptom Scale (PSS) and the Negative Symptom Scale (NSS) , which are summed to provide a total SPI score. Transcribed interview data were analyzed with software designed to assess the following speech pattern features: semantic coherence (the relatedness of phrases to one another) , the number of determiners (eg, "that," "which," "what") used in a phrase (determiner density) , and phrase length.Experienced clinicians diagnosed 11 participants with active psychosis by the end of the study. A computer program generated two models that predicted the development of active psychosis based on the data collected. One model based the prediction solely on a combination of the three speech pattern features ("Speech Model") and the other model based the prediction solely on SPI symptoms data ("SPI Model") (Table 1) .Table 1 Comparison of Predictive Models
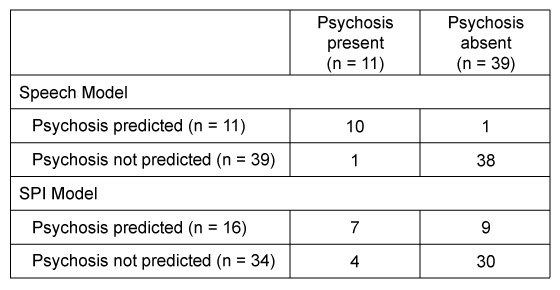
-Which of the following is accurate regarding the design of the study described in the passage?
A) The null hypothesis is that speech pattern features and scores on the SPI will predict psychosis with similar accuracy.
B) Speech pattern features are the dependent variables and the presence of psychosis is the independent variable.
C) The results suggest that if a person exhibits prodromal symptoms, the person will eventually develop psychosis.
D) The participants were assessed every three months for three years to monitor the progression and severity of psychotic symptoms.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q321: Passage
The diagnosis of a child with a
Q322: Passage
Poverty may be the most foundational risk
Q323: Passage
The diagnosis of a child with a
Q324: Passage
Religion establishes the beliefs and rituals surrounding
Q325: Passage
The diagnosis of a child with a
Q327: Which statement best identifies the promotion of
Q328: Passage
Poverty may be the most foundational risk
Q329: A study found that over time, compared
Q330: Passage
Religion establishes the beliefs and rituals surrounding
Q331: Passage
Psychotic disorders are characterized by a loss
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents