Passage
The tumor suppressor p53 is a homotetrameric protein with an N-terminal transactivation domain (TAD) , a proline-rich domain, a DNA-binding domain (DBD) , a tetramerization domain (TD) , and a C-terminal regulatory domain (REG) on each subunit (Figure 1) .
 Figure 1 Organization of the p53 domains (1-393 amino acids) Human double minute 2 (Hdm2) is a lysine-specific ubiquitin protein ligase that can change the half-life of some proteins, including p53, by signaling for their proteolytic cleavage. Under normal circumstances, Hdm2 binds p53 at the AD1 region within the TAD and attaches ubiquitin to a lysine residue. However, errors in DNA replication induce the phosphorylation of residue T18 on p53, which inhibits p53's association with Hdm2. The overexpression of Hdm2 has been correlated with the downregulation of tumor suppressor p53 in certain types of cancers. Changes in the NMR chemical shift (ppm) of amino acids in the AD1 region shown in Figure 2 provide evidence for the formation of a p53-Hdm2 complex.
Figure 1 Organization of the p53 domains (1-393 amino acids) Human double minute 2 (Hdm2) is a lysine-specific ubiquitin protein ligase that can change the half-life of some proteins, including p53, by signaling for their proteolytic cleavage. Under normal circumstances, Hdm2 binds p53 at the AD1 region within the TAD and attaches ubiquitin to a lysine residue. However, errors in DNA replication induce the phosphorylation of residue T18 on p53, which inhibits p53's association with Hdm2. The overexpression of Hdm2 has been correlated with the downregulation of tumor suppressor p53 in certain types of cancers. Changes in the NMR chemical shift (ppm) of amino acids in the AD1 region shown in Figure 2 provide evidence for the formation of a p53-Hdm2 complex.
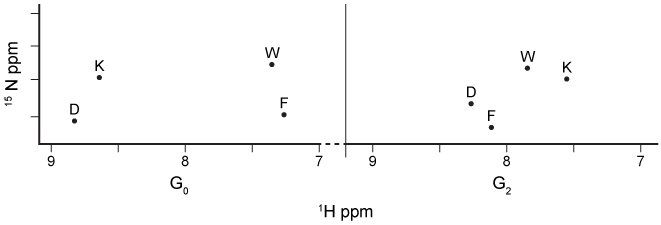 Figure 2 1H NMR spectrum of the AD1 region in 15N-labeled p53 during G0 and G2 phases of the cell cycleHdm2 also binds to Nedd8 ultimate buster 1 (NUB1) , which enhances signaling for the degradation of Nedd8 proteins. Preliminary data suggest that Hdm2 interacts differently with wild-type NUB1 (WTNUB1) than with mutant K159RNUB1. To assess the effect of Hdm2 on NUB1 and p53, the half-lives of p53 and Nedd8 protein variants were compared in cells that overexpress Hdm2 (Figure 3) .
Figure 2 1H NMR spectrum of the AD1 region in 15N-labeled p53 during G0 and G2 phases of the cell cycleHdm2 also binds to Nedd8 ultimate buster 1 (NUB1) , which enhances signaling for the degradation of Nedd8 proteins. Preliminary data suggest that Hdm2 interacts differently with wild-type NUB1 (WTNUB1) than with mutant K159RNUB1. To assess the effect of Hdm2 on NUB1 and p53, the half-lives of p53 and Nedd8 protein variants were compared in cells that overexpress Hdm2 (Figure 3) .
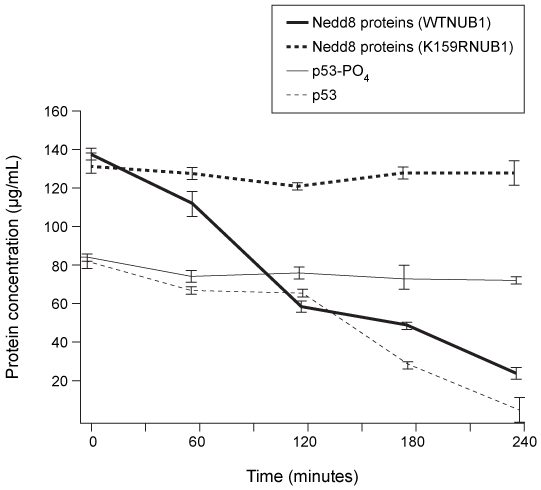 Figure 3 Half-lives of p53, phosphorylated p53 (p53-PO4) , and Nedd-8 proteins in cells with wild-type or mutant NUB1 over time
Figure 3 Half-lives of p53, phosphorylated p53 (p53-PO4) , and Nedd-8 proteins in cells with wild-type or mutant NUB1 over time
Adapted from Ferreon JC, Lee CW, Arai M, Martinez-yamout MA, Dyson HJ, Wright PE. Cooperative regulation of p53 by modulation of ternary complex formation with CBP/p300 and HDM2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106(16) :6591-6.
-Based on the data in Figure 2, which statement best supports the formation of a p53-Hdm2 complex in the absence of DNA errors?
A) Protons on hydrophilic amino acids of p53 are more shielded during G0.
B) Protons on hydrophilic amino acids of p53 are deshielded during G2.
C) Protons on hydrophobic amino acids of p53 are more shielded during G0.
D) Protons on hydrophobic amino acids of p53 are more shielded during G2.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q36: Passage
The liver plays a central role in
Q37: Passage
The bacterium Clostridium difficile secretes protein toxins
Q38: Passage
Spinocerebellar ataxia 3 (SCA3) is a neurodegenerative
Q39: Passage
The liver plays a central role in
Q40: Passage
Presynaptic nerve terminals release neurotransmitters via synaptic
Q42: Passage
Antimicrobial peptides are an important component of
Q43: Passage
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) is essential for
Q44: Passage
The tumor suppressor p53 is a homotetrameric
Q45: Passage
Antimicrobial peptides are an important component of
Q46: Passage
The tumor suppressor p53 is a homotetrameric
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents