Passage
Tumor hypoxia is a marker of resistance to chemotherapy and radiation. The low oxygen saturation in solid tumors activates hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) , which stimulate the expression of genes required for angiogenesis, erythropoiesis, and glucose utilization. Under normal conditions, HIF-DNA binding is interrupted by HIF-prolyl hydroxylases (HIF-PHDs) , enzymes that hydroxylate aliphatic residues such as leucine or proline on HIFs. These hydroxylated residues serve as markers for the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Researchers have proposed that changes in oxygen-dependent pathways such as the citric acid cycle can regulate HIF-PHD activity.Experiment 1A kinematic study was conducted to test the effect of citric acid cycle intermediates on HIF-PHDs. Fumarate and succinate were examined with purified HIF-PHD against increasing concentrations of 2-oxoglutarate (2-OG) , an HIF analog.
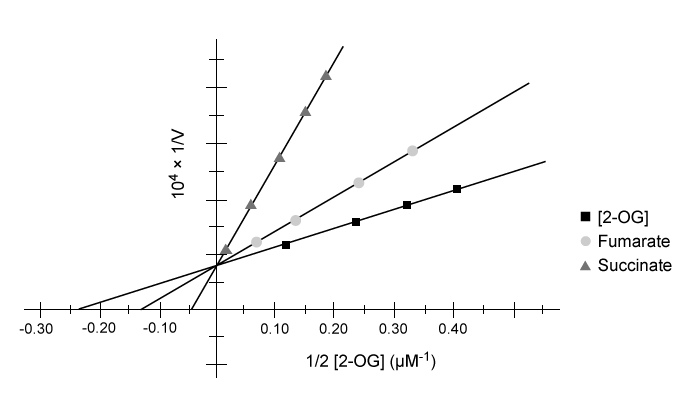 Figure 1 Activity of HIF-PHD exposed to succinate and fumarate in vitro based on 2-OG catalysisExperiment 2Researchers measured HIF-1a, a HIF subunit, using western blot analysis in wild-type (FH+) and fumarate-deficient (FH−) cells that were treated with fumarate under normoxic and hypoxic conditions (Figure 2) .
Figure 1 Activity of HIF-PHD exposed to succinate and fumarate in vitro based on 2-OG catalysisExperiment 2Researchers measured HIF-1a, a HIF subunit, using western blot analysis in wild-type (FH+) and fumarate-deficient (FH−) cells that were treated with fumarate under normoxic and hypoxic conditions (Figure 2) .
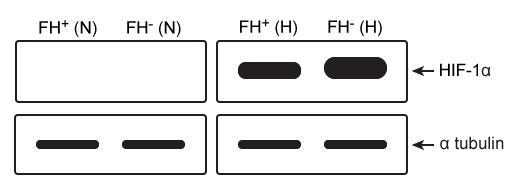 Figure 2 HIF-1a in FH+ and FH− cells grown in vitro under normoxic (N) and hypoxic (H) conditions
Figure 2 HIF-1a in FH+ and FH− cells grown in vitro under normoxic (N) and hypoxic (H) conditions
Adapted from Koivunen P, Hirsilä M, Remes AM, Hassinen IE, Kivirikko KI, Myllyharju J. Inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) hydroxylases by citric acid cycle intermediates: possible links between cell metabolism and stabilization of HIF. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(7) :4524-32.
-Which amino acid structure would most likely be hydroxylated by HIF-PHDs?
A) 
B) 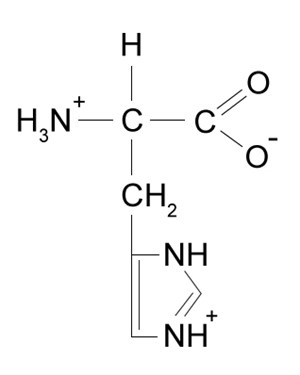
C) 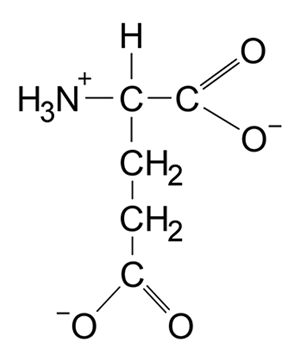
D) 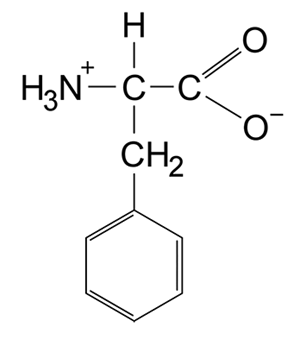
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q6: Passage
Leptin signaling is vital for maintaining adequate
Q7: Passage
The innate immune system relies heavily on
Q8: Passage
Leptin signaling is vital for maintaining adequate
Q9: Passage
Presynaptic nerve terminals release neurotransmitters via synaptic
Q10: Passage
Tumor hypoxia is a marker of resistance
Q12: Passage
Leptin signaling is vital for maintaining adequate
Q13: Passage
Tumor hypoxia is a marker of resistance
Q14: Passage
The innate immune system relies heavily on
Q15: Passage
Tumor hypoxia is a marker of resistance
Q16: Passage
The innate immune system relies heavily on
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents