Passage
Nerve cells must maintain the composition of their myelin sheaths to function properly. Galactocerebroside (GC) , shown in Figure 1, is a hydrolyzable lipid and an important component of the myelin sheath.
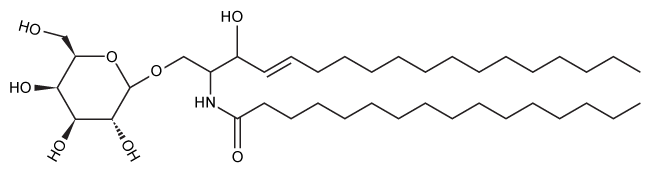 Figure 1 Structure of the myelin sheath component galactocerebrosideHomeostasis of GC is maintained by its dynamic synthesis and degradation, as shown in Figure 2. GC is synthesized by the enzyme ceramide galactosyltransferase (CGT) using UDP-galactose (UDP-Gal) and ceramide (Cer) as substrates. It is degraded by the enzyme galactocerebrosidase (GalC) , which hydrolyzes the glycosidic bond to release galactose (Gal) and ceramide. A deficiency in GalC activity leads to a buildup of GC, and prior research has connected this buildup with neurodegeneration.
Figure 1 Structure of the myelin sheath component galactocerebrosideHomeostasis of GC is maintained by its dynamic synthesis and degradation, as shown in Figure 2. GC is synthesized by the enzyme ceramide galactosyltransferase (CGT) using UDP-galactose (UDP-Gal) and ceramide (Cer) as substrates. It is degraded by the enzyme galactocerebrosidase (GalC) , which hydrolyzes the glycosidic bond to release galactose (Gal) and ceramide. A deficiency in GalC activity leads to a buildup of GC, and prior research has connected this buildup with neurodegeneration.
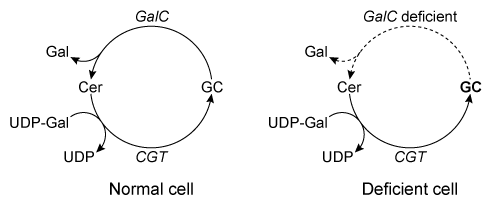 Figure 2 Schematic of GCT and GalC activity in healthy and GalC deficient cellsOver 100 inactivating GalC mutations have been identified. Five of the most common mutations are listed in Table 1. The changes to both DNA and amino acid sequence are shown.Table 1 Five Common Galactocerebrosidase Mutations
Figure 2 Schematic of GCT and GalC activity in healthy and GalC deficient cellsOver 100 inactivating GalC mutations have been identified. Five of the most common mutations are listed in Table 1. The changes to both DNA and amino acid sequence are shown.Table 1 Five Common Galactocerebrosidase Mutations
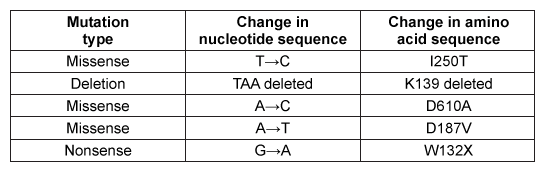
-Based on Table 1, the D187V form of GalC resulted from what type of nucleotide change?
A) A pyrimidine was replaced by a different pyrimidine
B) A pyrimidine was replaced by a purine
C) A purine was replaced by a pyrimidine
D) A purine was replaced by a different purine
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q134: Fatty acid oxidation and synthesis occur in
Q135: Amino acid catabolism releases nitrogen in the
Q136: Scientists could confirm that an allosteric effector
Q137: Passage
A newborn girl is diagnosed with a
Q138: Passage
Many lysosomal proteins are transported to the
Q140: Phospholipases release arachidonic acid from cell membranes
Q141: Passage
The K-ras gene codes for a small
Q142: A solution of which amino acid will
Q143: Passage
Nerve cells must maintain the composition of
Q144: Proline differs from the other standard amino
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents