Passage
The K-ras gene codes for a small guanine nucleotide-binding protein, which acts as a molecular activator in numerous signaling pathways that promote DNA replication along with cell growth and survival. K-ras mutations at codons 12 and 13 function as biological markers for diagnosis of tumors. The DNA of SW-480 cells, a line originating from a colon adenocarcinoma, is the standard positive control used to identify codon 12 mutations in K-ras testing.
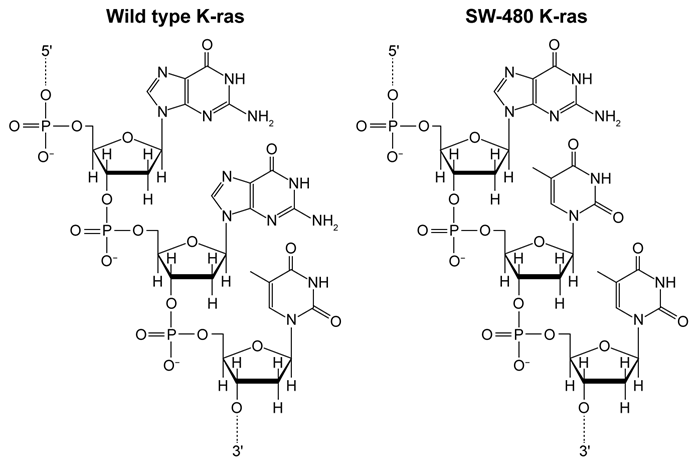 Figure 1 Structural comparison of K-ras codon 12 in wild-type cells and SW-480 cellsPCR sequence analysis has been the preferred method for studying genetic mutations such as those in K-ras. However, challenges in analyzing PCR amplicons have prompted the development of DNA melting curve analysis (MCA) . In the MCA technique, DNA is extracted from clinical samples and amplified by PCR. The amplified DNA is then melted (30-70°C) and analyzed by assessing the fluorescence (at 640 nm) of LC Green Plus, an intercalating dye that fluoresces when bound to double-stranded DNA (Figure 2) .
Figure 1 Structural comparison of K-ras codon 12 in wild-type cells and SW-480 cellsPCR sequence analysis has been the preferred method for studying genetic mutations such as those in K-ras. However, challenges in analyzing PCR amplicons have prompted the development of DNA melting curve analysis (MCA) . In the MCA technique, DNA is extracted from clinical samples and amplified by PCR. The amplified DNA is then melted (30-70°C) and analyzed by assessing the fluorescence (at 640 nm) of LC Green Plus, an intercalating dye that fluoresces when bound to double-stranded DNA (Figure 2) .
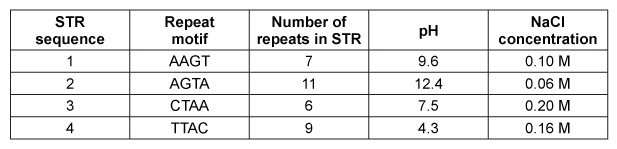
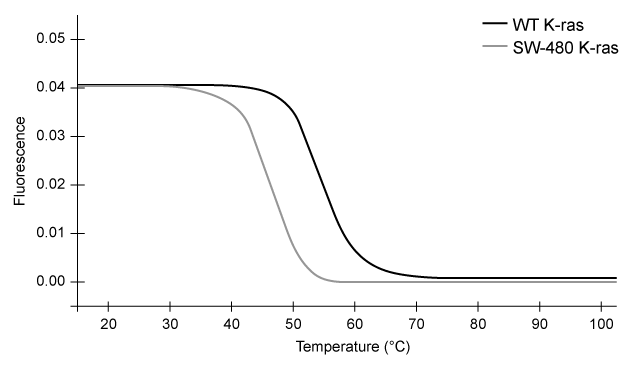 Figure 2 Melting curves of wild-type (WT) and SW-480 K-ras DNA.To study K-ras activity in colorectal cancer cells, short tandem repeats (STRs) were introduced into the K-ras gene. STRs are short stretches of DNA with repeating nucleotides, and four different STR sequences were inserted into the K-ras gene and analyzed via MCA under different experimental conditions (Table 1) .Table 1 Sequences Studied in K-ras DNA MCA Analysis.
Figure 2 Melting curves of wild-type (WT) and SW-480 K-ras DNA.To study K-ras activity in colorectal cancer cells, short tandem repeats (STRs) were introduced into the K-ras gene. STRs are short stretches of DNA with repeating nucleotides, and four different STR sequences were inserted into the K-ras gene and analyzed via MCA under different experimental conditions (Table 1) .Table 1 Sequences Studied in K-ras DNA MCA Analysis.
 Liu YP, Wu HY, Yang X, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of high resolution melting analysis for detection of KRAS mutations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2014;4:7521.
Liu YP, Wu HY, Yang X, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of high resolution melting analysis for detection of KRAS mutations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2014;4:7521.
-Assuming that additional mutations similar to the one shown in Figure 1 occur throughout the mutant K-ras gene, what would be the best explanation for the difference in denaturation between wild-type (WT) and mutant K-ras DNA?
A) Mutant DNA has a higher GC content than WT DNA.
B) Mutant DNA has a lower GC content than WT DNA.
C) WT DNA is longer than mutant DNA.
D) WT DNA is shorter than mutant DNA.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q150: A fatty acid undergoes complete β-oxidation to
Q151: An infant who experiences seizures and has
Q152: Under physiological conditions, peptide bond formation and
Q153: Which series depicts the order in which
Q154: Based on the titration curve of an
Q156: Passage
The K-ras gene codes for a small
Q157: Passage
Nerve cells must maintain the composition of
Q158: Passage
The K-ras gene codes for a small
Q159: During glycolysis, phosphofructokinase converts fructose 6-phosphate (F6P)
Q160: Passage
Nerve cells must maintain the composition of
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents