Passage
The recent advent of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) has led to the search for novel agents to combat tuberculosis. Mtb secretes over 70 serine proteases that may be used as viable drug targets. Hydrolase important for pathogenesis 1 (Hip1) is a serine protease found in Mtb with proteolytic activity that is required for dampening the host inflammatory response. Given the role of Hip1 in Mtb virulence, analyzing Hip1 substrate specificity is a critical step in designing selective inhibitors for effective tuberculosis treatment.Fluorogenic substrates are nonfluorescent compounds that release a fluorescent reporter group when acted upon by an enzyme. Such substrates are useful biomolecular imaging tools that allow monitoring of enzymatic activity in vitro and in vivo. A large library of peptides was screened against Hip1, and enzymatic cleavage was analyzed using mass spectrometry to facilitate the design of fluorogenic substrates (Figure 1) .
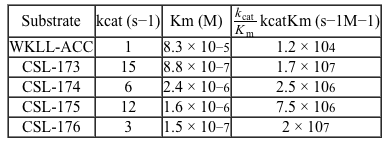
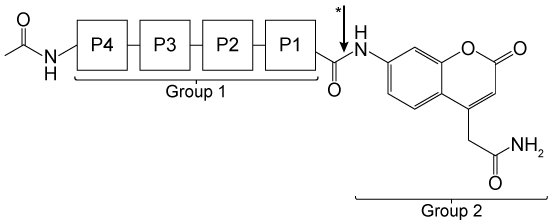 Figure 1 Schematic design of Hip1 fluorogenic substrates. P1, P2, P3, and P4 in Group 1 represent the positions of variable amino acids in the peptide. Group 2 depicts the fluorescent compound released on Hip1 cleavage.Researchers reported Michaelis-Menten kinetic parameters for substrates from two peptide families: the WKLL substrates and the CSL substrates.Table 1 Kinetic Parameters of Fluorogenic Substrates for Mtb Hip1
Figure 1 Schematic design of Hip1 fluorogenic substrates. P1, P2, P3, and P4 in Group 1 represent the positions of variable amino acids in the peptide. Group 2 depicts the fluorescent compound released on Hip1 cleavage.Researchers reported Michaelis-Menten kinetic parameters for substrates from two peptide families: the WKLL substrates and the CSL substrates.Table 1 Kinetic Parameters of Fluorogenic Substrates for Mtb Hip1
 Adapted from Lentz CS, Ordonez AA, Kasperkiewicz P, et al. Design of Selective Substrates and Activity-Based Probes for Hydrolase Important for Pathogenesis 1 (HIP1) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. ACS Infect Dis. 2016;2(11) :807-815.
Adapted from Lentz CS, Ordonez AA, Kasperkiewicz P, et al. Design of Selective Substrates and Activity-Based Probes for Hydrolase Important for Pathogenesis 1 (HIP1) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. ACS Infect Dis. 2016;2(11) :807-815.
-In further experiments researchers found that bacteria lacking Hip1 (knockout bacteria) were able to cleave WKLL-ACC but not the CSL substrates. How might these results be explained?
A) WKLL-ACC readily undergoes hydrolysis in the absence of an enzyme.
B) Knockout bacteria take up WKLL-ACC more readily than other substrates.
C) WKLL-ACC has a greater specificity for another protease.
D) Knockout bacteria have increased nonspecific protease activity.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q188: Passage
Leukocyte common antigen (LCA) enzymes play several
Q189: The graph below shows the effect of
Q190: 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (4HNE), shown below, interacts with proteins
Q191: Passage
The recent advent of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Q192: Passage
The recent advent of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Q194: During anaerobic exercise, the Cori cycle connects
Q195: Passage
Leukocyte common antigen (LCA) enzymes play several
Q196: Passage
The recent advent of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Q197: Passage
DNA polymerization is one of the most
Q198: Passage
DNA polymerization is one of the most
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents