Passage the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) Protein Is a a Chloride
Passage
The cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) protein is a chloride ion channel involved in the production of mucus, sweat, and digestive fluids. CFTR is composed of five domains (Figure 1) : Two transmembrane domains (TMD1 and TMD2) , two nucleotide binding domains (NBD1 and NBD2) , and one regulatory domain (R domain) .
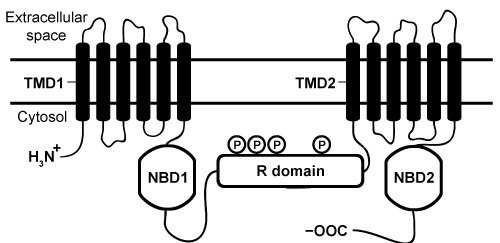 Figure 1 Schematic diagram of CFTR domainsThe NBD domains regulate CFTR activity by binding ATP, which causes a conformational change in the TMD domains. This change allows chloride ions to leave cells by passively crossing the membrane down their concentration gradient. The R domain regulates activity further through dynamic phosphorylation at several positions. The movement of chloride ions facilitates the movement of water out of the cell by osmotic pressure and helps keep secretions thin.Cystic fibrosis (CF) arises from recessively inherited mutations in the CFTR gene. The most common mutation is a three-base-pair deletion that removes a phenylalanine residue at position 508 in NBD1 (ΔF508) . This mutation causes the protein to fold incorrectly, making it more susceptible to degradation by proteases. The resulting decrease in CFTR abundance inhibits chloride ion transport, leading to thickening of normally thin secretions and increased risk of life-threatening pulmonary infections.
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of CFTR domainsThe NBD domains regulate CFTR activity by binding ATP, which causes a conformational change in the TMD domains. This change allows chloride ions to leave cells by passively crossing the membrane down their concentration gradient. The R domain regulates activity further through dynamic phosphorylation at several positions. The movement of chloride ions facilitates the movement of water out of the cell by osmotic pressure and helps keep secretions thin.Cystic fibrosis (CF) arises from recessively inherited mutations in the CFTR gene. The most common mutation is a three-base-pair deletion that removes a phenylalanine residue at position 508 in NBD1 (ΔF508) . This mutation causes the protein to fold incorrectly, making it more susceptible to degradation by proteases. The resulting decrease in CFTR abundance inhibits chloride ion transport, leading to thickening of normally thin secretions and increased risk of life-threatening pulmonary infections.
-A scientist proposed that phosphorylation of the R domain increases CFTR activity. Which of the following functional groups in the R domain could be removed by mutation to test this hypothesis in vivo?
A) Amide
B) Hydroxyl
C) Thiol
D) Carboxylic acid
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q165: Passage
Diabetic nephropathy (kidney disease) is characterized in
Q166: Polyglutaraldehyde (PGA) can form linkages with amines.
Q167: During protein folding, which of the following
Q168: Passage
The cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR)
Q169: Passage
Diabetic nephropathy (kidney disease) is characterized in
Q171: Passage
Diabetic nephropathy (kidney disease) is characterized in
Q172: A kinetics experiment reveals that the enzyme
Q173: During gluconeogenesis, the enzyme phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK)
Q174: The affinity of a protein for its
Q175: Passage
Diabetic nephropathy (kidney disease) is characterized in
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents